Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
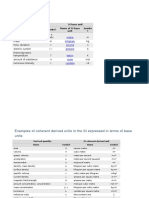
Dimension Alternatives Definition/Notes
Caricato da
Gopal VenkatramanDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dimension Alternatives Definition/Notes
Caricato da
Gopal VenkatramanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
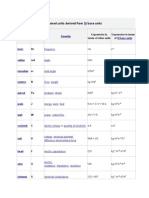
Quantity A: Acceleration, angular Abb number Absorbed radiation dose Absorbed dose rate Acceleration, linear Action Activity
of radioactive source Admittance, inductive Admittance, of a circuit Angular acceleration Angular moment of inertia Angular moment of motion Angular velocity Annealing point Area Attenuation B: Bandwidth Baud rate Bulk modulus C: Capacitance, electric Capacitive reactance Capacitive susceptance Circulation Characteristic impedance
Dimension s-2 1 m2.s-2 m2.s-3 m.s-2 kg.m2.s-1 s-1 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 s-2 kg.m2 kg.m2.s-1 s-1 K m2 m-1 s-1 bit.s-1 kg-1.m.s2
Alternatives rad.s-2 Dimensionless J.kg-1, Gy (gray) Gy.s-1 J.s Bq (becquerel) S (siemens) S (siemens) rad.s-2
Definition/Notes [AngularVelocity]/[Time] Inverse of refractive index. [Energy]/[Mass] [Absorbed dose]/[Time] [Velocity]/[Time] [Energy]*[Time], [Moment of motion]*[Distance] [Events]/[Time] 1/[Inductive impedance]. 1/[Circuit impedance]. [AngularVelocity]/[Time] [Mass]*[Distance2]
J.s rad.s-1
dB/m Hz baud Pa-1
[Moment of motion]*[Distance]. Like [action]. [Plane angle]/[Time] Temperature at which viscosity drops below 1012 Pa.s [Distance]*[Distance] [Ratio]/m. Applies to propagation. [Frequency] [Information]/[Time]. Also: information flux. [Pressure]/([Volume]/ [Volume]). Same as compressibility . [Charge]/[Potential] 1/(i[Angular frequency]. [Capacitance]) 1/[Capacitive reactance]. [Angular moment]/[Mass], [Velocity]*[Loop length] ([Mag.Permeability]/ [El.Permittivity])
kg-1.m-2.s4.A2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 m2.s-1 kg.m2.s-3.A-2
C.V-1, F (farad) (ohm) S (siemens) J.s.kg-1 V.A-1, , ohm
Charge, electric Charge, quantum Charge, molecular/ionic, quantum Charge density Charge/mass ratio Charge, molar Chemical potential, molar Circuit admittance Circuit impedance Collision cross section Compressibility Compression Compression modulus Compressive strength Concentration, molar Concentration, by mass Concentration, by volume Concentration, by weight Conductance, electric Conductivity, electric Conductivity, molar Conductivity, thermal Constringence Convergence Count of
s .A 1 1 m-3.s.A kg-1.s.A s.A.mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 m2 kg-1.m.s2 kg.m-1.s-2 kg-1.m.s2 kg.m-1.s-2 m-3.mol 1 1 1 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 kg-1.m-3.s3.A2 kg1 3 .s .A2.mol-1 kg.m.s-3.K-1 1 m-1 1
C (coulomb) Dimensionless Dimensionless C.m-3 C.kg-1 C.mol-1 J.mol-1 S (siemens) (ohm) Pa-1 N.m-2, Pa (pascal) Pa-1 N.m-2, Pa
[Current]*[Time] [Charge]/[Elementary charge quantum] [Charge of a molecule or ion]/ [Elementary charge quantum] [Charge]/[Volume] [Charge]/[Mass]. Same as specific charge [Charge]/[Quantity] [InternalEnergy]/ [QuantityOfSubstance] 1/[Circuit impedance]. [Distance]*[Distance]. Same as cross section [Pressure]/([Volume]/ [Volume]). Same as bulk modulus . [Force]/[Area]. ... same as pressure [Pressure]/([Volume]/ [Volume]). Same as compressibility . [Force]/[Area]. Same dimension as pressure. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as molar density. [Mass of substance]/[Total mass]. Same as mass concentration [Volume of substance]/[Total volume]. Same as volume concentration . [Mass of substance]/[Total mass]. Same as mass concentration 1/[Resistance]. 1/[Resistivity] [El.conductivity]/ [Concentration] [Heat flux]/ ([Distance]*[Temperature]) [Transversal striction]/ [Londitudinal elongation]. in optics, but not only ... This covers all kinds of
Dimensionless Dimensionless Dimensionless A.V-1, S (siemens) S.m-1 S.m2.mol-1 W.m-1.K-1 Dimensionless dioptry
events/instances Count rate Couple Critical angle of repose Cross section Cryoscopic constant Current, electric Current density (electric) Current intensity (electric) Current noise, variance nJ2 Curvature radius D: Density of electric charge Density of electric current Density of energy Density of mass Density of substance Dielectric constant Dielectric strength/rigidity Diffusion coefficient Diffusivity, thermal Dipole moment, electric Dipole moment, magnetic Dispersive power Dispersivity quotient Distance Dose of absorbed radiation Dose rate Drift speed
s-1 kg.m2.s-2 rad m2 kg.mol-1.K A m-2.A m-2.A s.A2 m m-3.s.A m-2.A kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m-3 m-3.mol 1 kg.m.s-3.A-1 m2.s-1 m2.s-1 m.s.A m2.A 1 m-1 m m2.s-2 m2.s-3 m.s-1
N.m or degree K/(mol/kg) A (ampere)
enumerations. [Events]/[Time] 2*[Force]*[Distance] for two non-aligned opposing forces. Steepest angle of a slope before a slide [Distance]*[Distance] [Temperature]/[Molality] [Current]/[Area]. Same as current intensity. [Current]/[Area]. Same as current density. [Current]2/[Bandwidth] of a line in plane/space or surface in space
A2/Hz
C.m-3
[Charge]/[Volume] [Current]/[Area]. Same as current intensity. [Energy]/[Volume]. [Mass]/[Volume]. Same as specific density. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration. [Permittivity]/[Permittivity of vacuum]. Same as relative permittivity [Potential]/[Distance]. Same as electric strength [Distance2]/[Time]. ([Temperatute]/[Time])/ [2Temperature]. [Charge]*[Distance] [Current]*[Area] Ratio of differences of refractive indices. [Refractive index]/ [Wavelength] in all Euclidean ndimensional spaces. [Energy]/[Mass]. [Absorbed dose]/[Time]. Steady-state speed of an
J.m-3
Dimensionless V.m-1
C.m J.T-1 Dimensionless
J.kg-1, Gy (gray) Gy.s-1
object. . Duration Dynamic viscosity E: Ebullioscopic constant Electric capacitance Electric charge Electric conductance Electric conductivity Electric conductivity, molar Electric current Electric dipole moment Electric field strength Electric field gradient Electric flux density Electric inductance Electric induction Electric intensity Electric permittivity Electric permittivity, relative Electric polarization Electric potential Electric quadrupole moment Electric resistance Electric resistivity Electric strength Electromagnetic vector potential Electromotive force s kg.m-1.s-1 kg.mol-1.K kg-1.m-2.s4.A2 s .A kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 kg-1.m-3.s3.A2 kg1 3 .s .A2.mol-1 A m.s.A kg.m.s-3.A-1 kg.s-3.A-1 m-2.s.A kg.m2.s-2.A-2 m-2.s.A kg.m.s-3.A-1 kg-1.m-3.s4.A2 1 m-2.s.A kg.m2.s-3.A-1 m2.s.A kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg.m3.s-3.A-2 kg.m.s-3.A-1 kg.m.s-2.A-1 kg.m2.s-3.A-1 s (second) Pa.s K/(mol/kg) C.V-1, F (farad) C (coulomb) A.V-1, S (siemens) S.m-1 S.m2.mol-1 A (ampere) C.m V.m-1 V.m-2 C.m-2 V.s.A-1, H (henry) C.m-2 V.m-1 F.m-1 Dimensionless C.m-2 W.A-1, J.C-1, V (volt) C.m2 V.A-1, (ohm) .m V.m-1 V.s.m-1, T.m V ([Force]/[Area])/[Velocity] [Temperature]/[Molality]. [Charge]/[Potential] [Current]*[Time] [Current]/[Potential]. Inverse of resistance. 1/[Resistivity]. [El.conductivity]/ [Concentration]. [Charge]*[Distance] [Potential]/[Distance]. Also called electric intensity [El.field strength]/ [Distance]. [Charge]/[Area]. Also called electric induction [Potential]/[dCurrent/dt] [Charge]/[Area]. More properly electric flux density [Potential]/[Distance]. More properly electric field strength [El.flux density]/[El.field strength]. [Permittivity]/[Permittivity of vacuum]. Same as dielectric constant [Charge]/[Area]. Like electric flux density [Power]/[Current], [Energy]/ [Charge] [Electric dipole]*[Distance], [Electric charge]*[Distance2] [Potential]/[Current] ([Resistance]*[Length])/ [Area]. [Potential]/[Distance]. Also called dielectric strength . [El.field strength]*[Time] or [Mag.flux density]*[Distance] [Potential]
(emf) Electrostriction coefficient Energy Energy, molar Energy, specific Energy density Energy flux Enthalpy Enthalpy, molar Enthalpy, specific Entropy Entropy, molar Entropy, specific Evolution rate on log-scale Expansion coefficient, thermal Exposure Extinction coefficient F: Fire point Flash point Force Force, thermodynamic Free energy Free energy, molar Free energy, specific Free enthalpy Free enthalpy, molar Free enthalpy, specific
kg-2.m-2.s6.A2 kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2 kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m2.s-3 kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2 kg.m2.s-2.K-1 kg.m2.s-2.K1 .mol-1 m2.s-2.K-1 s-1 K-1 kg-1.s.A m-1 K K kg.m.s-2 kg.m.s-2.mol1
m2.V-2 N.m, J (joule) J.mol-1 J.kg-1 J.m-3 J.s-1, W (watt) J J.mol-1 J.kg-1 J.K-1 J.K-1.mol-1 J.K-1.kg-1
([Volume]/[Volume])/ [Electric field strength]2. [Force]*[Distance], [Power]*[Time]. [Energy]/[Quantity]. [Energy]/[Mass]. [Energy]/[Volume]. [Energy]/[Time]. Same as power. Like energy and heat. [Enthalpy]/[Quantity]. Like molar heat. [Enthalpy]/[Mass]. Like specific heat. [Heat]/[Temperature]. [Entropy]/[Quantity]. [Entropy]/[Mass]. d{ln(Q)}/dt = (dQ/dt)/Q. Also relative evolution rate ([Length]/[Length])/ [Temperature]. [Charge]/[Mass]. Used for ionising radiations. Used for propagation of radiation. Temperature at which ignited vapour keeps burning Temperature at which vapour can be kept burning [Mass]*[Acceleration]. [Chemical potential]/ [Distance]. Also Helmholtz function. Like energy. [Free energy]/[Quantity]. Also molar Helmholtz function [Free energy]/[Mass]. Also specific Helmholtz function Also Gibbs function. Like energy. [Free enthalpy]/[Quantity]. Also molar Gibbs function [Free enthalpy]/[Mass]. Also specific Gibbs function
C.kg-1 dB/m
N (newton) N/mol J J.mol-1 J.kg-1 J J.mol-1 J.kg-1
kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2 kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2
Frequency of waves or events Frequency drift rate Friction Friction coefficient Fugacity G: Gain of a device g-factor of a particle Gradient, of electric field Gradient, of magnetic field Gradient, thermal Gravitational field intensity Gravitational field potential Gravity Gyromagnetic ratio H: Half life Hamiltonian Hardness Heat Heat, molar Heat, specific Heat capacity Heat capacity, molar Heat capacity, specific Heat | Thermal
s-1 s-2 kg.m.s-2 1 kg.m-1.s-2 1 1 kg.s-3.A-1 kg.m-1.s-2.A-1 K.m-1 m.s-2 m2.s-2 m.s-2 kg-1.s.A s kg.m2.s-2 kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2 kg.m2.s-2.K-1 kg.m2.s-2.K1 .mol-1 m2.s-2.K-1 kg.m.s-3.K-1
Hz (hertz) Hz.s-1 N (newton) Dimensionless Pa Dimensionless Dimensionless V.m-2 T.m-1 [Frequency]/[Time]. Tangential force between two moving surfaces. [Tangential force]/[Normal force]. Effective pressure in real gases. [Output]/[Input], likequantities ratio. Often in dB. [Magnetic moment]/([Spin]. [Bohr magneton]) [El.field strength]/ [Distance]. [Mag.flux density]/ [Distance]. [Temperature]/[Distance]. Same as temperature gradient [Force]/[Mass], [Acceleration]. Same as gravity [Energy]/[Mass]. [Force]/[Mass], [Acceleration]. Same as grav. field intensity [Mag.moment]/[Angular moment of motion]. typically of a radioactive substance [Force]*[Distance], [Power]*[Time]. Like energy [Force]/[Area]. Same as pressure. Like energy. [Heat]/[Quantity]. [Heat]/[Mass]. [Heat]/[Temperature]. [Heat capacity]/[Quantity]. [Heat capacity]/[Mass]. [Heat flux]/
Hz.T-1
J N.m-2 J J.mol-1 J.kg-1 J.K-1 J.K-1.mol-1 J.K-1.kg-1 W.m-1.K-1
conductivity Heat flux Heat flux density I: Illuminance Impact resistance Impedance, characteristic Impedance, inductive Impedance, of a circuit Impulse Inductance Induction, electric Inductive admittance Inductive impedance Information Information flux Intensity of electric current Internal energy Internal energy, molar Internal energy, specific Ion mobility Ionic force (strength) Ionic quantum charge Ionic strength (force) Irradiance J: Joule-Thomson coefficient
kg.m2.s-3 kg.s-3 cd.sr.m-2 kg.s-2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg.m.s-1 kg.m2.s-2.A-2 m-2.s.A kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 bit-1 bit.s-1 m-2.A kg.m2.s-2 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 m2.s-2 kg-1.m-1.s2.A m-3.mol 1 m-3.mol kg.s-3 kg-1.m.s2.K
J.s, W W.m-2 lm.m-2, lx (lux) J.m-2 V.A-1, , ohm (ohm) (ohm)
([Distance]*[Temperature]). [Heat]/[Time]. Like power. [Heat flux]/[Area]. Same as irradiance. [Luminous flux]/[Area]. [Energy]/[Area] ([Mag.Permeability]/ [El.Permittivity]). i[Angular frequency]. [Inductance] [Moment of motion], [Force]*[Time], [Mass]*[Velocity]. [Potential]/[dCurrent/dt], [Mag.flux]/[Current] [Charge]/[Area]. Same as electric flux density 1/[Inductive impedance]. i[Angular frequency]. [Inductance] One bit is the elementary information quantum. [Information]/[Time]. Also called baud rate. [Current]/[Area]. Same as current density. Like energy and heat. [Internal energy]/[Quantity]. Like molar heat. [Internal energy]/[Mass]. Like specific heat. [Velocity]/[Electric field strength] . Sum([Concentration]*[Ionic quantum charge]2). [Ion charge]/[Elementary charge quantum] Sum([Concentration]*[Ionic quantum charge]2). [Heat flux]/[Area]. Same as heat flux density [Temperature]/[Pressure].
V.s.A-1, Wb.A-1, H (henry) C.m-2 S (siemens) (ohm) bit baud
J J.mol-1 J.kg-1 m2.s-1.V-1
Dimensionless
W.m-2 K.Pa-1
K: Katalytic activity Kinematic viscosity K-space vector L: Lagrangian Length Linear stiffness Logarithmic ratio logb(A/A') Logarithmic ratio ln(A/A') Logarithmic ratio Log(P/P')/10 Logarithmic ratio Log(X/X')/20 Logarithmic scale differential Luminance Luminosity Luminous coefficient Luminous efficacy Luminous efficiency Luminous emittance Luminous energy Luminous flux Luminous intensity Luminous power M: Magnetic dipole moment Magnetic field gradient
mol.s-1 m2.s-1 m-1 kg.m2.s-2 m kg.s-2 1 1 1 1 1 cd.m-2 cd 1 cd.sr.kg-1.m1 3 .s 1 cd.sr.m-2 cd.sr.s cd.sr cd cd.sr m2.A kg.m-1.s-2.A-1
katal
[Quantity]/[Time]. Same as molar production rate [Dynamic viscosity]/ [Density] same as reciprocal space position. [Force]*[Distance], [Power]*[Time]. Like energy [Force]/[Displacement]. ... of a structure Applicable to any ratio of like quantities. Uses natural logarithm. Uses base-10 logarithm. Aplies only to power P. Aplies to voltages (X=V) and currents (X=I). dQ/Q, d{ln(Q)}, for any quantity Q. Also relative differential [Luminosity]/[Area] Same as luminous intensity [Luminous efficacy]/[683 lm/W]. Same as luminous efficiency [Luminous flux]/[Power] [Luminous efficacy]/[683 lm/W]. Same as luminous coefficient Same as illuminance, but for sources [Luminous flux]*[Time]. Also known as talbot [Luminosity]*[Solid angle]. Same as luminous power Same as luminosity [Luminosity]*[Solid angle]. Same as luminous flux [Current]*[Area]. Like magnetic moment. [Mag.flux density]/ [Distance].
J m (meter) N.m-1 log in any base b Np (neper) dB (decibel) dB (decibel) Dimensionless
cd (candle) Dimensionless lm/W Dimensionless lm.m-2, lx (lux) lm.s lm (lumen) cd (candle) lm (lumen) J.T-1 T.m-1
Magnetic field strength Magnetic flux Magnetic flux density Magnetic induction Magnetic intensity Magnetic moment Magnetic permeability Magnetic permeability, relative Magnetic quadrupole moment Magnetic susceptibility Magnetization Magnetogyric ratio Magnetomotive force (mmf) Magnitude of a star Mass Mass density Mass concentration Mass flow Mass production rate Mass, molar Modulus of compression Modulus of rigidity Mobility, ionic
m-1.A kg.m2.s-2.A-1 kg.s-2.A-1 kg.s-2.A-1 m-1.A m2.A kg.m.s-2.A-2 1 m3.A 1 m-1.A kg.s-1.A-1 A 1 kg kg.m-3 1 kg.s-1 kg.s-1 kg.mol-1 kg-1.m.s2 kg.m.s-2 kg-1.m-1.s2.A Pa-1 N, N.rad-1 m2.s-1.V-1 Dimensionless kg (kilogram) Dimensionless kg T.Hz-1 J.T-1 H.m-1 Dimensionless m.J.T-1 Dimensionless V.s, W.s.A-1, Wb (weber) Wb.m-2, T (tesla) Wb.m-2, T (tesla)
[Current]/[Distance]. Also called magnetic intensity [Potential]*[Time], [Power]/ [dCurrent/dt] [Mag.flux]/[Area]. Also called magnetic induction [Mag.flux]/[Area]. More properly magnetic flux density [Current]/[Distance]. More properly magnetic field strength [Current]*[Area] [Mag.flux density]/[Mag.field strength]. [Permeability]/[Permeability of vacuum]. [Mag.dipole]*[Distance] [Relative permeability]-1. [Mag.moment]/[Volume]. Like magnetic field strength [Angular moment of motion]/ [Mag.moment]. [Current]*[Number of turns] m-m'=-100.4(S/S'), where S,S' are the luminous fluxes of two stars [Mass]/[Volume]. Same as specific density. [Mass of substance]/[Total mass]. Also concentration by weight [Mass]/[Time]. Same as mass production rate [Mass]/[Time]. Same as mass flow. [Mass]/[Quantity] [Pressure]/([Volume]/ [Volume]). Same as compressibility 3 [Force]/[Angle]. Same as shear modulus. [Velocity]/[Electric field
Molality Molar charge Molar concentration Molar conductivity, electric Molar density Molar energy Molar enthalpy Molar entropy Molar free energy Molar free enthalpy Molar heat Molar heat capacity Molar internal energy Molar mass Molar production rate Molar refractivity Molar relaxivity Molar solubility Molar volume Molarity Molecular quantum charge Moment of force Moment of motion Mutual inductance
kg-1.mol s.A.mol-1 m-3.mol kg-1.m3 3 .s .A2.mol-1 m-3.mol kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.m2.s-2.K1 .mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.m2.s-2.K1 .mol-1 kg.m2.s2 .mol-1 kg.mol-1 mol.s-1 m3.mol-1 m3.s-1.mol-1 m-3.mol m3.mol-1 m-3.mol 1 kg.m2.s-2 kg.m.s-1 kg.m2.s-2.A-2
mol/kg C.mol-1 S.m-1.mol-1
J.mol-1 J.mol-1 J.K-1.mol-1 J.mol-1 J.mol-1 J.mol-1 J.K-1.mol-1 J.mol-1 katal
strength] . [Quantity]/[Mass]. A way to specify concentration of a solution. [Charge]/[Quantity] [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration [El.conductivity]/ [Concentration]. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration. [Energy]/[Quantity]. [Enthalpy]/[Quantity]. Like molar heat. [Entropy]/[Quantity]. [Free energy]/[Quantity]. Also molar Helmholtz function [Free enthalpy]/[Quantity]. Also molar Gibbs function [Heat]/[Quantity]. [Heat capacity]/[Quantity]. [Internal energy]/[Quantity]. Like molar heat. [Mass]/[Quantity] [Quantity]/[Time]. Like katalytic activity. [(r2-1)/(r2+2)]/ [Concentration], where r is the refractive index [Relaxation rate]/ [Concentration]. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration [Volume]/[Quantity]. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration or molar density [Charge of a molecule]/ [Elementary charge quantum] [Force]*[Distance]. [Mass]*[Velocity], [Mass flow]*[Distance]. [Potential]/[dCurrent/dt], [Mag.flux]/[Current]
Dimensionless N.m V.s.A-1, Wb.A-1, H (henry)
N: Notch resistance Number density Number density, molar Number of events/instances Number of turns O: Osmotic pressure P: Peltier coefficient Permeability, magnetic Permittivity, electric Permittivity, relative Phase angle Phase drift rate Pi coefficient, molar Piezzoelectric coefficient Plane angle Polarization, electric Position vector Potential, electric Power Prandtl number Propagation loss Poynting vector Pressure Probability of an event Probability density on ln-scale Q: Quadrupole moment, electric
kg.s-2 m-3 mol-1 1 1 kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m2.s-3.A-1 kg.m.s-2.A-2 kg-1.m-3.s4.A2 1 1 s-1 kg.m-1.s2 .mol-1 kg.m.s-3.A-1 1 m-2.s.A m kg.m2.s-3.A-1 kg.m2.s-3 1 m-1 kg.s-3 kg.m-1.s-2 1 1 m2.s.A
J.m-2
[Energy]/[Area] [Particles]/[Volume]. [Particles]/[Mol]. The Avogadro constant. This covers all kinds of enumerations. Often used in electric engineering.
Pa W.A-1, V H.m-1 F.m-1 Dimensionless rad rad.s-1 J.m-3 V.m-1 rad C.m-2 [Heat flux]/[Current]. [Mag.flux density]/[Mag.field strength]. [El.flux density]/[El.field strength]. [Permittivity]/[Permittivity of vacuum]. Dielectric constant. in exp(i(t+)) [Phase angle]/[Time]. [InternalEnergy]/ [Volume]. [Electric field strength]/ ([Length]/[Length]). [Charge]/[Area]. Like electric flux density. in all Euclidean ndimensional spaces. [Power]/[Current], [Energy]/ [Charge] [Energy]/[Time]. Equivalent to energy flux. [Kinematic viscosity]/ [Thermal diffusivity]. [Ratio]/m. Used for any other quantity. [El.field strength]/[Mag.field strength]. Like irradiance [Force]/[Area]. Real number lying in the interval [0,1]. [Probability]/[Naturallogarithmic ratio] [Electric dipole]*[Distance], [Electric charge]*[Distance2]
W.A-1, J.C-1, V (volt) J.s-1, W (watt) Dimensionless dB/m W.m-2 N.m-2, Pa (pascal) Np-1 C.m2
Quadrupole moment, magnetic Quantity of substance Quantum charge Quantum charge, molecular or ionic Quotient of dispersivity R: Radiance Radiation dose Radiation dose rate Radioactivity Radius of curvature Rotational stiffness Ratio of like quantities Reactance, capacitive Reciprocal space position Redox potential Reduction potential Refractive index Refractivity, molar Refractivity, specific Relative differential Relative evolution rate Relative permeability, magnetic Relative permittivity, electric Relative variation Relaxation rate Relaxation time
m3.A mol 1 1 m-1 kg.s-3.sr-1 m2.s-2 m2.s-3 s-1 m kg.m2.s-2.rad1
m.J.T-1 mol Dimensionless Dimensionless
[Mag.dipole]*[Distance]
[Charge]/[Elementary charge quantum] [Molecule/ion charge]/ [Charge quantum] [Refractive index]/ [Wavelength] ([Power]/[Area])/[Solid angle]. [Energy]/[Mass]. [Absorbed dose]/[Time]. [Events]/[Time]. of a line in plane/space or surface in space [Moment of force]/[Angle]. ... of a structure. Q1/Q2, with Q1 and Q2 having the same dimension 1/(i[Angular frequency]. [Capacitance]) same as k-space vector. Same as reduction potential. Same as redox potential. Light speeds ration (in a medium)/(in vacuum). [(r2-1)/(r2+2)]/[Concentration] [(r2-1)/(r2+2)]/[Specific density], dQ/Q, d{ln(Q)}, for any quantity Q. Also log-scale differential d{ln(Q)}/dt = (dQ/dt)/Q. Also evolution rate on log-scale [Permeability]/[Permeability of vacuum]. [Permittivity]/[Permittivity of vacuum]. Dielectric constant. Q/Q, for any quantity Q. 1/[Relaxation time]. Used in all branches of Science. Used in all branches of Science.
W.m-2.sr-1 J.kg-1, Gy (gray) Gy.s-1 Bq (becquerel) N.m.rad-1 Dimensionless (ohm)
1 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 m-1 kg.m2.s-3.A-1 kg.m2.s-3.A-1 1 m3.mol-1 m3.kg-1 1 s-1 1 1 1 s-1 s
V (volt) V (volt) Dimensionless
Dimensionless
Dimensionless Dimensionless Dimensionless
Relaxivity, molar Reluctance, magnetic Resistance, electric Resistance, thermal Resistance to impact Resistivity, electric Reynolds number RF attenuation S: Seeback coefficient Self-diffusion coefficient Settling rate Shear modulus Softening point Solid angle Solubility, molar Sonic attenuation Specific charge Specific density Specific energy Specific enthalpy Specific entropy Specific free energy Specific free enthalpy Specific heat Specific heat capacity Specific internal energy Specific refractivity
m3.s-1.mol-1 kg-1.m-1.s2.A2 kg.m2.s-3.A-2 kg-1.m-2.s3K kg.s-2 kg.m3.s-3.A-2 1 m-1 kg.m2.s-3.A1 .K-1 m2.s-1 s-1 kg.m.s-2 K 1 m-3.mol m-1 kg-1.s.A kg.m-3 m2.s-2 m2.s-2 m2.s-2.K-1 m2.s-2 m2.s-2 m2.s-2 m2.s-2.K-1 m2.s-2 m3.kg-1 J.kg-1 J.kg-1 J.K-1.kg-1 J.kg-1 J.kg-1 J.kg-1 J.K-1.kg-1 J.kg-1 sr (steradian) dB/m C.kg-1 typically dB/s N, N.rad-1 m.H-1 V.A-1, (ohm) K/W J.m-2 .m Dimensionless dB/m V.K-1
[Relaxation rate]/ [Concentration]. 1/[Permeability]. [Potential]/[Current] of a device. [T]/[Power]. [Energy]/[Area]. Same dimension as notch resistance ([Resistance]*[Length])/ [Area]. [Velocity]*[length]/ [Kinematic viscosity] [Ratio]/m. Applies to propagation. [Potential]/[Temperature]. Same as thermoelectric power [Distance2]/[Time]. [Ratio]/[Time]. [Force]/[Angle]. Same as modulus of rigidity Temperature at which hardness drops below a level. [Quantity]/[Volume]. Same as concentration [Power ratio]/m. Applies to propagation. [Charge]/[Mass]. Charge/mass ratio. [Mass]/[Volume]. Same as density of mass [Energy]/[Mass]. [Enthalpy]/[Mass]. Like specific heat. [Entropy]/[Mass]. [Free energy]/[Mass]. Also specific Helmholtz function [Free enthalpy]/[Mass]. Also specific Gibbs function [Heat]/[Mass]. [Heat capacity]/[Mass]. [Internal energy]/[Mass]. Like specific heat. [(r2-1)/(r2+2)]/[Specific
Specific volume Speed Spin Star magnitude Stiffness, linear Stiffness, rotational Strain point Strength, compressive Strength, dielectric Strength, electric field Strength, ionic Strength, magnetic field Strength, tensile Surface density of charge Surface element Surface energy Surface tension Susceptance, capacitive Susceptibility, magnetic Stress T: Temperature Temperature gradient Tensile strength Tension
m3.kg-1 m.s-1 1 1 kg.s-2 kg.m2.s-2.rad1
Dimensionless Dimensionless N.m-1 N.m.rad-1
K kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m.s-3.A-1 kg.m.s-3.A-1 m-3.mol m-1.A kg.m-1.s-2 m-2.s.A m2 kg.s-2 kg.s-2 kg-1.m-2.s3.A2 1 kg.m-1.s-2 K K.m-1 kg.m-1.s-2 kg.m-1.s-2 J/m2 N/m S (siemens) Dimensionless Pa, N.m-2 K (kelvin) N.m-2, Pa Pa, N.m-2 N.m-2, Pa C.m-2 N.m-2, Pa V.m-1 V.m-1
density] [Volume]/[Mass]. [Distance]/[Time]. Same as velocity. of a quantum particle m-m' = -100.4(S/S'), where S,S' are luminous fluxes of two stars [Force]/[Displacement]. ... of a structure. [Moment of force]/[Angle]. ... of a structure. Temperature at which viscosity drops below 1013.5 Pa.s [Force]/[Area]. Same dimension as pressure. [Potential]/[Distance]. Same as electric strength [Potential]/[Distance]. Also called electric intensity Sum([Concentration]*[Ionic quantum charge]2). [Current]/[Distance]. Also called magnetic intensity [Force]/[Area]. Same as pressure. [Charge]/[Area] [Distance]*[Distance]. Same as area [Energy]/[Area]. Same as surface tension. [Force]/[Length]. Same as surface energy. 1/[Reactance]. [Relative permeability]-1. [Force]/[Area]. Same as pressure. [Temperature]/[Distance]. Same as thermal gradient [Force]/[Area]. Same as pressure. [Force]/[Area]. Like pressure.
Thermal conductivity Thermal diffusivity Thermal expansion coefficient Thermal gradient Thermal resistance Thermodynamic force Thermoelectric power | Thermopower Thomson coefficient Time Torque Traction Traction coefficient Transmission loss U: V: van der Waals constant: a van der Waals constant: b van der Waals virial constant: A van der Waals virial constant: B Variance of current noise nJ2 Variance of voltage noise nV2 Vector potential, electromagnetic Velocity Verdet constant Virial coefficient: second
kg.m.s-3.K-1 m2.s-1 K-1 K.m-1 kg-1.m-2.s3K kg.m.s-2.mol1
W.m-1.K-1
K/W N/mol V.K-1 W.K-1.A-1 s (second) N.m N (newton) Dimensionless dB/m
kg.m2.s-3.A1 .K-1 kg.m2.s-3.A1 .K-1 s kg.m2.s-2 kg.m.s-2 1 m-1
[Heat flux]/ ([Distance]*[Temperature]). Same as heat conductivity ([Temperatute]/[Time])/ [2Temperature]. ([Length]/[Length])/ [Temperature]. [Temperature]/[Distance]. Same as temperature gradient of a device. [T]/[Power]. [Chemical potential]/ [Distance]. [Potential]/[Temperature]. Same as Seeback coefficient [Heat flux]/ ([Temperature]*[Current]). [Force]*[Distance]. Same as moment of force Maximum tangential force before slipping. [Traction]/[Weight]. [Ratio]/m. Used for any other quantity. a in (p+a/V2)(V-b)=RT. b in (p+a/V2)(V-b)=RT. A in p=(n/V)RT+(n/V)2(RTBA). B in p=(n/V)RT+(n/V)2(RTBA). [Current]2/[Bandwidth] [Voltage]2/[Bandwidth] [El.field strength]*[Time], [Mag.flux density]*[Distance] [Distance]/[Time]. Same as speed. ([Angle]/[Length])/[Magnetic flux density] A in p=(n/V)RT+A(n/V)2+B(n/V)3
kg.m5.s-2 m3 kg-1.m5.s2 .mol-2 kg-1.m3.mol-1 s.A2 kg2.m4.s-5.A-2 kg.m.s-2.A-1 m.s-1 kg-1.m-1.s2.A1 kg.m5.s2 .mol-2
Pa.m6
A2/Hz V2/Hz V.s.m-1, T.m
rad.m-1.T-1 Pa.(mol.m-3)-2
Virial coefficient: third Virial coefficient: fourth Viscosity, dynamic Viscosity, kinematic Voltage Voltage noise, variance nV2 Volume Volume concentration W: Wavelength Wavenumber Work function X: Y: Young modulus Z:
kg.m8.s2 .mol-3 kg.m11.s2 .mol-4 kg.m-1.s-1 m2.s-1 kg.m2.s-3.A-1 kg2.m4.s-5.A-2 m3 1 m m-1 kg.m2.s-2
Pa.(mol.m-3)-3 Pa.(mol.m-3)-4 Pa.s V V2/Hz Dimensionless
+C(n/V)4. B in p=(n/V)RT+A(n/V)2+B(n/V)3 +C(n/V)4. C in p=(n/V)RT+A(n/V)2+B(n/V)3 +C(n/V)4. ([Force]/[Area])/[Velocity] [Dynamic viscosity]/ [Density] [Potential], same as electromotive force [Voltage]2/[Bandwidth] [Area]*[Distance] [Volume of substance]/[Total volume] [Wave velocity]/[Frequency]. [Number of waves]/ [Distance]. [Energy] needed to remove an electron. [Stress]/([Length]/[Length]).
J, eV
kg.m-1.s-2
N.m-2, Pa
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDa EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- SI Dimensions of Physical Quantities PDFDocumento8 pagineSI Dimensions of Physical Quantities PDFPraveen AK0% (1)
- Easurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: IDocumento28 pagineEasurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: Ipankaj baviskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Travel: An Approximate Mathematical SolutionDa EverandTime Travel: An Approximate Mathematical SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics UnitsDocumento5 paginePhysics UnitsGopan KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit ConversionDocumento21 pagineUnit ConversioninsidereaderNessuna valutazione finora
- SI Base UnitsDocumento20 pagineSI Base UnitsSatish Kumar MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- SI Units EM Quantities PDFDocumento1 paginaSI Units EM Quantities PDFStefan BusoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDocumento6 paginePhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDNessuna valutazione finora
- Units With FormulaDocumento10 pagineUnits With Formulazeeshan arifNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied - Physics - Notes 1Documento248 pagineApplied - Physics - Notes 1Ashutosh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- AL-1 NotesDocumento244 pagineAL-1 NotesABDULLAH SHAHZADNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Si UnitsDocumento10 pagineBase Si UnitsJehana NaolNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics GlossaryDocumento30 paginePhysics Glossarywhiskey13Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Units & DimensionsDocumento19 pagineA Units & Dimensionsf20230069Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Exam Quick Revision NotesDocumento40 paginePhysics Exam Quick Revision NotesPinky Ann DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Bifilar Determination of EarthDocumento9 pagineBifilar Determination of EarthSehran AmjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics First TopicDocumento11 paginePhysics First TopicRj TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Named Units Derived FromDocumento11 pagineNamed Units Derived FromSidharth PothalNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocumento39 pagineSimple Harmonic MotionJenievie EspinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of SI Units And: PrefixesDocumento4 pagineTables of SI Units And: PrefixesZUBER AHMEDNessuna valutazione finora
- SI UnitsDocumento8 pagineSI UnitsRoy VeseyNessuna valutazione finora
- MS1124 Intro To Mech Eng (Week 3) - StudentDocumento15 pagineMS1124 Intro To Mech Eng (Week 3) - StudentSalman AlfaridziNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansys UnitsDocumento4 pagineAnsys UnitslllNessuna valutazione finora
- SI Units and Simple Mechanical and AC Electrical FormulaeDocumento4 pagineSI Units and Simple Mechanical and AC Electrical FormulaeAnonymous pMVR77x1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Named Units Derived FromDocumento5 pagineNamed Units Derived FromYuunari LingNessuna valutazione finora
- International UnitsDocumento10 pagineInternational Unitspilas_nikolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics FormulaeDocumento12 paginePhysics FormulaeKamlesh Kumar100% (2)
- FundamentalsofPhysics PDFDocumento233 pagineFundamentalsofPhysics PDFMamdoh Al-QuthamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 To 12 Physics in DetailsDocumento131 pagineGrade 10 To 12 Physics in DetailsXavier100% (1)
- Units and Conversion FactorsDocumento30 pagineUnits and Conversion FactorsBun YaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934Documento34 paginePhysics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934masairev8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Base Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento39 pagineBase Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineeringlukhman100% (1)
- Measurement: Quantities, Numbers and Units: Section 7Documento4 pagineMeasurement: Quantities, Numbers and Units: Section 7Claudia daguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Units, Dimensions Error AnalysisDocumento25 pagineUnits, Dimensions Error AnalysisVishal KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sources of Gravitational RadiationDocumento8 pagineSources of Gravitational RadiationFuzzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 To 12 Physics in DetailsDocumento131 pagineGrade 10 To 12 Physics in Detailschileshe normanNessuna valutazione finora
- Attenuation and Dispersion: MechanismsDocumento12 pagineAttenuation and Dispersion: MechanismsMordekhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Igcse Exam Revision NOTES - 2022Documento35 paginePhysics Igcse Exam Revision NOTES - 2022Okasha :DNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1Documento96 pagineModule 1Mariane CarandangNessuna valutazione finora
- M T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocumento3 pagineM T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolMark ArceNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundatin of Engeneering 2Documento16 pagineFoundatin of Engeneering 2sunshaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidades y Dimensiones PDFDocumento17 pagineUnidades y Dimensiones PDFISRAELNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 12 Physics PamphletDocumento131 pagineGrade 10 12 Physics PamphletBryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Cheat SheetDocumento8 pagineNuclear Cheat SheetM J RhoadesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics - 1 Chapter 1Documento41 paginePhysics - 1 Chapter 1Dreamrs TtyNessuna valutazione finora
- Part Two: Oscillations, Waves, & FluidsDocumento32 paginePart Two: Oscillations, Waves, & FluidssteveNessuna valutazione finora
- Oscillations PDFDocumento22 pagineOscillations PDFSanatan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Simple Pendulum: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineThe Simple Pendulum: ObjectiveAlexo ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics in Details g10-12Documento131 paginePhysics in Details g10-12Andrea Maluba100% (2)
- Physical Quantities: Length Mass Speed (Velocity) Pressure Power TemperatureDocumento7 paginePhysical Quantities: Length Mass Speed (Velocity) Pressure Power Temperaturepradipta satriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6B - CirgravDocumento35 pagine6B - CirgravLeighton ThompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Units and Significant FiguresDocumento15 pagineModule 1 Units and Significant FiguresferchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Documento10 pagineUltrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)SITI NURFATIHA JAMIANNessuna valutazione finora
- AcronymsDocumento143 pagineAcronymsyans77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Table I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit SymbolDocumento4 pagineTable I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit SymbolmayopollinNessuna valutazione finora
- Units and Measurment: Angles in Degree Angles in RadiansDocumento7 pagineUnits and Measurment: Angles in Degree Angles in RadiansRamana K GNessuna valutazione finora
- Dramidopanishad Prabhava SarvasvamDocumento89 pagineDramidopanishad Prabhava SarvasvamGopal Venkatraman100% (1)
- Ouvvai Kural Moolamum UraiyumDocumento61 pagineOuvvai Kural Moolamum UraiyumMuthukrishnan Subramanian100% (2)
- E Book VirothiDocumento42 pagineE Book Virothiapi-26417874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tirukuralin SanskritDocumento130 pagineTirukuralin SanskritGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kasi Mahatmyam in TamilDocumento32 pagineKasi Mahatmyam in TamilGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Details of Chitra Kavi in TamilDocumento46 pagineDetails of Chitra Kavi in TamilGopal Venkatraman100% (3)
- Kavyadarsa in TamilDocumento18 pagineKavyadarsa in TamilGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandhi IlakkanamDocumento7 pagineSandhi IlakkanamGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chidambara MummanikkovaiDocumento13 pagineChidambara MummanikkovaiGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shirdi Sai AratiDocumento83 pagineShirdi Sai AratiGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Saiva Adiyar VanakkamDocumento55 pagineSaiva Adiyar VanakkamGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ani Ilakkanam in TamilDocumento22 pagineAni Ilakkanam in TamilGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil Poetry IdentificationDocumento6 pagineTamil Poetry IdentificationGopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Tamil Poetry Using Context Free Grammar Using Tamil Grammar RulesDocumento9 pagineClassification of Tamil Poetry Using Context Free Grammar Using Tamil Grammar RulesCS & ITNessuna valutazione finora
- Samanubhuti 2012Documento114 pagineSamanubhuti 2012Gopal VenkatramanNessuna valutazione finora
- TUTORIAL CH 1 - Part 2Documento3 pagineTUTORIAL CH 1 - Part 2Adam MrsmNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal PR TermodinamikaDocumento10 pagineSoal PR TermodinamikaanjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideal Diatomic Gas: Internal Degrees of Freedom: Polyatomic Species Can Store Energy in A Variety of WaysDocumento61 pagineIdeal Diatomic Gas: Internal Degrees of Freedom: Polyatomic Species Can Store Energy in A Variety of WaysMarc EsplinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/43 October/November 2021Documento15 pagineCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/43 October/November 2021pvaidehi9826Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0702 FDDocumento49 pagineCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0702 FDKim balugayNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC - Thermal Physics and Kinetic Theory - (1999 - 2004) - SPQDocumento15 pagineCSEC - Thermal Physics and Kinetic Theory - (1999 - 2004) - SPQA.BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics0625-01 (Start2016-Mayjun2023) Mcq+Core+Un-editedDocumento1.118 paginePhysics0625-01 (Start2016-Mayjun2023) Mcq+Core+Un-editedAHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Session 6Documento2 pagineLab Session 6Saba AkbulutNessuna valutazione finora
- HyperWorks 10.0 Release Notes - Solvers - RADIOSS 10Documento11 pagineHyperWorks 10.0 Release Notes - Solvers - RADIOSS 10bsrkaushik1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Einstein's Theory of Specific Heats: Classical Concept Review 23Documento2 pagineEinstein's Theory of Specific Heats: Classical Concept Review 23Agres KrismantonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geothermal Production Engineering SkillDocumento9 pagineGeothermal Production Engineering SkillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Faroukhi - Monogram On Thermal CoductivityDocumento151 pagineFaroukhi - Monogram On Thermal CoductivitynitingkulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics: 1 Calorie 4.186 JDocumento16 pagineChapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics: 1 Calorie 4.186 Jطلحه سحيل صديقىNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento16 pagineChapter 2RXDoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Conductivity, Resistance and Specific Heat Capacity of Chemically-Treated, Widely-Used Timber For Building-EnvelopeDocumento21 pagineThermal Conductivity, Resistance and Specific Heat Capacity of Chemically-Treated, Widely-Used Timber For Building-EnvelopeAlif Mu'tashimNessuna valutazione finora
- Polimorfismos de Benzocaina PDFDocumento9 paginePolimorfismos de Benzocaina PDFDiegoAndrésYiZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of HeatDocumento101 pagineThe Nature of HeatfaezzuNessuna valutazione finora
- Polypropylene Glycol: Cautionary Response InformationDocumento2 paginePolypropylene Glycol: Cautionary Response InformationBenediktus Ma'dikaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME301A: Energy Systems - I Combustion Thermodynamics: Lecture 4-5Documento32 pagineME301A: Energy Systems - I Combustion Thermodynamics: Lecture 4-5Mukul ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific HeatDocumento2 pagineSpecific HeatVanessa Christonette SistosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 11 - Heat and ThermodynamicsDocumento40 pagineChapter - 11 - Heat and ThermodynamicsMohammed Aftab AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ترمودینامیک شیمیائی4Documento3 pagineترمودینامیک شیمیائی4api-3706290Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2, First Law of ThermodynamicsDocumento30 pagineChapter 2, First Law of ThermodynamicsMohamed AbdelaalNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I-21-22Documento50 paginePhysics I-21-22Ahmed BagradNessuna valutazione finora
- Calorimetry:-: Ms Ms Ms S M M MDocumento4 pagineCalorimetry:-: Ms Ms Ms S M M MSuperintendentHqrs CustomsStatisticsNessuna valutazione finora
- R-Value and CR Value Spreadsheet (Ver11)Documento8 pagineR-Value and CR Value Spreadsheet (Ver11)Souvik Roy ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Boyd - Reno Research PaperDocumento48 pagineBoyd - Reno Research Paperapi-249615264Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science8 - q1 - Mod6 - Heat and Temperature - FINAL07282020Documento32 pagineScience8 - q1 - Mod6 - Heat and Temperature - FINAL07282020Melerose Dela SernaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 11Documento10 pagineThermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 11Khirod Chandra BarikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Converter SpreadSheetDocumento14 pagineUnit Converter SpreadSheetrobertolaurinoNessuna valutazione finora