Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
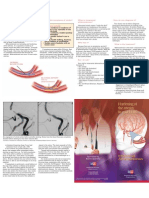
A Stroke Recovery Guide
Caricato da
manjukumard2007Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Stroke Recovery Guide
Caricato da
manjukumard2007Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Steps Against
Recurrent Stroke
(STARS)
Take steps against recurrent
stroke by making the
necessary changes
in your life.
What haened to me7
You had a stroke. The stroke you had was
most likely an ischemic (is-keem-ik)
stroke, the most common type of stroke.
Your Guide to Ischemic Stroke
lschemic
stroke.
An ischemic stroke occurs when a
blood clot blocks an artery and keeps
blood from reaching the brain. An
ischemic stroke often occurs after
cholesterol and other material
(plaques) have built up in the arteries.
You may have had a stroke as a result
of plaques that built up in the main
arteries to your brain. Or, your stroke
may be due to a blood clot that
traveled to your brain from your heart.
It may just be that your blood tends
to clot easily.
2
What are the risk factors for stroke7
A risk factor is a certain condition that
makes a person more likely to get a
disease or have a stroke. There are two
kinds of risk factors: the kind you cant
change and the kind you can.
UncontroIIabIe risk factors:
Age
Gender
Race
Family history
Previous stroke or transient
ischemic attack (TIA)
ControIIabIe risk factors:
High blood pressure
Atrialfbrillation
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
Circulation problems
Tobacco use and smoking
Alcohol use
Physical inactivity
Obesity
Your Guide to Ischemic Stroke
3
How can l reduce my risk of stroke7
You can reduce your stroke risk in a
number of ways. You may be abIe to
reduce your risk of stroke by making
some changes in your daiIy Iife:
If you smoke, stop.
Enjoy some form of physical activity
every day.
If you drink, limit the number of
alcoholic beverages you drink daily.
Work closely with your healthcare
professionals.Evenifyoufndit
diffcultattimes,dontgiveup.
You may need to take medicine to
reduce your stroke risk. For example,
some stroke survivors take drugs that
reduce the build up of plaque in the
arteries.
You may not be able to take some
of these drugs if you have certain
conditions.
Ask your healthcare professional
about the medicines you are taking
and why you are receiving some
and not others.
4
What shouId my bIood ressure be7
What eIse shouId l be doing7
Ask your healthcare professional what
your blood pressure and cholesterol
levels should be. Work together with
your healthcare professional to reach
and stay at these goals through lifestyle
modifcationsand/ortreatment.Once
you have reached them, do not stop
taking your medicines unless your
healthcare professional tells you to do
so. If you do, your levels could become
abnormal again and increase your risk
for a new stroke.
For most people, a blood pressure
readingof120/80mmHganda
total cholesterol level of less than
200mg/DLaredesirable.
5everaI treatment goaIs shouId be
reguIarIy evaIuated:
Yourbadcholesterol(LDL)and
your blood pressure. Keep a personal
and/orwrittenrecordofyourLDL
and blood pressure levels.
Your weight
If you have diabetes, your hemoglobin
A1c level
If you smoke, it is very important to
stop smoking and to keep track of
your progress.
5
What haens next7
Before you leave the hospital, be sure
to set up appointments with your
healthcare professional. Try not to
miss any, but if you do, call and make
a new one right away. Keeping your
appointments will help you stay on
track with your treatment.
It is very important that you follow up
with your healthcare professional and
continue the treatments that were
started while you were in the hospital.
Tyes of treatment
The following treatments are used to
help stroke survivors lower their risk of
recurrent stroke. Ask your healthcare
professional which treatments are right
for you. Then take the recommended
steps to reduce your risk.
If you have questions
about any treatment
you are taking, ask
your healthcare
professional.
6
AntiIateIet agentsAntiplatelet
agents are drugs that play a role in
keeping platelets in your blood from
sticking together and forming clots,
whichhelpskeepbloodfowingand
helps reduce your risk of a stroke or
heart attack.
AnticoaguIantsAnticoagulants
reduce the ability of blood to clot.
Healthcare professionals often prescribe
these drugs for their patients with
atrialfbrillationordeepveinthrombosis.
Patientswithatrialfbrillation,for
example, can form blood clots in the
heart. The clots could travel to the
brain and cause a stroke.
8Iood ressure medicinesBlood
pressure medicines such as angiotensin-
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
and angiotensin II receptor blockers
(ARBs) are drugs used to lower high
blood pressure. There are additional
medications such as diuretics (water
pills), calcium channel blockers and
beta blockers that may be prescribed
to help lower blood pressure.
ChoIesteroI-Iowering medicines
Statins are drugs that manage
cholesterol levels. In addition, your
healthcare professional might
prescribe other types of medicines
that lower cholesterol.
7
xerciseExercise helps raise good
cholesterol. It also keeps your arteries
fexible,whichinturnhelpskeepblood
fowingandlowersbloodpressure.
Once your healthcare professional says
you can, try to exercise for at least 30
minutes three to four times a week. For
example, walk, jog or ride a bike. Be
sure to consult with your healthcare
professional before beginning any
exercise program.
Keep moving! Move as much as you
can. For instance, if you park your car
far away from the store, you will get
a little more walking into your day.
Instead of sitting and watching TV,
work in the garden or clean a closet.
8
DietA healthy diet can help keep
plaques from building up in your arteries.
A low-fat, low-cholesterol diet can help
you reach and stay at your ideal weight:
Try to eat less than 200 mg of
cholesterol a day. Check the
nutrition labels of the food products
youeattofgureouthowmuch
cholesterol they contain.
High-fberfoods,suchasoatmeal,
dried beans and fruits, will help lower
your cholesterol level.
5moking cessationIf you smoke, stop!
Smoking causes arteries to narrow and
makes the blood more likely to clot. Both
of these are risk factors for stroke. It
also increases blood pressureanother
major risk factor for stroke.
If you dont stop smoking, you are
fvetimesmorelikelytohaveanother
stroke or a heart attack or to die.
When you quit, your risk will go
down quickly!
To help you quit, you may want to ask
your healthcare professional about
nicotine replacement therapy. You can
also join a stop-smoking program in
your community. Your family can help
you by making sure that any members
of your family who smoke also quit.
Learn more at
www.stroke.org/risk
9
NoTe The TIme wheN ANY SYmpTomS
fIRST AppeAR. If given within three
hours of the frst symptom, there is an
FDA-approved clot-buster medication
that may reduce long-term disability
for the most common type of stroke.
LeARN AbouT moRe SuddeN SIGNS
of STRoke AT
warning Signs of Stroke
Learn the many warning signs of a
stroke. Act fAST and cALL 9-1-1
ImmedIATeLY at any sign of a stroke.
use fAST to remember warning signs:
fAce: Ask the person to
smile. does one side of the
face droop?
A
ARmS: Ask the person to raise
both arms. does one arm drift
downward?
S
Speech: Ask the person to
repeat a simple phrase. Is their
speech slurred or strange?
T
TIme: If you observe any
of these signs, call 9-1-1
immediately.
F
NoTe The TIme wheN ANY SYmpTomS
fIRST AppeAR. If given within three
hours of the frst symptom, there is an
FDA-approved clot-buster medication
that may reduce long-term disability
for the most common type of stroke.
LeARN AbouT moRe SuddeN SIGNS
of STRoke AT
warning Signs of Stroke
1-800-5Tk0K5
(787-6537)
www.stroke.org
All publications are reviewed by National
Stroke Associations Publications Committee.
2011 National Stroke Association
3/11BG14
National Stroke Associations mission
is to reduce the incidence and impact
of stroke by developing compelling
education and programs focused on
prevention, treatment, rehabilitation
and support for all impacted by stroke.
A stroke is a brain attack that occurs
when a blood clot blocks an artery
or a blood vessel breaks, interrupting
bloodfowtoanareaofthebrain.
Brain cells begin to die.
CALL 9-1-1 lMMDlATLY lF
Y0U 5 0N 0k M0k 5lCN5
0F A 5Tk0K.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation EvidenceDocumento815 pagineSpinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation EvidenceHarish Pai K88% (8)
- ORTHOSIS - and ProthesisDocumento112 pagineORTHOSIS - and Prothesismanjukumard2007100% (1)
- AFO Orthometry FormDocumento2 pagineAFO Orthometry Formmanjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marma Scince Power of Self Healing 1Documento23 pagineMarma Scince Power of Self Healing 1manjukumard2007100% (5)
- Eng KafoDocumento20 pagineEng Kafomanjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marma - MassageDocumento1 paginaMarma - Massagemanjukumard2007100% (1)
- A Stroke RecoveryDocumento2 pagineA Stroke Recoverymanjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tools For Diagnosis of Knee InjuriesDocumento10 pagineTools For Diagnosis of Knee Injuriesmanjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Explaining StrokeDocumento20 pagineExplaining StrokeChrisTine M. MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Mobilizationw10Documento33 pagineNeural Mobilizationw10manjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- NiramayaDocumento5 pagineNiramayaIam WaitNessuna valutazione finora
- Health CareDocumento10 pagineHealth Caresonali mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pts (Peroneal Tendon Strain)Documento15 paginePts (Peroneal Tendon Strain)Yuni FridayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Klasifikasi Penyakit Dan Keadaan Yang Mempengaruhi Jaringan PeriodontiumDocumento16 pagine03 Klasifikasi Penyakit Dan Keadaan Yang Mempengaruhi Jaringan PeriodontiumFloba Ika SianturiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Disorders PDFDocumento38 pagineGenetic Disorders PDFEllen Mae PrincipeNessuna valutazione finora
- Zung Depression Rating Scale PDFDocumento2 pagineZung Depression Rating Scale PDFdienfahrezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHDocumento14 pagineSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHbhatubim100% (1)
- Homeopathic First Aid For Infants and Children PDFDocumento3 pagineHomeopathic First Aid For Infants and Children PDFRamesh Shah100% (1)
- Clinical Examination Spec BookletDocumento57 pagineClinical Examination Spec BookletShaima Mustafa50% (2)
- 2020 Mcqs Endondontic EmergencyDocumento17 pagine2020 Mcqs Endondontic Emergencyareej alblowi100% (4)
- Warfarin SodiumDocumento3 pagineWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 8. AdmissionsDocumento9 pagineCHAPTER 8. AdmissionsKumala MadurahayunirwanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Most CommonsDocumento80 pagineThe Most CommonsJmee8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study 2Documento4 pagineDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANessuna valutazione finora
- SelectionList R1 Web (MBBS BDS)Documento569 pagineSelectionList R1 Web (MBBS BDS)kaushikraj42starNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Research: Dr. Parminder NainDocumento53 pagineClinical Research: Dr. Parminder NainDr. PARMINDER NAINNessuna valutazione finora
- MarchDocumento122 pagineMarchZozo Mostafa100% (3)
- Health & Family Welfare Department: Government of West BengalDocumento2 pagineHealth & Family Welfare Department: Government of West BengalAnkit JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISDocumento15 pagineBIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISAnonymous KdUrkMIyJQ73% (56)
- Nitte News Jan-Dec 2010Documento88 pagineNitte News Jan-Dec 2010yvj_20006373Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preceptor PPT - HTMLDocumento28 paginePreceptor PPT - HTMLwld_58hNessuna valutazione finora
- Damage Control Orthopaedics, EvolvingDocumento17 pagineDamage Control Orthopaedics, EvolvingAzmi Farhadi100% (1)
- Definition of Deviated Nasal SeptumDocumento3 pagineDefinition of Deviated Nasal SeptumMank BayuNessuna valutazione finora
- GAS Turner-Stokes-2009 PDFDocumento13 pagineGAS Turner-Stokes-2009 PDFAndrea FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Low Back Pain in Adults - UpToDateDocumento25 pagineEvaluation of Low Back Pain in Adults - UpToDateJeissonPargaSalasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1Documento5 pagineRectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1yuuki konnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDocumento7 pagineHyperbaric Oxygen Therapy18juni1995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisDocumento111 paginePedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisYusriNessuna valutazione finora
- Vii. LCP'S Operations ManualDocumento54 pagineVii. LCP'S Operations ManualPearly RederaNessuna valutazione finora
- Corazon Aquino Delivery RoomDocumento5 pagineCorazon Aquino Delivery RoomJustine CagatanNessuna valutazione finora