Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Urine Extaction
Caricato da
Emmanuel Bierrow AsiamahDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Urine Extaction
Caricato da
Emmanuel Bierrow AsiamahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. Urine was collected from a person known to have ingested "a lot of aspirin".
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is known to be rapidly hydrolyzed in the body to salicylic acid that is then further metabolized to salicyluric acid (50-80%), salicyl 0-glucuronide (10-30%), and free salicylic acid (5-10%). In general terms, what would you have to do in order to extract the urine for quantitation of ingested aspirin [5 points]? Aspirin (USAN), also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. Salicylic acid, the main metabolite of aspirin, is an integral part of human and animal metabolism. While in humans much of it is attributable to diet, a substantial part is synthesized endogenously. Gas Chromatography (GC) is a widely used technique in forensic chemistry. Compounds that are not highly volatile or likely to decompose at the higher temperature used in GC are usually derivatised prior to analysis. The most common type of derivative is a methyl silane. This functional group increases the volatility of the compound. There are a number of different silyating reagents available. The choice of reagent depends upon the functional groups to be derivatised. The reagent used here (N-O-bis(trimethylsilyl) trifluororacetamide, BSTFA) is a multi-purpose reagent which is capable of derivatizing a wide range of functional groups. The mass spectral detector is probably the most important detector for GC in forensic chemistry. This is partly due to the low limits of detection that the detector has, but mainly because of the structural information provided by the fragmentation ions produced. In order to extract the urine for quantitation of ingested aspirin, Remove 5 ml of urine and adjust to a pH of 10-11 using NH4 OH (approximately 0.8ml) Place in a small separatory funnel. Add 5ml 1-chlorobutane. Shake, remove 4 ml of the organic layer into a test tube, and evaporate to dryness by blowing a steady stream of nitrogen over the tube. Make sure your sample is completely dry. Add 25ul BSFTA to the dry tube. The reaction will not work if any moisture is present. Cap and let stand 10 minutes. Warm if necessary. Inject 0.5 L of this onto the GC/MS. Repeat 2 more times. Determine the precision of the aspirin by calculating the standard deviation of the peak areas. Determine the identity of the aspirin using past data, and through the injection of pure samples provided to give an external standard calibration graph. Using the stock solutions, dilute this solution so that your calibration graph covers the concentration range 1 g/mL to 10 g/mL. Start your calibration standard preparation at the derivatization stage. Your calibration graph should have at least 5 points in it.
2. If extraction of cocaine is 80% efficient and GCMS quantitation shows that 150 mg of cocaine is present in the extracted sample, how much cocaine was present in the original sample [5 points]?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Aspirin ExperimentDocumento7 pagineAspirin ExperimentTrương Thị Bích LiễuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem-131 Lab-05 09-4 Synthesis of Aspirin (STD)Documento2 pagineChem-131 Lab-05 09-4 Synthesis of Aspirin (STD)Sairee AbianNessuna valutazione finora
- Staining TechniquesDocumento19 pagineStaining TechniquesSwayamprakash PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Report BacteriaDocumento11 pagineReport BacteriaSuzeanni JalilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2245-2246 AspirinDocumento2 pagine2245-2246 AspirinPhoenixNessuna valutazione finora
- Determine The Percentage of Active Substance in AspirinDocumento11 pagineDetermine The Percentage of Active Substance in Aspirinحسن كاظم ريسان B-4100% (1)
- Chomp Excersie 3Documento5 pagineChomp Excersie 3Omahri24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Challenger 350 Recommended Operating Procedures and TechniquesDocumento104 pagineChallenger 350 Recommended Operating Procedures and Techniquessebatsea100% (1)
- Postoperative Care in Thoracic Surgery A Comprehensive GuideDocumento397 paginePostoperative Care in Thoracic Surgery A Comprehensive GuideΑΘΑΝΑΣΙΟΣ ΚΟΥΤΟΥΚΤΣΗΣ100% (1)
- Aspirin SynthesisDocumento5 pagineAspirin SynthesisJohn C.W. ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 24 - Experiment B - Aspirin Synthesis and AnalysisDocumento5 pagineChapter 24 - Experiment B - Aspirin Synthesis and AnalysisNeen NaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Volumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonDocumento4 pagineVolumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonSusána SgfNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Lowry Protein AssayDocumento6 pagineModified Lowry Protein AssaywakeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1 Answer To Quide QuestionsDocumento3 pagineExercise 1 Answer To Quide QuestionsrickyNessuna valutazione finora
- C3 IrnmrDocumento10 pagineC3 IrnmrAldi StefanusNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Control IntroDocumento6 pagineQuality Control IntroAnonymous zwCJNlNessuna valutazione finora
- UST-FMS Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Nutrition Academic Year 2021-2022 Experiment No. 2 Titration of Amino AcidsDocumento5 pagineUST-FMS Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Nutrition Academic Year 2021-2022 Experiment No. 2 Titration of Amino AcidsNatalie Cu100% (1)
- LAB - Lung CapacityDocumento5 pagineLAB - Lung CapacityWinnie LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Correlation ExercisesDocumento1 paginaCorrelation ExercisesKrishnaMohan ThatipalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Recombinant ReportDocumento4 pagineRecombinant Report门门Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex HypothesistestDocumento22 pagineEx HypothesistestYana CovarNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicinal Chemistry Unit III Cholenergic Anti ChokenergicDocumento32 pagineMedicinal Chemistry Unit III Cholenergic Anti ChokenergicjalilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectrophotometric and Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids Present in Leaves of Ailanthus ExcelsaDocumento5 pagineSpectrophotometric and Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids Present in Leaves of Ailanthus ExcelsaRam VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- 921 Water DeterminationDocumento4 pagine921 Water DeterminationEspañola EloiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocumento3 pagineEnzymes Lab Reporttanu96tp59520% (1)
- Antacid Analysisrty4Documento4 pagineAntacid Analysisrty4Melced BenasasNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Practical ReportDocumento17 pagineOrganic Chemistry Practical ReportSteffi YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Clini TestDocumento9 pagineClini TestIsni Maulina SukmaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Acetyl Salicylic AcidDocumento5 pagineSynthesis of Acetyl Salicylic AcidSilvia AryaniNessuna valutazione finora
- QC in Clinical LaboratoriesDocumento28 pagineQC in Clinical LaboratoriesMustafa KhandgawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 04-Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocumento18 pagineLab 04-Cardiovascular PhysiologyWilson CheungNessuna valutazione finora
- Iaat12i5p615 PDFDocumento6 pagineIaat12i5p615 PDFsuresh kumar bakhtianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminum HydroxideIIDocumento21 pagineAluminum HydroxideIIbayadmomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation No. "18" "Lemon Peel Tincture, Usp" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsDocumento3 paginePreparation No. "18" "Lemon Peel Tincture, Usp" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsMEDELYN KEITH ESTANISLAONessuna valutazione finora
- UV Absorbance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento24 pagineUV Absorbance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StylePaula Denice Carlos BagunuNessuna valutazione finora
- DistillationDocumento12 pagineDistillationgeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - Bio 180 Problem Set IiDocumento2 pagineName: - Bio 180 Problem Set IiJoshua OliverosNessuna valutazione finora
- Amylase Assay 2Documento9 pagineAmylase Assay 2Rahman ImudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood PerssureDocumento16 pagineBlood Perssuretmondol34256Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment-6-Characteristics of Alkyl Halides PDFDocumento6 pagineExperiment-6-Characteristics of Alkyl Halides PDFDANA IZABEL RIVERANessuna valutazione finora
- Csir Net Examination Life Sciences December 2012 PDFDocumento77 pagineCsir Net Examination Life Sciences December 2012 PDFAbhay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit Tests of Chloride Sulphate Heavy Mattel PDFDocumento6 pagineLimit Tests of Chloride Sulphate Heavy Mattel PDFBrajesh Suman100% (2)
- Lab Report PDDocumento17 pagineLab Report PDhaikalNessuna valutazione finora
- How Temperature Effects Enzyme ActivityDocumento7 pagineHow Temperature Effects Enzyme ActivitywildimaginationNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento8 pagineLab ReportNAEEM MALIKNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base Titration - The Molar Mass of An Unknown, Diprotic AcidDocumento4 pagineAcid Base Titration - The Molar Mass of An Unknown, Diprotic AcidJakero VillarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of ParacetamolDocumento11 pagineSynthesis of ParacetamolFairodz Rowaon TuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Selection of Extraction SolventsDocumento3 pagineSelection of Extraction SolventsSyafiqah AfandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive SystemDocumento53 pagineDigestive SystemEra CaridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I: Ans: C. SP HybridizedDocumento2 pagineUnit I: Ans: C. SP HybridizedAfrah MNessuna valutazione finora
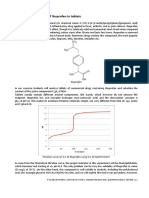
- 8B. Acid-Base Titration of Ibuprofen in TabletsDocumento2 pagine8B. Acid-Base Titration of Ibuprofen in TabletsAhmed Salih100% (1)
- Buffer SolutionDocumento24 pagineBuffer SolutionpumeanandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micropipetting: Transferring Minute Volumes Background of The ActivityDocumento2 pagineMicropipetting: Transferring Minute Volumes Background of The ActivityJj ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis LabDocumento4 pagineAP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Labpointweb50% (2)
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Kinetics StudyDocumento7 pagineEffect of Temperature On Enzyme Kinetics StudyYvonne MunNessuna valutazione finora
- HomeostasisDocumento4 pagineHomeostasisTanNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A P ValueDocumento4 pagineWhat Is A P ValueDurvesh MeshramNessuna valutazione finora
- Purification of Acetanilide Via RecrystallizationDocumento10 paginePurification of Acetanilide Via RecrystallizationLouisiana Sollestre0% (1)
- Isolation of Invertase Formal ReportDocumento3 pagineIsolation of Invertase Formal ReportGabbySantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of AspirinDocumento8 paginePreparation of AspirincrtgyhujikNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspirin Synthesis Lab Report PDFDocumento11 pagineAspirin Synthesis Lab Report PDFRobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex4-Preparation of AspirinDocumento6 pagineEx4-Preparation of AspirinKaran KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Aspirin - 460 - 19Documento5 pagineSynthesis of Aspirin - 460 - 19Nat WeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Inservice Education Sub: Community Health NursingDocumento17 pagineAssignment On Inservice Education Sub: Community Health NursingPrity DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Plumbing Breakup M 01Documento29 paginePlumbing Breakup M 01Nicholas SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Restorations: Dr. Dina NouriDocumento38 pagineComposite Restorations: Dr. Dina NouriCatherine LoyolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallurgical Test Report: NAS Mexico SA de CV Privada Andres Guajardo No. 360 Apodaca, N.L., C.P. 66600 MexicoDocumento1 paginaMetallurgical Test Report: NAS Mexico SA de CV Privada Andres Guajardo No. 360 Apodaca, N.L., C.P. 66600 MexicoEmigdio MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hamraki Rag April 2010 IssueDocumento20 pagineHamraki Rag April 2010 IssueHamraki RagNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 21 EnglishDocumento180 pagineMicrosoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 21 EnglishAlejandro CadarsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hmo Details November 2022 1Documento6 pagineHmo Details November 2022 1Saad BelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Uttarakhand District Factbook: Almora DistrictDocumento33 pagineUttarakhand District Factbook: Almora DistrictDatanet IndiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thai Guava Production PDF by VNRDocumento29 pagineThai Guava Production PDF by VNRDatta100% (2)
- Proposed Child Right's Policy FrameworkDocumento2 pagineProposed Child Right's Policy FrameworkCrisDBNessuna valutazione finora
- Butt Weld Cap Dimension - Penn MachineDocumento1 paginaButt Weld Cap Dimension - Penn MachineEHT pipeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem of Units and The Circumstance For POMPDocumento33 pagineThe Problem of Units and The Circumstance For POMPamarendra123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 21A Solenoid Valves Series DatasheetDocumento40 pagine21A Solenoid Valves Series Datasheetportusan2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom of AnimaliaDocumento6 pagineKingdom of AnimaliaBen ZerepNessuna valutazione finora
- Tcu Module Pe1 Lesson 1Documento7 pagineTcu Module Pe1 Lesson 1Remerata, ArcelynNessuna valutazione finora
- Figure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorDocumento3 pagineFigure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorElany Whishaw0% (1)
- White Vaseline: Safety Data SheetDocumento9 pagineWhite Vaseline: Safety Data SheetHilmi FauziNessuna valutazione finora
- Borelog CP.101Documento1 paginaBorelog CP.101radixkusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ra Concrete Chipping 7514Documento5 pagineRa Concrete Chipping 7514Charles DoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetra Pak Training CatalogueDocumento342 pagineTetra Pak Training CatalogueElif UsluNessuna valutazione finora
- Liebherr 2956 Manual de UsuarioDocumento27 pagineLiebherr 2956 Manual de UsuarioCarona FeisNessuna valutazione finora
- PPC Production PlantDocumento106 paginePPC Production PlantAljay Neeson Imperial100% (1)
- Chapter 4 CrystallizationDocumento13 pagineChapter 4 Crystallizationprosedur0% (1)
- Metabolism of Carbohydrates and LipidsDocumento7 pagineMetabolism of Carbohydrates and LipidsKhazel CasimiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 28 Attendence RegisterDocumento1 paginaForm 28 Attendence RegisterSanjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Module 1 - Five Healthy Habits Handout (English) PDFDocumento2 pagineAdult Module 1 - Five Healthy Habits Handout (English) PDFKennedy FadriquelanNessuna valutazione finora
- 99 AutomaticDocumento6 pagine99 AutomaticDustin BrownNessuna valutazione finora