Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Yearly Form1 2012
Caricato da
ainarahyuDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Yearly Form1 2012
Caricato da
ainarahyuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
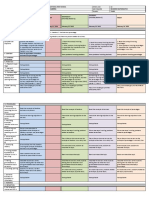
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK 1 2 (09.01.12 13.01.12)
CCTS
ORIENTATIONS WEEK from (04.01.12 06.01.12)
CHAPTER 1: Whole Numbers Perform computations involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers to solve problems. Understand the concept of whole numbers Students will be able to: 1. Count, read and write whole numbers. 2. Identify place value and value of each digit in whole numbers. 3. Round whole numbers. Students will be able to: 1. Add whole numbers. 2. Solve problems involving addition of whole numbers. 3. Subtract whole numbers. 4. Solve problems involving subtraction of whole numbers. Students will be able to: 1. Multiply two or more whole numbers. 2. Solve problems involving multiplication of whole numbers. 3. Divide a whole number by a smaller whole number. 4. Solve problems involving division of whole numbers. Students will be able to: 1. Perform computations involving any combination of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers, including the use of brackets. 2. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers, including the use of brackets.
5 Working out mentally Making inference Translating 5
5 Flash cards
3 (16.01.12 20.01.12)
Whole Numbers
Perform computations involving multiplication and division of whole numbers to solve problems
10
Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers to solve problems.
15
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK 4 5 (30.01.12 03.02.12)
CCTS
CHAPTER 2: Number Patterns and Sequences
Public Holiday Chinese New Year on 23.01.2012 27.01.2012 Recognise and extend Students will be able to: Making number patterns and 1. Describe the pattern of a given number generalizations sequences formed by sequence. Looking for counting on and counting 2. Extend number sequences. patterns back in intervals of any size. 3. Complete missing terms in given number Working out sequences. mentally 4. Construct number sequences based on Classifying given patterns. Finding all Recognise odd and even numbers and make general statements about them. Students will be able to: 1. Identify and describe odd and even numbers. 2. Make general statements about odd and even numbers. Students will be able to: 1. Identify the characteristics of prime numbers. 2. Determine whether a given number is a prime number. 3. Determine all the prime numbers less than 100.
possible solutions Identifying relations
Flash cards CD Rom Concrete materials
Understand the characteristics of prime numbers.
6 (06.02.12 10.02.12)
Number Patterns and Sequences
Public Holiday Birth of Prophet Muhammad on 5th February 2012 ( Sunday ) Understand the Students will be able to: Making characteristics and use the 1. Identify prime factors from a list of factors. generalizations knowledge of factors of 2. Find prime factor(s) of whole numbers. Looking for whole numbers. 3. Determine whether a number is a prime patterns factor of another whole number. Understand the characteristics and use the knowledge of common multiples and Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of whole numbers. Students will be able to: 1. Find the common multiples of two or three whole numbers. 2. Determine whether a number is the common multiple of two or three given numbers. 3. Determine the LCM of two or three given numbers.
Working out mentally Classifying Finding all possible solutions Identifying relations
Flash cards CD Rom Concrete materials 5 5
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA Number Patterns and Sequences LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the knowledge of common factors and Highest Common Factors (HCF) of whole numbers. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Find common factors of two or three whole numbers. 2. Determine whether a number is a common factor of two or three given whole numbers. 3. Determine the HCF of two or three given numbers. EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK
CCTS
6 (06.02.12 10.02.12)
Flash cards CD Rom Concrete materials
7 (13.02.12 17.02.12)
CHAPTER 3: Fractions
School Replacement ( Chinese New Year ) on 11th February 2012 ( Saturday ) Wednesday time table Understand and use the Students will be able to: knowledge of fractions as 1. Read fractions. Interpreting part of a whole. 2. Describe fractions as parts of a whole. Working out 5 3. Represent fractions with diagrams. mentally 4. Write fractions for given diagrams. Identifying Understand and use the knowledge of equivalent fractions. Students will be able to: 1. Find equivalent fractions for a given fraction. 2. Determine whether two given fractions are equivalent. 3. Compare the values of two given fractions. 4. Arrange fractions in order. 5. Simplify fractions to the lowest terms. Students will be able to: 1. Recognise mixed numbers. 2. Represent mixed numbers with diagrams. 3. Write mixed numbers based on given diagrams. 4. Compare and order mixed numbers on number lines. Students will be able to: 1. Recognise proper and improper fractions from given fractions. 2. Change mixed numbers into improper fractions. 3. Change improper fractions into mixed numbers.
relations Classifying Comparing and contrasting Arranging sequentially Translating
Concrete materials, Model fractions, Fraction chart,
Understand the concept of mixed numbers and their representations.
8 (20.02.12 24.02.12)
Fractions
Understand the concept of proper fractions and improper fractions.
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA Fractions LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of addition and subtraction of fractions to solve problems. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Perform addition involving: a. Fractions with common denominators. b. Fractions with different denominators. c. Whole numbers and fractions. d. Fractions and mixed numbers. e. Mixed numbers. 2. Perform subtraction involving: a. Fractions with common denominators. b. Fractions with different denominators. c. Whole numbers and fractions. d. Fractions and mixed numbers. e. Mixed numbers. 3. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition and subtraction of fractions. Students will be able to: 1. Multiply: a. A whole number by a fraction or mixed number. b. A fraction by a whole number. c. A fraction by a fraction (include mixed numbers). 2. Solve problems involving multiplication of fractions. 3. Divide: a. A fraction by a whole number. b. A fraction by a fraction. c. A whole number by a fraction. d. A mixed number by a mixed number. 4. Solve problems involving division of fractions. EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids Concrete materials CD Rom Folding paper
WEEK
CCTS
8 (20.02.12 24.02.12)
Interpreting Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating 5 10
9 (27.02.12 02.03.12
Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions to solve problems.
Classifying Comparing and contrasting Arranging sequentially
10
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
Fractions Students will be taught to : Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of fractions to solve problems. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: 1. Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of fractions, use of brackets. 2. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of fractions, including the use of bracket LEARNING OUTCOMES Teaching Aids
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
10 (19.03.12 23.03.12
Chapter 4: Decimals
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) CCTS Paper Paper 1 2 School Replacement ( Chinese New Year ) on 3rd March 2012 ( Saturday ) Thursday time table Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson Test 1 (05.03.12 09.03.12) Mid Semester One Break ( 10.03.12 18.03.12 ) Understand the relationship Students will be able to: 1 1 between decimals and Interpreting 1. Represent fractions 10 & 100 as decimals fractions. Arranging and vice-versa. sequentially 2. Represent fractions with denominators 10, Comparing and 5 10 100 and 1000 as decimals. contrasting 3. Read and write decimals to thousandths. Working out 4. Change fractions to decimals and vicementally versa. Understand the concept of place value and value of each digit in decimals. Students will be able to: 1. State the place value and value of each digit in decimals. 2. Compare the values of two given decimals. 3. Arrange decimals in order. 4. Round decimals to the nearest whole number or up to three decimal places. Students will be able to: 1. Add decimals. 2. Solve problems involving addition of decimals. 3. Subtract decimals. 4. Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals. Students will be able to: 1. Multiply two or more decimals. 2. Solve problems involving multiplications of decimals
Interpreting Arranging sequentially
Concrete materials Number line
Classifying
Identifying relations Translating
10
Decimals
Understand the concept of addition and subtraction of decimals to solve problems.
10
11 (26.03.12 30.03.12)
Decimals
Understand the concept of multiplication and division of decimals to solve problems.
20 Concrete materials Number line
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
3. Divide: a. A decimal by a whole number. b. A decimal by a decimal. c. A decimal by a fraction. Solve problems involving division of decimals.
Comparing and contrasting Working out mentally Classifying Identifying relations Translating
4.
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Decimals
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform computations involving combined operation of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals to solve problems.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals, including the use of brackets. 2. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals, including the use of brackets. Students will be able to: 1. Express percentages as the number of parts in every 100. 2. Change fractions and decimals to percentages and vice-versa.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids Concrete materials Number line
11 (26.03.12 30.03.12)
Working out mentally Classifying Identifying relations Translating
10
12 (02.04.12 06.04.12)
Chapter 5: Percentages
Understand the concept of percentages and the relationship between percentages and fractions or decimals.
Comparing and contrasting Working out mentally Translating Identifying relations Making inference
10
Concrete materials Discount chart CD Rom
13 (09.04.12 13.04.12)
Percentages
Perform computations and solve problems involving percentages.
Students will be able to: 1. Find the percentage of a quantity. 2. Find the percentage one number is of another. 3. Find a number given the percentage. 4. Find the percentage of increase or decrease. 5. Solve problems involving percentages.
10
15
School Replacement ( Hari Raya Qurban ) on 14h April 2012 ( Saturday ) Thursday time table
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
Chapter 6: 14 (16.04.12 20.04.12) Integers Understand and use the knowledge of integers. Students will be able to: 1. Read and write integers. 2. Represent integers on number lines. 3. Compare the values of two integers. 4. Arrange integers in order. 5. Write positive or negative numbers to represent word descriptions.
Comparing and contrasting Working out mentally Translating Looking for patterns
20
Integers in context Maths game
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Integers
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform computations involving addition and subtraction of integers to solve problems.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Add integers. 2. Solve problems involving addition of integers. 3. Subtract integers. 4. Solve problems involving subtraction of integers.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
15 (23.04.12 27.04.12)
Arranging sequentially Drawing diagrams
10
Integers in context Maths game
16 (30.04.12 04.05.12)
Chapter 7: Algebraic Expressions
Understand the concept of unknowns.
17 (07.05.12 11.05.12)
Algebraic Expressions
18 (14.05.12 18.05.12)
Chapter 8: Basic Measurement
Students will be able to: Interpreting 1. Use letters to represent unknown numbers. Classifying 2. Identify unknowns in given situations Working out Understand the concept of Students will be able to: mentally algebraic terms. 1. Identify algebraic terms with one unknown. Identifying 2. Identify coefficients in given algebraic terms relations with one unknown. Translating 3. Identify like and unlike algebraic terms with one unknown. 4. State like terms for a given term. Public Holiday Wesak Day on 5th May 20112( Saturday ) State Public Holiday Hol Day of Pahang State on 7th May 2012 ( Monday ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: algebraic expressions. 1. Recognise algebraic expressions. 2. Determine the number of terms in given algebraic expressions. 3. Simplify algebraic expressions by combining the like terms. Understand the concept of Students will be able to: length to solve problems. 1. Measure the length of objects. 2. Convert one metric unit to another (mm, cm, Working out mentally m and km). Making inference 3. Estimate lengths of objects in appropriate
10
Everyday situations CD Rom
10
15
10
15
10
Measurement Tool
Real situation
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
4. Understand the concept of mass to solve problems. units. Use the four operations to solve problems involving length.
Identifying relations Translating
19 (21.05.12 25.05.12)
Basic Measurement
Students will be able to: 1. Read and write integers. 2. Represent integers on number lines. 3. Compare the values of two integers. 4. Arrange integers in order. 5. Write positive or negative numbers to represent word descriptions. LEARNING OUTCOMES First Semester Break (26.05.12 10.06.12)
Measurement Tool
10
Real situation
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
Public Holiday Birthday of Yang Di Pertuan Agong on 2nd June 2012 ( Saturday ) 22 23 (18.06.12 22.06.12) Basic Measurement Understand the concept of time in seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years. Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson MID YEAR EXAMINATION ( 11.06.12 15.06.12 ) Students will be able to: 1. Determine the appropriate measurement of time for certain events. 2. Convert measurement of time in different units (seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years). 3. Estimate the time intervals of events. 4. Use the four operations to solve problems involving time. Students will be able to: 1. Read and write times in twelve-hour system. 2. Read and write times in twenty-four hour system. 3. Convert time in twelve-hour system to twenty-four hour system and vice-versa. 4. Determine the interval between two given times. 5. Solve problems involving time. 1. Students will be able to: 2. Recognise angles. 3. Denote and label angles. 4. Measure angles using protractors. 5. Draw angles using protractors. 6. Recognise, compare and classify angles as acute, right, obtuse and reflex.
Measurement Tool
10
15
Real situation
24 (25.06.12 29.06.12)
Basic Measurement
Understand and use times in the twelve-hour and twenty-four hour system to solve problems.
Measurement Tool
10
15
Real situation
25 (02.07.12 06.07.12)
Chapter 9: Lines and Angles
Understand the concept of angles.
Drawing diagrams Interpreting Identifying relations
10 Protractor Angles in classroom CD Rom Chart
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
7. 8. 9. 26 (09.07.12 13.07.12) Lines and Angles Understand the concept of parallel and perpendicular lines. 1. 2. 3. 4. Draw acute, right, obtuse and reflex angles using protractors. Determine angles on straight lines equal 180. Determine one whole turn is 360. Students will be able to: Determine parallel lines. Determine perpendicular lines. State that the angle formed by perpendicular lines is 90. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Identify intersecting lines. 2. Determine the properties of vertical, complementary and supplementary angles. 3. Determine the value of an angle on a line, given the adjacent angle. 4. Solve problems involving angles formed by intersecting lines. Students will be able to: 1. Recognise polygons. 2. Name polygons (triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, heptagon and octagon). 3. Determine the number of sides, vertices and diagonals of given polygons. 4. Sketch polygons.
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Lines and Angles
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use properties of angles associated with intersecting lines to solve problems.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids Protractor Angles in classroom CD Rom Chart
27 (16.07.12 20.07.12)
Drawing diagrams Interpreting Identifying relations
10
10
28 (23.07.12 27.07.12)
Chapter 10: Polygons
Understand the concept of polygons.
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
Model GSP Geoboard 5 5 chart
29 30 (06.08.12 10.08.12) Polygons
Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson Test 3 (30.07.12 03.08.11) State Public Holiday Nuzul Al Quran Day on 6th August 2012 ( Monday ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: Interpreting symmetry. 1. Determine and draw the line(s) of symmetry Arranging of shapes. sequentially 2. Complete shapes given part of the shapes Comparing and and the line of symmetry. contrasting 3. Draw designs using the concept of Working out symmetry. mentally
Classifying Identifying relations
20 Concrete materials Number line
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
Translating
31 (13.08.12 17.08.12)
Polygons
Identify and use the geometric properties of triangles to solve problems.
Students will be able to: 1. Determine and draw symmetry line(s) of given triangles. 2. Draw triangles using protractors and rulers. 3. State the geometric properties of the different types of triangles and name the triangles. 4. Determine that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180. 5. Solve problems involving triangles. LEARNING OUTCOMES
Concrete materials Number line 5 10
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
32 (27.08.12 31.08.12)
Polygons
MID SEMESTER 2 BREAK ( 18.08.12 26.08.12 ) Public Holiday Hari Raya Puasa on 19th 20th August 2012 (Sunday & Monday) Identify and use the Students will be able to: Comparing and geometric properties of 1. Determine and draw symmetry line(s) of contrasting quadrilaterals to solve given quadrilaterals. Working out problems. 2. Draw a quadrilateral using protractor and mentally ruler. Translating 3. State the geometric properties of the Identifying different types of quadrilaterals and name relations quadrilaterals. Making inference 4. Determine that the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360. 5. Solve problems involving quadrilaterals. Public Holiday National Day on 31st August 2012 ( Friday ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: Working out perimeter to solve 1. Identify the perimeter of a region. mentally problems. 2. Find the perimeter of a region enclosed by Identifying straight lines. relations 3. Solve problems involving perimeters
Translating
10
Concrete materials Discount chart CD Rom
33 (03.09.12 07.09.12)
Chapter 11: Perimeter and Area
10
Understand the concept of area of rectangles to solve problems.
Students will be able to: 1. Estimate the area of a shape. 2. Find the area of a rectangle. 3. Solve problems involving areas Students will be able to: 1. Identify the heights and bases of triangles,
10
Grid paper Geoboard
34
Perimeter and
Understand the concept of area of triangles,
Working out
10
10
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM ONE MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
(10.09.12 14.09.12) Area parallelograms and trapezium to solve problems. parallelograms and trapeziums. 2. 3. 4. Find the areas of triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums. Find the areas of figures made up of triangles, rectangles, parallelograms or trapeziums. Solve problems involving the areas of triangles, rectangles, parallelograms and trapeziums.
mentally Identifying relations Translating
Grid paper Geoboard
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
34 (17.09.12 21.09.12)
Chapter 12: Solid Geometry
Public Holiday Malaysia Day on 16th September 2012 (Sunday) Understand geometric Students will be able to: Classifying properties of cubes and 1. Identify geometric solids. Drawing cuboids. 2. State the geometric properties of cubes and diagrams cuboids. Identifying 3. Draw cubes and cuboids on: relations a. Square grids. Translating b. Blank papers. 4. Make models of cubes and cuboids by: c. Combining given faces. d. Folding given layouts of solids. Understand the concept of volume of cuboids to solve problems Students will be able to: 1. Estimate the volume of cuboids. 2. Find the volume of cuboids. 3. Solve problems involving volume of cuboids.
Model
10
35 (26.09.12 28.09.12) 36 - 42
Solid Geometry
10
10
Discussion and Remedy for previous lesson ( 24.09.12 28.09.12 ) Revision and Remedy ( 01.10.12 31.10.12 ) State Public Holiday Birthday of Sultan Pahang on 24th October 2012 ( Wednesday ) Public Holiday Hari Raya Aidil Adha on 26th October 2012 ( Friday ) Final Year Examination ( 29.10.12 12.10.12) Activity after End year exam
11
ainarahyusmkm2012
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- CH - 4 Mix and Yield Variance Ahmed FinalDocumento8 pagineCH - 4 Mix and Yield Variance Ahmed FinalYohannes MeridNessuna valutazione finora
- The Global Supermarket ActivityDocumento3 pagineThe Global Supermarket ActivityKeyjey GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ielts Writing Task 1-Type 2-Comparisons - UpdatedDocumento15 pagineIelts Writing Task 1-Type 2-Comparisons - UpdatedDung Nguyễn ThanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Book PDFDocumento23 paginePractice Book PDFCally Chew100% (1)
- Ratio and RateDocumento19 pagineRatio and RateJade ivan parrochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Percetages TDY-302Documento36 paginePercetages TDY-302madhu jhaNessuna valutazione finora
- (Download) SSC - CGL Tier-II Exam Paper-I (Arithmetical Ability) Held On - 16-09-2012 - SSCPORTAL PDFDocumento12 pagine(Download) SSC - CGL Tier-II Exam Paper-I (Arithmetical Ability) Held On - 16-09-2012 - SSCPORTAL PDFShivnandan VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Poker BlueprintDocumento171 pagineThe Poker BlueprintBlake Mason100% (10)
- Burn Rate vs. Earned ValueDocumento1 paginaBurn Rate vs. Earned Valueyamanta_rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 6 PTDocumento4 pagineMath 6 PTArnel De QuirosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ielts Task 1Documento1 paginaIelts Task 1Mehmet KontiNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH3QDocumento38 pagineMATH3QRZ ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- fx-220 PLUS fx-85MS fx-82MS fx-300MS fx-350MS: (2nd Edition / S-V.P.A.M.)Documento52 paginefx-220 PLUS fx-85MS fx-82MS fx-300MS fx-350MS: (2nd Edition / S-V.P.A.M.)Nicat NezirovNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics ExampleDocumento18 pagineMathematics ExampleCharityNessuna valutazione finora
- Tlecommercialcooking2 141007183946 Conversion Gate01Documento3 pagineTlecommercialcooking2 141007183946 Conversion Gate01Kite D. LegismaNessuna valutazione finora
- BM - DLL - Week 2Documento3 pagineBM - DLL - Week 2Nimrod CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Percentage (176-189)Documento15 pagine10 Percentage (176-189)Shahabjan BalochNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajasthan State Public Procurement PortalDocumento21 pagineRajasthan State Public Procurement PortalUNIVERSHAL GEMNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-Reception of Milk Dairy and Food EngineeringDocumento11 pagine4-Reception of Milk Dairy and Food EngineeringDAKSHINA PANDEYNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 01Documento59 pagineUnit 01Nazmeen AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gross Profit Variation Analysis With IllustrationDocumento6 pagineGross Profit Variation Analysis With IllustrationVanessa Andrea OyardoNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPITALIZED-COSTgradient Rev 1Documento13 pagineCAPITALIZED-COSTgradient Rev 1niaz kilam100% (2)
- Mathematics 5 q3 w1Documento6 pagineMathematics 5 q3 w1Alex BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.5.identifying Appropriate Test Statistic Involving Population ProportionDocumento22 pagine4.5.identifying Appropriate Test Statistic Involving Population Proportionmuffinfluffy78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maharaja Surajmal Institution: Minor Project ReportDocumento52 pagineMaharaja Surajmal Institution: Minor Project ReportRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost and Returns From Mango CultivationDocumento30 pagineCost and Returns From Mango Cultivationtejash.solanki87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clarke Interviews Eli GoldrattDocumento19 pagineClarke Interviews Eli Goldrattclarke_ching100% (3)
- Solution Book - FINAL ApptitudeDocumento35 pagineSolution Book - FINAL ApptitudeMaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- People MatterDocumento30 paginePeople Matterf1nerdNessuna valutazione finora
- PPP - Homework 5Documento17 paginePPP - Homework 5Wiratha Nungrat67% (9)