Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tetanus
Caricato da
Queenie ArugayCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tetanus
Caricato da
Queenie ArugayCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TETANUS
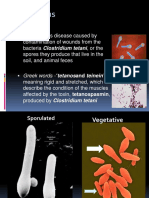
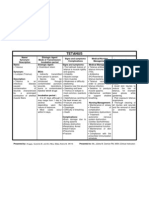
Name/ Synonym/ Description Name: Tetanus Synonym: Lockjaw (Trismus) Description: Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by contamination of wounds characterized by a prolonged contraction of skeletal muscle fibers Etiologic Agent/ Signs and symptoms Mode of Transmission/ /Complications Incubation period Etiologic Agent: Signs and symptoms: Clostridium tetani The hallmark feature of tetanus is muscle rigidity MOA: and spasms. Indirectly transmitted Irritability from person to person. Muscle cramps Spores may be Sore muscles introduced through Weakness or difficulty contaminated puncture swallowing wounds, lacerations, Spasms near the wound burns or contaminated Sweating and fever injected street drugs. Trismus or lockjaw is most common. (sardonic Incubation period : smile) 3 to 21 days although it Opisthotonus (arching of may range from 1 day to the back known as) several months Fracture and joints depending upon the dislocation nature of exposure. Dysphagia Most cases occur Difficulty of breathing within14 days. Death Complications: Brain damage due to during spasms Airway obstruction Respiratory Arrest Heart Failure Pneumonia Fracture Medical/Nursing Management Medical Management: Tetanus antitoxin tetanus immune globulin (TIG). Antibiotics (PO/Parenteral) to fight tetanus bacteria. Tetanus vaccine in order to prevent future tetanus infection. Sedative to paralyze muscle spasms. Mechanical ventilator to support shallow breathing. Nursing Management: Maintenance of airway Prevention of complication (respiratory dysfunction) Treatment of autonomic nervous lack of dysfunction system oxygen (cardiac dysrhythmias) Maintenance of proper gastrointestinal function Maintenance of skin integrity Compliance with the prescribed immunization schedule. Preventive Measures Preventive Measures: Active immunization Protect the skin from being penetrated by the tetanus bacteria. Precautions should be taken to avoid stepping on nails by wearing shoes. Avoid skin injuries to reduce the risk of tetanus, for example wear gloves while gardening. Post exposure tetanus prophylaxis Thorough cleaning of all injuries and wounds and the removal of dead or severely injured tissue.
Presented by: Arugay, Queenie B. and De Alba, Elizia Andre M. SN13
Presented to: Ms. Julieta M. Damian RN, MSN (Clinical Instructor)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Couple Therapy Clinician Guide For Partners With DepressionDocumento28 pagineCouple Therapy Clinician Guide For Partners With Depressionelias_reyes100% (1)
- Problem Solving in OncologyDocumento262 pagineProblem Solving in OncologyorzsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Psych NBME Form 4Documento2 paginePsych NBME Form 4Christine CassidyNessuna valutazione finora
- Referat TetanusDocumento51 pagineReferat TetanusDoddy Kusumah RonosulistyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection Muscle Spasms: TETANUS (Ragonton & Orcajada) Tetanus, Also Known As Lockjaw, Is AnDocumento2 pagineInfection Muscle Spasms: TETANUS (Ragonton & Orcajada) Tetanus, Also Known As Lockjaw, Is AnwendyNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Medical Services NC IIDocumento159 pagineEmergency Medical Services NC IIQueenie Arugay100% (2)
- Policy MemoDocumento4 paginePolicy Memoapi-340053591Nessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Values HR RR BPDocumento28 pagineNormal Values HR RR BPKthrine CrronNessuna valutazione finora
- NICU Protocol 100Documento76 pagineNICU Protocol 100Catherine Lee100% (1)
- RPD 2016 Quiz 1 Study GuideDocumento9 pagineRPD 2016 Quiz 1 Study Guideapi-296866881Nessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento23 pagineTetanusDhynie Soesila WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Palsy: Submitted By: Prerna Sharma M.SC Nursing, 4 SemesterDocumento97 pagineCerebral Palsy: Submitted By: Prerna Sharma M.SC Nursing, 4 Semestervarshasharma05100% (2)
- TetanusDocumento31 pagineTetanusreresNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal ShockDocumento50 pagineNeonatal ShockBenazir Nabilla RojwaaNessuna valutazione finora
- !tetanus MDocumento12 pagine!tetanus MInam KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- In The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and MercifulDocumento49 pagineIn The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and Mercifulcute_honiya100% (1)
- Tetanus NoteDocumento4 pagineTetanus NoteTaufik KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Status InternusDocumento12 pagineStatus InternusPriscaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus PDFDocumento10 pagineTetanus PDFVina MuspitaNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento18 pagineTetanusMichael EatonNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento3 pagineTetanusRoma Nova Pascual CabarrubiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangDocumento28 pagineTetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangJean SarocamNessuna valutazione finora
- Clostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Documento6 pagineClostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Raiden EiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus 160530145856Documento25 pagineTetanus 160530145856Gargi ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento129 pagineTetanusErina Erichan OtoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayDocumento5 pagineWhat Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayraechcmNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: DefinisiDocumento9 pagineTetanus: DefinisiRiz Sanfebrian AdiatmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Signs and SymptomsDocumento6 pagineSigns and Symptomsdareine22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus Disease ProcessDocumento2 pagineTetanus Disease ProcessMaverick LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Guide To Raising A Healthy ChildDocumento3 pagineProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Guide To Raising A Healthy ChildjunNessuna valutazione finora
- Meningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyDocumento39 pagineMeningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyKhemz Dalde LimNessuna valutazione finora
- 19: 05 24 Sept 2011 Tetanus: SymtompsDocumento5 pagine19: 05 24 Sept 2011 Tetanus: SymtompsVania ParamithaNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento23 pagineTetanusNadya Noor Mulya Putri100% (1)
- Tetanus.89898989 (Autosaved)Documento15 pagineTetanus.89898989 (Autosaved)Abdulla AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Tetanus ComplicationDocumento6 pagineManagement of Tetanus ComplicationsusiNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento7 pagineTetanusRaven ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento37 pagineTetanusMuwanga faizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ADocumento14 pagineTetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ArikaaristadNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Surgery Lecture OnDocumento23 pagineTetanus: Surgery Lecture OnJasonWalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus (Clostridium Tetani)Documento29 pagineTetanus (Clostridium Tetani)ped medNessuna valutazione finora
- 54 TetanusDocumento25 pagine54 Tetanusghofran001997Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellulitis: Elmundo, Cristina Lu V. ReporterDocumento51 pagineCellulitis: Elmundo, Cristina Lu V. Reportercring cringNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento3 pagineTetanusSUALI RAVEENDRA NAIKNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Documento20 pagineTetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Stefanie BlueNessuna valutazione finora
- 351255266-Tetanus Id enDocumento14 pagine351255266-Tetanus Id enRezki IndriyantiyusufNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento5 pagineTetanusasmaeserNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus As A Childhood Disease Common in Children Under Age 5Documento12 pagineTetanus As A Childhood Disease Common in Children Under Age 5Adediran DolapoNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento2 pagineTetanussyaiful_snNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDocumento16 pagineTetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDjameica GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of TetanospasminDocumento23 pagineEffect of Tetanospasminaparna ranjith markoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of TetanospasminDocumento23 pagineEffect of Tetanospasminaparna ranjith markoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus ADocumento3 pagineTetanus ASadaqat KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus - WikipediaDocumento72 pagineTetanus - WikipediaAtul MhetreNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus Definition: Tetanus Is An Infectious Disease Caused by Clostridium TetaniDocumento4 pagineTetanus Definition: Tetanus Is An Infectious Disease Caused by Clostridium TetaniHoney FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram + DiseasesDocumento30 pagineGram + DiseasesveerdedajiNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanuswDocumento11 pagineTetanuswFe Marie JisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus - The DiseaseDocumento6 pagineTetanus - The Diseasemanjunath mamathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDocumento14 pagineTetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyAldyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoDocumento44 pagineTetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoArjay VisitacionNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of TetanusDocumento7 pagineManagement of TetanusamutiarNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento7 pagineTetanusallah akbarNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento4 pagineTetanusAjay Pal NattNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: "Lock Jaw"Documento10 pagineTetanus: "Lock Jaw"Atoillah IsvandiaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgery Lecture On: Dr. Ehsanur RezaDocumento23 pagineSurgery Lecture On: Dr. Ehsanur Rezaiga sukmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal TetanusDocumento44 pagineNeonatal TetanusJake MillerNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento3 pagineTetanusmake_jajoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anisa A. Edris BSN January 25, 2012 Group A5: Central Nervous SystemDocumento4 pagineAnisa A. Edris BSN January 25, 2012 Group A5: Central Nervous SystemEynie EdrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Lo MSK 5-1Documento8 pagineLo MSK 5-1FirmanHidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan-Dearborn Department of BiologyDocumento14 pagineTetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan-Dearborn Department of BiologyRashid MajeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Rnheals Application Form ADocumento1 paginaRnheals Application Form ANica NixNessuna valutazione finora
- TetanusDocumento1 paginaTetanusQueenie ArugayNessuna valutazione finora
- Sigmund FreudDocumento10 pagineSigmund FreudQueenie ArugayNessuna valutazione finora
- 1432.full 2Documento10 pagine1432.full 2Gokull ShautriNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Surgical ManagementDocumento57 pagineComplications of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Surgical ManagementJoan LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- GERUND EXERCISES Finifabioariani 21000415201008Documento3 pagineGERUND EXERCISES Finifabioariani 21000415201008k5hq5v7q2cNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Instrumentation, MLT 2760, BCC, Assessment Test 2Documento9 pagineClinical Instrumentation, MLT 2760, BCC, Assessment Test 2alphacetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alzheimer's Research PaperDocumento5 pagineAlzheimer's Research PaperJosh BarnutNessuna valutazione finora
- KARUNA ANAND, Plaintiff, CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF CORRECTIONS AND REHABILITATION and DOES 1 Through 30, Inclusive, Defendants.Documento29 pagineKARUNA ANAND, Plaintiff, CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF CORRECTIONS AND REHABILITATION and DOES 1 Through 30, Inclusive, Defendants.clinicianNessuna valutazione finora
- Epic Meal Plan: Name: Nicole Torres Age: 60 Height: 156cm Occupation: Retired Condition: GoutDocumento8 pagineEpic Meal Plan: Name: Nicole Torres Age: 60 Height: 156cm Occupation: Retired Condition: GoutYvette Angelique Cabalquinto MandrezaNessuna valutazione finora
- # of The Distal RadiusDocumento98 pagine# of The Distal RadiusabhinavaiimsNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Total Abdominal Hysterectomy?Documento8 pagineWhat Is A Total Abdominal Hysterectomy?Iuthisam HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- NHPPD Calculating StaffingDocumento3 pagineNHPPD Calculating Staffingodin9360343Nessuna valutazione finora
- Articulo RevisionDocumento8 pagineArticulo RevisionvictorNessuna valutazione finora
- EPC Referral FormDocumento1 paginaEPC Referral FormCarlos GuerrettaNessuna valutazione finora
- App Ashcraft's Pediatric Surgery 5th EditionDocumento8 pagineApp Ashcraft's Pediatric Surgery 5th EditionAndri Feisal NasutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Activator and High Pull Headgear Combination Therapy PDFDocumento9 pagineEffects of Activator and High Pull Headgear Combination Therapy PDFDilesh PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollock 2001Documento14 paginePollock 2001Segura RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Research ProjectDocumento16 pagineResearch Projectapi-373572658Nessuna valutazione finora
- Viapath JobDocumento6 pagineViapath JobRebeca UrseNessuna valutazione finora
- (SUS) Sabbagh Universal Spring2Documento12 pagine(SUS) Sabbagh Universal Spring2Ali HmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Nej M 200009073431001Documento8 pagineNej M 200009073431001Asri Ani NurchasanahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceftazidime (Zeptrigen)Documento4 pagineCeftazidime (Zeptrigen)105990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) : Printer-Friendly PDFDocumento4 pagineIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) : Printer-Friendly PDFdaryl ann dep-asNessuna valutazione finora