Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Acute Pain Related To Injury
Caricato da
Erickson Caisido GarciaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acute Pain Related To Injury
Caricato da
Erickson Caisido GarciaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
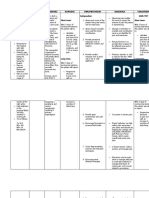
Assessment Objective: - (+) DOB -Complains to chest pain on the thoracostomy site -Facial grimaces upon movement -Reports
of pain on the thoracostomy area, described as sharp provoked by breathing nonradiating, with a pain scale of 7 out of 10
Diagnosis Acute pain related to nflammation of the parietal pleura as evidenced by DOB, complains of chest pain and facial grimaces upon movement. Inference: Acute pain is pain that comes on quickly and usually lasts a short time. It serves as a warning of injury or illness. Acute pain can range from mild to severe and is often caused by an injury or sudden illness.
Planning Short Term: After 3-4 hours of nursing interventions, the patients pain will decrease from 7 to 3 as verbalized by the patient. Long Term: After 2-3 days of nursing interventions, the patient will demonstrate activities and behaviors that will prevent the recurrence of pain.
Intervention Independent: 1.Assess patient pain for intensity using a pain rating scale, for location and for precipitating factors. 2. Assess the response to medications every 5 minutes 3.Provide comfort measures. 4. Establish a quiet environment. 5. Elevate head of bed. 6. Monitor vital signs, especially pulse and blood pressure, every 5 minutes until pain subsides. 7. Teach patient relaxation techniques and how to use them to reduce stress.
Rationale 1.To identify intensity, precipitating factors and location to assist in accurate diagnosis. 2. Assessing response determines effectiveness of medication and whether further interventions are required. 3. To provide nonpharmacological pain management. 4. A quiet environment reduces the energy demands on the patient. 5. Elevation improves chest expansion and oxygenation. 6. Tachycardia and elevated blood pressure usually occur with angina and reflect compensatory mechanisms secondary to sympathetic
Evaluation Short Term: Patient shall have verbalized a decrease in pain from a scale of 7 to 3. Long Term: The patient shall have demonstrated activities and behaviors that will prevent the recurrence of pain
nervous system stimulation. 7. Anginal pain is often precipitated by emotional stress that can be relieved nonpharmacological measures such as relaxation.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocumento4 pagineAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug Studycrianne_1180% (5)
- NCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsDocumento4 pagineNCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsKevin Sam AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocumento4 pagineNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Altered ComfortDocumento2 pagineNCP Altered ComfortMadz Tajal0% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternNecheal BaayNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento6 pagineAcute Pain NCPPesky Pescante-MonterolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineChinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanKenji ToleroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar Day 1 Psyche KarlDocumento4 pagineFdar Day 1 Psyche KarlKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPDidith AbanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute PainIsrael Soria EsperoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento5 pagineNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain NCPRyan PanNessuna valutazione finora
- CloxacillinDocumento1 paginaCloxacillinYzracle Bermejo FlorentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 8fDocumento2 pagineNCP 8fRaiel B. Buenviaje RN0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Documento2 pagineNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. BeredoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired ComfortDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Impaired ComfortgmindalanoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Fracture Risk For InfectionDocumento3 pagineNCP Fracture Risk For InfectionMiggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma 2° To MVADocumento1 paginaAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma 2° To MVARachel Saavedra100% (3)
- NCP - Risk For FallsDocumento5 pagineNCP - Risk For FallsMae CeaesarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineNursing Care PlanRaphael Reyes Enriquez100% (1)
- DeficientDocumento2 pagineDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDocumento2 pagineNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For InfectionDocumento3 pagineRisk For InfectioncamziiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocumento8 pagineAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- NCP 2Documento3 pagineNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- TramadolDocumento1 paginaTramadolAi RouNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Documento1 paginaNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Weakness NCPDocumento1 paginaBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDocumento2 pagineNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaCholecystectomy Nursing Care PlanJor Garcia100% (1)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 pagineNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocumento3 paginePost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Documento8 pagineRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocumento1 paginaFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CTTDocumento2 pagineNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento3 pagineNCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityAemz Alacasnap Ainegud100% (1)
- Exit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseDocumento2 pagineExit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseGayle RavanchoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPMichael John F. NatividadNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PainDocumento4 pagineNCP PainFlauros Ryu JabienNessuna valutazione finora
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocumento1 paginaOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDocumento1 paginaASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 paginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Vit K Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineVit K Drug StudyPrisHee YhaRz SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationGiselle EstoquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LocDocumento2 pagineNCP LocMel RodolfoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041Nessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocumento1 paginaNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDocumento33 pagineDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Infection NewDocumento3 pagineNCP Infection NewXerxes DejitoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute PainDocumento2 pagineNCP Acute PainLyka Mae DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCrissa AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Preoperative Problem: Acute PainDocumento7 paginePreoperative Problem: Acute Painمالك مناصرةNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs OsmacDocumento5 pagineDrugs OsmacErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocumento6 pagineAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs OsmacDocumento5 pagineDrugs OsmacErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs OsmacDocumento5 pagineDrugs OsmacErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs OsmacDocumento5 pagineDrugs OsmacErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- OmeprazoleDocumento1 paginaOmeprazoleErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- OmeprazoleDocumento2 pagineOmeprazoleErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- FdarDocumento1 paginaFdarErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- TOR RequestDocumento1 paginaTOR RequestErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar CompleteDocumento1 paginaFdar CompleteErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clindamycin (Cleocin)Documento2 pagineClindamycin (Cleocin)Erickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs OsmacDocumento5 pagineDrugs OsmacErickson Caisido GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento6 pagineIntroductionRea Paulline Paguio FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora