Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Common Emitter
Caricato da
Ravi TejaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Common Emitter
Caricato da
Ravi TejaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
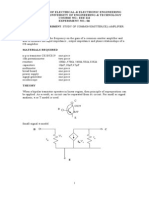
EXP . NO. 1. Common Emitter Amplifier With and Without Feedback 1.
AIM: To Design and Study the response of a Common Emitter Amplifier without and with feedback. The gain and band width are to be calculated from the response. 2. COMPONENTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. BJT (BC107BP) Resistors (33k, 6.8k, 1.5k, 470, 1k) Capacitors (10UF, 10UF, 47UF) DC source AC source Oscilloscope 1No. 5No. 3No. 1No. 1No. 1No.
3. THEORY: Very often CE configuration is used as a transistor amplifier. The function of the amplifier is to amplify the signal without any distortion. So it is important to stabilize the amplification of the amplifier. By stabilization of voltage or current gain, we mean that the amplification becomes essentially independent of the h-parameters of the transistor. A simple and effective way to obtain voltage gain stabilization is by adding an emitter resistor Re to the common emitter amplifier. But due to Re the gain of the amplifier decreases, to avoid this degeneration a large capacitor called bypass capacitor is connected in parallel with Re. Frequency response of an amplifier is defined as the variation of gain with respective frequency. The gain of the amplifier increases as the frequency increases from zero till it becomes maximum at lower cut-off frequency and remains constant till higher cut-off frequency and then it falls again as the frequency increases. At low frequencies the reactance of coupling capacitor CC and bypass capacitor Ce is quite high and which is responsible for gain loss. At high frequencies the reactance of inter electrode capacitance is very small and behaves as a short circuit. Due to these capacitors the voltage gain drops at high frequencies. At mid frequencies the effect of coupling capacitors and bypass capacitor is negligible and acts like short circuit, where as inter electrode capacitors acts like open circuit. So, the circuit becomes resistive at mid frequencies and the voltage gain remains constant during this range.
4. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
CE AMPLIFIER WITHOUT FEEDBACK 5. PROCEDURE: Without Feedback i. Open multisim software by clicking the icon on desktop. ii. Place the AC source, DC source, Ground, Oscilloscope and other components on circuit window by selecting them from component toolbar. iii. Connect the components as shown in the figure. iv. Simulate the circuit by clicking run button on simulation toolbar. v. Observe the input and output waveforms on oscilloscope by double on it. vi. Stop the simulation by clicking stop button on simulation toolbar. vii. Now select simulate analysis AC analysis for frequency response. viii. Set the start frequency, stop frequency, sweep frequency and vertical scale, then click the output tab select the output variable for analysis and click the simulate button. ix. Observe the graph on graph viewer. Note down the output voltage for different frequencies and calculate voltage gain, lower cutoff frequency, upper cutoff frequency and bandwidth by plotting on semi-log graph.
With Feedback i. Repeat steps 4 to 9 by removing bypass capacitor. 6. OBSERVATIONS:
S.NO
FREQUENCY VOUT
GAIN= VOUT /VIN
GAIN in dB =20*log(VOUT/VIN)
7. CALCULATIONS: i. Determine lower cut-off frequency (fL) and upper cut-off frequency (fH) from the graph. ii. Calculate Band width = (fH fL) 8. RESULT: Hence studied the response of a common emitter amplifier with and without feedback and calculated g ain and band width. i. ii. iii. Lower cut-off frequency (fL) = Upper cut-off frequency (fH) = Band width (fH fL) =
Gain CE amplifier without feedback CE amplifier with feedback
Bandwidth
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Eca Lab Manual PDFDocumento56 pagineEca Lab Manual PDFrppvch100% (5)
- EEL 3304C - Design and Experiment Project Lab # 4 Common-Emitter AmplifierDocumento4 pagineEEL 3304C - Design and Experiment Project Lab # 4 Common-Emitter AmplifierHarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECADDocumento110 pagineECADJanica Janelle ReloxeNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementation of Electronic Cruise Control System in A BikeDocumento5 pagineImplementation of Electronic Cruise Control System in A BikeRanga SriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lenovo Thinkpad X200Documento62 pagineLenovo Thinkpad X200dirkstrangerNessuna valutazione finora
- SisoTool TutorialDocumento3 pagineSisoTool TutorialJefferson P. MouraNessuna valutazione finora
- Interrupt handling: Understanding interrupts, interrupt systems, and interrupt handling flowDocumento30 pagineInterrupt handling: Understanding interrupts, interrupt systems, and interrupt handling flowKalpit SeksariaNessuna valutazione finora
- TC PLC Lib Controller ToolboxDocumento180 pagineTC PLC Lib Controller ToolboxPedro VieiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Example An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureDocumento23 pagineExample An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureAthiyo MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- TA3020 Audio Amplifier Module v3b ManualDocumento6 pagineTA3020 Audio Amplifier Module v3b ManualCristi VasilacheNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverter 12VDC To 220VAC 100 Watt by Power Transistor 2N3055Documento19 pagineInverter 12VDC To 220VAC 100 Watt by Power Transistor 2N3055Bank100% (1)
- Auto Ingenuity Scantool User GuideDocumento122 pagineAuto Ingenuity Scantool User GuideiBusinessLogicNessuna valutazione finora
- AFM To MAF ConversionDocumento11 pagineAFM To MAF ConversionRonnie Peterson100% (1)
- Vehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationDocumento80 pagineVehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationSaheb Amrinder100% (6)
- Buffer AmplifierDocumento9 pagineBuffer AmplifierDicky D.M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- ST 2651Documento94 pagineST 2651Shrikant Jahagirdar50% (2)
- 2 X 6W Car Radio Amplifier Plus Solid State Switch: Protections DescriptionDocumento8 pagine2 X 6W Car Radio Amplifier Plus Solid State Switch: Protections DescriptionMiloud ChouguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Systems With SolutionsDocumento72 pagineControl Systems With Solutionsdevraj22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Self Balancing With Pid ControlDocumento7 pagineSelf Balancing With Pid Controlengrumar100% (1)
- Scientech 2801Documento89 pagineScientech 2801Santiago Alberto Ramirez MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Vehicles and Power Electronics Presentation at Universidad Technica Federico Santa MariaDocumento41 pagineElectric Vehicles and Power Electronics Presentation at Universidad Technica Federico Santa Mariaowzaque_370% (1)
- Scientech 2272A BDocumento67 pagineScientech 2272A BbianNessuna valutazione finora
- Class de Inverters and Rectifiers For DC-DC ConversiondDocumento8 pagineClass de Inverters and Rectifiers For DC-DC ConversiondRon HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction: PID Controller Design: Sistemas de ControlDocumento15 pagineIntroduction: PID Controller Design: Sistemas de ControlPatricio EncaladaNessuna valutazione finora
- OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble CodesDocumento42 pagineOBD-II Diagnostic Trouble CodesLarisa MateiNessuna valutazione finora
- Design ProjectDocumento22 pagineDesign ProjectRobert T KasumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects at STrobotix ElectronicsDocumento42 pagineProjects at STrobotix ElectronicsM SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- PID Tuning Guide V - 1Documento14 paginePID Tuning Guide V - 1ibubu23100% (1)
- Vlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada II Sem SyllabusDocumento16 pagineVlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada II Sem Syllabusrv prasad50% (2)
- Modeling A Cruise Control SystemDocumento23 pagineModeling A Cruise Control SystemAl Mutiry Muard100% (3)
- EI2357 - Virtual Instrumentation Laboratory Manual - DgprideDocumento30 pagineEI2357 - Virtual Instrumentation Laboratory Manual - DgprideNanda003100% (1)
- Unit 5 DSP SystemDocumento30 pagineUnit 5 DSP SystemSiddhasen Patil100% (2)
- CHAPTER 3 - Signal GeneratorsDocumento31 pagineCHAPTER 3 - Signal Generatorsumar_khalif100% (3)
- Interface Lab ReportDocumento8 pagineInterface Lab ReportSharfuddin ZishanNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSI Device Numbers PDFDocumento6 pagineANSI Device Numbers PDFS.M.Touhidur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Integrated Circuits - EC2254Documento77 pagineLinear Integrated Circuits - EC2254Muthu LakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Si Solar Cell 1D: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.2aDocumento14 pagineSi Solar Cell 1D: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.2aHarold PuinNessuna valutazione finora
- AM Modulation Using IC 1496Documento4 pagineAM Modulation Using IC 1496shaan76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control Engineering I PDFDocumento15 pagineControl Engineering I PDFkipkorir kemboiNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino Cheat Sheet: Basics 1: Using Digital I/O, Analog Reading, Serial As Output, Basic TimerDocumento3 pagineArduino Cheat Sheet: Basics 1: Using Digital I/O, Analog Reading, Serial As Output, Basic TimerSriHariKalyanBNessuna valutazione finora
- Oscillator PDFDocumento4 pagineOscillator PDFJoshua DuffyNessuna valutazione finora
- DLK PDFDocumento191 pagineDLK PDFMisha KulibaevNessuna valutazione finora
- Elect Machine Total 2012Documento22 pagineElect Machine Total 2012NGOUNENessuna valutazione finora
- Ece V Analog Communication (10ec53) AssignmentDocumento2 pagineEce V Analog Communication (10ec53) AssignmentAbdul AzeezNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic System Design LabDocumento25 pagineElectronic System Design Labsramiz_1987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mwoc Final Lab Manual 28-08-2010Documento77 pagineMwoc Final Lab Manual 28-08-2010downloadscribdpdfNessuna valutazione finora
- RC CoupledDocumento3 pagineRC CoupledRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocumento29 pagineBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualDocumento74 pagineSharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualSharmila83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study CE Amplifier Gain & ImpedanceDocumento3 pagineStudy CE Amplifier Gain & ImpedancesabitavabiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECA ManualDocumento62 pagineECA ManualAnonymous gP8ivl7fNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Date:: Experiment 08 BJT High Frequency ResponseDocumento5 pagineName: Date:: Experiment 08 BJT High Frequency ResponseJuay Mae RianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc ManualDocumento116 pagineAdc ManualAnnalakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Documento11 pagineWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Mannual PDFDocumento26 pagineLab Mannual PDFssptc Magazine100% (1)
- ECD1223 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS LAB 1: COMMON-EMITTER AMPLIFIER BIASING & GAINDocumento10 pagineECD1223 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS LAB 1: COMMON-EMITTER AMPLIFIER BIASING & GAINSam LiangNessuna valutazione finora
- AEC LabManualDocumento30 pagineAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CBCC Amp 2Documento5 pagineCBCC Amp 2sru_1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eca Lab ManualDocumento78 pagineEca Lab ManualNageswariah.MNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc Lab Manual PDFDocumento74 pagineAdc Lab Manual PDFJega Deesan75% (4)
- DRLSEDocumento12 pagineDRLSEmanavalanNessuna valutazione finora
- DRLSEDocumento12 pagineDRLSERavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- CallingDocumento3 pagineCallingRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4rt App Voter Eligibility With Error MessageDocumento4 pagine4rt App Voter Eligibility With Error MessageRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- MRG EligibilityDocumento4 pagineMRG EligibilityRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hex Code For ColoursDocumento15 pagineHex Code For ColoursRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shifting BTW 2 ActivitiesDocumento6 pagineShifting BTW 2 ActivitiesRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4rt App Voter EligibilityDocumento2 pagine4rt App Voter EligibilityRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierDocumento4 pagineVoltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierRavi Teja82% (11)
- Hello 1stDocumento3 pagineHello 1stRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Package Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Public Class ExtendsDocumento2 paginePackage Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Import Public Class ExtendsRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- RC CoupledDocumento3 pagineRC CoupledRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage Series Feedback AmplifierDocumento5 pagineVoltage Series Feedback AmplifierRavi Teja71% (7)
- 2nd App LableDocumento3 pagine2nd App LableRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- RC OscillatorDocumento8 pagineRC OscillatorRavi TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Common EmitterDocumento3 pagineCommon EmitterRavi Teja100% (1)
- Foundation of Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocumento410 pagineFoundation of Switching Theory and Logic Designsahooavinash100% (1)
- ECA Lab ManualDocumento63 pagineECA Lab ManualsivadanamsNessuna valutazione finora
- ColpittsDocumento8 pagineColpittsRavi Teja100% (1)
- ColpittsDocumento8 pagineColpittsRavi Teja100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics and PeriodicityDocumento51 pagineQuantum Mechanics and Periodicitynxumalopat2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Techno ReadDocumento11 pagineTechno ReadCelrose FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Papal InfallibilityDocumento6 paginePapal InfallibilityFrancis AkalazuNessuna valutazione finora
- CimoryDocumento1 paginaCimorymauza.collection12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microalgae PDFDocumento20 pagineMicroalgae PDFaris_nurhidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- SM pc300350 lc6 PDFDocumento788 pagineSM pc300350 lc6 PDFGanda Praja100% (2)
- The Philosophy of EmoDocumento2 pagineThe Philosophy of EmoTed RichardsNessuna valutazione finora
- An Exploratory Study of Personal Calendar UseDocumento23 pagineAn Exploratory Study of Personal Calendar UseManas Tungare100% (1)
- [4]Documento693 pagine[4]Ali Mohammed AlkafajyNessuna valutazione finora
- LOGIC - Key Concepts of Propositions, Arguments, Deductive & Inductive ReasoningDocumento83 pagineLOGIC - Key Concepts of Propositions, Arguments, Deductive & Inductive ReasoningMajho Oaggab100% (2)
- FullertonDocumento15 pagineFullertonSuman MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffie Hellman WriteupDocumento3 pagineDiffie Hellman WriteupSumitThoratNessuna valutazione finora
- Lenti Title IX DismissedDocumento31 pagineLenti Title IX DismissedDePauliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageDocumento5 pagineQualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageoobyddNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanaDocumento93 pagineLiterature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanasiesmannNessuna valutazione finora
- Certification Exam: Take A Business OnlineDocumento15 pagineCertification Exam: Take A Business OnlineezerkaNessuna valutazione finora
- UBD PlantDocumento8 pagineUBD PlantMahmoud DibNessuna valutazione finora
- Tiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBDocumento33 pagineTiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBponyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Experiences and Challenges Faced of The Public School Teachers Amidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study in The PhilippinesDocumento21 pagineThe Experiences and Challenges Faced of The Public School Teachers Amidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study in The PhilippinesDE LOS REYES MARY ZEALANessuna valutazione finora
- Commonwealth scholarships to strengthen global health systemsDocumento4 pagineCommonwealth scholarships to strengthen global health systemsanonymous machineNessuna valutazione finora
- Teresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Documento2 pagineTeresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Pam Otic-ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Signals SyllabusDocumento1 paginaSignals SyllabusproNessuna valutazione finora
- Mario, You Might Need ThisDocumento436 pagineMario, You Might Need ThisJk McCreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated Syllabus - ME CSE Word Document PDFDocumento62 pagineUpdated Syllabus - ME CSE Word Document PDFGayathri R HICET CSE STAFFNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Research PaperDocumento31 pagineFull Research PaperMeo ĐenNessuna valutazione finora
- 489-F Latest JudgmentDocumento15 pagine489-F Latest JudgmentMoving StepNessuna valutazione finora
- History E XDocumento13 pagineHistory E XTamboli Shaikh Muaavvir AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thematic Language-Stimulation TherapyDocumento19 pagineThematic Language-Stimulation TherapyPipa Yau100% (1)
- 677 1415 1 SMDocumento5 pagine677 1415 1 SMAditya RizkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lindtner, Ch. - Madhyamakahrdayam of BhavyaDocumento223 pagineLindtner, Ch. - Madhyamakahrdayam of Bhavyathe Carvaka100% (2)


















































































![[4]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/396226966/149x198/c657f32573/1545578422?v=1)




















