Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Engineering Technology: Form 4 and 5
Caricato da
pendekarpendawoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Engineering Technology: Form 4 and 5
Caricato da
pendekarpendawoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EDARAN TERHAD
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION MALAYSIA
The Integrated Curriculum For Secondary School (ICSS) Syllabus
uiuuuuuu
ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
FORM 4 AND 5
Technical and Vocational Curriculum Division Technical Education Department 2006
THE NATIONAL PHILOSOPHY ( RUKUN NEGARA )
Our nation Malaysia is dedicated to achieving a greater unity for all her peoples; maintaining a democratic way of life; creating a just society in which the wealth of the nation shall be equitably distributed; ensuring a liberal approach to her rich and diverse cultural traditions; building a progressive society, orientated towards modern science and technology. WE, the people of Malaysia, pledge our united efforts to attain these ends guided by the following principles: BELIEF IN GOD LOYALTY TO KING AND COUNTRY SUPREMACY OF THE CONSTITUTION THE RULE OF LAW MUTUAL RESPECT AND GOOD SOCIAL BEHAVIOUR
National Education Philosophy
Education in Malaysia is an on-going effort towards further developing the potential of individuals in a holistic and integrated manner, so as to produce individuals who are intellectually, spiritually, emotionally and physically balanced and harmonious, based on firm belief in God. Our efforts are focused towards creating Malaysian citizens who are knowledgeable and competent, who possess high moral standards, and who are responsible and capable of achieving a high level of personal well-being and able to contribute to the harmony and prosperity of the family, the society and the nation at large.
ii
ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS I. INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY PERIODS 1.0 1.1 Development of Engineering Technology Technology and Society Definition of Engineering Technology 1.2 Changes in society according to the development in technology a. Relationship of technology with business and economy progress II. MANUFACTURING PERIODS 1.0 1.1 Introduction to Manufacturing Manufacturing System a. Input b. Processes i. Processing of materials ii. Management c. Output 2.0 2.1 Tools Classification of common hand tools a. Marking, measuring and Testing tools b. Holding devices c. Driving tools 65 2
c. Cutting tools
3.0 3.1
Engineering Materials Types of material a. Ferrous metals i. Steel ii. Cast iron b. Non ferrous metals i. Copper ii. Aluminium iii. Brass iv. Tin c. Non metallic materials i. Polymer ii. Concrete iii. Ceramic
3.2
Mechanical characteristics of metals and their uses, advantages and disadvantages of types of material Manufacturing Processes Machining processes and use of machine a. b. c. d. e. Lathe machine Milling machine Shaping machine Grinding machine Drilling machine
4.0 4.1
4.2
Joining techniques a. Assemble using screw, bolt and nut, and rivet b. Basic principles and
uses of the following processes : i. Soldering ii. Brazing iii. Oxy-acetylene gas welding iv. Arc welding v. Adhesive c. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each joining technique 4.3 Casting processes a. Types of casting i. Sand casting ii. Mould casting iii. Wax casting b. Main uses of each process c. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each process 4.4 Presswork processes a. Shearing b. Bending c. Drawing 4.5 Plastic moulding and shaping processes a. Types of plastic molding and shaping: i. Compress/solid Moulding ii. Injection moulding iii. Transferring moulding iv. Extrude moulding v. Blow moulding vi. Vacuum moulding b. Main uses of each process c. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each
process
5.0 5.1
Environmental Control Types of pollutions and current issues: a. Air, water, chemical waste, radioactive waste b. Recycle 54
III. COMMUNICATION PERIODS 1.0 1.1 Introduction to Communication Brief explanation on communication processes a. Human Human b. Human Machine c. Machine Human d. Machine Machine 2.0 2.1 2.2 Electronic Communication Brief explanation on basic communication concepts Main components in radio, amplifier and power supply Active and passive components (resistor, capacitor, coil, diode, transistor, integrated circuit and transformer) 2.3 Signal transmitter and receiver a. Types of modulation i. AM ii. FM b. Radio waves i. Radio ii. Television iii. Radar iv. Satellite
c. Transmission line i. Telephone ii. Intercom iii. Facsimile d. Fiber optic i. Principles of fiber Optic ii. Advantages and disadvantages of fiber optic
3.0 3.1
Computer System Basic principles a. Analogue b. Digital
3.2
Computer operating processes a. Input b. Storage c. Processing d. Output
3.3
Computer interface a. Human b. Machine
3.4
Introduction to multimedia and internet 62 PERIODS
IV. TRANSPORTATION AND POWER 1.0 1.1 Introduction to Transportation and Power Needs for transportation a. Work b. Social interaction c. Recreation d. Transportation of goods and people e. Development of the country 2.0 Transportation
2.1
Transportation system Land transport Water transport Air transport
2.2
Preparing process in transportation system a. Planning and research b. Construction c. Administration d. Maintenance
2.3
Transportation of people and goods. a. Lorry, taxi, bus, etc. b. Train, MRT and LRT c. Conveyor system, lift and escalator d. Elevator and crane Energy Resources Types of energy resources a. Renewable b. Non- renewable
3.0 3.1
3.2
Sources of energy and generating electrical energy a. Hydro b. Thermal c. Nuclear d. Solar
3.3
Motors and generators a. Direct current (DC) b. Alternating current (AC)
3.4
Engine a. Types of engines i. 2 stroke ii. 4 stroke iii. Diesel iv. Turbine
3.5
Magnetic levitation and transportation system Control Hydraulic control a. Principles of force, pressure, work and power b. Component, symbol and function c. Simple hydraulic circuit
4.0 4.1
4.2
Pneumatic control a. Component, symbol and function b. Simple pneumatic circuit Electric control a. Component, symbol and function b. Simple electric control circuit
4.3
4.4
Electronic control a. Component, symbol and function i. Diode ii. Thyristor b. Electronic control circuit
5.0 5.1
Future of Transportation and Power Technology Trends and future development of transportation and power technology Environmental Control Pollution caused by transportation and power industries a. Energy wastage b. Pollutant and material waste c. Congestion and traffic
6.0 6.1
control
V. CONSTRUCTION PERIODS 1.0 1.1 Overview of Construction Technology Concept of construction technology a. Definition of construction technology b. Elements of construction i. Material ii. Tools and machine iii. Worker iv. Method v. Management c. Types of construction projects i. Light construction engineering - Housing building - Government office building - Commercial building - Industrial building ii. Heavy construction engineering - Highway - Water supply project - Industrial complex d. Purposes of construction i. Storage ii. Shelter iii. Manufacturing iv. Transportation v. Communication vi. Recreation e. Construction flow chart i. Planning - Design - Management ii. Construction - Building structure - Fixing system - Completing project iii. Maintenance - Hand over project to clients - Occupancy
69
- Renovation
1.2
Importance of construction technology a. Effects of construction technology. b. Manpower and organization involved in construction industry Preparation of Construction Projects. Starting a project a. Allocation ( Financial source) b. Professional staff c. Feasibility study d. Problem solving e. Making decision based on suggestion from consultant Acquisition of site a. Choice of site b. Cost i. Land ii. Land status iii. Location iv. Site contour v. Material vi. Labour vii. Interest c. Purchasing real estate i. Negotiation ii. Legality Surveying of construction site a. Study available information b. Land survey equipment i. Purpose of survey ii. Levelling survey equipment iii. Field work iv. Plotting c. Practical soil work d. Characteristics of soil i. Cohesion ii. Non-cohesion Designing and Planning Projects.
2.0 2.1
2.2
2.3
3.0
3.1
Project design a. Definition of design b. Professional involved i. Engineer ii. Architect iii. Planner c. Pre-design factors i. Function ii. Shape iii. Cost iv. Strength v. Material d. Design process Working drawings and details a. Working drawings b. Working drawing set i. Engineering drawing ii. Site drawing iii. Architectural drawing iv. M & E drawing v. Structural drawing c. Details
3.2
4.0 4.1
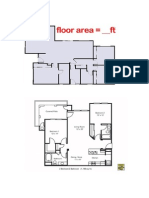
Management of Construction Activities Contract management a. Definition of contract b. Types of contract i. Negotiation tender ii. Open tender c. Types of contractors d. Cost estimation i. Floor area ii. Volume iii. List of quantity
4.2
Management of construction project a. Construction activity b. Administration at construction site c. Gantt chart d. Critical flow chart
5.0
Management of Resources
5.1
Worker and labourer a. Types of workers i. Site work ii. Constructing structure iii. Completing structure iv. Machinery work Materials and tools a. Purchasing procedure b. Acquiring materials i. Stock ii. Purchase on demand iii. Lump-sum contract c. Acquiring tools i. Purchase ii. Rent / lease Construction Materials a. Concrete i. Ingredients ii. Properties iii. Concrete usage iv. Preparing and mixing v. Concrete placement vi. Compaction vii. Curing b. Wood i. Plank ii. Plywood c. Metal i. Steel ii. Aluminium iii. Copper d. Brick e. Glass f. Soil and aggregate g. Tar and bitumen h. Plastic i. Rubber j. Paint
5.2
5.3
5.4
Construction equipment i. Light tools ii. Construction machines Construction of Structure
6.0
6.1
Preparation a. Acquiring permit or permission b. Site clearing c. Identify location of structure i. Use of centre line ii. Use of site line d. Site lay-out i. Entry and exit ii. Accommodation iii. Utility ( electricity, water and telephone ) iv. Security Earthwork I. Stabilizing earth ii. Loosening soil iii. Excavating iv. Adding earth to site v. Disposing of earth vi. Clearing
6.2
6.3
Construction of foundation a. Types of foundation i. Pad foundation ii. Cantilever base foundation iii. Raft foundation iv. Piling foundation - Friction - Bearing Super structure construction a. Construct frame structure i. Timber frame - Floor - Wall - Roof ii. Reinforced concrete frame - Beam - Column b. Construct load bearing wall
6.4
6.5
Structure enclosure a. Enclosing roof b. Enclosing walls - installing door
- installing window 7.0 7.1 Future of Construction Technology Trends and future development in construction technology Environmental Control Management of construction waste and solid waste i. Types of waste ii. Recycling 8.2 Erosion control a. Methods used to control erosion i. Hydro seeding ii. Trenching iii. Gunniting VI. INDUSTRIAL DESIGN PERIODS 1.0 1.1 1.2 2.0 2.1 Introduction to Design. Design as a problem solving activity Purpose of design Ways to Design Design processes a. Ways to fulfill basic needs b. Clarifying problems c. Obtaining and thinking of ideas d. Obtaining solution e. Making and modelling solutions f. Testing design if it functions and to solve problems 3.0 Recording and Presenting Design Ideas 28
8.0 8.1
3.1
Methods of recording and presenting ideas a. Plane and perspective drawings b. Enhance parts of drawing c. Detail drawings d. Present and arrange ideas of design e. Using other media. f. Ways of making model
4.0 4.1
Using Information In Design Methods a. Acquiring information b. Presenting information c. Presenting operation d. Writing report
5.0 5.1
Methodology of Design Implementation of design methodology a. Situation for design b. Design brief c. Research and study d. Solution e. Product or model f. Testing
6.0 6.1
Design Factors Human factors in design a. Methods of design considering the following factors : i. Body and human movement ii. Safety iii. Growth and ageing vi. Needs of disabled or ailing people v. Vision, colours and lighting
6.2
Function factors in design a. Methods of design to fulfill functions i. Observing existing functions ii. Methods to clarify function
6.3
Aesthetic factors in design a. Aesthetic elements i. Line ii. Shape iii. Arrangement iv. Structure v. Colour vi. Texture b. Arrangement i. Rhythm ii. Symmetry iii. Proportion iv. Repetition c. Sources of inspiration d. Industrial packaging
6.4
Strength factors in design Methods of designing for strength: a. Definition of structure b. Types of load i. Compact ii. Tension iii. Torque iv. Shear c. Structure in nature. For example: honeycomb d. Methods of beam design to support and control flat plate and frame for firmness and toughness in order to strengthen boxes
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Public BudgetingDocumento15 paginePublic BudgetingTom Wan Der100% (4)
- Jesus Christ Was A HinduDocumento168 pagineJesus Christ Was A Hinduhbk22198783% (12)
- 1990 Pekoz Design of Cold-Formed Steel Screw ConnectionsDocumento15 pagine1990 Pekoz Design of Cold-Formed Steel Screw ConnectionsmabuhamdNessuna valutazione finora
- Saptamsa - D7Documento4 pagineSaptamsa - D7Nabeel IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- PsychFirstAidSchools PDFDocumento186 paginePsychFirstAidSchools PDFAna ChicasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bird Beak ActivityDocumento4 pagineBird Beak Activityapi-314222661Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preview of Introduction To Manufacturing Processes and Materials Manufacturing Engineering and Materials ProcessingDocumento20 paginePreview of Introduction To Manufacturing Processes and Materials Manufacturing Engineering and Materials ProcessingAnonymous 8209ZTNessuna valutazione finora
- AeronauticalDocumento294 pagineAeronauticalJustin LouNessuna valutazione finora
- 1999, 2003 - Purple Triangles - BrochureDocumento32 pagine1999, 2003 - Purple Triangles - BrochureMaria Patinha100% (2)
- Introduction To Civil Engineering (VTU I/II Sem ECE&M Module 1 (A) Notes)Documento3 pagineIntroduction To Civil Engineering (VTU I/II Sem ECE&M Module 1 (A) Notes)sathish_ya100% (9)
- Attery: User Guide Dict Release 2020Documento47 pagineAttery: User Guide Dict Release 2020diegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic Vs CA - Land Titles and Deeds - GR No. 127060Documento3 pagineRepublic Vs CA - Land Titles and Deeds - GR No. 127060Maya Sin-ot ApaliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal and Public TransportDocumento386 paginePersonal and Public TransportJordanMorrallNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Applications of Composites: Composite Materials, Vol. 3Da EverandEngineering Applications of Composites: Composite Materials, Vol. 3Bryan R. NotonValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Mitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationDocumento4 pagineMitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationGabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Soap StudyDocumento25 pagineReport On Soap StudyAbhishek JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Digest GR No 90501 NetDocumento4 pagineCase Digest GR No 90501 Netlawnotesnijan100% (1)
- Urban Design Checklist For Study PDFDocumento6 pagineUrban Design Checklist For Study PDFabhi krishNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope of Architecture Board ExamDocumento12 pagineScope of Architecture Board Examjudd trajeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Tle Exam - Set BDocumento13 pagineSample Tle Exam - Set Bjc belga100% (3)
- Syllabi For The Subjects in The Architecture Licensure ExaminationDocumento7 pagineSyllabi For The Subjects in The Architecture Licensure ExaminationNatalie Williams100% (1)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Let Reviewer UniversityDocumento4 pagineTechnology and Livelihood Education: Let Reviewer UniversitymaryjeandolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus PDFDocumento12 pagineSyllabus PDFಜಗದೀಶ್ ಎ ಎಂNessuna valutazione finora
- Infra Teaching PlanDocumento4 pagineInfra Teaching PlanPiyush BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering management-QUIZ-ANSWER-KEYDocumento5 pagineEngineering management-QUIZ-ANSWER-KEYDave CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- AeroDocumento217 pagineAeroDemo UserNessuna valutazione finora
- MID EXAM - CIVIL - Architecture & Town Planning - ADIL HAMZA - SU-17-01-074-022#.Documento5 pagineMID EXAM - CIVIL - Architecture & Town Planning - ADIL HAMZA - SU-17-01-074-022#.Adil HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drones in Construction NotesDocumento11 pagineDrones in Construction NotesGeorge DamisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thái Văn Quân Võ Thành Tài Võ Đức Rin Lê Xuân Mừng Nguyễn Văn HùngDocumento32 pagineThái Văn Quân Võ Thành Tài Võ Đức Rin Lê Xuân Mừng Nguyễn Văn Hùnghkt jungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3Documento2 pagineWeek 3api-323356286Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocumento14 pagineBasic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringSudalai MadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Acecipe - 5. Design and Manufacturing EngineeringDocumento3 pagineAcecipe - 5. Design and Manufacturing EngineeringMaryedNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Plant Site DeterminationDocumento1 paginaIndustrial Plant Site DeterminationFirst LastNessuna valutazione finora
- CED M.TechDocumento53 pagineCED M.TechNIHILSORATHIANessuna valutazione finora
- All MBSDocumento4 pagineAll MBSPratik BishtNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To Group 6'S PresentationDocumento18 pagineWelcome To Group 6'S PresentationKhắc Hoàng BùiNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Student ProgramDocumento19 pagineInternship Student ProgramMohd Qazar YusopNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Semester CivilDocumento12 pagine7th Semester CivilDebanjan BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento6 pagineChapter 1shjahsjanshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Civil EngineeringDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Civil EngineeringHanumantha Raju100% (1)
- ECE 6141 Advanced Pavement Materials 02.8.2024Documento6 pagineECE 6141 Advanced Pavement Materials 02.8.2024jc7muriNessuna valutazione finora
- CGC Unit 15 Test Answer KeyDocumento3 pagineCGC Unit 15 Test Answer KeyZiyangLiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Model Exit Exam For Architecture With Answer KeysDocumento19 paginePre Model Exit Exam For Architecture With Answer KeysMesganaw Mathewos80% (5)
- Assistant Director, Town PlanningDocumento21 pagineAssistant Director, Town PlanningKiran Ugalmugale100% (1)
- Chapter 4: RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS (Remove Those Not Applicable)Documento3 pagineChapter 4: RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS (Remove Those Not Applicable)Justine Marie RoperoNessuna valutazione finora
- Top CollegesDocumento16 pagineTop Collegesaamir ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Set B - Tle ExamDocumento13 pagineSet B - Tle ExamMark Anthony LibecoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 Engineering ProfessionDocumento7 pagine1.0 Engineering Professionعبد الرزاق عمرNessuna valutazione finora
- Tle Major Test Set 015Documento13 pagineTle Major Test Set 015Charmaine NiebresNessuna valutazione finora
- CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 1st Semester Anna UniversityDocumento25 pagineCIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 1st Semester Anna UniversityJinu Madhavan100% (1)
- Manufacturing Industries Worksheet Padhleakshay - CompressedDocumento25 pagineManufacturing Industries Worksheet Padhleakshay - Compresseddjbruteforce7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire and LifeDocumento6 pagineFire and LifeRamil S. ArtatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Fighter RobotDocumento62 pagineFire Fighter RobotAly Abd ElmotalebNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope, Disciplines, Relevance of Civil EnggDocumento39 pagineScope, Disciplines, Relevance of Civil EnggShreevas NandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaysia: Untversiti TT'NDocumento8 pagineMalaysia: Untversiti TT'N佳俐Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Dan Jawaban Uas 2017Documento8 pagineSoal Dan Jawaban Uas 2017wahyu dinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bcme SyllabusDocumento3 pagineBcme Syllabusgdr naiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Element of Civil Engg.Documento15 pagineElement of Civil Engg.Roshan BudhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 16Documento37 pagine1 16abel dequinaNessuna valutazione finora
- CTHM Lab Manual MistDocumento71 pagineCTHM Lab Manual MistSyed HabeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1Documento27 pagineUnit - 1ವಿನಯ್ ಎಮ್. ಆರ್Nessuna valutazione finora
- Third and Fourth Year Curriculum For Civil EngineeeringDocumento38 pagineThird and Fourth Year Curriculum For Civil EngineeeringAnthony MulengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Batatota Popwer Plant Project 1 PDFDocumento16 pagineBatatota Popwer Plant Project 1 PDFAnonymous DfaS5nSimJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture II & III PTMM Kelas ADocumento6 pagineLecture II & III PTMM Kelas ARizky ParamytaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan TE-IIDocumento7 pagineLesson Plan TE-IIPrabesh AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- E4sem1 Ce Wt1&Wt2 CeDocumento5 pagineE4sem1 Ce Wt1&Wt2 CeSai KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bài Giảng Cơ Khí-2021 - OnlineDocumento115 pagineBài Giảng Cơ Khí-2021 - OnlineMinh Tường NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Paper GeologyDocumento4 pagineReaction Paper Geologyclarissa bibatNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFDocumento7 pagine3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFkingNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Infrastructure in DevelopmentDa EverandThe Role of Infrastructure in DevelopmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanoelectronics: Materials, Devices, Applications, 2 VolumesDa EverandNanoelectronics: Materials, Devices, Applications, 2 VolumesRobert PuersNessuna valutazione finora
- Dumbell WorkoutDocumento1 paginaDumbell WorkoutpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ramalan FIZIK SPM 2013Documento1 paginaRamalan FIZIK SPM 2013pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Floor Plan 55Documento2 pagineFloor Plan 55pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan Homestay KluangDocumento1 paginaPlan Homestay KluangpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Essays NilamDocumento13 pagineEssays NilampendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Percubaan PMR 2012 KHB ERT PahangDocumento16 paginePercubaan PMR 2012 KHB ERT PahangpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadual Giliran Pengawas PeperiksaanDocumento2 pagineJadual Giliran Pengawas PeperiksaanpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambar Nota InductionDocumento4 pagineGambar Nota InductionpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover ExerciseDocumento1 paginaCover ExercisependekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan k2Documento6 pagineSoalan k2pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Does The Label The BatteryDocumento3 pagineWhat Does The Label The BatterypendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- AnswerDocumento2 pagineAnswerpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan k2Documento4 pagineSoalan k2pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan k2Documento6 pagineSoalan k2pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento13 pagineElectromagnetic Inductionkaushik247Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kaler SriDocumento2 pagineKaler SripendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- FizikDocumento65 pagineFizikpendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover ExerciseDocumento1 paginaCover ExercisependekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadual Gred F5Documento1 paginaJadual Gred F5pendekarpendawoNessuna valutazione finora
- Budget Cal EngDocumento25 pagineBudget Cal EngMiza M MokhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- PED100 Mod2Documento3 paginePED100 Mod2Risa BarritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary Task Harry PotterDocumento3 pagineVocabulary Task Harry PotterBest FriendsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics - Grade 9 - First QuarterDocumento9 pagineMathematics - Grade 9 - First QuarterSanty Enril Belardo Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFDocumento9 pagineA Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFgskodikara2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fortune 2010Documento14 pagineFortune 2010Stefan JenkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- 115 FinargDocumento294 pagine115 FinargMelvin GrijalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Context: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationDocumento4 pagineContext: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationAR ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Tender Documents-Supply and Installation of TVET Equipment and Tools (4) (23) Feb FinalDocumento166 pagineTender Documents-Supply and Installation of TVET Equipment and Tools (4) (23) Feb Finalracing.phreakNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Courts in Granting Bails and Bail Reforms: TH THDocumento1 paginaRole of Courts in Granting Bails and Bail Reforms: TH THSamarth VikramNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectification or Correction of Sale DeedDocumento4 pagineRectification or Correction of Sale Deedsumanth_0678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rape and Challenging Contemporary ThinkingDocumento17 pagineRape and Challenging Contemporary ThinkingKirthna MadhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- In Christ Alone My Hope Is FoundDocumento9 pagineIn Christ Alone My Hope Is FoundJessie JessNessuna valutazione finora
- Not For Profit Governance WeilDocumento224 pagineNot For Profit Governance WeillkjhmnvbNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume of Masterchef Contestant, Melissa GutierrezDocumento3 pagineResume of Masterchef Contestant, Melissa GutierrezMikhail GalatinovNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 p7 Kids AvikdeDocumento2 pagine50 p7 Kids AvikdebankansNessuna valutazione finora
- Class NotesDocumento16 pagineClass NotesAdam AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- International Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)Documento22 pagineInternational Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)repositoryIPBNessuna valutazione finora
- Amtek Auto Analysis AnuragDocumento4 pagineAmtek Auto Analysis AnuraganuragNessuna valutazione finora