Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bones 1
Caricato da
Stephanie TalbotDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bones 1
Caricato da
Stephanie TalbotCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
BURSITIS- inflammation of the connective tissue which surrounds the joints CARPEL TUNNEL SYNDROME- compression of the median nerve where it enters the hand through the carpel tunnel @ the wrist CREPITUS-palpable or auditory crunching produced by the crunching together of bony fragments DELAYED UNION-slower than average healing of a fracture DISLOCATION-a condition that occurs when the articular surfaces of a joint is no longer in anatomical contact w/ each other FIBROMYALGIA- chronic pain of unknown origin MULTIPLE MYELOMA- malignant neoplasm of the plasma cells of the bone marrow NON-UNION-failure of the ends of a fractured bone to meet OSTEOMYELITIS- infection of the bone & bone marrow OSTEOPOROSIS- chronic bone loss which causes a decrease in bone density, leading to increased risk of fractures OSTEOSARCOMA- primary neoplasm of the bone PERONEAL NERVE COMPRESSION-compression of the peroneal nerve on the lateral aspect of the knee, over the head of the fibuladrop foot STRAIN- injury to the musculotendinous unit caused by excessive force or stretching SPRAIN-partial rupture of a joints ligament, due to wrenching or twisting of the joint.
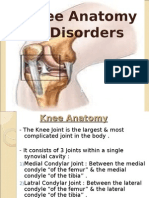
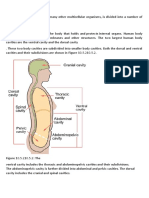
EO 1.2: RELATE THE STRUCTURE & FXN OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM TO THE CARE OF CLIENTS W/ ALTERATIONS IN PHYSICAL MOBILITY. Structure of musculoskeletal system: 1. Bones- spongy & compact Classification: a) Long- ex. femur, humerus Components: 1. Epiphysis 2. Metaphysic 3. Diaphysis
2.
3. 4. 5.
Periosteum- fibrous connective tissue which covers & protects bone 5. Bone marrow- storage area for fat, produces all blood cells b) Short- ex. Carpals, tarsals c) Flat-ex. scapula d) Irregular- ex. Skull, sternum etc Fxn: protect vital organs, support body tissues, assist movement, haematopoiesis & storage mineral salts Articulations Classification: a) Synarthrosis- fixed joints (fibrous) b) Amphiathrosis- slightly moveable joints (cartilagous) c) Diarthrosis- freely moveable (synovial) d) Joint capsule- fibrous sheath surrounding articulation of the bone Fxn: hold bones together securely & give skeleton mobility Skeletal muscle Fxn: facilitate voluntary movement, maintain posture & production of body heat Ligaments & tendons Fxn: provision joint stability, allowing restricted movement as well as binding muscle to bone Cartilage Fxn: absorption of weight, shock, stress & strain, as well as protection of bones, joints, and joint tissue
4.
EO 1.3: ID AGE RELATED CHANGES IN THE STRUCTURE & FXN OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM. A. Decreased bone density- teach safety tips B. Increase bone prominence- prevent pressure on boney prominences C. Kyphotic posture- widened gate, shift in the center of gravity- teach proper mechanics, instruct sit in supportive chairs w/ arms D. Cartilage degeneration E. Decreased ROM F. Muscle atrophy & decreased strength G. Slowed movement
EO 1.9: DESCRIBE THE CLASSIFICATION, ACTION AND NSG IMPLICATIONS FOR THE FOLLOWING MEDICATIONS A. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS a. SALICYLATES i. ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID (ASPIRIN) a) M.of .A: inhibits prostaglandin, thus decreasing inflammatory process & body temp, decrease platelet aggregation & thus blood clotting, relieves pain by inhibiting COX (need to synthesis prostaglandins) b) S.E: anorexia, N&V, diarrhea, dizziness, confusion, hearing loss, heart burn, stomach pain, tinnitus, uticaria, ulceration, agranulocytosis. b. NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS) i. IBUPROFEN (MOTRIN) & NAPROXEN (NAPROSYN) a) M.of.A: inhibition prostaglandin synthesis thus relieving pain b) S,E: anorexia, N&V, diarrhea, edema, rash, Purpura, tinnitus, fatigue, light headedness. ii. CELECOXIB (CELEBREX) a) M.of.A: inhibit COX-2 b) S.E: headache, dizziness, sinusitis, rash, nausea, flatulence, diarrhea B. ANTI-GOUT DRUGS a. COLCHINCINE (Novocolchine) i. M.of.A: inhibition migration leukocytes to inflamed site ii. S.E: GI irritation b. ALLOPURINOL (ZYLOPRIM) & SULFINPYRANZONE (ANTURANCE) i. M.of.A: decrease uric acid synthesis, thus decreasing serum uric acid ii. S.E: anorexia, N&V, diarrhea, stomatitis, dizziness, headache, rash, puritis, malaise, metallic taste iii. NSG: increase fluid intake C. SKELETAL MUSCLE RLEAXANTS a. CYCLOBENZAPRINE (FLEXERIL) i. M.of.A: UNKOWN ii. S.E: GI upset b. DIAZEPAM (VALIUM) i. M.of.A: D. CORTICOSTEROIDS a. PREDNISONE i. M.of.A: suppression inflammation & adrenal fxn to decrease inflammation ii. S.E: N&V, diarrhea, abdominal distention, increased appetite, sweating, headache, depression, flush, mood changes
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- This Study Resource Was: Head-To - Toe Assessment Documentation SampleDocumento2 pagineThis Study Resource Was: Head-To - Toe Assessment Documentation SampleA Sung100% (3)
- Cardiac Surgery MCQDocumento43 pagineCardiac Surgery MCQprofarmah100% (7)
- Strategic Considerations in Treatment Planning Deciding When To Treat, Extract, or Replace A Questionable Tooth PDFDocumento12 pagineStrategic Considerations in Treatment Planning Deciding When To Treat, Extract, or Replace A Questionable Tooth PDFItzel Marquez100% (1)
- PACES 21 - Communication Skills and EthicsDocumento10 paginePACES 21 - Communication Skills and EthicsDrShamshad Khan100% (1)
- Final Exam Review Sheet1 Mental Health NursingDocumento20 pagineFinal Exam Review Sheet1 Mental Health NursingStephanie Talbot100% (56)
- UCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011Documento142 pagineUCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011ak100007100% (5)
- Skin Assessment FormDocumento2 pagineSkin Assessment FormOng KarlNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthopaedic SlidesDocumento163 pagineOrthopaedic SlidesVivian ChepkemeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of BonesDocumento3 pagineDisorders of BonesAnonymous 0pSLjJYNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurogenic, Osteogenic, Dicogenic, Referred Pain A. Referred PainDocumento24 pagineNeurogenic, Osteogenic, Dicogenic, Referred Pain A. Referred PainWilliam AaronNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal SystemDocumento10 pagineSkeletal SystemJamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Avn On ScriptDocumento13 pagineAvn On Scriptclaire.deveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracturesgoutosteosprain 2Documento199 pagineFracturesgoutosteosprain 2Rose Cristille Yeso JocsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Legg Calve PerthesDocumento7 pagineLegg Calve PerthesNelhbenson LaurenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 2 Semester 2Documento88 pagineYear 2 Semester 2JSeasharkNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Skeletal SystemDocumento6 pagineAnatomy of The Skeletal SystemPauline JoyceNessuna valutazione finora
- Persiapan Operasi ORIFDocumento38 paginePersiapan Operasi ORIFamir hamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lumbar Spondylosis Case Study CT2Documento27 pagineLumbar Spondylosis Case Study CT2hnihnn02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocumento26 pagineMus Culo SkeletalCristy Ellain EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Spinal StenosisDocumento14 pagineSpinal StenosisHONGJYNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal SystemDocumento104 pagineSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 2 Study Guide (1146)Documento7 pagineExam 2 Study Guide (1146)S. MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocumento23 pagineAnkylosing Spondylitispatel divya100% (1)
- ArthritisDocumento21 pagineArthritisBasil KuriakoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Pathology NotesDocumento20 pagineMusculoskeletal Pathology Notesdinia fitrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFDocumento20 pagineMusculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFvevestephaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle PhysiologyDocumento7 pagineMuscle PhysiologyNicole Erin TomaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal DisorderDocumento7 pagineSkeletal Disorderhxqf25mbvvNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System ReviewerDocumento4 pagineMuscular System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Askep Low Back PainDocumento16 pagine1 Askep Low Back PainBr Komarudin100% (1)
- Presentation (MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUESDocumento37 paginePresentation (MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUESDaniellaNessuna valutazione finora
- OsteoarthritisDocumento4 pagineOsteoarthritisDharti PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- WK 2 NFK 202Documento88 pagineWK 2 NFK 202JSeasharkNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR JaneDocumento73 pagineArthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR Janeumanantini06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocumento19 pagineAnkylosing SpondylitisZulhida YuniNessuna valutazione finora
- Knee Anatomy & Disorders: By: Nour Abu Al-Sha'arDocumento28 pagineKnee Anatomy & Disorders: By: Nour Abu Al-Sha'arAlisha FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 - Knee Joint - D3Documento28 pagine7 - Knee Joint - D3aslooclt100% (1)
- Fracture Fixation and ArthroplastyDocumento39 pagineFracture Fixation and Arthroplastyzony khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSDocumento79 pagineMuscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSPaulhotvw67100% (4)
- ATM FotografiasDocumento21 pagineATM FotografiasBenjamin O. ZuñigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular DiseasesDocumento24 pagineMuscular DiseasesMaria Theresa FortunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Refratt OsteoartritisDocumento24 pagineRefratt OsteoartritisSulung Ade PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- OsteoarthritisDocumento29 pagineOsteoarthritisniekoNessuna valutazione finora
- ArthritisDocumento20 pagineArthritisPdianghunNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesDocumento4 pagineUnit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesEricBuguinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 H:oDocumento8 pagineLecture 2 H:oShanaz TalukdarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Does Thoracic Spondylosis Mean? Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocumento4 pagineWhat Does Thoracic Spondylosis Mean? Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmenttiarmayantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 62 Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento5 pagineChapter 62 Musculoskeletal SystemRichard MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13Documento27 pagineChapter 13Zaky DavidiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human CavitiesDocumento14 pagineHuman CavitiesDrexel DalaygonNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Definition of Disease: Start in The Teens and 20sDocumento4 pagineI. Definition of Disease: Start in The Teens and 20sAriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento9 pagineMusculoskeletal SystemEduardson PHNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal TraumaDocumento63 pagineMusculoskeletal Traumarobby pardiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- MSK Lo For WednesdayDocumento22 pagineMSK Lo For WednesdayKesyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System ReviewerDocumento4 pagineSkeletal System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Bone Injury InflammationDocumento24 pagine3 Bone Injury InflammationGwyneth Koleen LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Bone Joint and Muscle Disorders of DogsDocumento15 pagine2 Bone Joint and Muscle Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento31 pagineStructure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemSaminathan KayarohanamNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Dr. H. Busjra M Nur MSC Dept. Physiology Fkui / FkumjDocumento56 pagineDr. Dr. H. Busjra M Nur MSC Dept. Physiology Fkui / FkumjRahdan NurNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis - Dont EraseDocumento3 pagineOsteoarthritis - Dont EraseLynlyn AlforqueNessuna valutazione finora
- General Osteology: DefinitionsDocumento45 pagineGeneral Osteology: DefinitionsAndreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthopedic NursingDocumento237 pagineOrthopedic Nursingɹǝʍdןnos100% (24)
- Spinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsDa EverandSpinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Back Pain and Other Spine DisordersDa EverandA Simple Guide to Back Pain and Other Spine DisordersNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of DelegationDocumento16 paginePrinciples of DelegationStephanie Talbot100% (1)
- CardiacDocumento43 pagineCardiacStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily OrganizationDocumento4 pagineDaily OrganizationStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Prioritization, DelegationDocumento5 paginePrioritization, DelegationStephanie Talbot100% (1)
- Module 10.3: Children Who Have Alterations in Tissue PerfusionDocumento23 pagineModule 10.3: Children Who Have Alterations in Tissue PerfusionStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- STD'S BacterialDocumento2 pagineSTD'S BacterialStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7.2 Drug ChartDocumento1 paginaModule 7.2 Drug ChartStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Tests GI SystemDocumento1 paginaLaboratory Tests GI SystemStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocumento13 pagineIncreased Intracranial PressureStephanie Talbot100% (1)
- Diverticulosis OutlineDocumento3 pagineDiverticulosis OutlineStephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- NSG Fundamentals Final Exam Review Guide1Documento34 pagineNSG Fundamentals Final Exam Review Guide1Stephanie TalbotNessuna valutazione finora
- Knox ComplaintDocumento16 pagineKnox ComplaintDan LehrNessuna valutazione finora
- General Consideration in EsophagectomyDocumento4 pagineGeneral Consideration in EsophagectomyDabessa MosissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phlebotomy TechnacianDocumento1 paginaPhlebotomy Technacianapi-78318377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tomografia UrotacDocumento12 pagineTomografia Urotacnoeg_909929Nessuna valutazione finora
- Occlusal Dysesthesia or Phantom BiteDocumento14 pagineOcclusal Dysesthesia or Phantom BitebryanabauerNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocumento4 pagineName of Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationClariss AlotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Home Oxygen Nov2014Documento32 pagineBook Home Oxygen Nov2014AdrianNessuna valutazione finora
- LEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsDocumento11 pagineLEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Documento7 pagineGroup 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Crissan Jejomar AbanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Studi Kasus: Kehamilan Dengan: Dengan Katub Jantung Prostetik Mekanik Dan Penggunaan AntikoagulanDocumento10 pagineStudi Kasus: Kehamilan Dengan: Dengan Katub Jantung Prostetik Mekanik Dan Penggunaan AntikoagulanMonyet...Nessuna valutazione finora
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)Documento4 pagineDAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)mkpnurdinNessuna valutazione finora
- WaiverDocumento1 paginaWaiveromega3fitnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology I Final Exam: Part 1: Multiple ChoiceDocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology I Final Exam: Part 1: Multiple ChoiceDigaale YareNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob2 Sas 40Documento7 pagineOb2 Sas 40????Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2Documento10 paginePediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2k sagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ma. Cricel T. Dela Cruz, RMTDocumento4 pagineMa. Cricel T. Dela Cruz, RMTMa. Cricel T. Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Petroleum As A Cancer CureDocumento4 paginePetroleum As A Cancer Curedaurel100% (1)
- Kode Nama Barang Stok Selling Price Disc: KemasanDocumento9 pagineKode Nama Barang Stok Selling Price Disc: KemasanEny EndarwatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 SURG1 OncoDocumento8 pagine2.4 SURG1 OncoGeriz Daniella VigoNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Mahmoud - Salmonella - A Dangerous Foodborne Pathogen-Intech (2011)Documento450 pagineB. Mahmoud - Salmonella - A Dangerous Foodborne Pathogen-Intech (2011)kiệt lêNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Notebook 1.1.3 Part 2 - Notebook - Day 2Documento6 pagineVirtual Notebook 1.1.3 Part 2 - Notebook - Day 2Justice JensenNessuna valutazione finora
- Things To Read: A. Trauma: Fractures and DislocationsDocumento4 pagineThings To Read: A. Trauma: Fractures and DislocationsHanien YeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 358 Muhammad Zul SikkDocumento3 pagine358 Muhammad Zul SikkMar Yana MamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 5 - Fa - Gas Exchange - T2 - QSDocumento3 pagineSec 5 - Fa - Gas Exchange - T2 - QSnoorlailyNessuna valutazione finora