Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Capacity and Demand in Units Period Regular Time Overtime Subcontract Demand
Caricato da
Vinay KumarDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Capacity and Demand in Units Period Regular Time Overtime Subcontract Demand
Caricato da
Vinay KumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. List and explain various pure strategies and mixed strategies 2.
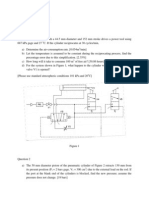
Distinguish between aggregate planning and master production schedule. 3. Beta associates produces accounting machine that have a seasonal demand pattern. We are required to plan for the optimum production rates and inventory levels for the next four quarter periods. The available production capacities during regular time and overtime, as well as other cost data are as follows:
Period 1 2 3 4 Regular time 1200 900 1000 700 capacity and demand in units Overtime Subcontract 150 800 200 800 350 800 350 800 Demand 1200 1100 1800 1500
Available initial inventory = 110 units, Desired final inventory = 140 units RT cost/unit = Rs 100, OT cost/ unit = Rs 125 and SC cost /unit = Rs 145 Inventory cost/ unit / period = Rs 15, the cost of unused capacity = `Rs 40/ unit (a) Formulate the problem as a transportation model (b) Solve the model and infer the results.
4. A company produces calculators and has forecast demand over the next four quarters as shown below. Each quarter has 60 working days.
quarter units 1 2000 2 1500 3 1700 4 2000
The company maintains a constant work force of 40 employees, and there are no subcontractors available who can meet its quality standards. The company can, however go on overtime if necessary and encourage customers to back-order calculators. Production and cost data are as follows Production capacity: Initial inventory: 400 units Regular time hours = 40 employees x (60 days/quarter) x (8 hr/day). Overtime hours = 40 employees x (60 days/quarter) x (4 hr/day). Standard labour hours/unit = 15 hr. Labour cost: RT cost = Rs 10/hr, OT cost = Rs 15/hr
Material and overhead (regular time) = Rs 100/unit Material and overhead (overtime) = Rs60/unit Cost of unutilized capacity during regular time = Rs 60/unit Back ordering cost Rs 5/unit/period Inventory carrying cost = Rs 10/unit/period. Formulate this problem as a transportation problem and solve.
5. A firm producing Hand trolley has the following Master production schedule.
Week Demand 1 200 2 3 4 240 5 6 240 7 8 220
Each hand trolley has a bin, two wheel assemblies, two handle bars and a mounting base. Each wheel assembly has a wheel and two bearings. Order quantities, lead times and inventories on hand at the beginning of period 1 are shown below
Part Hand trolley Bin Wheel assemblies Handle bars Mounting base Wheel Bearing Order quantity 350 400 800 850 250 600 1500 Lead time (week) 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 Inventory on hand 220 250 120 105 250 300 200
A shipment of 800 wheel assemblies is already scheduled to be received at the beginning of week 2. Also another shipment of 250 mounting base is scheduled to be received at the beginning of week 3. Complete the material requirements plan for the bin, wheel assemblies, handle bars, mounting base, wheel and bearing and show what quantities of orders must be released and when they must be released in order to satisfy the MPS.
6. What are the three major inputs for an MRP system? Explain 7. A company makes Q model from components R, S and T. Component R is made from two units component X and one unit component of Y. Component T is made from one unit of component Y and three units of component Z. i) Draw the product tree structure and bill of material. ii) Using the given information calculate the gross requirements if the company plans to build 100 units of its Q model if you have these inventories: 150 units of component T and 200 units of component R.
8. Explain the following i) MRP ii) CRP iii) BOM iv) MRP logic v) Time phasing 9 The forecast for a group of items manufactured in a firm is shown below. Quarter Demand 1 420 2 370 3 620 4 720 5 600 6 200 7 300 8 400
The firm estimates that it costs Rs. 225 per unit to increase the production rate, Rs. 275 per unit to decrease the production rate, Rs. 80 per unit per quarter to carry the items on inventory and Rs. 150 per unit if subcontracted. Given these costs, evaluate the following mixed strategy. The company decides to maintain a constant production rate of 250 units per quarter and permit 20% overtime when the demand exceeds the production rate. The incremental cost of overtime is Rs. 25 per hour. It plans to meet the excess demand by hiring and firing of workers. (10 marks)
10 A company manufactures Iron box. The MPS of the final assembly is as shown below. Month Projected requirements 1 __ 2 3500 3 3000 4 4500 5 _ 6 1000 7 4000 8 5500
The initial stock on hand is 1150 units. The carrying cost is Rs. 2.5 per/month and the lead time is one month. The ordering cost per order is Rs. 6000. Develop an EOQ solution and calculate the total relevant costs
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pom Sol 10Documento5 paginePom Sol 10amritranjan123_34249Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Example PDFDocumento6 pagineManufacturing Example PDFAbdul RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ISYE 3450 Homework 1Documento2 pagineISYE 3450 Homework 1Brandon HarrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Supp KDocumento14 pagineSupp Kshazarafia100% (1)
- Engineering Economics Exercises - SolutionsDocumento4 pagineEngineering Economics Exercises - SolutionsMehmet ZirekNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 2-Product Process and ScheduleDocumento67 pagineChap 2-Product Process and Schedulemuath wardatNessuna valutazione finora
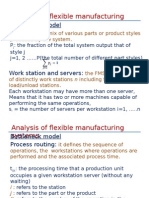
- Quantitative Analysis of Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento9 pagineQuantitative Analysis of Flexible Manufacturing SystemJaydeep PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20Documento11 pagineEEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20ayeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I DME I 13 09 2021Documento68 pagineUnit I DME I 13 09 2021Vaibhav JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Assignment - RevisedDocumento4 pagineHome Assignment - RevisedLê Quỳnh Anh100% (1)
- ALDEPDocumento1 paginaALDEPAmandeep Singh GujralNessuna valutazione finora
- Mech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentDocumento10 pagineMech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentArunNessuna valutazione finora
- ChipDocumento7 pagineChipOmkar ManeNessuna valutazione finora
- Meeting Minutes With HODsDocumento4 pagineMeeting Minutes With HODsRushi Padmanabhuni100% (1)
- Tutorial Pneumatic CircuitDocumento5 pagineTutorial Pneumatic CircuitMuhammad Abdullah0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Resource PlanningDocumento70 pagineChapter 3 Resource PlanningHieu TruongNessuna valutazione finora
- Unsolved Problems On Brakes and ClutchesDocumento8 pagineUnsolved Problems On Brakes and ClutchesAuthorized EarthlingNessuna valutazione finora
- 604 I.c.engine (Me-604) Exp. ManualDocumento35 pagine604 I.c.engine (Me-604) Exp. Manualnavaneet gupta100% (1)
- Lathe Machine Lab ReportDocumento5 pagineLathe Machine Lab ReportEdgar ThorpeNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 1 (ME 461)Documento6 pagineAssignment No 1 (ME 461)Jayant Raj SauravNessuna valutazione finora
- MEP Internship Training Report Main PageDocumento40 pagineMEP Internship Training Report Main PageHhNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 02 - Machine DesignDocumento2 pagineAssignment 02 - Machine DesignRatan Sadanandan O MNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.HW Chap 13-1,11,13,15Documento7 pagine6.HW Chap 13-1,11,13,15Jyothi VenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 MRP ErpDocumento22 pagineChapter 5 MRP ErpKelly ObrienNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Communication Lab Manual For VI Semester B.Tech (Electronics Engineering)Documento25 pagineDigital Communication Lab Manual For VI Semester B.Tech (Electronics Engineering)Nikolai RossanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Documento27 pagineMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Flow and Equivalence PDFDocumento6 pagineCash Flow and Equivalence PDFIscandar Pacasum DisamburunNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment o Tom at I OnDocumento22 pagineAssignment o Tom at I OnphyrdowsNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-Markov ChainDocumento29 pagine04-Markov ChainazizNessuna valutazione finora
- Epm AssignmentDocumento20 pagineEpm AssignmentRahulNessuna valutazione finora
- CS2202 DPSD 2 MarksDocumento78 pagineCS2202 DPSD 2 MarksVenkat RamananNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Speed Control Based On IotDocumento5 pagineAutomatic Speed Control Based On IotDhruva CasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Waiting Lines/ Queuing Theory OutlineDocumento17 pagineUnit 6 Waiting Lines/ Queuing Theory OutlineHadiBiesNessuna valutazione finora
- 150 199 PDFDocumento49 pagine150 199 PDFSamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Visit ReportDocumento5 pagineField Visit Reportpramod100% (1)
- Modern Control Technology Components & Systems (2nd Ed.)Documento2 pagineModern Control Technology Components & Systems (2nd Ed.)musarraf172Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento5 pagineAssignment 2aiao90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2: in Chapters 3 and 4Documento4 pagineAssignment 2: in Chapters 3 and 4Menna SultanNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Calculation: by Ashish S. RautDocumento11 pagineLoad Calculation: by Ashish S. RautRutanshu Lawhale100% (3)
- Mechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersDocumento6 pagineMechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersSaravanan MathiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Bit Synchronous Up CounterDocumento15 pagine3 Bit Synchronous Up CounterMaruf MorshedNessuna valutazione finora
- SylableDocumento3 pagineSylabledebelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Agv Ex 1Documento1 paginaAgv Ex 1Lương Bảo HânNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB#05 Objective To Create An Arena Model Using Data Modules and Observe The Results of The Simulation Run Task #1Documento8 pagineLAB#05 Objective To Create An Arena Model Using Data Modules and Observe The Results of The Simulation Run Task #1Aisha AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Static and Dynamic Balancing ApparatusDocumento19 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Static and Dynamic Balancing ApparatusOmkarNessuna valutazione finora
- EC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualDocumento41 pagineEC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualRamkumar Sivakaminathan100% (1)
- EENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Documento4 pagineEENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Jamil NahraNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To ProblemsDocumento23 pagineAnswers To ProblemsYuvahraani Ravichandran100% (4)
- Thread Cutting and Knurling To Make Nut and BoltDocumento3 pagineThread Cutting and Knurling To Make Nut and BoltHassan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 8088 Instruction SetDocumento33 pagine8088 Instruction SetGetzi Jeba LeelipushpamNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 ASSMTs PERT-CPM - Sir Hussain Saleem 25102018 RevisedDocumento2 pagine2018 ASSMTs PERT-CPM - Sir Hussain Saleem 25102018 RevisedMuhammad AmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Six Sigma Project - Abhishta - BehrDocumento16 pagineLean Six Sigma Project - Abhishta - BehrAbhishta SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6Documento12 pagineTutorial 6hazemNessuna valutazione finora
- Rail Bhawan ReportDocumento34 pagineRail Bhawan ReportNikhil MohiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Model of The PMSG Based On Wind Energy Conversion SystemDocumento7 pagineMathematical Model of The PMSG Based On Wind Energy Conversion SystemIRJIENessuna valutazione finora
- MRP CaseStudies2008Documento24 pagineMRP CaseStudies2008Sachin ElfNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.guess Questions - Problems - QuestionsDocumento34 pagine2.guess Questions - Problems - QuestionsKrishnaKorada67% (9)
- (2015 Onwards) : M.Sc. Software Systems Degree Examin Tions, April 2018Documento6 pagine(2015 Onwards) : M.Sc. Software Systems Degree Examin Tions, April 2018Aravind KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Documento31 pagineCost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Artha sarokarNessuna valutazione finora
- Alagappa University Collaborative Institution B.com (4th Semester) - Internal 1 - Cost and Management AccountingDocumento3 pagineAlagappa University Collaborative Institution B.com (4th Semester) - Internal 1 - Cost and Management AccountingSREENAVIN PNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ: Supply Chain Management: A User-Based Definition of QualityDocumento21 pagineMCQ: Supply Chain Management: A User-Based Definition of QualityVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Content University Library Copyright Permission RequestDocumento4 pagineContent University Library Copyright Permission RequestVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Documento1 paginaTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Vinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- State PDFDocumento1 paginaState PDFVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SPP 40 Series Sponsored BE MTech Projects CollegewiseDocumento145 pagineSPP 40 Series Sponsored BE MTech Projects CollegewiseVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Spyros@isye - Gatech.edu WWW - Isye.gatech - Edu/ SpyrosDocumento3 pagineSpyros@isye - Gatech.edu WWW - Isye.gatech - Edu/ SpyrosVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Idea GenerationDocumento3 pagineIdea GenerationVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- TbactDocumento7 pagineTbactVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chief Guest: Dr. N. Muthukumar Mr. Amit KumarDocumento1 paginaChief Guest: Dr. N. Muthukumar Mr. Amit KumarVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Resource Planning Module 1: To Create BOMDocumento6 pagineEnterprise Resource Planning Module 1: To Create BOMVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- About DSCE Conference Objectives: Call For PapersDocumento2 pagineAbout DSCE Conference Objectives: Call For PapersVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Good PracticesDocumento1 paginaGood PracticesVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sma MCQDocumento2 pagineSma MCQVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuzzy LogicDocumento51 pagineFuzzy LogicVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Furore 2017 ReportDocumento9 pagineFurore 2017 ReportVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Scrap Reduction in Piston Machining ShopDocumento3 pagineScrap Reduction in Piston Machining ShopVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chopra4 - PPT - ch03 - Supply Chain ManagementDocumento28 pagineChopra4 - PPT - ch03 - Supply Chain ManagementTia MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ChecklistDocumento2 pagineSafety ChecklistAnonymous nF3tseUAGeNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Recognition PowerPoint PDFDocumento11 pagineAircraft Recognition PowerPoint PDFNick TsangNessuna valutazione finora
- EDTO Module 2 - Basic ConceptsDocumento63 pagineEDTO Module 2 - Basic ConceptsLbrito01100% (1)
- Astralloy-V Bars enDocumento2 pagineAstralloy-V Bars enRjgandhi65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel Flat Products For Building - The Grades in EN 10088-4 ExplainedDocumento28 pagineStainless Steel Flat Products For Building - The Grades in EN 10088-4 ExplainedLeo TuckerNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding Technology Solutions To Geothermal Energy Production Challenges - tcm153-574191Documento5 pagineWelding Technology Solutions To Geothermal Energy Production Challenges - tcm153-574191JulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Do 0354Documento1 paginaDo 0354Thavasi NadarNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper and Brass Catalogue July 2014 EditionDocumento33 pagineCopper and Brass Catalogue July 2014 Editionga6ba5100% (1)
- 4050 Douglas StreetDocumento4 pagine4050 Douglas Streett3hbiggyNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Management Plan: North Carolina Department of Transportation Rail DivisionDocumento71 pagineProject Management Plan: North Carolina Department of Transportation Rail DivisionSheikh Yasir ZaheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 History CH 4Documento6 pagineClass 9 History CH 4Yash PlayNessuna valutazione finora
- Dipankar RoyDocumento3 pagineDipankar RoysandeephwrNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Protection of Tanks FRPDocumento5 pagineCorrosion Protection of Tanks FRPaarmasp100% (1)
- Lampiran I SEOJK 21 (Harta Benda)Documento23 pagineLampiran I SEOJK 21 (Harta Benda)Yandra WindesiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ferrocement BoatDocumento10 pagineFerrocement BoatNihil In-lineNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Overview of Offshore PlatformDocumento25 pagine01 Overview of Offshore Platformojooreo100% (1)
- GRP Pipe SystemsDocumento6 pagineGRP Pipe Systemsgc_panchaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Presentation For Transport (Combined)Documento160 pagineFinal Presentation For Transport (Combined)Sharif HafifyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma List 2020Documento64 paginePharma List 2020shriya shettiwar86% (7)
- Deck Machinery BrochureDocumento28 pagineDeck Machinery BrochureCamelia GabrielaNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A 453 Grade 660Documento4 pagineAstm A 453 Grade 660Bruno_jfNessuna valutazione finora
- Expenditure Cycle Business ActivitiesDocumento23 pagineExpenditure Cycle Business ActivitiesBear CooporNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Standard MandatoriDocumento31 pagineDatabase Standard MandatorizalzizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shipboard Firefighting: CODE FT0012Documento17 pagineShipboard Firefighting: CODE FT0012Luis Fernando HRNessuna valutazione finora
- SL No IS Codes Name of The Code 1 2 3 Building MeasurementsDocumento9 pagineSL No IS Codes Name of The Code 1 2 3 Building MeasurementsRajesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- 620N - 620X - 621 - 622 - 642 - 642X - Timetable 27 January 2015Documento16 pagine620N - 620X - 621 - 622 - 642 - 642X - Timetable 27 January 2015David WangNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Structures DesignDocumento15 pagineSteel Structures Designsmg26thmayNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.stress ReliefDocumento2 pagine3.stress ReliefRajeevSangamNessuna valutazione finora
- Scania Press - TrademarkDocumento2 pagineScania Press - TrademarkAnonymous zPUXs8aONessuna valutazione finora