Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)
Caricato da
Sheh Muhammad AfnanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)
Caricato da
Sheh Muhammad AfnanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHM 096
TUTORIAL 2 (Chemical Equilibrium)
Jan 2013
1.
Write the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for each of the following reactions: a) b) c) d) e) f) 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) The decomposition of solid potassium chlorate to solid potassium chloride and oxygen gas. 4HCl(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) + 2Cl2(g) 2NO2(g) + 7H2(g) 4H2O(l) + 2NH3(g) H2O(g) + C(s) CO(g) + H2(g) The reduction of solid copper (II) oxide with hydrogen gas to produce copper metal and water at o 500 C. 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) are 2.50, 1.35 x 105 and 8.70 moles respectively in a 12-L flask. Calculate the equilibrium constant 7 Kc. (1.08 x 10 )
2.
The number of moles of H2, O2, and H2O present at equilibrium for the reaction:
3.
The equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction: 2HCl(g) H2(g) + Cl2(g) is 0.0213 at 400 C. If 20.0 o moles of HCl(g) are heated at 400 C, what amounts of HCl(g), H2(g) and Cl2(g) would be present in the equilibrium mixture? (H2 = Cl2 = 2.26 moles; HCl = 15.48 moles)
o
4.
The equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction: 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) is 2.24 x 10 at 1273 C. Calculate the Kp for the reaction at the same temperature. 20 (1.76 x 10 )
22 o
5.
A 2.50 mole sample of NOCl was placed in a 1.50-L container at 400 C. When equilibrium has established, it was found that 28% NOCl has dissociated according to the reaction: 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc (0.0356)
6.
Consider the reaction: H2(g) + CO2(g) H2O(g) + CO(g) 0.80 mole of H2 and 0.80 mole of CO2 are placed in a 5-dm container at 1650 C. At equilibrium, 0.25 mole of CO was found in the equilibrium mixture. Calculate the equilibrium constant K c. (0.2)
3 o
7.
For the reaction:
2NO2(g) N2O4(g) , the value of Kc is 0.5 at 450 C.
o o
A 1-L container consists of 2.0 moles NO2 and 2.0 mole N2O4 450 C. Is the mixture at equilibrium? If not, in which direction must the reaction proceed to reach equilibrium? 8. Kc and Kc are the equilibrium constants for reactions I and II respectively. I. II. a) b) c) 9. 3H2(g) + N2(g) 2NH3(g) /2 H2(g) + N2(g) NH3(g)
Write the equilibrium constant expressions for Kc and for Kc . Derive a mathematical relationship between Kc and Kc . A reaction vessel contains an equilibrium mixture of 0.11 M N 2(g), 1.91 M H2(g) and 0.25 M NH3(g) o at 500 C. Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kc for reaction I. (0.082) Calculate also the equilibrium constant, Kc for reaction II. (0.29)
4 o
For the reaction: 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) 2NOCl(g), Kp is 6.5 x 10 at 35 C. At equilibrium, the partial pressure PNO = 0.35 atm and PCl2 = 0.10 atm. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of NOCl. (28.2 atm)
10.
For the reaction: C(s) + 2H2(g) CH4(g), Kp is 0.262 at 1000 C. At equilibrium, the partial pressure PH2 = 1.22 atm. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of CH4(g). (0.39 atm)
o
11.
1.0 mole of PBr5 is added to a 1-dm container at 200 C and is allowed to attain equilibrium according to the reaction: PBr5(g) PBr3(g) + Br2(g) The equilibrium mixture contains 0.61 mole of PBr5(g) a) b) Calculate the partial pressure of each of the components in the container. (PPBr5 = 23.7 atm; PPBr3 = 15.15 atm) Calculate the Kp for the reaction. (Kp = 9.68)
12.
Phosgene gas (COCl2) is a highly toxic chemical. 3.00 x 102 mol of the gas was placed in a 1.50-L container. It was heated to 800K. An equilibrium is established: COCl2 (g) CO(g) + Cl2(g) The equilibrium pressure of CO was 0.497 atm. Calculate: a) b) the number of mol of CO in the equilibrium mixture. the equilibrium constant Kc and Kp.
(0.01135 mol, 4.60 x 103, 0.302)
13.
Consider the reversible system: 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) 2NOCl(g) Predict the direction of equilibrium shift: a) b) if a small amount of Cl2(g) is introduced into the mixture at equilibrium. if the volume of the container is doubled. Predict the effect of decreasing temperature on the equilibrium system: N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) b) H = +66 kJ
14.
a)
N2(g) and O2(g) are both colourless, while NO2(g) is dark brown. Would you expect the colour of the mixture becomes darker or lighter as the temperature is lowered? H = 92.5 kJ
15.
Consider the equilibrium system : PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) PCl5(g) Predict the effect on the equilibrium if: a) b) c) d) the equilibrium system is heated the volume of the container is decreased PCl3 is removed continuously Some argon gas (Ar) is added.
16.
Methane is formed by the reaction: C(s) + 2H2(g) CH4(g). H = 75 kJ Which of the following changes would increase the proportion of methane at equilibrium? a) b) c) d) increase the pressure increase the temperature add a catalyst add more carbon, C(s)
o
17.
For the reaction: 3H2(g) + N2(g) 2NH3(g) , the equilibrium constant Kc = 1.2 at 375 C. A mixture o containing [H2] = 0.76 M, [N2] = 0.60 M, and [NH3] = 0.48 M was heated to 375 C. a) b) What is the Kc value for the reaction: 2NH3(g) 3H2(g) + N2(g) ? Which component gases would show a decrease in concentration at equilibrium? (0.833)
18.
Gas XY is produced by the reaction between gas X 2 and gas Y2 according to the equation: X2(g) + Y2(g) 2XY(g) In one experiment, 1.0 mole each of X2 and Y2 was mixed at 20 atm and 400 C in a container of 1 3 dm . At equilibrium, 0.8 mole of XY was found in the equilibrium mixture. The experiment was o repeated at 800 C at the same pressure, and 0.6 mole of XY was found in the equilibrium mixture. a) b) c) Is the reaction between X2 and Y2 endothermic or exothermic? o What is the value of Kc at 400 C? (Kc = 1.78) o Would you expect the value of Kc at 800 C to be larger or smaller or the same compared to that o at 400 C?
o o
19.
The following equilibrium system is set up in a closed container. The K c value is 46.9 at 400 C. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g) H = 113 kJ
Use the Le Chateliers Principle to decide whether each of the following statements is TRUE or FALSE. a) b) c) d) e) f) 20. When some H2 is injected into the equilibrium mixture, the equilibrium position shifts to the right. o Adjusting the temperature to 100 C will produce more HCl. Doubling the volume of the container will cause a decrease in the concentration of Cl 2. o The value of Kp = Kc at 400 C. Adding a few drops of aqueous NaOH has no effect on the equilibrium system. Adding some argon (Ar) gas will increase the concentrations of Cl2 and H2.
For the reaction: CH4(g) + H2O(g) CO(g) + 3H2(g) , the values of Kc at different temperatures are given below. Kc = 1.78 x 10 Kc = 4.68 x 10
3 2
at 800 C at 1000 C
o o
Kc = 5.67 at 1500 C a) b) 21. At which temperature would you expect the concentrations of products to be the highest? Is the forward reaction endothermic or exothermic? H = 75 kJ
Methane is formed by the reaction: C(s) + 2H2(g) CH4(g). a) b) c) d) removing H2. increasing the pressure increasing the temperature adding more carbon, C(s) C(s) + CO2(g) 2CO(g)
What would be the effect, if any, of each of the following changes on the equilibrium position?
22.
Consider the equilibrium system: At 900 C, Kc is 0.238.
o
H = +172.5 kJ
a) What is the value of Kp? (22.9) b) How will the system respond if additional amount of solid carbon are added? Why? c) What effect dose an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel have on the position of equilibrium? d) What would happen to the value of Kc if the temperature is raised?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chapter 6-Chemical Equilibrium - ItaDocumento10 pagineChapter 6-Chemical Equilibrium - ItaPAKK20622P Syarifah Nor Izzah binti Syed Abd HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibrium Tutorial QuestionDocumento4 pagineChemical Equilibrium Tutorial QuestionHANIS HADIRAH BINTI HASHIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 2018Documento2 pagineWorksheet 2018joanneNessuna valutazione finora
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsDa EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Problem Set On Chemical EquilibriumDocumento1 paginaProblem Set On Chemical EquilibriumIvy CustodioNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM213 TUTORIAL3 - Chemical Equilibrium - Sept 2017Documento5 pagineCHM213 TUTORIAL3 - Chemical Equilibrium - Sept 2017mijaniallNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Equilibrium WorksheetDocumento5 pagineAp Equilibrium Worksheetburcak gecNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 (Question) PDFDocumento2 pagineTutorial 1 (Question) PDFhaziq ajizNessuna valutazione finora
- Subjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticeDocumento21 pagineSubjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticehappyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumDocumento5 pagineTutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Chemistry Questions To Be Covered in Phase 2 (Master Tutors) - 2Documento13 pagine50 Chemistry Questions To Be Covered in Phase 2 (Master Tutors) - 2Chiluba EzronNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical - Equilibrium Examp ExcDocumento7 pagineChemical - Equilibrium Examp Excjuan pabloNessuna valutazione finora
- EquiDocumento12 pagineEquirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14-ChemicalEquilibriumDocumento5 pagineChapter 14-ChemicalEquilibriumKhurram KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14Documento20 pagineChapter 14Angelica UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Test, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFDocumento18 pagineTest, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFTarun Gupta0% (2)
- Chemical Equilibrium and K: Review Worksheet IDocumento2 pagineChemical Equilibrium and K: Review Worksheet ISachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Eq. R C MukarjeeDocumento48 pagineChemical Eq. R C MukarjeevaibhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide EquilibriumDocumento6 pagineStudy Guide Equilibriumnoobiekids2016Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 7 (Equilibrium) - Questions PDFDocumento2 pagineTutorial 7 (Equilibrium) - Questions PDFdinsaqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop Session For Chapter 14-Chemical Equilibria 1 2012 To 2 2012Documento4 pagineWorkshop Session For Chapter 14-Chemical Equilibria 1 2012 To 2 2012AmiwryNessuna valutazione finora
- CEQ Ex EDocumento28 pagineCEQ Ex EChess EnjoyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium Worksheet (TB)Documento1 paginaEquilibrium Worksheet (TB)Rahayu CamscanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 3Documento3 pagineChem 3Lovey ChandiNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM131 HomeworkDocumento1 paginaCHM131 HomeworkEdgar MagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium FR AP Chem ReviewDocumento5 pagineEquilibrium FR AP Chem ReviewAnnie Cai0% (1)
- GENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)Documento25 pagineGENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)ewin TijaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Chemical EquilibriumDocumento20 pagine8 - Chemical EquilibriumAbhimanyu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 1412. Chapter 15. Chemical Equilibrium - Homework - Ky35 PDFDocumento20 pagineCHEM 1412. Chapter 15. Chemical Equilibrium - Homework - Ky35 PDFSamarth KulatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibrium QuestionsDocumento3 pagineChemical Equilibrium QuestionsOwusuasare ChrispakNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium Doc 2Documento5 pagineEquilibrium Doc 2Alex IoannouNessuna valutazione finora
- Day-3 Chemical EquilibriumDocumento6 pagineDay-3 Chemical EquilibriumpriyanshuNessuna valutazione finora
- WORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumDocumento4 pagineWORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumAndrej ZafirovikjNessuna valutazione finora
- (Template) U3A Review QuestionsDocumento3 pagine(Template) U3A Review QuestionsnahvimohaddasehNessuna valutazione finora
- ch16 CompressDocumento2 paginech16 CompressOlsa NdoshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase EquilibriaDocumento6 paginePhase EquilibriaIlwandy KosasihNessuna valutazione finora
- LE2 ProbsetDocumento5 pagineLE2 ProbsetChris Andrew MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Soal Kimia - KesetimbanganDocumento5 pagineBank Soal Kimia - KesetimbanganWelly TansilNessuna valutazione finora
- AP General Equilibrium Free Response QuestionsDocumento5 pagineAP General Equilibrium Free Response QuestionsCynNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium WorksheetDocumento6 pagineEquilibrium WorksheetGiselleNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Questions On Chemical Equilirbium FDocumento8 pagineBest Questions On Chemical Equilirbium Flakshit singhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical EquilibriumDocumento12 pagineChemical EquilibriumAkshith IsolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Psi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Documento30 paginePsi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Tricyver ChienNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Documento4 pagine2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Erika Mae Adoja Espejo100% (1)
- Tutorial 5 Equilibrium AnswerDocumento4 pagineTutorial 5 Equilibrium AnswerNor AishahNessuna valutazione finora
- EqDocumento3 pagineEqrajaijahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial For PPT 8 (3) - TaggedDocumento9 pagineTutorial For PPT 8 (3) - TaggedNg Cheuk HeiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerDocumento6 pagine1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerNur Afiqah Mohd ZakiNessuna valutazione finora
- For The Following Reactions: A) N (G) + 3H (G) 2NH (G) : Example: Write The Appropriate Equilibrium ExpressionDocumento67 pagineFor The Following Reactions: A) N (G) + 3H (G) 2NH (G) : Example: Write The Appropriate Equilibrium ExpressionjillNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Study QuestionsDocumento2 pagineChapter 13 Study QuestionsКанат ТютеновNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice MC With AnswersDocumento13 paginePractice MC With AnswersGavel ZoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Questions Chapter 6: Chemical EquilibriumDocumento3 pagineRevision Questions Chapter 6: Chemical EquilibriumNajiha TahirNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 Practice QuestionsDocumento17 pagineChapter 15 Practice QuestionsKim LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical EquilibriumDocumento5 pagineChemical EquilibriumPriyansh PiyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers For Tuto 3 and 4 (Chem)Documento8 pagineAnswers For Tuto 3 and 4 (Chem)Aina AqilahNessuna valutazione finora
- III Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewDocumento3 pagineIII Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewChinmaya Ranjan BiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17 Thermodynamics KeyDocumento5 pagineChapter 17 Thermodynamics KeyJanzelle BorbonNessuna valutazione finora
- A Kinetic Study of Potassium Iodide With Potassium Persulfate Using Iodine Clock ReactionDocumento8 pagineA Kinetic Study of Potassium Iodide With Potassium Persulfate Using Iodine Clock ReactionRizki SeptiardiNessuna valutazione finora
- BET Surface Are MeasurementsDocumento16 pagineBET Surface Are MeasurementsKwan ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailing For Structure ConcreteDocumento318 pagineDetailing For Structure ConcreteletuananhbNessuna valutazione finora
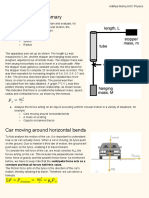
- HSC Physics Circular Motion SummaryDocumento5 pagineHSC Physics Circular Motion SummaryShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chemical Bonding GameDocumento12 pagineThe Chemical Bonding GameZara RejusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Smardt Ac Catalogue TD-0081Documento47 pagineSmardt Ac Catalogue TD-0081DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 5950 - Worked Example 3Documento9 pagineBS 5950 - Worked Example 3mustafurade1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentDocumento6 pagineFoundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentViswanathan NaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Load Calculation: ProjectDocumento16 pagineHeat Load Calculation: ProjectprinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Table 2 Quantity To Be Measured Instrument S.L. UnitDocumento4 pagineTable 2 Quantity To Be Measured Instrument S.L. UnitAdrian RamroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber Communication 10ec72 SolutionDocumento73 pagineOptical Fiber Communication 10ec72 Solutionshashank gupta100% (1)
- Grinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainDocumento8 pagineGrinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainMd MehtabNessuna valutazione finora
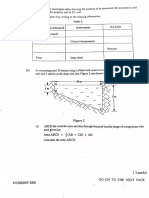
- Finite Element Studies of Ambuklao and Caliraya DamDocumento12 pagineFinite Element Studies of Ambuklao and Caliraya Dammark_zarcoNessuna valutazione finora
- T2 Skript CH 4Documento26 pagineT2 Skript CH 4Muhammad SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer IntroductionDocumento13 pagineHeat Transfer IntroductionKhaled Mosharraf MukutNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of Environmental Chemical EngineeringDocumento48 pagineJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of Environmental Chemical EngineeringAKASHNessuna valutazione finora
- Petrochemical and Refinery Piping General Weld Inspection ReDocumento6 paginePetrochemical and Refinery Piping General Weld Inspection RealiNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic Loading-Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic LoadingDocumento6 pagineComposite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic Loading-Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic LoadingKarrar MonarchNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer SheetDocumento4 pagineAnswer SheetDanny Lanos100% (1)
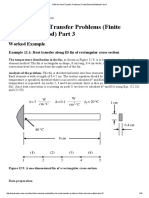
- FEM For Heat Transfer Problems (Finite Element Method) Part 3Documento16 pagineFEM For Heat Transfer Problems (Finite Element Method) Part 3Sibilla UnniNessuna valutazione finora
- Anadolu University: Lecture 3 - Dimensions, Tolerances and Surfaces Spring 2007Documento56 pagineAnadolu University: Lecture 3 - Dimensions, Tolerances and Surfaces Spring 2007hiren_mistry55Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration Testing of Small Satellites: Part 2: Test Configuration, Fixtures, and InstrumentationDocumento12 pagineVibration Testing of Small Satellites: Part 2: Test Configuration, Fixtures, and InstrumentationYoussef wagdyNessuna valutazione finora
- He3492 LS H PDS Reg - Europe en V1 PDS Eur 37603 10049218Documento2 pagineHe3492 LS H PDS Reg - Europe en V1 PDS Eur 37603 10049218Attef BedawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 5 Engine, Drive Train and CompressorDocumento104 pagineTopic 5 Engine, Drive Train and CompressorIvancito HV100% (1)
- Twinning of West Trunk Sewer Contract 2 - Tunnel Association of Canada PresentationDocumento43 pagineTwinning of West Trunk Sewer Contract 2 - Tunnel Association of Canada PresentationAndrew CushingNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of CSDA and Extrapolated Ranges of Electrons in Some Selected Solvents in The Energy Range of 0.01-100 MeVDocumento5 pagineStudy of CSDA and Extrapolated Ranges of Electrons in Some Selected Solvents in The Energy Range of 0.01-100 MeVVagner Ferreira CassolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Properties of Matter Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineThermal Properties of Matter Formula SheetanishkadiyalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bam Workshop EvisiveDocumento47 pagineBam Workshop EvisiveZhen LINessuna valutazione finora
- How To Avoid A Climate DisasterDocumento2 pagineHow To Avoid A Climate DisasterRaghdi HaneneNessuna valutazione finora
- RR Trent 60Documento39 pagineRR Trent 60Ricardo Cabrera Osinaga100% (6)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDa EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDa EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (21)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDa EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNessuna valutazione finora
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDa EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDa EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDa EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- High School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryDa EverandHigh School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDa EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (20)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookDa EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Da EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDa EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)