Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Theory of Machine
Caricato da
Vaibhav Vithoba NaikDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Theory of Machine
Caricato da
Vaibhav Vithoba NaikCopyright:
Theory of machine
Module 1.
Basic Kinematics Kinematics CHAIN and mechanism Inversion of Chain Special Mechanism
T.V.S.
Theory of machine Important Terminologies and Definition 1. Machine It is device which takes in the available energy and converts it into useful work. When the mechanism is required to transmit the power or to do some particular type of work, it then becomes a Machine. Example: Shaper, Lathe machine
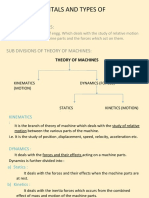
2. Mechanics( Theory of Machine) Branch of engineering which deals with the relative motion and forces between the various machine elements. Kinematics of machine Deals with the relative motion without considering the forces Dynamics of machine Deals with the forces and effect of forces on the machine component when they act on them.
3. Kinetics of machine Deals with the forces, which are formed due to combined action of mass and motion of machine elements.
4. Statics Deals with the forces and its effect on the machine part while the latter is at rest.
5. Resistant body A body is said to be resistant body if it is able to transmit the forces with the least possible deformation. Example: spring, belt oils in hydraulic presses
6. Kinematic Link Links are individual parts of a mechanism. Each parts of a machine which has a relative motion to some other parts is known as Kinematic link.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine 7. Kinematic Chain When the kinematic pairs are coupled in such a way that the last linked is joined the first link to transmit the definite motion it is called a kinematic chain. 8. Kinematic Pair The two links of the machine when in contact with each other are said to form a pair if the relative motion between them is successfully constrained. 9. Inversion The method of obtaining the different mechanism by fixing the different links in a kinematic chain is known as inversion of the mechanism. 10. Structure It is the assemblage of a number of resistant bodies having no relative motion between then and meant for carrying loads having a straining action. Example: a railway bridge.
11. Mechanism When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, the chain is known as mechanism. It may be used for transmitting or transforming motion. Example: Engine indicator, Typewriter.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine Differentiate between Machine and Structure.
Sr no 1 2
Machine Has relative motion between the members Transforms available energy into possible work. Members are meant to transmit motion and forces. Example Shaper,lathe
Structure Has no relative motion Does not transform.
Members are meant to accept load Example :Bridge.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
TYPE OF CONSTARINED MOTIONS. 1. Completely constrained motion. 2. Incompletely constrained motion. 3. Successfully constrained motion. 1. Completely constrained motion. When the motion between a pair is limited to definite direction irrespective of the direction of force applied, then the motion is said to be a completely constrained motion. Example: The motion of the square bar in square hole. The motion of shaft with collars at each end in a circular hole.
2. Incompletely constrained motion. When the motion between a pair can take place in more than one direction, then the motion is said to be a completely constrained motion. Example: The motion of the circular bar in circular hole.
3. Successfully constrained motion. When the relative motion between the link is not completely constrained by itself but it is made by some other means is called successfully constrained motion. Example: Shaft in Footstep Bearing The motion IC engine valve and piston in reciprocating inside an engine cylinder.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
Kinematic Link 1) Links are individual parts of a mechanism. 2) Each parts of a machine which has a relative motion to some other parts is known as Kinematic link. Character tics of Kinematic link 1. Should have relative motion. 2. Must be a resistant body.
Classification of the LINK 1. Depending upon the nature of the resistant bodies a) Rigid link. b) Flexible link. c) Fluid link. 2. Depending upon the points at which the link is attached to mechanism a) Binary link b) Ternary link c) Quaternary link
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
Depending upon the nature of the resistant bodies 1. Rigid link The links which do not undergo appreciable transformation while transmitting the required motion and forces is known as rigid link. Example: Piston ,Connecting Rod of Steam engine. 2. Flexible Link The links which are partly deformed transformation while transmitting the required motion and forces in such a way that they don effect the required transmission of motion is known as Flexible link Example: Chain, Belt and Spring 3. Fluid Link The link which transmit the motion by fluid pressure as compression are called fluid link. Example: Liquid used in Hydraulic presses
Depending upon the points at which the link is attached to mechanism 1. Binary link The link which is attached to two points in the mechanism is called Binary Link. 2. Ternary link The link which is attached to three points in the mechanism is called Ternary Link. 3. Quaternary link The link which is attached to four points in the mechanism is called Quaternary Link.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine 2. Kinematic Pair The two links of the machine when in contact with each other are said to form a pair if the relative motion between them is successfully constrained. Classification of kinematic pair I. According to the relative motion between them II. Sliding pair. Turning pair. Rolling pair. Screw pair. Spherical pair.
According to Nature of the contact Lower pair. Higher pair.
III.
According to type of closure Self closed pair. Force closed pair.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine According to the relative motion between them 1. Sliding pair. A sliding pair is said to be formed by two links such a manner that one link is constrained to have a sliding motion relative to other link. Example: Piston and Cylinder, Cross head and guides of Steam engine.
2. Turning pair A turning pair is said to be formed by two links such a manner that one link is constrained to turn or revolve relative to other link. Example: Shaft with collar in circular hole. 3. Rolling pair. A Rolling pair is said to be formed by two links such a manner that one link is constrained to have a rolling motion over the other link. Example: Ball bearing forms Rolling pair. 4. Screw pair. When the two elements of pairs are connected in such a way that one element can turn about the other by means of screw threads is known as Screw Pair. Example: Bolt and nut is example of Screw Pair. 5. Spherical pair. When the two elements of pairs are connected in such a way that one element turn or swivels about the other fixed element, the pair formed is known as Screw Pair. Example: Ball and socket is example of Spherical Pair.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
According to Nature of the contact 1. Lower pair. When the two element of a pair have a surface contact when the relative motion takes place and the surface of one element slides over the other, the pair forced is known as lower pair. Example: The motion of piston and cylinder in the engine.
2. Higher pair. When the two element of a pair have a line or point contact when the relative motion takes place and the motion between the two element is partially turning and partly sliding then the pair formed is know as Higher pair. Example: The motion of cam and follower
T.V.S.
Theory of machine Kinematic pairs according to nature of mechanical constraint a. Self Closed pair When the elements of a pair are held together mechanically in such a way that only the required kind of relative motion occurs , all the lower pairs and some of the higher pairs are closed pairs. Example: The lower pair is known as closed pair. b. Force Closed pair or Unclosed pair When two links of a pair are not connected mechanically but kept in contact either due to force of gravity or some spring action, they constitute an unclosed pairs. Example: The motion of cam and follower
T.V.S.
Theory of machine 3. MECHANISM When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, the chain is known as mechanism. It may be used for transmitting or transforming motion. Example: Engine indicator, Typewriter. Types of Mechanism i. Simple mechanism (a mechanism with four links) ii. Compound mechanism (a mechanism with more than four link)
Differentiate between Machine and Mechanism
Sr no 1.
Machine It is like the human body, it transforms energy into useful work. It relates to energy only. It has many link. Ex: lathe, shaper.
Mechanism It is like a frame work and has a definite motion between various links. It relates to motion. It also has many links. Ex. watt indicator,typwriter
2 3 4 5
T.V.S.
Theory of machine Grashof's Law The sum of the length of shortest and longest link must be equal or less than the sum of the length of the other two link length, if there is to be a continuous relative motion between the two links. In a four-bar linkage, we refer to the line segment between hinges on a given link as a bar where: s = length of shortest bar l = length of longest bar p, q = lengths of intermediate bar
Grashof's theorem states that a four-bar mechanism has at least one revolving link if s + l <= p + q (1) and all three mobile links will rock if
s+l>p+q (2) The inequality (1) is Grashof's criteria The Link opposite to the frame is called Coupler Link and the link which are hinged to the frame are called side link. The link which is free to rotate through 3600 with respect to second link will be said to revolve relative to the second link (not necessarily a frame). If it is possible for all four bar to become simultaneously aligned, such a state is called change point. Case 1 2 3 4 5 Criterion s+l < p+q s+l < p+q s+l < p+q s+l = p+q s+l < p+q Shortest link frame slide coupler any any Category double crank crank rocker double rocker change point triple rocker
T.V.S.
Theory of machine From the table we can see that for a mechanism to have a crank, the sum of the length of shortest and longest link must be equal or less than the sum of the length of the other two link. However this condition is necessary but not sufficient. Mechanism satisfying this condition falls into following three categories. 1) When the shortest link is the side link, the mechanism is crank rocker mechanism. The shortest link is the CRANK in the mechanism. 2) When the shortest link is the Frame, the mechanism is double crank mechanism. 3) When the shortest link is the coupler link, the mechanism is Double rocker mechanism.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
Types of Kinematic chain 1. Four bar chain 2. Single slider crank chain. 3. Double slider crank chain Inversion of the following types 1. Four bar chain a) Beam engine. b) Coupling rod of Locomotives. c) Watts indicator mechanism. d) Pantograph. 2. Single slider crank chain. a) Pendulum pump or Bull engine. b) Oscillating cylinder engine. c) Rotary IC engine. d) Crank and slotted lever quick return mechanism. e) With worth quick return mechanism. 3. Double slider crank chain. a) Elliptical trammel b) Scotch yoke mechanism. c) Oldhams coupling.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine Kinematic inversion of the mechanism The method of obtaining the different mechanism by fixing the different links in a kinematic chain is known as inversion of the mechanism. Inversion of Four bar chain A four bar consist of four turning pair. It is the basic chain and is shown in the figure.
1. BEAM ENGINE
1. Beam engine is also called as Crank and lever mechanism. It consist of four link 2. In this mechanism, when the crank rotated about the fixed centre A, the lever oscillates about the fixed center D. 3. The end E of the lever CDE is connected to piston rod which reciprocates due to the rotation of the crank. 4. Purpose: Convert rotary motion into reciprocating motion.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
2. Coupling rod of locomotive
1. The coupling rod of the locomotive consists of four links as shown in figure. 2. In this mechanism, the link AB and BC act as crank and are connected to the respective wheel. 3. The link CD act as a coupling rod and the link AB is fixed in order to maintain a constrain motion between them. 4. Purpose: meant for transmitting rotary motion from one wheel to another wheel.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine 3. Watts indicator mechanism A watt indicator mechanism has a four link as shown in figure.
1) The four links are fixed link at A, link AC, link CE, and link BFD. 2) It may be noted that BF and FD forms one link because two parts have no relative motion between them. 3) The link CE and BFD act as lever.
4) The displacement of link BFD is directly proportional to the pressure of gas or steam which acts on the indicator plunger. 5) On any small displacement of the mechanism, the tracing point E at the end of the link CE traces out approximately straight line. 6) The initial position of the mechanism is shown in full line whereas the dotted lines shows the position of mechanism when the gas or steam pressure acts on the indicator plunger.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
4. Pantograph A pantograph is an instrument used to reproduce an enlarged or reduce scale and as exactly as possible the path described by a given point.
1. It is a based on four based kinematic chain. 2. It consists of jointed parallelogram ABCD. 3. It is made up of bar connected by turning pair. It has a four turning pair.
4. Link BA and BC are extended to O and E respectively such that OA/OE = AD/BE. 5. For all relative position of bars the triangle OAD and OBE are similar and the point O,D,E are in straight line. 6. The point E describes the same path as described by point D.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
Slider crank chain: This is a kinematic chain having four links. It has one sliding pair and three turning pairs. Link 2 has rotary motion and is called crank. Link 3 has got combined rotary and reciprocating motion and is called connecting rod. Link 4 has reciprocating motion and is called slider. Link 1 is frame (fixed). This mechanism is used to convert rotary motion to reciprocating and vice versa. Double slider crank chain: It is a kinematic chain consisting of two turning pairs and two sliding pairs. Scotch Yoke mechanism. Turning pairs 1&2, 2&3; Sliding pairs 3&4, 4&1. Inversions of double slider crank mechanism: Elliptical trammel. This is a device which is used for generating an elliptical profile. Oldham coupling. This is an inversion of double slider crank mechanism, which is used to connect two parallel shafts, whose axes are offset by a small amount. 5.
T.V.S.
Theory of machine
T.V.S.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1-Basic ConceptsDocumento47 pagine1-Basic Conceptsjaved hussainNessuna valutazione finora
- 50998335YG1M - Design of Machine Elements - II - Solution ManualDocumento80 pagine50998335YG1M - Design of Machine Elements - II - Solution ManualKetan V. JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kom Lecture NotesDocumento134 pagineKom Lecture Noteslakshmigsr6610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simplemechanism 180302020307Documento58 pagineSimplemechanism 180302020307Kunal GadgilNessuna valutazione finora
- C6 6Documento34 pagineC6 6alejandro sanchez100% (1)
- 3.05B - Mock Drill Report - DISH 10.03.14Documento4 pagine3.05B - Mock Drill Report - DISH 10.03.14Vaibhav Vithoba Naik88% (8)
- Safety in Working at HeightDocumento106 pagineSafety in Working at HeightVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (12)
- 19 UlabourlawshbDocumento197 pagine19 UlabourlawshbSaipramod JayanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Machine Unit 1Documento122 pagineTheory of Machine Unit 1Deepak PrajapatNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFDocumento40 pagineUNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFAravind MuddebihalNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrail Safety Question and AnswerDocumento20 pagineIndustrail Safety Question and AnswerVaibhav Vithoba Naik89% (19)
- Ducts Pressure Losses Board: Carpark Souq Waqif Ahu - A Basement-1Documento2 pagineDucts Pressure Losses Board: Carpark Souq Waqif Ahu - A Basement-1Karthy GanesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration in Pumps PDFDocumento5 pagineVibration in Pumps PDFonspsnonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nandipur 425MW CCPP Gas Turbine Operation ManualDocumento268 pagineNandipur 425MW CCPP Gas Turbine Operation ManualMuhammad Awais100% (6)
- XT Mojo Owner - S ManualDocumento121 pagineXT Mojo Owner - S ManualthisisganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- P 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Documento35 pagineP 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (9)
- Mechanics of Machines II ExamsDocumento2 pagineMechanics of Machines II ExamsCharles OndiekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersDocumento6 pagineMechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersSaravanan MathiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.05A - Onsite Emergency Plan - Rev 10 - 2013Documento47 pagine3.05A - Onsite Emergency Plan - Rev 10 - 2013Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics of Machinery Lecturer Notes All 5 UnitsDocumento45 pagineKinematics of Machinery Lecturer Notes All 5 Unitskumaravel07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kom Unit 2Documento24 pagineKom Unit 2Muthuvel M100% (3)
- SY215C 9 Excavator PDF Valve Throttle (Revisi) PDFDocumento93 pagineSY215C 9 Excavator PDF Valve Throttle (Revisi) PDFSohibul AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Sets For MECHANICS OF MACHINESDocumento11 pagineProblem Sets For MECHANICS OF MACHINESzxzxzx207Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Machinery: Chapter 1 Introduction SummaryDocumento9 pagineDesign of Machinery: Chapter 1 Introduction SummaryJulianSamayoa100% (2)
- Mechanics of Machines PDFDocumento7 pagineMechanics of Machines PDFChamala Daksheeswara Reddy100% (1)
- Fluid MachinesDocumento161 pagineFluid MachinesHaroon GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 and 3 Mechanics of MachinesDocumento21 pagineUnit 2 and 3 Mechanics of MachinesYogaraja JeyarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocumento13 pagineDynamics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M58% (12)
- TOMDocumento21 pagineTOMHarikrishna ShenoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 6603 - Finite Element Analysis: Part A Questions With Answers Unit 1Documento14 pagineMe 6603 - Finite Element Analysis: Part A Questions With Answers Unit 1Karthik SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- KOM Important QuestionsDocumento12 pagineKOM Important QuestionsJithin KNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocumento18 pagineKinematics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M94% (16)
- Theory of MachinesDocumento6 pagineTheory of MachinesYogesh DandekarNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Internal Expanding BrakeDocumento26 pagine02 Internal Expanding Brakeahmed albeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Som Part B CDocumento16 pagineSom Part B CSrini VasanNessuna valutazione finora
- DYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS FullDocumento4 pagineDYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS FullSudipta NathNessuna valutazione finora
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of MechanismsDocumento30 pagineSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of MechanismsVijayan GopalsamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Machines Flywheel)Documento22 pagineTheory of Machines Flywheel)Rajesh VenkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam1 PracticeDocumento9 pagineExam1 PracticeashwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- KDM 6Documento54 pagineKDM 6KarthikeyanRamanujamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tom-I Question Bank UpdatedDocumento174 pagineTom-I Question Bank Updatedkiran_wakchaureNessuna valutazione finora
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 MarksDocumento20 pagine081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 Markssara vanaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsDocumento18 pagineME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsshivendrakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MvneDocumento125 pagineMvnesunilNessuna valutazione finora
- ChapterDocumento47 pagineChapterIsmail ibrahim100% (2)
- Tribology Question PapersDocumento6 pagineTribology Question PapersAvinashKshirsagarNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Question Bank Fo RMV Unit V Continuous Systems 06 05 2018 Additional PDFDocumento4 pagine05 Question Bank Fo RMV Unit V Continuous Systems 06 05 2018 Additional PDFNABIL HUSSAIN0% (1)
- Unit Ii PDFDocumento17 pagineUnit Ii PDFManojKumar MNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Mechanism and KinematicsDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Mechanism and Kinematicsfieramina83% (6)
- Vibration 2 Marks For All Intrance ExamDocumento11 pagineVibration 2 Marks For All Intrance ExamSeeandgrow ByabdulsamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid-Mechanics-Ace Text Book SolutionDocumento45 pagineFluid-Mechanics-Ace Text Book SolutionShazeb LaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Machines - Lab ManualDocumento28 pagineTheory of Machines - Lab ManualHoneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Balancing of Rotating Masses NM RepairedDocumento25 pagineModule 5 Balancing of Rotating Masses NM RepairedRuchindra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics Kinematics Machines Manual Solution PDFDocumento2 pagineDynamics Kinematics Machines Manual Solution PDFFerney Alexis33% (3)
- Solutions Manual Theory of Machine and MDocumento8 pagineSolutions Manual Theory of Machine and MAhmet Yüksel ToprakNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento13 pagineQuestion BankMohanraj SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II Curves & SurfacesDocumento57 pagineUnit II Curves & Surfacesvishwajeet patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Columns and Struts Unit-15Documento25 pagineColumns and Struts Unit-15Andree GeorgeaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME424 201516 Unit4 PDFDocumento56 pagineME424 201516 Unit4 PDFharshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocumento18 pagineDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Chapter 3-BreakDocumento37 pagineChapter 3-Breakkibromgidey12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics of Machines PDFDocumento133 pagineKinematics of Machines PDFarjunNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Theory of Machine R S Khurmi Solution 2 DLDocumento2 paginePDF Theory of Machine R S Khurmi Solution 2 DLNewy Newton0% (1)
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - P. MurugaperumalDocumento224 pagineGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - P. MurugaperumalVickraman S100% (1)
- Computer Aided Machine DrawingDocumento16 pagineComputer Aided Machine DrawingAmit Bhagure0% (1)
- Important QuestionsDocumento8 pagineImportant QuestionsdineshbabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsDa EverandDifferential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple MechanismDocumento48 pagineSimple MechanismMudit MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- BiomaterialsDocumento39 pagineBiomaterialsNehanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento44 pagineUnit 1Prabal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Aim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryDocumento6 pagineAim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryAvinash RNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.04.2019 Fire Traingle and Its Importance.Documento1 pagina16.04.2019 Fire Traingle and Its Importance.Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- 22.04.2019 - Confined Space A Dangerous SpaceDocumento1 pagina22.04.2019 - Confined Space A Dangerous SpaceVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Safeguard of W Omen and C Hildren Provisions in Standard Bidding DocumentDocumento23 pagineSafeguard of W Omen and C Hildren Provisions in Standard Bidding DocumentVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 18.04.2019 Type of Fire ExtinguisherDocumento1 pagina18.04.2019 Type of Fire ExtinguisherVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (2)
- DO's and DON'Ts Working in Confined SpaceDocumento1 paginaDO's and DON'Ts Working in Confined SpaceVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (3)
- Safety 3Documento57 pagineSafety 3Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento54 pagine1Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- The SKF Code of Conduct PDFDocumento9 pagineThe SKF Code of Conduct PDFVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento54 pagine1Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview: Safety Officers & SupervisorsDocumento25 pagineInterview: Safety Officers & SupervisorsVaibhav Vithoba Naik0% (1)
- 2Documento43 pagine2Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety While Working On PipelinesDocumento6 pagineSafety While Working On PipelinesVaibhav Vithoba Naik0% (1)
- Safety 4Documento59 pagineSafety 4Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Straight Line Motion Mechanisms OldDocumento28 pagineStraight Line Motion Mechanisms OldVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (4)
- 2Documento43 pagine2Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.6 Non Sparking ToolsDocumento5 pagine5.6 Non Sparking ToolsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Safety Health Envt. ManagementDocumento20 pagine3 Safety Health Envt. ManagementVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals and Types of MechanismDocumento60 pagineFundamentals and Types of MechanismVaibhav Vithoba Naik88% (8)
- Steering System (Notes On Tom)Documento8 pagineSteering System (Notes On Tom)Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocumento21 pagineSecond Law of ThermodynamicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 .Basic KinematicsDocumento24 pagineModule 1 .Basic KinematicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 .Basic KinematicsDocumento24 pagineModule 1 .Basic KinematicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Lathe MachineDocumento34 pagineLathe MachineVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- Mechanical Project TurbochargerDocumento12 pagineMechanical Project Turbochargerinduscad100% (6)
- Kranzle Profijet Catalog-2019 - EN - 16220Documento1 paginaKranzle Profijet Catalog-2019 - EN - 16220Music NetNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Gear Inspection & MaintenanceDocumento11 pagineLifting Gear Inspection & MaintenanceNhien ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Karburator Sepeda MotorDocumento26 pagineKarburator Sepeda MotorIpunxzz PoenyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Cbaa CBBB Cbab Cbba CBDB CBDC Cbac Cbda Cjaa Repair Manual EngDocumento393 pagineEngine Cbaa CBBB Cbab Cbba CBDB CBDC Cbac Cbda Cjaa Repair Manual EnglaurentiupauNessuna valutazione finora
- Conveyor Belt Using Geneva Mechanism: Presented by Bishnu Jasleen Kaur Pranshu Tiwari Amit Kumar RaiDocumento11 pagineConveyor Belt Using Geneva Mechanism: Presented by Bishnu Jasleen Kaur Pranshu Tiwari Amit Kumar RaibishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Brayton Cycle With RegenerationDocumento6 pagineBrayton Cycle With RegenerationMeshal Al-mutairi100% (1)
- Irjet V3i4662 PDFDocumento12 pagineIrjet V3i4662 PDFJeevan Landge Patil100% (1)
- Actuated Ball Valve 357 D - BDKDocumento4 pagineActuated Ball Valve 357 D - BDKfarhanakhtar ansariNessuna valutazione finora
- Frame and Covers 17887-2 Atlas Copco Construction Tools ABDocumento52 pagineFrame and Covers 17887-2 Atlas Copco Construction Tools ABВадим БалабанNessuna valutazione finora
- Reliance Sugar Balancing 24-01-2021Documento7 pagineReliance Sugar Balancing 24-01-2021Engineer Reliance Sugar Pvt. Ltd.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix G-List of Equipment Code and Provisional Requirement of RFID Tags and QR CodesDocumento6 pagineAppendix G-List of Equipment Code and Provisional Requirement of RFID Tags and QR CodesCALVIN CHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Simulation of Gearless Transmission Mechanism1Documento8 pagineAnalysis and Simulation of Gearless Transmission Mechanism1ganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceiling Cassette Type Air Conditioners Installation InstructionsDocumento20 pagineCeiling Cassette Type Air Conditioners Installation InstructionsPham GiapNessuna valutazione finora
- Huafengdongli 495 4100 Series OperationmanualDocumento7 pagineHuafengdongli 495 4100 Series Operationmanualdaryl100% (27)
- Keyway and Effect of KeywayDocumento3 pagineKeyway and Effect of KeywayHardik ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Versa-Matic Pump Company: Pump Model Model E4 Elima-Matic Bolted SeriesDocumento2 pagineVersa-Matic Pump Company: Pump Model Model E4 Elima-Matic Bolted SeriesdeepaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sil16 2Documento4 pagineSil16 2Conrado Pinho JuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- 1465304832-Eurolab EngDocumento22 pagine1465304832-Eurolab EngicaanmpzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat Long Term StorageDocumento2 pagineCat Long Term Storagesimon60sNessuna valutazione finora
- Bought Out Test Certificates & Installation / Mainteinance Manual ListDocumento3 pagineBought Out Test Certificates & Installation / Mainteinance Manual ListMohamed Sayed AbdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Remote Engine StarterDocumento12 pagineRemote Engine StarterRELOJERIANessuna valutazione finora
- 2-1 Structure and FunctionDocumento107 pagine2-1 Structure and FunctionElectromecanica Leon Electromecanica Leon Leon100% (1)
- Purepower Pw1000G Engine: This Changes Everything™Documento2 paginePurepower Pw1000G Engine: This Changes Everything™milton garciaNessuna valutazione finora