Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Matlab Code For Advanced DSP
Caricato da
Udoy PaulTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Matlab Code For Advanced DSP
Caricato da
Udoy PaulCopyright:
Formati disponibili
% Downloadable MATLAB code, copyright Amritanshu Palaria % H2 ground state from a non-relativistic Hartree Fock treatment using STO-4G
basis set and Born Oppenheimer approximation % Program written by Amritanshu Palaria @ NCN, Apr 12, 2006 % For theoretical reference, please see "Computational Physics" by Thijssen clear all; % initialization Z=1,S=1,A=0,F=0,V=0,D=0,g=0,Vecp=0,Vec=0,Val=0,EVal=0; for y=1:41 clear T,S,A,F,V,D,g,Vecp,Vec,Val,EVal; % y = 11; disp('Step '); disp(y); r = 0.45+0.05*y; % distance between nucleii in a.u.(units of a0, ie. Bohr radius)... since the problem is essentially 1-D, this is all that is needed disp('H-H bondlength'); disp(r); NNr=1/r; % alphas for the 4 Gaussian basis functions for each H atom alpha1 = [13.00773 1.962079 0.444529 0.1219492]; alpha = [alpha1 alpha1]; asize=size(alpha); % one H nucleus at origin, the other at r ra=[0 0 0 0 r r r r]; % the location of the atom with the ith basisfunction % first 4 basis fns come from the atom at origin % the next 4 come from the one at r % the S (overlap), T (K.E.) and A (Coulomb) matrices for i=1:8 % run over all basis functions for j=1:i % do not run over all basis functions to exploit symmetry % intermediate variables as = alpha(i)+alpha(j); ap = alpha(i)*alpha(j); rat=ap/as; % location of the gaussian resulting from product of % the 2 gaussian basis functions rp=(alpha(i)*ra(i)+alpha(j)*ra(j))/as; S(i,j)=(pi/as)^1.5*exp(-rat*(ra(i)-ra(j))^2); S(j,i)=S(i,j); % using symmetry T(i,j)=0.5*rat*(6-4*rat*(ra(i)-ra(j))^2)*S(i,j); T(j,i)=T(i,j); % using symmetry if (rp==0) F0=1+sqrt(pi)/2*erf(sqrt(as*(rp-r)^2))/sqrt(as*(rp-r)^2); elseif (rp==r) F0=sqrt(pi)/2*erf(sqrt(as*(rp-0)^2))/sqrt(as*(rp-0)^2)+1; else F0=sqrt(pi)/2*(erf(sqrt(as*(rp-0)^2))/sqrt(as*(rp-0)^2)+erf(sqrt(as*(rpr)^2))/sqrt(as*(rp-r)^2)); end A(i,j)=-2*pi*Z/as*exp(-rat*(ra(i)-ra(j))^2)*F0; A(j,i)=A(i,j); % using symmetry end end S T A [V,D]=eig(S); % gives eigenvectors in columns of V, this diagnolizes S for i=1:asize(2) V(:,i)=V(:,i)/(D(i,i)^0.5); end % the two-electron integrals P taking care of all symmetries % it is noted that the gaussian functions evaluate to REAL values % and the g operator is real and symmetric w.r.t. 1 and 2 for i=1:8 for j=1:i % do not run over all basis functions to exploit symmetry as1=alpha(i)+alpha(j); ap1=alpha(i)*alpha(j); rp=(alpha(i)*ra(i)+alpha(j)*ra(j))/as1; for k=1:i-1 % do not run over all basis functions to exploit symmetry for l=1:k % do not run over all basis functions to exploit symmetry as2=alpha(k)+alpha(l); ap2=alpha(k)*alpha(l); rq=(alpha(k)*ra(k)+alpha(l)*ra(l))/as2; if ((rp-rq)==0) F0=1; else F0=sqrt(pi)/2*erf(sqrt(as1*as2*(rp-rq)^2/(as1+as2)))/sqrt(as1*as2*(rprq)^2/(as1+as2)); end g(i,j,k,l)=2*pi^2.5/as1/as2/(as1+as2)^0.5*exp(-ap1*(ra(i)-ra(j))^2/as1ap2*(ra(k)-ra(l))^2/as2)*F0; g(k,l,i,j)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(j,i,k,l)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry
http://nanohub.org/resources/1719/download/h-h_gnd_state_hf.m[11/30/2012 9:23:18 PM]
g(i,j,l,k)=g(i,j,k,l); g(j,i,l,k)=g(i,j,k,l); g(k,l,j,i)=g(i,j,k,l); g(l,k,i,j)=g(i,j,k,l); g(l,k,j,i)=g(i,j,k,l);
% % % % %
using using using using using
symmetry symmetry symmetry symmetry symmetry
end k=i; for l=1:j as2=alpha(k)+alpha(l); ap2=alpha(k)*alpha(l); rq=(alpha(k)*ra(k)+alpha(l)*ra(l))/as2; if ((rp-rq)==0) F0=1; else F0=sqrt(pi)/2*erf(sqrt(as1*as2*(rp-rq)^2/(as1+as2)))/sqrt(as1*as2*(rprq)^2/(as1+as2)); end g(i,j,k,l)=2*pi^2.5/as1/as2/(as1+as2)^0.5*exp(-ap1*(ra(i)-ra(j))^2/as1ap2*(ra(k)-ra(l))^2/as2)*F0; g(k,l,i,j)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(j,i,k,l)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(i,j,l,k)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(j,i,l,k)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(k,l,j,i)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(l,k,i,j)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry g(l,k,j,i)=g(i,j,k,l); % using symmetry end end end end % Self-consistent loop C=ones(1,asize(2)); %initial guess nor=C*S*C' disp('Initial Guess'); C=C/nor Elast=1; EVal=0; P=C'*C; count=0; rplot=-2:0.01:3; % range in atomic units (bohr) for plotting the probability density % figure(); % Generating Fock matrix while((abs(EVal(1)-Elast))>0.000001) count=count+1; disp('Step #'); disp(count); Elast=EVal(1) for i=1:8 for j=1:8 J=0; for k=1:8 for l=1:8 J=J+P(k,l)*g(i,j,k,l); end end F(i,j)=T(i,j)+A(i,j)+J; end end % solve the generalized eigenvalue problem FC=ESC % inverse of V is its conjugate transpose because V is unitary Fp=V'*F*V; % modified Fock matrix [Vecp,Val]=eig(Fp); Vec=V*Vecp; EigVal=diag(Val,0) [EVal,index]=sort(EigVal); disp('Ground State eigenvalue from this step is (in a.u., i.e. Hartree):'); Erec(count)=EVal(1) % lowest eigenvalue GrCoeff=Vec(:,index(1)); % eigenvector corresponding to ground state disp('C matrix from this step is:'); C=GrCoeff.' %new C matrix, this is normalized w.r.t. S ie. C*S*C'=1 disp('Input density matrix for next step is:'); P=0.8*P+0.2*C'*C %new input density matrix GndWvFn=C(1:4)*exp(-(alpha(1:4)).'*(rplot.*rplot))+C(5:8)*exp(-(alpha(5:8)).'*((rplotr).*(rplot-r))); % ground state wavefunction from STO-4G approximation % Uncomment the next 4 lines if you need a plot of probability with step of convergence % hold on; % plot(rplot,(abs(GndWvFn)).^2,'r--','LineWidth',1.5); % xlabel('r position'); % ylabel('Probability density'); % title('Plot of the probability density vs. r position with step of convergence');
http://nanohub.org/resources/1719/download/h-h_gnd_state_hf.m[11/30/2012 9:23:18 PM]
end Qs=0; for i=1:8 for j=1:8 for k=1:8 for l=1:8 Qs=Qs+g(i,j,k,l)*C(i)*C(j)*C(k)*C(l); end end end end disp('The final total energy (including nuclear-nuclear repulsion) after convergence for this H-H bond is '); Eg(y)=2*C*(T+A)*C'+Qs+NNr; % the energy from h for each e, the e-e interaction and the nucleus-nucleus interaction added disp(Eg(y)); if Eg(y)==min(Eg) rmin = r; Erecmin = Erec; WvFnmin = GndWvFn; end end figure(); plot([0.5:0.05:2.5],Eg,'bo','LineWidth',2); title('Plot showing total energy from Hartree Fock treatment of H-H using Born Oppenheimer approximation'); xlabel('H-H bondlength'); ylabel('Total energy (in a.u.)'); disp('The least energy bond length (A) for H-H is '); disp(rmin*0.529177); disp('The energy (Hartree) of this bond is '); disp(min(Eg)); figure(); plot(Erecmin,'ro','LineWidth',2); axis([1 count min(Erecmin) max(Erecmin)+0.1]); title('Plot showing convergence of Fock level with every step for the least energy H-H bondlength '); xlabel('Step of convergence'); ylabel('Fock energy level (in a.u.)'); %plot of final probabiliy density figure(); plot(rplot,(abs(WvFnmin)).^2,'LineWidth',2.5); xlabel('r position'); ylabel('Probability density'); title('Plot of the probability density of electrons vs. r position for the least energy H-H bond'); axis tight;
http://nanohub.org/resources/1719/download/h-h_gnd_state_hf.m[11/30/2012 9:23:18 PM]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- KT - Specs High Power Busbar Trunking Metal Enclosure 800 To 5000A Al V20180607Documento5 pagineKT - Specs High Power Busbar Trunking Metal Enclosure 800 To 5000A Al V20180607Udoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Group DetailsDocumento1 paginaGroup DetailsUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Analysis of Negotiable Instruments ActDocumento32 pagineCritical Analysis of Negotiable Instruments ActUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics1stPaper EditionDocumento2 paginePhysics1stPaper EditionUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- ASDF A New Data Format For AstronomyDocumento12 pagineASDF A New Data Format For AstronomyUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 07Documento4 pagineLecture 07Rizwan MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- References: ND NDDocumento3 pagineReferences: ND NDUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Projected Revenue: Red30 - Revenues 2019 (In Millions USD)Documento1 paginaProjected Revenue: Red30 - Revenues 2019 (In Millions USD)Udoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- All Figures For SlidesDocumento7 pagineAll Figures For SlidesUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 TheoryDocumento8 pagineCH 2 TheoryUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- UCDocumento1 paginaUCUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- The Standard Lorem Ipsum Passage, Used Since The 1500sDocumento2 pagineThe Standard Lorem Ipsum Passage, Used Since The 1500sUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
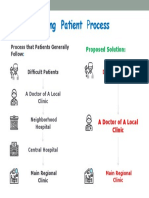
- Local clinic to regional help for patients in needDocumento1 paginaLocal clinic to regional help for patients in needUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- ComputerDocumento2 pagineComputerUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Joining Letter BranchDocumento3 pagineJoining Letter BranchUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Anaesthetic Check-UpDocumento4 paginePre Anaesthetic Check-UpUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated ResumeDocumento6 pagineUpdated ResumeUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire On Inland Transport Co EmissionsDocumento3 pagineQuestionnaire On Inland Transport Co EmissionsUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.5 Heros Journey PDFDocumento1 pagina1.5 Heros Journey PDFUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
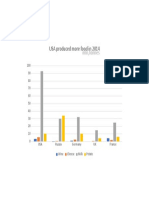
- USA Produced More Food in 2014: MLN, TonnesDocumento1 paginaUSA Produced More Food in 2014: MLN, TonnesUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- NFPA 70 E Training Manual-Training PDFDocumento77 pagineNFPA 70 E Training Manual-Training PDFUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Patient Process at Local ClinicsDocumento1 paginaImproving Patient Process at Local ClinicsUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Nec Code Rules and Design PracticeDocumento13 pagineBasic Nec Code Rules and Design PracticeSiswoyo Suwidji100% (1)
- Research ProposalDocumento12 pagineResearch ProposalUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- 501 Word Analogy QuestionsDocumento120 pagine501 Word Analogy Questionsapi-3740182100% (27)
- You Can Download Professional Powerpoint Diagrams For FreeDocumento2 pagineYou Can Download Professional Powerpoint Diagrams For FreeUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Should Be Improved: Local Clinic Neighborhood Hospital Central Hospital Main Regional ClinicDocumento1 paginaProcess Should Be Improved: Local Clinic Neighborhood Hospital Central Hospital Main Regional ClinicUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Safety & PreventionDocumento13 pagineFire Safety & PreventionUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnesium As A Biodegradable and Bioabsorbable Material For Medical ImplantsDocumento4 pagineMagnesium As A Biodegradable and Bioabsorbable Material For Medical ImplantsUdoy PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Circuit CalculationDocumento46 pagineShort Circuit Calculationratnesh_xp1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Application of ISO/IEC 17020:2012 For The Accreditation of Inspection BodiesDocumento14 pagineApplication of ISO/IEC 17020:2012 For The Accreditation of Inspection BodiesWilson VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento34 pagineIntroductionmarranNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacologyAnesthesiology RevalidaDocumento166 paginePharmacologyAnesthesiology RevalidaKENT DANIEL SEGUBIENSE100% (1)
- Distinguish Between Tax and FeeDocumento2 pagineDistinguish Between Tax and FeeRishi Agarwal100% (1)
- Colour Ring Labels for Wireless BTS IdentificationDocumento3 pagineColour Ring Labels for Wireless BTS Identificationehab-engNessuna valutazione finora
- Ramdump Memshare GPS 2019-04-01 09-39-17 PropsDocumento11 pagineRamdump Memshare GPS 2019-04-01 09-39-17 PropsArdillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Documento16 pagineCourse: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Amyna Rafy AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Daftar Penerima Kuota Telkomsel Dan Indosat 2021 FSEIDocumento26 pagineReport Daftar Penerima Kuota Telkomsel Dan Indosat 2021 FSEIHafizh ZuhdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Assignment ScribdDocumento4 pagineIndividual Assignment ScribdDharna KachrooNessuna valutazione finora
- The Botanical AtlasDocumento74 pagineThe Botanical Atlasjamey_mork1100% (3)
- Kahveci: OzkanDocumento2 pagineKahveci: OzkanVictor SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- (Variable Length Subnet MasksDocumento49 pagine(Variable Length Subnet MasksAnonymous GvIT4n41GNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento42 pagineModule 2DhananjayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action ResearchDocumento1 paginaReflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action Researchronan.villagonzaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines Tax Related DeclarationsDocumento16 pagineGuidelines Tax Related DeclarationsRaghul MuthuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheology of Polymer BlendsDocumento10 pagineRheology of Polymer Blendsalireza198Nessuna valutazione finora
- Newcomers Guide To The Canadian Job MarketDocumento47 pagineNewcomers Guide To The Canadian Job MarketSS NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Exor EPF-1032 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineExor EPF-1032 DatasheetElectromateNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Marketing SurveillanceDocumento19 paginePost Marketing SurveillanceRamanjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Testbanks ch24Documento12 pagineTestbanks ch24Hassan ArafatNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacity PlanningDocumento19 pagineCapacity PlanningfarjadarshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Employee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Documento7 pagineEmployee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Anonymous dozzql7znKNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment ManagerDocumento234 pagineEnvironment ManagerAbhishek kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NGPDU For BS SelectDocumento14 pagineNGPDU For BS SelectMario RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrosteel Castings Limited (ECL) - Technology That CaresDocumento4 pagineElectrosteel Castings Limited (ECL) - Technology That CaresUjjawal PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Amul ReportDocumento48 pagineAmul ReportUjwal JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Law of EntrophyDocumento22 pagineSecond Law of EntrophyMia Betia BalmacedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Um 0ah0a 006 EngDocumento1 paginaUm 0ah0a 006 EngGaudencio LingamenNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptDocumento2 pagine14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptsubiNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenDocumento13 pagineProblems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenSabriThabetNessuna valutazione finora