Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Relationships Among Means Medians and Modes
Caricato da
animenald89Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Relationships Among Means Medians and Modes
Caricato da
animenald89Copyright:
Formati disponibili
RELATIONSHIPS AMONG MEANS, MEDIANS, AND MODES
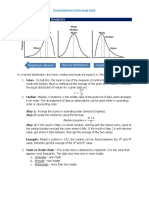
The most complete information about a distribution is obtained when all three measures of central tendency are reported. Each provides different kind of information that the teacher may need to better understand class performance. Measures of Central Tendency summarize the average or typical performance of the class as a whole. FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION SYMMETRICAL LOWER HALF OF THE DISTRIBUTION MIRRORS THE UPPER HALF Figure 1 Mean, median and mode will coincide Median will lie between the mean and the mode Mean, Median and Mode in a MEAN = MEDIAN = MODE Symmetrical Distribution SCORES 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FREQUENCY 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Scores
SKEWED SCORES ARE PILED UP AT EITHER THE HIGH OR THE LOW END OF DISTRIBUTION, AND THERE IS A TAIL AT THE OTHER END. Tail determines whether the distribution is positively skewed or negatively skewed Figure 2 Positively skewed tail is pointed towards the high end Mean, Median and Mode in a MEAN > MEADIAN > MODE
Symmetrical Distribution
SCORES 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
FREQUENCY 0 1 1 2 2 3 4 5 7
Frequency
Mean = 3.12 Median = 3.00 Mode = 1.00
Frequency 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Mean = 5.00 Median = 5.00 Mode = 5.00
tail
Scores
Negatively skewed tail is pointed towards the low end MEAN < MEADIAN < MODE FREQUENCY 7 5 4 3 2 2 1 1 0
Mean, Median and Mode in a Symmetrical Distribution
Figure 3
SCORES 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Frequency
Mean = 6.88 Median = 7.00 Mode = 9.00
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5
tail
USE THE MEAN UNDER THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS: Scores If sampling is important If other statistics require or call for a mean If there are no extreme scores in the distribution or if the teacher wants the extreme scores to play a significant role in determining central tendency USE THE MEDIAN UNDER THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS: If distributions contain extreme scores, whose effects the teacher wants to minimize. If the data exist only as ranks. If a rapid measure of central tendency is required. USE THE MODE UNDER THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS: If the most typical value is desired. If central tendency must be estimated quickly
Solutions to Figure 1 SCORE S 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FREQUENCY fx 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 n=25 Solutions to Figure 2 SCORES 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FREQUENCY fx 0 1 1 2 2 3 4 5 7 n=25 Solutions to Figure 3 SCORES 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FREQUENCY fx 7 5 4 3 2 2 1 1 0 63 40 28 18 10 8 3 2 Mode = 2 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 8 8 8 8 8 (9 9 9 9 9 9 9) =6.88 Median = 2 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 (7)8 8 8 8 8 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 Mean = _fx_ n =__172__ 25 0 8 7 12 10 12 12 10 7 fx=78 Mode = (1 1 1 1 1 1 1)2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 =3.12 Median = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 (3) 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 Mean = _fx_ n =__78__ 25 9 16 21 24 25 16 9 4 1 fx =125 Mode = 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 (5 5 5 5 5) 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8 9 =5 Median = 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 (5) 5 5 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8 9 Mean = _fx_ n =__125__ 25
0 n=25 fx=172
Western Mindanao State University
College of Education
Normal Road, Zamboanga City
A Report in
PED 111 (Assessment of Curriculum)
entitled
RELATIONSHIPS AMONG MEAN MEDIAN AND MODE
To be reported by:
LAMATA RONALD SAN JUAN A.K.A ANIME
Professional Education Certificate Student
To be submitted to:
DR. ANNA LOUISA R. PEREZ
Course Professor
September 2012
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Statistics (Ii) : Pie Chart Mode, Median and MeanDocumento8 pagineStatistics (Ii) : Pie Chart Mode, Median and MeanBliss ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Analysis For Business: DR - Wael Abdelhaleem Ahram Canadian University Tutorial#4 Spring 2022Documento26 pagineQuantitative Analysis For Business: DR - Wael Abdelhaleem Ahram Canadian University Tutorial#4 Spring 2022Mina OsamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Ainque...... GUMAPIDocumento85 pagineReport Ainque...... GUMAPIAngelica TalastasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure of Central TendencyDocumento24 pagineMeasure of Central Tendencymariell quitorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Central Tendency FormulaDocumento18 pagineWhat Is The Central Tendency FormulaCarel Faith AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central Tendency Ungrouped DataDocumento28 pagineMeasures of Central Tendency Ungrouped DataDionne Rei BontiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Demo PowerpointDocumento24 pagineFinal Demo PowerpointFlordeliz100% (2)
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento33 pagineMeasures of Central Tendencyvikassharma7068Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento40 pagineMeasures of Central TendencyAnagha AnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central Tendency PositionDocumento12 pagineMeasures of Central Tendency PositionCaren Pelayo JonelasNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure of Central TendencyDocumento40 pagineMeasure of Central TendencybmNessuna valutazione finora
- Mean, Median and ModeDocumento2 pagineMean, Median and ModeminnsukichawwwnNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Numerical MeasureDocumento11 pagineTopic 1 Numerical MeasureNedal AbuzwidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability and Stochastic Process-5Documento19 pagineProbability and Stochastic Process-5Neha NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter3 - Measures of Central Tendency Ungrouped DataDocumento25 pagineChapter3 - Measures of Central Tendency Ungrouped DataDionne Rei BontiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Claudia-3m CorrectedDocumento34 pagineClaudia-3m CorrectedLeoncio LumabanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento45 pagineCH 03Ansari MustakNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 EdtechDocumento8 pagineLesson 3 Edtechapi-268563289Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento40 pagineMeasures of Central TendencyAnagha AnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento18 pagineMeasures of Central TendencyK M TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento45 pagineCH 03zaloriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ken Black QA 5th Chapter 3 SolutionDocumento47 pagineKen Black QA 5th Chapter 3 SolutionRushabh VoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 EPS 550 SP 2010Documento30 pagineLecture 2 EPS 550 SP 2010Leslie SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics 12e Chapter 03Documento45 pagineStatistical Techniques in Business and Economics 12e Chapter 03Abdullah Hasib50% (2)
- Central TendencyDocumento45 pagineCentral TendencyAggarwal YashvardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.6 - Measures of Central TendencyDocumento25 pagine5.6 - Measures of Central TendencyGERRYNessuna valutazione finora
- LEC5 Measures of Central TendencyDocumento169 pagineLEC5 Measures of Central TendencyAldrin MndzNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure of Central Tendency: Measure of Location: GoalsDocumento7 pagineMeasure of Central Tendency: Measure of Location: GoalsDebashish MahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3Documento49 pagineTopic 3NURUL SYAFIQAH BINTI NORIHSANNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Tech in BusinessDocumento20 pagineQuantitative Tech in BusinessHashir KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento58 pagineChapter 4meia quiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1 Mean Median Mode and RangeDocumento21 pagine6.1 Mean Median Mode and RangeGilbert Guzman TurarayNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Statistics You Should Know For The PMP Certification ExamDocumento5 pagineBasic Statistics You Should Know For The PMP Certification ExamIan SecretariaNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDocumento28 paginePPT2 Central Tendency and Variabilityzy- SBGNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic MeassurementDocumento61 pagineBasic MeassurementROGELIO JUNIO JRNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Collecting, Displaying, and Analyzing Data: Study Guide / Review For Mastery: Mean, Median, Mode, and RangeDocumento2 pagineChapter 7: Collecting, Displaying, and Analyzing Data: Study Guide / Review For Mastery: Mean, Median, Mode, and RangeMaisyarah YuniarNessuna valutazione finora
- Stat 3Documento42 pagineStat 3mamatha_mba269690Nessuna valutazione finora
- M1. Understanding A Data SetDocumento41 pagineM1. Understanding A Data SetMYo OoNessuna valutazione finora
- EDA - Lesson 3 - FinalDocumento4 pagineEDA - Lesson 3 - FinalJimlyn Grace GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure of SkewnessDocumento44 pagineMeasure of SkewnessJen Benemerito AggabaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Central Tendency 1 Ungrouped DataDocumento24 pagineMeasurement of Central Tendency 1 Ungrouped Dataolalekan.beckleyNessuna valutazione finora
- List The Importance of Data Analysis in Daily LifeDocumento22 pagineList The Importance of Data Analysis in Daily LifeKogilan Bama Daven100% (1)
- Chapt3 OverheadsDocumento8 pagineChapt3 OverheadsGouri DasNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 - Measure of Central TendencyDocumento9 pagineCH 2 - Measure of Central TendencyhehehaswalNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSIGNMEN4Documento15 pagineASSIGNMEN4Harshita Sharma100% (1)
- 1st WeekDocumento40 pagine1st WeekJohn Ericson PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Tendency & Dispersion: Dr. Saryono, Skp.,Mkes. Medical Biochemistry and Research Methodology UnitDocumento52 pagineCentral Tendency & Dispersion: Dr. Saryono, Skp.,Mkes. Medical Biochemistry and Research Methodology UnitPupujja LoupelypoperzagataNessuna valutazione finora
- 221 Chapter3 StudentDocumento16 pagine221 Chapter3 StudentMichael Z ChuNessuna valutazione finora
- Three: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDocumento45 pagineThree: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedMohd Jasmee Mohd MokhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical AnalysisDocumento23 pagineStatistical AnalysisMohammad Sabir HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Central TendencyDocumento20 pagineCentral Tendencyגרסיה רואנהNessuna valutazione finora
- Goals in StatisticDocumento149 pagineGoals in StatisticJay Eamon Reyes Mendros100% (1)
- M3 LessonDocumento6 pagineM3 LessonBebe LumabaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 Measures of Central Tendency - Ungrouped Data High SchoolDocumento22 pagineLesson 7 Measures of Central Tendency - Ungrouped Data High SchoolAlbec Sagrado BallacarNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilization of DataDocumento64 pagineUtilization of DataBeethovenMarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Jerome StatisticsDocumento12 pagineJerome StatisticsSoraya ChocNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento25 pagineMeasures of Central TendencyDanica MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 11 Measure of Center and VariabilityDocumento35 pagineWeek 11 Measure of Center and Variabilityghemarie castilloNessuna valutazione finora
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Characteristics of Normal DistributionDocumento12 pagineCharacteristics of Normal DistributionMuhammad SatriyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asia Pacific Business SchoolsDocumento11 pagineAsia Pacific Business SchoolsSanjana Singh100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Introductory Statistics 9th Edition Mann Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Introductory Statistics 9th Edition Mann Solutions Manual PDFilorlamsals100% (13)
- AgStat 2.22019 Mannula PDFDocumento132 pagineAgStat 2.22019 Mannula PDFDrvijay KalpandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of QuantsDocumento15 pagineStudy of Quantsutkarshrajput64Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skew Gaussian Process For Nonlinear RegressionDocumento26 pagineSkew Gaussian Process For Nonlinear RegressionShafayat AbrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Statwiki JamesDocumento57 pagineStatwiki JameshermancxNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal - Distribution ZDocumento29 pagineNormal - Distribution ZSean EstrabonNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Market Share of Five Competing Internet ProvidersDocumento6 pagineC. Market Share of Five Competing Internet ProvidersKaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterisation of Alluvial Gold Exploration Data To Improve GoldDocumento11 pagineCharacterisation of Alluvial Gold Exploration Data To Improve GoldAntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal DistributionDocumento15 pagineNormal DistributionsoftenNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrologic Frequency AnalysisDocumento149 pagineHydrologic Frequency AnalysisAndersson PFNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Statistics & Operations Research FYUP Course StructureDocumento71 pagineDepartment of Statistics & Operations Research FYUP Course StructureAbdullah MasoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Measures of Dispersion, Skewness and Kurtosis: Class Activity 4: Basic Business Statistics For Data AnalysisDocumento9 pagineTopic: Measures of Dispersion, Skewness and Kurtosis: Class Activity 4: Basic Business Statistics For Data AnalysisAdwaita MandvikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Satisfaction Regarding Human Resource Management Practices in Government Colleges at Sirajganj District of BangladeshDocumento9 pagineTeachers Satisfaction Regarding Human Resource Management Practices in Government Colleges at Sirajganj District of BangladeshShawn VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Interpretation of Data ReportDocumento9 pagineThe Interpretation of Data ReportglemarmonsalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biostat Lecture NoteDocumento116 pagineBiostat Lecture NoteMiki SileshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive MeasuresDocumento73 pagineChapter 3 Numerical Descriptive MeasuresTasya Asdiga0% (1)
- Frequency Distributions and Graphs2Documento8 pagineFrequency Distributions and Graphs2Ron InaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Commerce - 2nd EditionDocumento227 pagineCommerce - 2nd EditionHilal Ahmed100% (1)
- Grain Size AnalysisDocumento7 pagineGrain Size AnalysisMd. Asif HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 2a AP Statistics Name D2ct263enury6r Cloudfront NetDocumento16 pagineTest 2a AP Statistics Name D2ct263enury6r Cloudfront NetAN NGUYENNessuna valutazione finora
- STA301 - Statistics and Probability Solved 301Documento15 pagineSTA301 - Statistics and Probability Solved 301Ali HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- BAHIRDAR ComputerSci&Eng FinalDocumento201 pagineBAHIRDAR ComputerSci&Eng FinalTsegaye Andargie100% (7)
- Module in Inferential Statistics With Additional Exercises Edited Until August 2022 by Tats2020Documento90 pagineModule in Inferential Statistics With Additional Exercises Edited Until August 2022 by Tats2020Rosita MaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 - Lecture 4 - Descriptive Statistics - SlidesDocumento20 pagine2021 - Lecture 4 - Descriptive Statistics - SlidesFanelo FelicityNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento17 pagineChapter 3Kharil Naim SallehNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Repeated Measures ANOVA ProblemsDocumento29 pagineSolving Repeated Measures ANOVA ProblemsBeba EchevarriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brown - Warner - 1985 How To Calculate Market ReturnDocumento29 pagineBrown - Warner - 1985 How To Calculate Market ReturnFaisal KhalilNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Part 2 CommerceDocumento176 pagineMathematics Part 2 CommerceHrishikesh ShindeNessuna valutazione finora