Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Wu1c3 by Adel Khamis
Caricato da
Adel KhamisDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Wu1c3 by Adel Khamis
Caricato da
Adel KhamisCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter Three -1- Unit one
Light as wave motion
:Light
Light is a branch of …………………•
.… waves
It consists of …………….. field and•
…………… field perpendicular to each other and ……………
…. to the direction of
propagation, therefore it
considers as (longitudinal –
transverse) waves, and it
(required / not required)
.medium to propagate
:Propagation of light
……………………………………… Light propagates in•
..………
:Reflection of light
.…………………………………………………………………… : Definition
:The laws of reflection
……………………………………………………………………………
..…
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -2- Unit one
:Refraction of light
efi
niti
:on
…
…
…
…
…
…
…
………………………………………………
If the angle of incident is zero, the ray fall (normal /•
…………………… perpendicular) to the surface, it
..…
:.G.R
When the ray incident with angle equal zero it•
.suffers no refraction
………………………………………..………………………•
..…………
The optical piece used in the experiment is semi•
circular prism, and the light beam fall on the plane
.surface
………………………………………..………………………•
..…………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -3- Unit one
:The laws of refraction
:First Law states
…………………………………………………………………………………
:Second law states
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
:)Refractive index (n
sinφ C
refractiveindex (n) = =
sinθ V
………………………… :Definition
c
n=
v
.…………………………………………
:G.R
.The value of refractive index is greater than one
.………………………………………………………………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -4- Unit one
:)Relative refractive index (1n2
..………………………………………………………………… : Definition
v1 sin φ
1 n2 = =
v2 sin θ
•F
………… actors affected on relative refractive index
..…………… ,..…
……… Factor affected on absolute refractive index•
..……………………
:Relation between relative and absolute index
The first medium * The first medium * The first medium *
(1) has velocity of (air) has velocity (air) has velocity
light = V1 of light = C of light = C
The second * The second * The second *
medium (2) has medium (1) has medium (2) has
velocity of light = velocity of light = velocity of light =
V2 V1 V2
.......... . ..........
n12 == 1 n2 =
..........
............ .......... .
..…… C = ……… x .……… C = ………. x
… n… V… = n… V
V1 ..........
=
V2 ..........
..........
1 n2 =
..........
•
....... ....... .......
1 n2 = = =
....... ....... .......
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -5- Unit one
The angle of incidence in a medium is 60° and the•
angle of refraction in the other medium is 30°, the
relative refractive index from the first to the second
medium is ……………………….. and that from the
..………………………… second to the first is
………………………………… = Refractive index of air•
.………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -6- Unit one
:Snell’s law
).related to absolute refractive index( *
........
1 n2 = (1)
.........
)related to velocity( *
.........
1 n2 = ( 2)
.......... .
)From (1) and (2
*
n 2 .......... ..
= (3)
n1 .......... ...
*
sin φ V1
but = (4)
sinθ V2
)From (3) and (4
n1 sin ........ =n2 sin .......
:Prove that
•
1
1 n2 =
2 n1
………………………………………………………………•
………………………………………………………………
…………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -7- Unit one
:N.B
The medium, which has less velocity, considered•
optically (denser/ less dense) than the medium,
.which has great velocity
:What is meant by
The absolute refractive index of glass = 1.5
..………………………………………………………………………………
:Give reason for
Light passing into a denser medium is bent toward •
.the normal
………………………………………………………………•
..…………
Light passing into less denser medium is bent away•
.from the normal
………………………………………………………………•
..……………
You can see your image at window glass nightly,•
.while you can’t see it at day time
………………………………………………………………•
..……………
:Examples
Given that the velocity of light in air = 3x10 8 m/s•
and that in water equal 2x108 m/s, if a light ray fall
with angle of 30° with water surface, find the angle
.between refracted ray and reflected ray
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -8- Unit one
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]’84° 45 [
A light ray falls on the surface of glass of absolute•
refractive index 1.5 with angle of incidence that is
.equal to 30°. Find the angle of refraction
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]19.47° [
Given that the absolute refractive index for water is•
:4/3 and that for glass is 3/2 find
.a) The relative refractive index from water to glass
.b) The relative refractive index from glass to water
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]8/9 ,9/8 [
An incident ray by an angle 48.5° on one face of a•
glass rectangular block (n = 1.5) the angle of
refraction is …………………… and the angle of
……………… emerge is
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -9- Unit one
:Give reason
When white light refract, it•
.separated into seven colors
……………………………………………•
……………………………………………
……………………………………………
:)Interference of light (young experiment
Explain an experiment to illustrate the interference of
:light by using of double slit
…………………….……………………………
…………….…………………………….………
…….…………………………….………………
………………………….………………………
……………………………………………………
…………………………………
:Where
R
∆y = λ
d
..………………… = ∆y•
…………………… = d•
…………………… = R•
………………… = λ•
:.N.B
.)meter (m) = ……………… Angstrom (Å 1
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -10- Unit one
:Give reason for
.Monochromatic light is used in Young’s experiment•
………………………………………………………………•
……………
The fringes become clear when the distance•
.between two slits become small
.……………………………………………………………………………
.Red light is preferred to violet in young experiment•
.……………………………………………………………………………
In young’s experiment when a red light of•
frequency 1x1015 Hz is used the distance between
the fringes was 2 mm. Calculate the distance when
.violet light of frequency 0.6x1015 Hz is used
.……………………………………………………………………………
.……………………………………………………………………………
.……………………………………………………………………………
]3.3x10-3m [
What is the benefit of double slit in young•
.experiment
………………………………………………………………•
……………
:Diffraction of light
……………… …………………………………………… :Definition•
…………………………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -11- Unit one
The aperture or the slit must be (equal or•
less than / larger than) the wavelength of the
.light
If the aperture has circular shape•
the diffraction appear at the screen
as airy’s disk, where it consists of …
………………. at the middle followed
.by ………………… rings
If the aperture has rectangular•
………………………………… shape the diffraction appear as
………
:Give reason
Sound waves diffract at edges of the doors and windows but light
.not
.………………………………………………………………………………
:Question
What do you know about Airy’s disk
……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………….………………
.…………
:Light as wave motion
:Light considers as wave motion because
.………………………………………………………………………… •
.………………………………………………………………………… •
.………………………………………………………………………… •
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -12- Unit one
.………………………………………………………………………… •
.………………………………………………………………………… •
:Critical angle and total reflection
When a ray of light passes•
from a denser optical medium
to a less dense medium, it
refracts ………………. the
.normal
By increasing of the incident angle, the refracted•
.angle will (increase/ decrease) to reach ……….°
By increasing of the incident angle, the emerge ray•
…………… will return at the same medium forming
...………………
:Critical angle
.…………………………………………………………………… : Definition
If the incident angle is smaller than the critical•
angle the ray will ……………….; while it will …………
……… if the angle of incident is greater than the
.critical angle
Find the relation between the critical angle•
:and the absolute reflective index
1 :Prove that•
n=
sin φ c
………………………………………… ……………………………
……
……………………………………………………………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -13- Unit one
……………………………………………………………………………
If the critical angle for a medium to air is 45° then•
..…………… the absolute refractive index is
]1.4 [
:N.B
= anm•
1
n=
sin φ c
= mna•
1 n 2 = sin φ c
:Totally reflection
…………………………………………………………………… Definition
:.G.R
The totally reflection is preferred than the normal•
.reflection
………………………………………………………………•
……………
:Factors required for total reflection•
………………………………………………………………•
……………
………………………………………………………………•
……………
If the critical angle of water is 45° and for glass =•
40°. Find the relative refracted index between glass
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -14- Unit one
and water. And find the critical angle of light from
.glass to water
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
]’65° 22 ,0.90903 [
Calculate the critical angle between glass and•
water given that their refractive indexes are 1.6
.and 1.33 respectively
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]56° 13 [
:.N.b
:From less dens medium to dens medium
If φ = 0 then …………………………………………………•
)…… (G.R
………………………………………………………………•
.……………
……………………………………………… If φ > 0 then•
………………
:From dens medium to less dens medium
……………………………………………… If φ = 0 then•
………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -15- Unit one
………………………………………… If φc > φ > 0 then•
………………
If φ = φc then …………………………………………...……,•
……… = θ
……………………………………………… If φ > φc then•
……………
:Application of totally reflection
:)Fiber optics (Optical fibers
It is a fine hollow fiber of a•
transparent material has (small/
.high) critical angle
When the incident ray enters, it falls at the surface •
with an angle greater than the critical angle,
..………………… therefore the ray will
Then the ray will emerge from the other end of the •
.fiber
It is widely used as ………………. in medicine and …•
.………………….. in communications
:Mirage
.…………………… :Definition
..………………………………
..………………………………
The layer of air with contact to the•
earth surface (high / low) in temperature and
)became (dens / less dens
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -16- Unit one
The upper layer will be (denser / less dens) than•
.the lower layer
The ray falls from the object will refract many time•
through the layer of hot air (increasing/ decreasing)
.of its angle
When the angle of incident becomes (greater/•
smaller) than the critical angle the ray will …………
.……………… ……. forming
:Totally reflected prism
.It is used to change the path of light rays either by 90 or 180
Draw a diagram to change the path of light ray by •
..………180°. Which used in
.Draw a diagram for binoculars•
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -17- Unit one
Draw a diagram to change the path of light ray by •
..……… 90°. Which used in
:Give reason
.The reflected prism is preferred to metallic mirrors•
………………………………………………………………•
……………………………..…………………………………
.….……………………
Reflected prism is painted with cryolite (reflected•
.)layer
………………………………………………………………•
……………………………..…………………………………
.….……………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -18- Unit one
A
3
2
1
φθθφα θ1
θ2
φ1
φ2
α
Deviat
ion
with a
triang
ular
:prism
From the
previous
:diagram
= A + 3
..………
θ1 + φ2
… = + 3
.……
A = …
)(1 ….. + ……….
)(2 α = ……… + ……….
)3( ………… - ……… = 1
)4( ………… - ……… = 2
)From (2) and (3) & (4
……… - ……… + .……… - ……… = α
)……… + .……( - .……… + ………… = α
)From equation (1
..……… - .……… + .……… = α
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -19- Unit one
:Where
A is ………………………... and it called ………………•
………………… or ……………… or …..……………… or
…
...……………………… α is•
...……………………… φ1 is•
...……………………… θ2 is•
:.N.B
The emergent ray always emerge towards ………………… of the
.prism
n
A
θ2
φ2
θ1
φ1
α
:Example
A ray•
falls on a
prism
whose
angle is
45°, the
angle of
incidence
is 60°,
the ray emerges normal to the other side of the
prism, find the refractive index of the prism and the
.angle of deviation
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -20- Unit one
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
.……………………
]15 ,1.225 [
)Angle of deviation (α
..………………………………………………………………… : Definition
:Factors affected on the angle of deviation
.…………………………………•
.…………………………………•
.…………………………………•
:Tracing the path of the ray through the prism
The deviation angle decrease by increasing of the•
incident angle to a certain value then it increases
.by increasing of the incident angle
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -21- Unit one
φ1
α
………… The ray will ……………… = φ1 .……………… = φ1
..………… ………………… = φ2 ..……………… = θ1
.… .……………… = α
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -22- Unit one
.……………… = θ2 ……… Reflected ray
… The immerge ray ……
………………
:Notes
From the graph of minimum deviation, when the•
angle of incident increases then the angle of
deviation ………….. until it reaches …………… then
by increasing the angle of incident, the angle of
.……… deviation will
If the angle of incident is less than the value in•
which the graph starts therefore the prism acts as
..……………
The minimum angle of incident is corresponding to•
angle of incident at the second face equal …………
… and the emigrant ray will be ………….. to the
second surface of the prism, and the emerge angle
…………… =
:In the case of minimum deviation
.The refracted ray will be ……….. to the base of prism
θ1 = ф2 = θ
..…………… = A
........
θ=
..........
And
φ1 = θ2 = φ
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -23- Unit one
..…… - ..……… = α
......... + .........
φ=
..........
*
sin φ
n=
sinθ
..... + .....
sin
.....
n=
.....
sin
.....
:Examples
In an experiment it was found that the angle of•
minimum deviation is 48.2°, given that the angle of
the prism is 58.8°. find the refractive index of the
.material of the prism
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]1.64 [
A triangular prism of refractive angle 60° adjusted•
to the minimum deviation position; when the angle
.of min. dev. is 37.2° find its refractive index
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
]1.5 [
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -24- Unit one
Experiment to determine the ray path through a
:glass prism and its refractive index
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
………………………………………………•
:The dispersion of light by a triangular prism
The angle of deviation depends on ……………
….., which depends on …………………... Therefore,
each color of light going to deviate by a certain angle,
.deference than the other color
:Give reason for
When beam of white light falls on a triangular•
prism adjusted in min. deviation, the emergent ray
.)deviated into different colored rays (spectrum
………………………………………………………………•
..……………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -25- Unit one
The violet ray has the biggest deviation (max. α).•
.)but the red ray has the least deviation (min. α
………………………………………………………………•
..……………
:Question
The relation between the angle of deviation and•
the wavelength of light is (directly / inversely)
.proportional
The relation between angle of refraction at the first•
face and angle of incident at the second face is
.(directly / inversely) proportional
Draw a graphical relation between angle of•
refraction at the first face θ1 and angle of incident
at the second face φ2
………………………… The mathematical relation is•
..…………………
………… The intersected point with Y axis indicates•
……………………
………… The intersected point with X axis indicates•
……………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -26- Unit one
Trace the light ray in the opposite figure where n =•
1.5
:The thin prism
It is a triangular prism, with an angle not more than•
.10°. It is always in a position of minimum deviation
In case of the small angles the angle in radian unit•
.is equal to its sin
......... + .......
n= 2
.......
2
......... + ........
n=
.......... .
..……… + ………… = nΑ
..………… - .……… = α
)……… - ..……( α = A
:The relation between α and A can be drawn as
A
α
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -27- Unit one
………………………………… :Mathematical relation•
………
……………………………………………………… Slope•
…
………………= The point of intersection with Y-axes•
…
…………… = The point of intersection with X – axes•
…
:The relation between α and n can be drawn as
n
α
………………………………… :Mathematical relation•
………
……………………………………………………… Slope•
…
:Factors affects α
..…….……………………•
……………………………•
:.N.B
Rule Case of application
……………………… All cases Min Thin
......................… deviation prism
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -28- Unit one
……………………………………
..…
X Min Thin
deviation prism
X X Thin
prism
:In case of thin prism for the red color
………………… = αr
:In case of thin prism for the blue color
..…………………… = αb
αb - αr) known as the angular size; it is also known(•
as ………………… or ………………………. or ….………
..…………………… …….. or
…………………………………… :Define angular size•
…………………………………………… …………………
..………………………………
:Give reasons
.Thin prism is always in minimum deviation•
………………………………………………………………•
.……………
)Prove that the angular size equals A (nb - nr
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -29- Unit one
:Factors affect angular size
………………………………………………………………•
.……………
………………………………………………………………•
.……………
A thin prism has an angle of 5° its refractive index•
… 1.6 produces angle of deviation that is equal to
..………………
]3° [
A ray of light falls on a thin prism with an angle of •
deviation 4° and its refractive angle 8° its refractive
………………… index is
]1.5 [
:)Depressive power (ω
.…………………………………………………………………… : Definition
..………………………………………………………………………… :Rule
:Prove that
αb − αr nb − nr
ω= =
α n −1
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Chapter Three -30- Unit one
:)Factor affects Depressive Power (ω
………………………………………………………………•
.……………
:.N.B
α = αy = ………….. (Relation between α for the blue•
)color and α for the red color
n = ny = ………….. (Relation between n for the blue•
)color and n for the red color
…………………………………………………… = )α (total
..…………………………………………… = )αb - αr (total
…………………………………………………… = )α (total
..…………………………………………… = )αb - αr (total
2008/2009 Work Sheet
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Refractive Index of Liquids PDFDocumento7 pagineRefractive Index of Liquids PDFDevang TRIVEDINessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookDocumento15 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Eu3c6 by Adel KhamisDocumento31 pagineEu3c6 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- EU2C4 by Adel KhamisDocumento49 pagineEU2C4 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookDocumento6 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Eu1c3 by Adel KhamisDocumento26 pagineEu1c3 by Adel KhamisAdel Khamis50% (2)
- Wu3c7 by Adel KhamisDocumento7 pagineWu3c7 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Wu5c15 by Adel KhamisDocumento19 pagineWu5c15 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Wu1c2 by Adel KhamisDocumento15 pagineWu1c2 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Wu3c6 by Adel KhamisDocumento20 pagineWu3c6 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Wu5c12 by Adel KhamisDocumento17 pagineWu5c12 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su5c15 by Adel KhamisDocumento14 pagineSu5c15 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Eu1c2 by Adel KhamisDocumento25 pagineEu1c2 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su1c2 by Adel KhamisDocumento12 pagineSu1c2 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su3c7 by Adel KhamisDocumento6 pagineSu3c7 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su5c14 by Adel KhamisDocumento10 pagineSu5c14 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su4c9 by Adel KhamisDocumento8 pagineSu4c9 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Su2c5 by Adel KhamisDocumento9 pagineSu2c5 by Adel KhamisAdel Khamis100% (1)
- ME22Documento3 pagineME22Earon Michael CorreosNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 7 A Simple Charles' Law ExperimentDocumento11 pagineExperiment 7 A Simple Charles' Law Experimentiah_guevarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Defect & Binding Energy 3Documento8 pagineMass Defect & Binding Energy 3Alagh DineshNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10Documento224 paginePhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10Vishwajeet Aman100% (1)
- Dynamics11lecture PDFDocumento89 pagineDynamics11lecture PDFEngra FithreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Khalid Yousaf BS Civil Engineering The University of Lahore 1-km Raiwind Road LahoreDocumento83 pagineKhalid Yousaf BS Civil Engineering The University of Lahore 1-km Raiwind Road LahoreKhalid Yousaf100% (1)
- Bridge Loading Idealisation For Grillage AnalysisDocumento8 pagineBridge Loading Idealisation For Grillage AnalysisHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Plane Stress ProblemDocumento14 pagineThe Plane Stress ProblemSaif RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems in PhysicsDocumento22 pagineSolved Problems in Physicsvasudevan m.vNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet in Science 4 Third QuarterDocumento8 pagineWorksheet in Science 4 Third QuarterElmalyn BernarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Reynolds NUmberDocumento6 pagineDetermination of Reynolds NUmbermujette godmalin100% (5)
- Gears DesignDocumento5 pagineGears DesignSandy PandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis 2 IDocumento15 pagineAnalysis 2 IMiliyon TilahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Transition MetalsDocumento44 pagineChemistry of Transition MetalsAqilah MahabirNessuna valutazione finora
- BuccaneerDocumento7 pagineBuccaneerAlessandro GonzálezNessuna valutazione finora
- GyroscopesDocumento15 pagineGyroscopesgeenjunkmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil LabDocumento30 pagineSoil LabAnonymous eg41HYENessuna valutazione finora
- P H y S I C S Part - I Multiple Correct Answer(s) TypeDocumento28 pagineP H y S I C S Part - I Multiple Correct Answer(s) TypeUdayNessuna valutazione finora
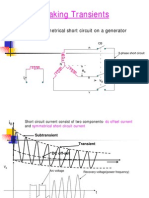
- Circuit BreakerDocumento50 pagineCircuit BreakerDeanna GrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I-D - Defects in SolidsDocumento16 pagineUnit I-D - Defects in Solidsjyoti kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Channel Lining and Pier Scour Design ManualDocumento53 pagineChannel Lining and Pier Scour Design ManualAdeRatihIspandiariNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 11360 1985Documento24 pagineIs 11360 1985Avijit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Hydraulics - DrSolomon Chapters 1 - 3Documento135 pagineEssentials of Hydraulics - DrSolomon Chapters 1 - 3Jôssŷ FkrNessuna valutazione finora
- (MATH1014) (2016) (S) Midterm Scchanan 86434Documento9 pagine(MATH1014) (2016) (S) Midterm Scchanan 86434aragornbfrerNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetism N: Alan MurrayDocumento23 pagineElectromagnetism N: Alan MurrayCocis PeTrisorNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs SsDocumento15 pagineCs SsYuniaYayukNessuna valutazione finora
- Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method14Documento1 paginaRobin Grayson Gold Recovery Method14JavierMamaniVelasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials 15 05227 v2Documento19 pagineMaterials 15 05227 v2Nassereddine YassineNessuna valutazione finora
- Powder MetallurgyDocumento33 paginePowder MetallurgyMohanakumara K CNessuna valutazione finora