Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electric Motor Tech. Writ
Caricato da
Jonathan Brylle CardinalDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electric Motor Tech. Writ
Caricato da
Jonathan Brylle CardinalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
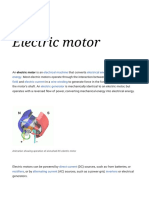
Electric motor is an electrical and mechanical (electromechanical) device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force. The reverse process, producing electrical energy from mechanical energy, is done by generators such as an alternator or a dynamo. Some electric motors can also be used as generators, for example, a traction motor on a vehicle may perform both tasks. Electric motors and generators are commonly referred to as electric machines. Electric motor have 8 important and important parts of it. Centrifugal switch is an electric switch that operates using the centrifugal force created from a rotating shaft. Most commonly that of an electric motor or gasoline engine. Stator is the stationary part of a rotor system or a siren, found in an Electric motor. Rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator. It rotates causes the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged. Drum motor (or Drive pulley) is a geared motor drive enclosed within a steel shell providing a single component driving pulley for conveyor belts. Cooling fan is a machine used to create flow within a fluid, typically a gas such as air to avoid overheating its inner parts. Power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load to electric power converters from electrical energy to another form of energy (mechanical, chemical, solar). Terminal box is an enclosure which includes, mounts, and protects one or more terminal boards, it may include a cover and such accessories as mounting hardware, brackets, locks, and conduit fittings. Bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion between moving parts to only the desired motion. Ampre's force law, was created by Andr-dMarie Ampre in 1820. Electric motors of increasing efficiency were constructed from 1821 through the end of the 19th century, but commercial exploitation of electric motors on a large scale required efficient electrical generators and electrical distribution networks. The first commercially successful motors were made around 1873 by Znobe Gramme Electric motors are found in applications as diverse as industrial fans, blowers and pumps, machine tools and household appliances. They may be powered by direct current or a battery powered portable device or motor vehicle, or by alternating current from a central electrical distribution grid or inverter. Small motors may be found in electric wristwatches. Medium-size motors of highly standardized dimensions and characteristics provide convenient mechanical power for industrial uses. The very largest electric motors are used for propulsion of ships, pipeline compressors, and water pumps with ratings in the millions of watts. Electric motors may be classified by the source of electric power, by their internal construction, by their application, or by the type of motion they give. Some devices convert electricity into motion but do not generate usable mechanical power as a primary objective, and so are not generally referred to as electric motors. For example, magnetic solenoids and loudspeakers are usually described as actuators and transducers respectively, instead of motors. Some electric motors are used to produce torque or force.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Wireway Selection Size Calculator 03132011Documento6 pagineWireway Selection Size Calculator 03132011Bandi ThaguruNessuna valutazione finora
- Science - Grade 10: Electricity and MagnetismDocumento16 pagineScience - Grade 10: Electricity and MagnetismJames AlforteNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipefill PDFDocumento8 paginePipefill PDFAlaa RamadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Owner Manual TD60 Volvo PENTA-oiLDocumento52 pagineOwner Manual TD60 Volvo PENTA-oiLDavid Poma0% (1)
- CompressorDocumento6 pagineCompressorproxywarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorDocumento2 pagineElectric MotorUday MusmadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Paper (Draft)Documento2 pagineReaction Paper (Draft)chapatz100% (2)
- Electric Motor: History and DevelopmentDocumento22 pagineElectric Motor: History and DevelopmentVijay MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- AC generators:AC Generators Are Known As Single-Phase Generators and Are Limited To 25kWDocumento9 pagineAC generators:AC Generators Are Known As Single-Phase Generators and Are Limited To 25kWJera ObsinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor DataDocumento1 paginaMotor Dataabuzar12533Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorDocumento1 paginaElectric MotorSomya RajpurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorsDocumento1 paginaElectric MotorsGoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorDocumento2 pagineElectric MotorLAKSHYA SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor - WikipediaDocumento26 pagineElectric Motor - Wikipediadoriclo999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorDocumento4 pagineElectric MotorDHANA sekharNessuna valutazione finora
- For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeDocumento6 pagineFor Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeSubramanian SakthivelNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric EngineDocumento2 pagineElectric EngineOpreanDan100% (1)
- Electric Generator GutulescuDocumento7 pagineElectric Generator GutulescuDaniel MariusNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor: For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Engine, SeeDocumento28 pagineElectric Motor: For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Engine, SeeNABONGO2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorDocumento6 pagineElectric MotorAnfield FaithfulNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor1Documento2 pagineElectric Motor1Hitman KillerNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Motor WikiDocumento55 pagineDC Motor Wikisupratim05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric GeneratorsDocumento5 pagineElectric GeneratorsReyes AlhynNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsDocumento6 pagine2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsAnonymous E4Rbo2sNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangle Multi Drill HolderDocumento43 pagineTriangle Multi Drill HolderSendhilNathan100% (1)
- Unit 18. GeneratorsDocumento10 pagineUnit 18. GeneratorsКаранда МарияNessuna valutazione finora
- Alex - Roco Tarea 3.Documento6 pagineAlex - Roco Tarea 3.alexNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor: For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Engine, SeeDocumento112 pagineElectric Motor: For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Engine, SeesundaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi Rotor Wind Mill Power Generation: AbstractDocumento32 pagineMulti Rotor Wind Mill Power Generation: AbstractAnonymous j0aO95fgNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento4 pagineElectric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento10 pagineElectrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSalooNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Science Electrical / HVACDocumento16 pagineBuilding Science Electrical / HVACManjeet CinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor and GeneratorDocumento6 pagineElectric Motor and GeneratorJesell JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Generator: Specialized Types of GeneratorDocumento3 pagineElectric Generator: Specialized Types of GeneratorErRANaveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 Module 5 - What's ItDocumento6 pagineQ2 Module 5 - What's Itleo markNessuna valutazione finora
- AC GeneratorDocumento16 pagineAC Generatorsheikhiyad60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science 5 ReviewerDocumento4 pagineScience 5 ReviewerAngelica VersolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subtructure WorksDocumento1 paginaSubtructure WorksRazakMaidenNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric MotorsDocumento16 pagineElectric MotorsReszler ArnoldNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes in GeneratorDocumento3 pagineNotes in GeneratorNins SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento5 pagineIntroductionjayantabhbasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Indiction Generator TheoryDocumento4 pagineIndiction Generator Theoryraghu_mnNessuna valutazione finora
- GhostDocumento10 pagineGhostAlçacio Carlos MutevuieNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Electrical MachineDocumento27 pagineChapter 5 Electrical MachineBirhex FeyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Generating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasDocumento4 pagineGenerating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasAnonymous j0aO95fgNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of The Actuators PDFDocumento5 pagineTypes of The Actuators PDFDravvy SahayamNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motors of Use As Given at The W PDFDocumento399 pagineElectric Motors of Use As Given at The W PDFjimNessuna valutazione finora
- AC and DC MotorDocumento13 pagineAC and DC MotorrikechNessuna valutazione finora
- Generadores de Corriente CONTINUA InglesDocumento3 pagineGeneradores de Corriente CONTINUA InglesJoel ArancibiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Energy Conversion SystemsDocumento11 pagineWind Energy Conversion Systemsankita1231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alternator Synchronous Generator and The Types of AlternatorsDocumento4 pagineAlternator Synchronous Generator and The Types of AlternatorsJosephNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento6 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNessuna valutazione finora
- Portable Generator: Created On Tuesday, 11 February 2014 00:12 Written by Super UserDocumento4 paginePortable Generator: Created On Tuesday, 11 February 2014 00:12 Written by Super UserAhmed AtefNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelDocumento6 pagineStudy of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelSaru TVNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor-Generator - WikipediaDocumento7 pagineMotor-Generator - Wikipediahema FawzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final DcacDocumento4 pagineFinal DcacPEE JAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocumento16 pagineElectromechanical Energy ConversionJayvie TumangNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Motor: Cleanup Quality StandardsDocumento26 pagineElectric Motor: Cleanup Quality Standardsketemaa100% (1)
- Disscussion of TheoryDocumento5 pagineDisscussion of Theoryjamesbergano18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Project - Generators and MotorsDocumento4 pagineScience Project - Generators and MotorsApril GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ele3114 EvolutionsDocumento8 pagineEle3114 EvolutionsKawooya CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternator (Automotive)Documento4 pagineAlternator (Automotive)Cornel BicaNessuna valutazione finora
- AC Machine (Generator-Alternator) - WPS OfficeDocumento88 pagineAC Machine (Generator-Alternator) - WPS OfficeJohnray HabolNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsDa EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Timeline ScheduleDocumento73 pagineGeneric Timeline ScheduleJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- (2021-10-01 - 2021-10-17) Demo - Tabao - 37.26kWp - New ReportDocumento9 pagine(2021-10-01 - 2021-10-17) Demo - Tabao - 37.26kWp - New ReportJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Declaration Checklist.10.19-JfcDocumento2 pagineHealth Declaration Checklist.10.19-JfcJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- FB San Pablo BOM For RSD RectificationDocumento1 paginaFB San Pablo BOM For RSD RectificationJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet Solis 15 20K LVDocumento2 pagineDatasheet Solis 15 20K LVJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- (2021-10-17 - 2021-10-17) Demo - Tabao - 37.26kWp - New ReportDocumento2 pagine(2021-10-17 - 2021-10-17) Demo - Tabao - 37.26kWp - New ReportJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Project: Eu-Smile UOM DC Cables Anajawan: PV Cable, 6 SQ - Mm. (Red) PV Cable, 6 SQ - Mm. (Black) MC4 Connector, 4-6 SQ - MMDocumento7 pagineProject: Eu-Smile UOM DC Cables Anajawan: PV Cable, 6 SQ - Mm. (Red) PV Cable, 6 SQ - Mm. (Black) MC4 Connector, 4-6 SQ - MMJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet Solis 3P (3 20) K 4GDocumento2 pagineDatasheet Solis 3P (3 20) K 4GJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Voltage Drop CalcDocumento12 pagineDC Voltage Drop CalcJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Scaffold CalculatorDocumento3 pagineScaffold CalculatorJonathan Brylle Cardinal50% (2)
- Smart Logger 1000 ADocumento1 paginaSmart Logger 1000 AJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Battery Sizing CalculatorDocumento6 pagineBattery Sizing Calculatormfisol2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Expenses: Savings Time Deposit Current AccountDocumento1 paginaExpenses: Savings Time Deposit Current AccountJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper Building Wire Type THHNTHWN 21 PDFDocumento2 pagineCopper Building Wire Type THHNTHWN 21 PDFEmilySisnerosMenorias100% (1)
- Li-Vs-La LEAD ACID AND LITIUM ION PDFDocumento28 pagineLi-Vs-La LEAD ACID AND LITIUM ION PDFJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- MERALCO Electric Bill MonitoringDocumento6 pagineMERALCO Electric Bill MonitoringJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Youth Devotional 05-21Documento15 pagineYouth Devotional 05-21Jonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Clartop FeasibilityDocumento9 pagineClartop FeasibilityJacquelyn Ann CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Philippine GovernmentDocumento5 pagineThe History of Philippine GovernmentJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sentence StructureDocumento3 pagineSentence StructurepcaseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To LiteratureDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To LiteratureJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento5 pagineCase StudyJonathan Brylle CardinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pool, Car, Policy,, March, 2018 DECEMBERDocumento2 paginePool, Car, Policy,, March, 2018 DECEMBERRiyaz BasheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Petronas Details RAPID Project Contract AwardsDocumento9 paginePetronas Details RAPID Project Contract AwardsIzzadAfif1990100% (1)
- Agro IndustrialDocumento126 pagineAgro IndustrialKt PalominoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHQ250Jackleg BrochureDocumento2 paginePHQ250Jackleg BrochurePieroGamarraGarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 21ih-In-Valv Solenoide InoxDocumento1 pagina21ih-In-Valv Solenoide InoxMonica CarrenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Cut MudDocumento53 pagineGas Cut Mudabnou_223943920Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mariner 904 B-Manual - Eng PDFDocumento45 pagineMariner 904 B-Manual - Eng PDFDamir MilisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Filters Vessels Cartridges Hydrocarbon FiltrationDocumento21 pagineFuel Filters Vessels Cartridges Hydrocarbon FiltrationVidyasenNessuna valutazione finora
- TECHNICAL DATA Iveco Engine N45 and N67Documento6 pagineTECHNICAL DATA Iveco Engine N45 and N67Join DigitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipgcl Summer Training Report PPCLDocumento41 pagineIpgcl Summer Training Report PPCLAnkit SarohaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Condensate ReservoirsDocumento11 pagineGas Condensate ReservoirsMaisam AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- CYL100 HomeworkDocumento1 paginaCYL100 HomeworkYash GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation2 Power Point/ Improve Cooking StoveDocumento67 paginePresentation2 Power Point/ Improve Cooking StoveRamon Chua Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Task 3 2Documento23 pagineLearning Task 3 2Nikki EbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Public TransportationDocumento1 paginaBenefits of Public TransportationHaritharan ManiamNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Drive: Navigation MenuDocumento2 pagineTop Drive: Navigation MenuMauricio Quispe HurtadoNessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 s12 QP 11 PDFDocumento24 pagine9702 s12 QP 11 PDFLawrence Lim Ah KowNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Science Cell As A Unit of Life: SystemsDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To Science Cell As A Unit of Life: SystemsAzizan IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Turolla Catalog Group 3 Gear PumpsDocumento36 pagineTurolla Catalog Group 3 Gear Pumpsdwilson fppNessuna valutazione finora
- Haval h2 Brochure Rev3Documento20 pagineHaval h2 Brochure Rev3api-286844184Nessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet SP 2000wDocumento2 pagineDatasheet SP 2000wWilliam Boyle Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gulf Oil Marine - Product RangeDocumento8 pagineGulf Oil Marine - Product RangeObydur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Source Rock Evaluation in July Field Gulf of Suez Egypt by Gamal Ragab GaafarDocumento22 pagineSource Rock Evaluation in July Field Gulf of Suez Egypt by Gamal Ragab GaafarDr. Gamal Ragab Gaafar0% (1)
- Essay ExplosivesDocumento43 pagineEssay ExplosivesOscar PamosNessuna valutazione finora
- D9x13SeriesII 10091Documento6 pagineD9x13SeriesII 10091madal25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tablas de Filtros Motores ClarkeDocumento1 paginaTablas de Filtros Motores ClarkeLeonardo Ramirez100% (1)
- Alternative-Refrigerants R22 GBDocumento12 pagineAlternative-Refrigerants R22 GBMon PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Efficiency Best Practices Handbook For SMEsDocumento30 pagineEnergy Efficiency Best Practices Handbook For SMEssundharNessuna valutazione finora