Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Biomolecules Question
Caricato da
Dr.CharinDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Biomolecules Question
Caricato da
Dr.CharinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
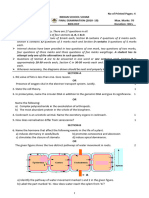
The table below refers to structures that may be found in bacterial cells or liver cells.
Place a tick () in the box if the structure is found in the cell and a cross (x) in the box if it is not. (4)
Read through the following passage about lipids, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Lipids contain the elements hydrogen, carbon and oxygen joined together by .......................... bonds. Triglycerides are lipids that consist of three ............................................... molecules joined to a ............................................... molecule. These molecules are joined together by a chemical process called a ............................................... reaction. Triglycerides that have double bonds between carbon atoms are known as ............................................... triglycerides. (5) The diagram below shows some of the organelles found in a eukaryotic cell.
(a) Name the parts of the Golgi apparatus labelled A and B. (2) (b) Some of the proteins synthesised by ribosomes are transported to the Golgi apparatus. Describe what happens to these proteins in the Golgi apparatus. (3) A student was given three unknown, colourless carbohydrate solutions labelled A, B and C. She tested each one by heating it with Benedicts reagent. The table below shows her results.
(a) State two conclusions that can be made about solutions A and B. (2) (b) Describe the process that the student would now need to carry out in order to show that solution C contained a non-reducing sugar. (3) The tips of three onion roots were cut off and each was used to make a root tip squash. (a) Name a suitable stain that can be used to show chromosomes in a root tip squash. (1) (b) The number of cells observed in each phase of mitosis was counted and these results are shown in the table below.
The number of cells observed in a phase is directly proportional to the length of that phase. Using these results, put the phases in order starting with the longest phase and ending with the shortest phase. (1) (c) The appearance of the chromosomes from part of a root tip squash is shown below.
(i) The cells labelled P1 and P2 are both in prophase. Suggest an explanation for the difference in appearance between the two cells. (3) (ii) Write the letter A on the illustration to label a cell that is undergoing anaphase. (1) (iii) Describe what happens during anaphase.
Describe the roles of protein molecules in facilitated diffusion and active transport. (5) Experiments were carried out to compare the uptake by cells of a substance (substance X) in the presence and absence of a respiratory inhibitor. A respiratory inhibitor is a substance that prevents the formation of ATP. In each experiment the cells were incubated in a solution of substance X for five hours. The concentration of substance X in the cytoplasm was measured throughout. The graph below shows the changes in the concentration of substance X in the cell cytoplasm during the experiments.
Describe the changes in the concentration of substance X in the cytoplasm of the cells incubated with the respiratory inhibitor present, during the five hours of the experiments. (2) Suggest an explanation for the changes you have described. (2)
Protein synthesis involves the process of transcription followed by translation. The diagram below shows part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. It shows a sequence of seven bases.
(i) Name the pyrimidine bases shown in this sequence. (1) (ii) Write down the sequence of bases on the strand of DNA that coded for this mRNA. (1) In some prokaryotic cells, the production of mRNA during transcription can occur at a rate of 50 bases per second. Calculate how long it would take to produce a mRNA molecule that coded for a protein containing 200 amino acids. Show your working. (3) Describe the process of translation. (5) In prokaryotic cells, a molecule of mRNA can be translated as soon as it is made. Suggest an explanation for this. (2)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cell Struc (Q)Documento26 pagineCell Struc (Q)rkblsistemNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY AND HEALTH SCIENCES EXERCISESDocumento10 pagineBIOLOGY AND HEALTH SCIENCES EXERCISESAKAYEZU Body santiveNessuna valutazione finora
- CSIR Life Sciences Paper 2 Model QuestionsDocumento12 pagineCSIR Life Sciences Paper 2 Model QuestionsImmanuel VinothNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 10thDocumento226 pagineBio 10thMukeshNessuna valutazione finora
- set-3 BiologyXIDocumento6 pagineset-3 BiologyXIavishank584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio QuestionsDocumento2 pagineBio QuestionsBrian MachariaNessuna valutazione finora
- As Task Checklistis Topics 1-4Documento9 pagineAs Task Checklistis Topics 1-4rkblsistemNessuna valutazione finora
- set-1_BiologyXIDocumento5 pagineset-1_BiologyXIavishank584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biof111 General Biology Total Marks: 90 (Closed Book) Duration: 90minDocumento5 pagineBiof111 General Biology Total Marks: 90 (Closed Book) Duration: 90minHetNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 3 Marks - ImpDocumento5 pagineBio 3 Marks - ImpmayyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry SAQsDocumento37 pagineBiochemistry SAQscarolinegatwiri08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Exam IDocumento10 paginePractice Exam IDavid KwonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2004 June Module 1Documento11 pagine2004 June Module 1navin-10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Practise Questions Unit 1 Module 2Documento16 pagineBiology Practise Questions Unit 1 Module 2ashtigosineNessuna valutazione finora
- General InstructionsDocumento4 pagineGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Test BankDocumento11 pagineChapter 11 Test Bankanon_747148947Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N RnaDocumento6 pagineHapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N Rnamaxwell amponsahNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper S5 BilogyDocumento8 pagineQuestion Paper S5 BilogyMutaganda Ami fideleNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Function MCQs and Codon TranslationDocumento5 pagineGene Function MCQs and Codon TranslationJon Hosmer0% (1)
- Ch. 3 Student Packet (A&P 1) With AnswerDocumento5 pagineCh. 3 Student Packet (A&P 1) With AnswerAlex ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Biology Exam Review Questions OnlyDocumento20 pagineAp Biology Exam Review Questions Onlyapi-57781915100% (1)
- 1.3 Reading GuideDocumento7 pagine1.3 Reading GuideriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP BIO EXAM ESSAY Q'SDocumento37 pagineAP BIO EXAM ESSAY Q'SBeatrice MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- BC1M01 2Documento2 pagineBC1M01 2Winnet MaruzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - 10 - First TermDocumento8 pagineBiology - 10 - First TermSuvadip SanyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Previous Years Public Exam Questions: Bio-Botany Section-B (3 Marks)Documento8 paginePrevious Years Public Exam Questions: Bio-Botany Section-B (3 Marks)sureshkumar1712Nessuna valutazione finora
- HL Test March 2014Documento11 pagineHL Test March 2014daniurresta67% (3)
- Unit 3 Exam CellsDocumento8 pagineUnit 3 Exam Cellsapi-110789702Nessuna valutazione finora
- BioK DP Notes 2.7Documento18 pagineBioK DP Notes 2.7Lal ÖzşahinNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential steps ribosome biogenesis eukaryotic cellsDocumento2 pagineEssential steps ribosome biogenesis eukaryotic cellsNgoc Minh NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- BiologytestDocumento4 pagineBiologytestEnz JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 6Documento4 pagineCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 6Unique InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento43 pagineUnit 1青木ケイNessuna valutazione finora
- Honors Biology - Final Exam Review, KirkpatrickDocumento4 pagineHonors Biology - Final Exam Review, KirkpatrickJoseph LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixed Worksheet - Paper 2 Section B - SLDocumento51 pagineMixed Worksheet - Paper 2 Section B - SLAditya RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisDocumento46 pagine1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisHuseyn AgazadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Biology QuestionsDocumento10 pagineStructural Biology QuestionsthebigdreemerNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Biology Olympiad English Part BDocumento6 pagine2015 Biology Olympiad English Part BInstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION On The MakingDocumento12 pagineCOMPREHENSIVE QUESTION On The Makingjose randyNessuna valutazione finora
- HL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingDocumento192 pagineHL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingFaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Biology 03 Chemistry of LifeDocumento30 pagineEssential Biology 03 Chemistry of LifeRic Tang100% (1)
- Biol2131asgn4 SWDocumento5 pagineBiol2131asgn4 SWAbhishek Isaac MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Combine PDFDocumento106 pagineCombine PDFМөнхгэрэл ГанбатNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 1 Chem 251 2011Documento6 pagineMidterm 1 Chem 251 2011Orlando CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Revision Ahh (2019)Documento10 pagineBiology Revision Ahh (2019)DJ Catcher QuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Essay QuestionsDocumento6 pagineBiology Essay Questionsintothelight2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Some Midterm Free ResponsesDocumento4 pagineSome Midterm Free Responsesjenh191Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Biology TestDocumento8 pagineEnglish Biology TestTesa TogatoropNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Term XI_26 marchDocumento6 pagineFinal Term XI_26 marchavishank584Nessuna valutazione finora
- set-2_ BiologyXIDocumento5 pagineset-2_ BiologyXIavishank584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aqa 74011 SQPDocumento24 pagineAqa 74011 SQPRobert EdwardsNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Article Synoptic QuestionsDocumento4 pagineScientific Article Synoptic QuestionsannishNessuna valutazione finora
- BICD 110 Wi15 Problem Set#1Documento7 pagineBICD 110 Wi15 Problem Set#1golemisgreeaaaatNessuna valutazione finora
- Microscope Lab Goals and OutcomesDocumento3 pagineMicroscope Lab Goals and OutcomesPaulina NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Beckers World of The Cell Chapter 14 Questions and Answers TestbankDocumento27 pagineBeckers World of The Cell Chapter 14 Questions and Answers TestbankiremsenakNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Exercise: Long QuestionDocumento12 pagineBiology Exercise: Long QuestionTing Fung Brenda ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ssabsa: 2004 BIOLOGYDocumento30 pagineSsabsa: 2004 BIOLOGYJennifer StanleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomedical Engineering Challenges: A Chemical Engineering InsightDa EverandBiomedical Engineering Challenges: A Chemical Engineering InsightNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Microscope: E.G. During DissectionDocumento2 pagineLight Microscope: E.G. During DissectionDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocumento15 pagineBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Organelles in Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 pagineOrganelles in Animal and Plant CellsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogenoalkanes TestDocumento4 pagineHalogenoalkanes TestDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Green ChemistryDocumento8 pagineGreen ChemistryDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Hours 1 Structure and BondingDocumento2 pagineStudy Hours 1 Structure and BondingDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Level Reaction RatesDocumento12 pagineAdvanced Level Reaction RatesDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts and Hydrocarbons PDFDocumento6 pagineBasic Concepts and Hydrocarbons PDFDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox Equilibria: ReviewDocumento10 pagineRedox Equilibria: ReviewMohamed HanafyNessuna valutazione finora
- IAL EntropyDocumento5 pagineIAL EntropystoopidNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table Group 2 NotesDocumento4 paginePeriodic Table Group 2 NotesDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- HalogenoalkaneDocumento2 pagineHalogenoalkaneDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- AlcoholsDocumento12 pagineAlcoholsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Green ChemistryDocumento8 pagineGreen ChemistryDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Enthalpy Changes ExplainedDocumento4 pagineEnthalpy Changes ExplainedDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- As Biology Core Practical 1Documento5 pagineAs Biology Core Practical 1Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogenoalkanes Structural IsomersDocumento5 pagineHalogenoalkanes Structural IsomersDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- HalogenoalkaneDocumento2 pagineHalogenoalkaneDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 2Documento2 paginePractical 2Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkanes & Alkenes NoteDocumento9 pagineAlkanes & Alkenes NoteDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table Group 2 NotesDocumento4 paginePeriodic Table Group 2 NotesDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocumento6 pagineBasic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDocumento8 pagineBIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 06Documento6 paginePractical 06Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Hours 1 Structure and BondingDocumento2 pagineStudy Hours 1 Structure and BondingDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- As Biology Core Practical 1Documento5 pagineAs Biology Core Practical 1Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDocumento8 pagineBIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- As Biology Core Practical 1Documento5 pagineAs Biology Core Practical 1Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- As Biology Core Practical 1Documento5 pagineAs Biology Core Practical 1Dr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effects of Oar-Shaft Stiffness andDocumento9 pagineThe Effects of Oar-Shaft Stiffness andValentina DiamanteNessuna valutazione finora
- CP I-O Modules PDFDocumento91 pagineCP I-O Modules PDFVlad ChioreanNessuna valutazione finora
- RenderingDocumento6 pagineRenderingJuno PajelNessuna valutazione finora
- r48 2000e3 Rectifier User ManualDocumento26 paginer48 2000e3 Rectifier User Manualjose luis rivera sotoNessuna valutazione finora
- MỘT SỐ CÂU HỎI TRẮC NGHIỆM ÁP DỤNG CHUYÊN ĐỀ GIỚI TỪ TRONG ĐỀ THI ĐHDocumento6 pagineMỘT SỐ CÂU HỎI TRẮC NGHIỆM ÁP DỤNG CHUYÊN ĐỀ GIỚI TỪ TRONG ĐỀ THI ĐHPhương ThảoNessuna valutazione finora
- AR M205 BrochureDocumento4 pagineAR M205 BrochurenickypanzeNessuna valutazione finora
- The War Archives - Machinery of Conflict. British Military Trucks of WWIIDocumento84 pagineThe War Archives - Machinery of Conflict. British Military Trucks of WWIISebastijan Kerše100% (10)
- Megger FORMDocumento1 paginaMegger FORMCOSMOPOLITAN M&ENessuna valutazione finora
- World Ranking For Industrial Trucks DHF 2015Documento2 pagineWorld Ranking For Industrial Trucks DHF 2015MA TotalforkliftNessuna valutazione finora
- Wattgate 381 Audio Grade Duplex Socket - y CableDocumento20 pagineWattgate 381 Audio Grade Duplex Socket - y Cableapi-11530725100% (1)
- DCT PIR insulation technical data sheetDocumento4 pagineDCT PIR insulation technical data sheetHenky MantophaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Din en 50155 (Vde 0115-200) - 2008-03Documento42 pagineDin en 50155 (Vde 0115-200) - 2008-03Collins Akhimien100% (1)
- Fischer Carbene Complexes in Organic SynthesisDocumento9 pagineFischer Carbene Complexes in Organic SynthesisNorah AltayyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete The Table With The Missing WordsDocumento2 pagineComplete The Table With The Missing WordssoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- CrankDocumento9 pagineCrankKresna BayuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Community School: Research Aspect 2 ReportDocumento13 pagineA Community School: Research Aspect 2 ReportMarsha MianNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.phase Feeding and Feeding SystemsDocumento21 pagine13.phase Feeding and Feeding SystemsAsfand Ali SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference UMDNS Codes PDFDocumento69 pagineReference UMDNS Codes PDFPumps RnDNessuna valutazione finora
- Naval Noise Psycho-Acoustic Backpropagation NNDocumento12 pagineNaval Noise Psycho-Acoustic Backpropagation NNSilvia FlorentinaNessuna valutazione finora
- AbstractsDocumento224 pagineAbstractsFrankmerced Emerzon Farfan HuancaNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual ConsoleDocumento45 pagineUser Manual Consoledhana0809Nessuna valutazione finora
- FH400 73158464 Pca-6.140Documento431 pagineFH400 73158464 Pca-6.140IgorGorduz100% (1)
- Ajhgaa English O6Documento28 pagineAjhgaa English O6dhirumeshkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Papaya Burger - Chapter 1 6Documento129 paginePapaya Burger - Chapter 1 6Nicole Velasco NuquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Estudio CarmenaDocumento11 pagineEstudio CarmenaAlfredo BalcázarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversification in Flavoured Milk: A ReviewDocumento6 pagineDiversification in Flavoured Milk: A ReviewInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 56 - Narration and SequenceDocumento14 pagineExercise 56 - Narration and SequenceLéoKostasNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Four Aspects of EmotionsDocumento13 pagineUnderstanding the Four Aspects of EmotionsRaymond FaeldoñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4: Input/Output Programming of 8051 CPUDocumento7 pagineChapter 4: Input/Output Programming of 8051 CPUIsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- NPC PrintPlay DeckDocumento19 pagineNPC PrintPlay DeckBenjamin Pappa Bach FossumNessuna valutazione finora