Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
sm9 007
Caricato da
Sadie HnatowDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
sm9 007
Caricato da
Sadie HnatowCopyright:
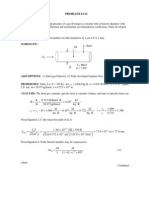
PROBLEM 9.
7
KNOWN: Large vertical plate with uniform surface temperature of 130C suspended in quiescent air at 25C and atmospheric pressure. FIND: (a) Boundary layer thickness at 0.25 m from lower edge, (b) Maximum velocity in boundary layer at this location and position of maximum, (c) Heat transfer coefficient at this location, (d) Location where boundary layer becomes turbulent. SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Isothermal, vertical surface in an extensive, quiescent medium, (2) Boundary layer assumptions valid. -6 2 PROPERTIES: Table A-4, Air Tf = ( Ts + T ) / 2 = 350K, 1 atm : = 20.92 10 m /s, k =
0.030 W/mK, Pr = 0.700. ANALYSIS: (a) From the similarity solution results, Fig. 9.4 (see above right), the boundary layer thickness corresponds to a value of 5. From Eqs. 9.13 and 9.12,
y = x ( Grx / 4 )
1/ 4
(1)
2 m 1 3 2 Grx = g ( Ts T ) x / = 9.8 (130 25 ) K x 3 / 20.92 106 m 2 / s = 6.718 109 x 3 2 350K s
(2)
1/ 4 3 y 5 ( 0.25m ) 6.718 109 ( 0.25 ) / 4 = 1.746 102 m = 17.5 mm.
(b) From the similarity solution shown above, the maximum velocity occurs at 1 with f ( ) = 0.275. From Eq. 9.15, find
(3) <
u=
2 1/2 2 20.92 106 m 2 / s 3 1/ 2 Grx f ( ) = 6.718 109 ( 0.25 ) 0.275 = 0.47 m/s. x 0.25m
y max = 1/ 5 (17.5 mm ) = 3.5 mm.
< <
The maximum velocity occurs at a value of = 1; using Eq. (3), it follows that this corresponds to a position in the boundary layer given as (c) From Eq. 9.19, the local heat transfer coefficient at x = 0.25 m is
1/ 4 1/ 4 3 Nu x = h x x/k = ( Grx / 4 ) g ( Pr ) = 6.718 109 ( 0.25 ) / 4 0.50 = 35.7 h x = Nu x k/x = 35.7 0.030 W/m K/0.25 m = 4.3 W/m 2 K.
The value for g(Pr) is determined from Eq. 9.20 with Pr = 0.700. (d) According to Eq. 9.23, the boundary layer becomes turbulent at xc given as
< <
Ra x,c = Grx,c Pr 109
1/ 3 = 0.60 m. x c 109 / 6.718 109 ( 0.700 )
COMMENTS: Note that = 1/Tf is a suitable approximation for air.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- sm9 012Documento2 paginesm9 012Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 14Documento82 pagineCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- CH 14Documento82 pagineCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 010Documento1 paginasm9 010Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 009Documento1 paginasm9 009Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 011Documento1 paginasm9 011Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 008Documento1 paginasm9 008Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 128Documento1 paginasm8 128Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 121Documento1 paginasm8 121Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 006Documento1 paginasm9 006Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 003Documento1 paginasm9 003Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 002Documento1 paginasm9 002Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 004Documento1 paginasm9 004Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 005Documento1 paginasm9 005Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm9 001Documento1 paginasm9 001Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 127Documento2 paginesm8 127Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 129Documento2 paginesm8 129Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 124Documento2 paginesm8 124Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 126Documento1 paginasm8 126Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 120Documento1 paginasm8 120Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 123Documento1 paginasm8 123Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 125Documento1 paginasm8 125Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 122Documento3 paginesm8 122Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 116Documento2 paginesm8 116Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 114Documento2 paginesm8 114Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 119Documento1 paginasm8 119Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 118Documento1 paginasm8 118Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 117Documento3 paginesm8 117Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- sm8 115Documento3 paginesm8 115Sadie HnatowNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)