Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
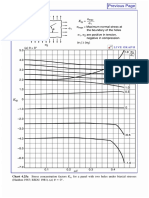
0.1 1 10 Chart 2.1 Stress Concentration Factors K: KTN KT
Caricato da
ysapeDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
0.1 1 10 Chart 2.1 Stress Concentration Factors K: KTN KT
Caricato da
ysapeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
rid
Infinite width
Ktn Ktn
h = Thickness
0.1
Chart 2.1
r/d
10
Stress concentration factors Ktn for opposite deep hyperbolic notches in an infinitely wide thin element in tension (Neuber, 1958).
Minr
Min r
Elliptical notch
U-shaped notch
**
Elliptical hole or U-shaped slot in an infinite thin element. Major axis of elliptical hole or U-shaped slot * 2t
tlr
Chart 2.2 Stress concentration factors Ktg for an elliptical or U-shaped notch in a semi-infinite thin element in tension (Seika 1960; Bowie 1966; Baratta and Neal 1970).
Ktg
Ktn
2r/H
Chart 2.3 Stress concentration factors Ktg and K1n for a tension strip with opposite semicircular edge notches (Isida 1953; Ling, 1968).
HId = 2
Ktn
#/d = 1.15
Semicircular (Isida 1953; Ling 1968)
For semicircular notch (t/r = 1.0)
rid
Chart 2.4 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a flat tension bar with opposite U-shaped notches (from data of Flynn and Roll 1966; Appl and Koerner 1969; Isida 1953; Ling 1968).
Ktn
Kt
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
d/H
0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
1.0
Chart 2.5 Stress concentration factors K1n for aflattension bar with opposite U-shaped notches (calculated using Neuber 1958 theory, Eq. 2.1), r/H from 0.001 to 0.05.
tn
a
max
1% stress increase rid Chart 2.6 Stress concentration factors K1n for aflattest specimen with opposite shallow U-shaped notches in tension (calculated using Neuber 1958 theory, Eq. 2.1).
Kt*
Ktu - Stress concentration factor for U notch (a = O) Kta = Stress concentration factor for corresponding V notch (Angle a)
Ktu
Chart 2.7 Stress concentration factors Kta for a flat tension bar with opposite V-shaped notches (from data of Appl and Koerner 1969).
Ktn
rid
Chart 2.8 Stress concentration factors Ktn for tension loading of a semi-infinite thin element with a deep hyperbolic notch, tension loading in line with middle of minimum section (approximate values; Neuber 1958).
Semicircular
4-1-05 a
-^ = 1.5,2 a
Ktn
rid
Chart 2.9 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a flat tension bar with a U-shaped notch at one side, (from photoelastic data of Cole and Brown 1958). Tension loading in line with middle of minimum section.
(a) aid = 0.25
Ktn
H-d = 2r
U-notch
rid
(b)a/d= 1.0
HId
Ktn
H-d = 2r
rid
Chart 2.10 Stress concentration factors Ktn for opposing notches with flat bottoms in finite-width flat elements in tension (Neuber 1958; Hetenyi and Liu 1956; Sobey 1965; ESDU 1981). (a) a/d = 0.25; (b)a/d = 1.0.
a = 2r
amax occurs at points A
rlt
Kt
alt
Chart 2.11
Stress concentration factors Kt for notches withflatbottoms in semi-infiniteflatelements in tension (Rubenchik 1975; ESDU 1981).
a/H-^0 (infinite width)
K-tn
b/a
Chart 2.12 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a tension bar with infinite rows of semicircular edge notches (from data of Atsumi 1958).
TJ- = (lsida 1953; Ling 1968) Single notch
Ktn
Four symmetrical notches 6/H=1
a/H
Chart 2.13 Stress concentration factors K1n for tension bar with infinite rows of semicircular edge notches (from data of Atsumi 1958).
1 Notch
Ktg
c/a
Chart 2.14 Stress concentration factors Ktg for tension case of aflatbar with semicircular andflatbottom notches, H/r = 18 (photoelastic tests by Durelli, Lake, and Phillips 1952).
Ktg For end notch 6 Notches (Photoelasticity, Hetenyi, 1943)
Ktg
Ktg For infinite | number of notches (H= ^\ Weber (1942) | | ^i ' Row of holes (Schulz, 1942)
Mathematical Solution
6 Notches (Photoelasticity, Hetenyi, 1943)
b/a
Chart 2.15 Stress concentration factors Ktg for tension case of aflatbar with semicircular notches, H/r = 18. (photoelastic tests by Durelli, Lake, and Phillips 1952).
Ktg
HIr
Chart 2.16 Stress concentration factors Ktg for tension case of aflatbar with two semicircular notches, b/a 2, c/a = 3 (from photoelastic tests by Durelli, Lake, and Phillips 1952).
Spherical depression
Ktg
Cylindrical groove
h0/h
Chart 2.17 Stress concentration factors Ktg for a uniaxially stressed infinite thin element with opposite shallow depressions (dimples) (Cowper 1962).
rid
Effect of Poisson's ratio
Infinity
Ktn Ktn
0.03
0.1
rid
10
Chart 2.18 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a deep hyperbolic groove in an infinitely wide member, three dimensional case, in tension (Neuber 1958 solution).
K-tn
Semicircular
rid
Chart 2.19 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a tension bar of circular cross section with a Ushaped groove. Values are approximate.
Ktn
Ktn
0.1
0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
d/D
0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
1.0
Chart 2.20 formulas).
Stress concentration factors Ktn for a grooved shaft in tension with a U-shaped groove, r/d from 0.001 to 0.05 (from Neuber 1958
^tn
1% stress increase
rid
Chart 2.21 Stress concentration factors Ktn for a test specimen of circular cross section in tension with a U-shaped groove (curves represent calculated values using Neuber 1958 theory).
(a) a/d = 0.25
Did
D-d = 2r
Ktn
U-groove
rid
(b)a/d = 1
Ktn
D-d = 2r
rid
Chart 2.22 Stress concentration factors Ktn for flat bottom grooves in tension (Neuber 1958 formulas; ESDU 1981). (a) a/d = 0.25; (b) a/d = I .
rid
Infinite width
Ktn
Ktn
h = Thickness
0.03
0.1
rid
10
Chart 2.23 Stress concentration factors Ktn for opposite deep hyperbolic notches in an infinitely wide thin element, two-dimensional case, subject to in-plane moments (Neuber 1958 solution).
Ktn
2r/H Chart 2.24 Stress concentration factors Ktn for bending of aflatbeam with semicircular edge notches (Isida 1953; Ling 1967).
HId = 2
H/d=^.2
Ktn
Semicircular (Isida 1953; Ling 1967)
For semicircular notch ( t / r = 1.0)
rid
Chart 2.25 Stress concentration factors Ktn for bending of a flat beam with opposite U notches, (from data of Frocht 1935; Isida 1953; Ling 1967).
Ktn
Ktn
0.1 0.2 0.3
0.4 0.5
d/H
0.6
0.7
0.8 0.9
1.0
Chart 2.26 formulas).
Stress concentration factors K1n for bending offlatbeam with opposite U notches, r/H from 0.001 to 0.05 (from Neuber 1958
Ktn
1% stress increase
rid
Chart 2.27 Stress concentration factors Km for bending of aflatbeam with opposite shallow U notches (curves represent calculated values using Neuber 1958 theory).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Article 1Documento9 pagineArticle 1archana100% (1)
- Sterengthening of Expansive Soil To Reduce Settlement: Smita G.M, Vishwanath C.SDocumento6 pagineSterengthening of Expansive Soil To Reduce Settlement: Smita G.M, Vishwanath C.SkertaningNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Coir Geotextile For Road Construction Some IssuesDocumento5 pagineApplication of Coir Geotextile For Road Construction Some IssuesChampakali DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Geotextiles inDocumento17 pagineApplication of Geotextiles inPrashant SunagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Geotextiles in IndiaDocumento14 pagineUse of Geotextiles in IndiaMahmood MuftiNessuna valutazione finora
- Coir Geo-Textiles PDFDocumento5 pagineCoir Geo-Textiles PDFEr Shubham JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Weight Aggregate Concrete by Using Coconut Shell: S. A. Kakade, Dr. A. W. DhawaleDocumento3 pagineLight Weight Aggregate Concrete by Using Coconut Shell: S. A. Kakade, Dr. A. W. DhawaleGelo LibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Study of Geotextile Effect On Improving Soil Bearing Capacity in Aggregate Surfaced Roads PDFDocumento7 pagineExperimental Study of Geotextile Effect On Improving Soil Bearing Capacity in Aggregate Surfaced Roads PDFmojeebmashalNessuna valutazione finora
- Coir Geotex in Rural RoadsDocumento43 pagineCoir Geotex in Rural RoadsKrishna PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- VI. Hasil Data Percobaan: Tegangan Terhadap ArusDocumento4 pagineVI. Hasil Data Percobaan: Tegangan Terhadap ArusHakim Achmad RifanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coir Geotextiles Are Eco Friendly and Economical Solution For Soil ErosionDocumento6 pagineCoir Geotextiles Are Eco Friendly and Economical Solution For Soil ErosionKrishna PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Using Coconut Fiber - An AlternativeDocumento4 pagineConcrete Using Coconut Fiber - An AlternativeSenthil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AAPA IG6 Selection and Design of Flexible Pavements ReducedDocumento68 pagineAAPA IG6 Selection and Design of Flexible Pavements Reducedrefika ivan0% (1)
- Coconuts: Coconut Bug Repellent and Coconut BiodieselDocumento25 pagineCoconuts: Coconut Bug Repellent and Coconut Biodieselvemcintosh219Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation For Cluster DS (O) 16Documento8 pagineCalculation For Cluster DS (O) 16Hamza NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Soil Mechanics Part IIDocumento34 pagineChapter 3 Soil Mechanics Part IImmNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Survey of A Selected Study Area in Somalilan-Wageningen University and Research 487916Documento150 pagineSoil Survey of A Selected Study Area in Somalilan-Wageningen University and Research 487916Nimco CadayNessuna valutazione finora
- L-05 Soil Survey of A Selected Study Area in SomalilandDocumento148 pagineL-05 Soil Survey of A Selected Study Area in SomalilandMohamed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- GeoTextiles PDFDocumento6 pagineGeoTextiles PDFAsım DavulcuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Coir Fiber. Discuss About The Polymeric Structrue of Different Cellulosic Fiber.Documento12 pagineAssignment On Coir Fiber. Discuss About The Polymeric Structrue of Different Cellulosic Fiber.Md. Mozammel Haque ShakibNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Franz PDFDocumento8 pagine10 Franz PDFJoanne WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Vibration of SDF SystemsDocumento14 pagineFree Vibration of SDF Systemspattrapong pongpattraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Fibre Reinforced Concrete - FinalDocumento24 pagineBio Fibre Reinforced Concrete - FinalHimalayJariwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Ménard Pressuremeter Modulus in Finite Element Models For Retaining Walls DesignDocumento11 pagineUse of Ménard Pressuremeter Modulus in Finite Element Models For Retaining Walls DesignAgustin MOLINERO GUERRANessuna valutazione finora
- Boulanger & Idriss - 2003Documento21 pagineBoulanger & Idriss - 2003suazologNessuna valutazione finora
- USCS For Engineering Purpose (ASTM D 2487)Documento1 paginaUSCS For Engineering Purpose (ASTM D 2487)Mohamad HartadiNessuna valutazione finora
- (Eng) Tutorial Input of Buckling LengthsDocumento30 pagine(Eng) Tutorial Input of Buckling LengthsVlad MosNessuna valutazione finora
- SP Os PL Cal 0004 Appendix ADocumento3 pagineSP Os PL Cal 0004 Appendix ARYZKI EFENDI SIMANULANGNessuna valutazione finora
- Unified Soil Classification System (USCS)Documento17 pagineUnified Soil Classification System (USCS)حسين عمران محيسنNessuna valutazione finora
- Cam-Clay Plasticity, Part II Implicit Integration of Constitutive Equation Based On A Nonlinear Elastic Stress PredictorDocumento16 pagineCam-Clay Plasticity, Part II Implicit Integration of Constitutive Equation Based On A Nonlinear Elastic Stress PredictorAyman AbedNessuna valutazione finora
- Estimation of Rock Mass Deformation Modulus Using Variations in Transmissivity and RQD With Depth PDFDocumento8 pagineEstimation of Rock Mass Deformation Modulus Using Variations in Transmissivity and RQD With Depth PDFmdanieeeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas For Computing Geometry and CriticalDocumento6 pagineFormulas For Computing Geometry and Criticalpramods_8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theory and Practice of The Fall Cone TestDocumento13 pagineTheory and Practice of The Fall Cone TestsivabathyNessuna valutazione finora
- ISSMGE BulletinDocumento47 pagineISSMGE BulletinAnders ModNessuna valutazione finora
- Metodo MRMRDocumento12 pagineMetodo MRMRRaul Carrasco PolancoNessuna valutazione finora
- GE June 1993 - Flownet Diagrams - The Use of Finite Differences and A Spreadsheet To Determine Potential Heads PDFDocumento7 pagineGE June 1993 - Flownet Diagrams - The Use of Finite Differences and A Spreadsheet To Determine Potential Heads PDFRajni SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Tensile Test Data Using MS ExcelDocumento22 pagineAnalysis of Tensile Test Data Using MS ExcelLokesh SangabattulaNessuna valutazione finora
- 428 The Red Book, Basics of Foundation Design 2023Documento548 pagine428 The Red Book, Basics of Foundation Design 2023Elisângela AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation: Design Notes and AssumptionDocumento4 pagineDissertation: Design Notes and AssumptionHamza NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Materials Lection - 9Documento13 pagineComposite Materials Lection - 9yigitciftci_Nessuna valutazione finora
- Large Deflections of Cantilever BeamsDocumento4 pagineLarge Deflections of Cantilever BeamsHasan Ayouby100% (1)
- Jgere 15 00002Documento31 pagineJgere 15 00002Jennifer MillerNessuna valutazione finora
- History of GeotextilesDocumento6 pagineHistory of Geotextilesachmad sidiq100% (1)
- GeoCops V1.0 PDFDocumento58 pagineGeoCops V1.0 PDFAdry SarijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interaction of Shotcrete With Rock and RockboltsDocumento16 pagineInteraction of Shotcrete With Rock and RockboltsJaime Salazar L100% (1)
- Ijser: Predicting (NK) Factor of (CPT) Test Using (GP) : Comparative Study of MEPX & GN7Documento8 pagineIjser: Predicting (NK) Factor of (CPT) Test Using (GP) : Comparative Study of MEPX & GN7chin_kbNessuna valutazione finora
- TCC81 Foundation PadsDocumento2 pagineTCC81 Foundation PadsMario Sajulga Dela CuadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian Method To Geotechnical Problems With Large DeformationsDocumento16 pagineApplications of Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian Method To Geotechnical Problems With Large DeformationsMarkoNessuna valutazione finora
- CIVE1129 - Lecture Notes - Bearing Capacity PDFDocumento14 pagineCIVE1129 - Lecture Notes - Bearing Capacity PDFLee Tin YanNessuna valutazione finora
- AutoCAD Structural Detailing - Formwork Drawings Users Manual PDFDocumento0 pagineAutoCAD Structural Detailing - Formwork Drawings Users Manual PDFEranda RanasinghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Engineering SyllabusDocumento27 pagineEnvironmental Engineering SyllabusSuganya PeriasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- 02C PDFDocumento27 pagine02C PDFFelipe MerchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chart 3.1 Stress Concentration Factors KDocumento25 pagineChart 3.1 Stress Concentration Factors KFelipe MerchanNessuna valutazione finora
- I°il - A - : o Maximum Normal Stress at The Boundary of The Holes Gi, CJ Positive in Tension, Negative in CompressionDocumento31 pagineI°il - A - : o Maximum Normal Stress at The Boundary of The Holes Gi, CJ Positive in Tension, Negative in CompressionFelipe MerchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Aid For Triangular Bracket Plates Using AISC SpecificationsDocumento10 pagineDesign Aid For Triangular Bracket Plates Using AISC Specificationsmaroco1098100% (7)
- Lab Session 2Documento7 pagineLab Session 2usamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Concentration FactorsDocumento30 pagineStress Concentration Factorssjois_hsNessuna valutazione finora
- 05Documento56 pagine05batmanbittuNessuna valutazione finora
- Reluctance: I. Magnetic Circuit ConceptDocumento12 pagineReluctance: I. Magnetic Circuit ConceptMahabub HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Vibration (A Beginners Guide)Documento151 pagineMachine Vibration (A Beginners Guide)mavric44493% (30)
- Measurement of Heavy Vehicle Dynamic Wheel Forces Using A Bolt-On Transducer - YangDocumento6 pagineMeasurement of Heavy Vehicle Dynamic Wheel Forces Using A Bolt-On Transducer - YangysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiated Sound Power Dome Shape PanelDocumento6 pagineRadiated Sound Power Dome Shape PanelysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- A DMAP Alter To Calculate The Contributions of Individual Modes in A Modal ComplexDocumento9 pagineA DMAP Alter To Calculate The Contributions of Individual Modes in A Modal ComplexkkayaturkNessuna valutazione finora
- B&K Structural TestingDocumento49 pagineB&K Structural TestingAshok100% (2)
- Ebook Dynamic Analysis of Structure Using Experimental Data PDFDocumento299 pagineEbook Dynamic Analysis of Structure Using Experimental Data PDFysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Bolt GroupsDocumento4 pagine17 Bolt GroupsPhalgun MoturuNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 RMS PDFDocumento4 pagine8 RMS PDFraymund12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Test IosipepcuDocumento9 pagineShear Test IosipepcuysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Centroid InertiaDocumento9 pagineCentroid InertiaMiguel PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Polygon Area and CentroidDocumento3 paginePolygon Area and CentroidSumann BallaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 14turbomachinery Design ConsiderationsDocumento36 pagineLesson 14turbomachinery Design ConsiderationsysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing PlanDocumento18 pagineMarketing PlanysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Area and Moment of Inertia of A PolygonDocumento2 pagineArea and Moment of Inertia of A PolygonysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Airplane Dynamics ModelingDocumento27 pagineAirplane Dynamics ModelingysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- $$AD A273 Test Method PDFDocumento188 pagine$$AD A273 Test Method PDFysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Loan Processing Service in Low-Cost-CountryDocumento28 pagineLoan Processing Service in Low-Cost-CountryysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Bolt GroupsDocumento4 pagine17 Bolt GroupsPhalgun MoturuNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Bolt GroupsDocumento4 pagine17 Bolt GroupsPhalgun MoturuNessuna valutazione finora
- Area and Moment of Inertia of A PolygonDocumento2 pagineArea and Moment of Inertia of A PolygonysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 SlidingcontactbearingsDocumento43 pagine13 SlidingcontactbearingsMohammad AamirNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Computational AeroelasticityDocumento56 pagineComputational AeroelasticityysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Industry Practice To Migrate Risks in Financial Service OutsourcingDocumento24 pagineIndustry Practice To Migrate Risks in Financial Service OutsourcingysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- WrittenArticle Budgeting Nov4Documento4 pagineWrittenArticle Budgeting Nov4ysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview Airtraffic 1Documento16 pagineOverview Airtraffic 1ysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- CoupleLoadSystemAnalysisTheory CraigBamptonMethod.Documento26 pagineCoupleLoadSystemAnalysisTheory CraigBamptonMethod.ysapeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element ModelsDocumento22 pagineA Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element ModelsTomaspockNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Analysis of Students Competencea in Mathematics and Their Performance in Physics Among Students in Secondary School in NigeriaDocumento47 pagineA Comparative Analysis of Students Competencea in Mathematics and Their Performance in Physics Among Students in Secondary School in NigeriaAyomipo OlorunniwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol Prism 1Documento2 pagineVol Prism 1Moneyball7Nessuna valutazione finora
- PV Row SpacingDocumento2 paginePV Row Spacingpandi27100% (1)
- Third Periodical Test Math 9Documento3 pagineThird Periodical Test Math 9Ma Elena ClaroNessuna valutazione finora
- ScaraDocumento8 pagineScararwurdigNessuna valutazione finora
- Model QP With SolutionDocumento90 pagineModel QP With SolutionMurali Karthik VNessuna valutazione finora
- JIF 419 - Webex 1 (10.9.2016) - Structure of A CrystalDocumento22 pagineJIF 419 - Webex 1 (10.9.2016) - Structure of A CrystalmareasanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- TeselasiDocumento15 pagineTeselasiMohd Rizal Abdul HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Voice LeadingDocumento46 pagineVoice Leadingvicher2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paq r17-m2 PDFDocumento9 paginePaq r17-m2 PDFpamani1981freeNessuna valutazione finora
- CG - Unit-II MCQDocumento23 pagineCG - Unit-II MCQSE 18 Ganesh pawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle1 PDFDocumento8 pagineCircle1 PDFSweet EmmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cad Commands LibraryDocumento11 pagineCad Commands LibraryAvdija HamzićNessuna valutazione finora
- Jem Foundation Schools Summative Assessment I 2012-2013 Subject-Maths STD - IvDocumento3 pagineJem Foundation Schools Summative Assessment I 2012-2013 Subject-Maths STD - IvhusnsonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Himpunan Buka Dan Himpunan TutupDocumento8 pagineHimpunan Buka Dan Himpunan Tutupred 16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Resonance-Kinematics PDFDocumento60 pagineResonance-Kinematics PDFAnuj jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Riley Dynamics PDFDocumento253 pagineSolucionario Riley Dynamics PDFElsa Vasquez VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento154 pagineChapter 3Lucas WeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 30149Documento5 pagine3 30149ali_raza117Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics: Grade 7 PhysicsDocumento68 pagineKinematics: Grade 7 PhysicsHaryanti Putri RizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key Cat-1Documento2 pagineAnswer Key Cat-1adityaemmanuel1313Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel MATH Sstudent Book2 IGCSE UNIT 9Documento10 pagineEdexcel MATH Sstudent Book2 IGCSE UNIT 9kashifmushirukNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncert Sol c12 Maths ch11Documento64 pagineNcert Sol c12 Maths ch11Nishchay GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Curvilinear Motion: General & Rectangular Components: Today's ObjectivesDocumento19 pagineCurvilinear Motion: General & Rectangular Components: Today's ObjectivesAtef NazNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics Detailed Final Exam NotesDocumento43 pagineBiomechanics Detailed Final Exam Notesmasoud masoudiNessuna valutazione finora
- TCET FE EM Resource Book (2020-2021)Documento272 pagineTCET FE EM Resource Book (2020-2021)KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Algebra 1 19Documento3 pagineFinal Algebra 1 19Le KienNessuna valutazione finora
- Periyar University: B.Sc. MathematicsDocumento64 paginePeriyar University: B.Sc. MathematicsSiva SankaranNessuna valutazione finora
- GeogebraDocumento14 pagineGeogebradominic lumberioNessuna valutazione finora
- 511 Mat1 - 2019Documento8 pagine511 Mat1 - 2019King YashasNessuna valutazione finora