Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Topic 3-190912 - 110426
Caricato da
gunungledang84Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Topic 3-190912 - 110426
Caricato da
gunungledang84Copyright:
Formati disponibili
COURSE NOTES
COURSE TITLE COURSE CODE
: :
INTRODUCTION TO CHILD DEVELOPMENT EPD 1063 MAIZATUL AKHMA SAAT TOPIC 3
COURSE LEADER : CHAPTER :
COURSE: EPD 1063/INTRODUCTION TO CHILD DEVELOPMENT FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
TOPIC 3: Pre-natal Development
3.0
Introduction - What is conception? Conception begins with a process of fertilization. Fertilization is defined as follows: Fertilization: is the process by which the sperm and the ovum (the male and female gametes) combine through sexual intercourse, in-vitro fertilization, or artificial insemination (test tube) to create a single cell called ZYGOTE, which then duplicates itself again and again by cell division (replication) to form a baby when the gestation period is completed. In human, it is a 9 months period.
3.1
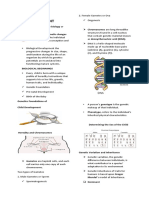
Gene Gene is the basic unit of heredity or building block (first observed and proposed by Watson and Cricks) that contain all hereditary material passed from the biological parents to their children. This gene is coded in the sperm and the ovum as described above. Thus, the children will inherit of the gene from the each of their biological parents to form a complete set of gene determining various characteristics such as hair colours, eye colours, some inherited diseases, and etc. Each cell in human body contains an estimated 60000 to 100000 genes, which are made of the chemical DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA). DNA is unique because it represents the genetic building block or signature. No two DNAs from two individuals are alike. Currently, modern technology enables the use of DNA to associate individuals who are related to each other. Other instances include the use of DNA in Crime Scene Investigation (CSI) to validate the presence of individuals in any crime scenes.
COURSE: EPD 1063/INTRODUCTION TO CHILD DEVELOPMENT FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
3.2
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA as described above carries the biochemical instructions (building blocks) that tell the cells how to make the proteins that enable them to carry out each specific body function. DNA is a string of helical combinations of bio-chemical building blocks. Each combination will produce certain Since the number of possible characteristics of the individuals.
combinations is large, thus, it is near impossible that two individuals will produce the same DNA. This is the basic of all building blocks in mankind.
3.3
What determines sex? A baby will inherit 23 chromosomes from the sperm and another 23 chromosomes from the ovum. Together, they formed 23 such pairs. Inherited birth defects will arise if extra chromosomes are formed during the formation of zygote. This results in down syndrome or mongolism first found by Mendel. 22 pairs are AUTOSOMES; these chromosomes that are not related to sexual expression 23rd pair is related to the sex chromosomes (1 from the father and 1 from the mother, which governed the babys sex). responsible to determine the sex of the baby. Therefore, the father is Further, the chances of
producing a female and a male baby is 50 %: 50 % respectively. Thus, there is no inclination on the potential of producing male baby over female baby. Any combinations of X with X will give rise to female individual and any combinations of X with Y will result in male individual. This is as shown below:
MOTHER (XX)
FATHER (XY)
COURSE: EPD 1063/INTRODUCTION TO CHILD DEVELOPMENT FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
BABY GIRL (XX)
BABY BOY (XY)
3.4
Prenatal development There are three (3) stages of prenatal development: 1) Germinal Stage (Fertilization to 2 weeks) First 2 weeks of prenatal development is characterized by rapid cell division, increasing complexity and differentiation and implantation in the wall of the uterus.
2) Embryonic Stage (2 8 weeks) Second stage of gestation (2 8 weeks) is characterized by rapid growth and development of major body systems and organs. Rapidly and constantly developing organs, and major body system; this includes respiratory, digestive and central nervous system. At this point in time, the embryo is the most vulnerable and critical period. This explains the critical time during the first trimester of pregnancy. The success rate of the embryo surviving this stage develops to a full individual is much higher upon completion of this embryonic stage. Normally defective embryos rarely survive beyond the first trimester, or 3 months period, and we call it a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. This is
COURSE: EPD 1063/INTRODUCTION TO CHILD DEVELOPMENT FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
nature way of propagating healthy offspring. Charles Darwin calls it the Theory of Natural Selection where the fittest will survive.
3)
Fetal Stage (8 weeks to birth) o Final stage of gestation (from 8 weeks to birth) is characterized by increased detail of body parts and greatly enlarged body size. o Fetus grows very rapidly where organs and body systems become more complex and grows 20 times compare to its previous length. o Fetus started to breathe, kicking, and hiccups as well as sucking their thumbs. o Scientist and the doctors can observe the fetal movement and development through ultrasound technology. o Ultrasound can reveal the sex of the fetus as well
3.5
Tutorial activity 1) How does conception normally occur? 2) How does heredity operate in determining sex and transmitting normal and abnormal traits? 3) What role do heredity and environment play in physical health, intelligence and personality?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY by Prof NGASSAPADocumento315 pagineESSENTIALS OF HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY by Prof NGASSAPAJumbe Mohamed100% (3)
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocumento141 pagineGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third Weekmutumamiguel15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio. HWDocumento4 pagineBio. HWTeya Bautista75% (4)
- Cad Module 11 PDFDocumento7 pagineCad Module 11 PDFGecelo Ceniza0% (2)
- Life's Greatest MiracleDocumento2 pagineLife's Greatest MiracleJessa Mae Cuenco50% (4)
- 100 Conceptions NewDocumento250 pagine100 Conceptions NewRa ViNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EmbryologyDocumento3 pagineIntroduction To EmbryologyDr Md Abedur Rahman100% (3)
- Animals and Plant ReproductionDocumento56 pagineAnimals and Plant ReproductionZyan Subaan VacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter#3 Developmental PsychologyDocumento32 pagineChapter#3 Developmental Psychologyfatima bilalNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Abpd1203 T3Documento20 pagine07 Abpd1203 T3Kelly LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 7 Hand OutsDocumento4 pagineWEEK 7 Hand OutsZia DipzNessuna valutazione finora
- DP Chap 3Documento8 pagineDP Chap 3fatima bilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof Ed2editedDocumento60 pagineProf Ed2editedEdelyn CuriosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesDocumento45 pagineBiological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesFrance BejosaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Basic Concepts of Human Reproduction and Biological / Developmental IssuesDocumento52 pagineThe Basic Concepts of Human Reproduction and Biological / Developmental Issues-------Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Ed. 1 - Module 10Documento6 pagineProf. Ed. 1 - Module 10Jomar NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 101 (Sim-Sdl) - 49-77Documento29 pagineEduc 101 (Sim-Sdl) - 49-77Joselle VillarbaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocumento142 pagineGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekSalma LyambilaNessuna valutazione finora
- EmbryogenesisDocumento9 pagineEmbryogenesisSanchita SabatNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocumento11 pagineModule 4 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarkhill Veran TiosanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dev Psych - Module 2Documento4 pagineDev Psych - Module 2The Lyric ListsNessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC9 Module 4Documento10 pagineEDUC9 Module 4Jomarc Cedrick GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocumento143 pagineGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekSam MumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module - Wk3&4 - The Psychological DevelopmentDocumento18 pagineModule - Wk3&4 - The Psychological Developmentaudree d. aldayNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocumento11 pagineModule 4 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesWai MagnayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tayabas Western Academy: Date SubmittedDocumento6 pagineTayabas Western Academy: Date SubmittedPaul Arvin DeChavez LimboNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocumento32 pagineDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMelanie SerquiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3A - PRENATAL PERIOD-2Documento27 pagineUnit 3A - PRENATAL PERIOD-2iamsathya2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Guide: Introduction To EmbryologyDocumento23 pagineLecture Guide: Introduction To EmbryologyAldrin Hardy PabloNessuna valutazione finora
- moduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorDocumento11 paginemoduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorRecxs Baludio AtchaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genealogy and Genetics ApaDocumento14 pagineGenealogy and Genetics Apamabro1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 101 ReviewerDocumento27 pagineEduc 101 ReviewerRolando AmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocumento21 pagineDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMay ann AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 (13) Lifespan Psychology ModDocumento10 pagineUnit-2 (13) Lifespan Psychology Modashish1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - PDF - Download For Offline ViewingDocumento24 pagineChapter 3 - PDF - Download For Offline ViewingJavier De SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Sped Lesson 1 3Documento10 pagineChapter 4 Sped Lesson 1 3jessaroxiehernaezcastenNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentDocumento5 pagineModule 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentRachel Joy SaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdf&rendition 1Documento29 paginePdf&rendition 1saravanan.kavinilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 31Documento18 pagineGroup 31Venus Camelon GastallaNessuna valutazione finora
- The First Nine MonthsDocumento9 pagineThe First Nine MonthsSayeed KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - The Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesDocumento19 pagineChapter 4 - The Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesELOISA N. CASANE100% (1)
- The Prenatal Development.. PPT PresentationDocumento38 pagineThe Prenatal Development.. PPT PresentationalexandravisteriaNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodDocumento42 pagineUNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodJenno Lloyd Samaniego DariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of The Learners at Various Stages Unit 1: Pre-Natal PeriodDocumento4 pagineDevelopment of The Learners at Various Stages Unit 1: Pre-Natal PeriodDarlene Dacanay David67% (3)
- Unit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Documento94 pagineUnit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Charm MarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocumento15 pagineHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Caadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Documento36 pagineCaadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Joan Rosanne CaadlawonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bsed Fil 1101 - Ed101 - Module 11 - Group 5Documento19 pagineBsed Fil 1101 - Ed101 - Module 11 - Group 5Jessabelle D CasanovaNessuna valutazione finora
- HiiDocumento19 pagineHiiTruptimayiGiriNessuna valutazione finora
- ED 101 Module 10 Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento16 pagineED 101 Module 10 Prenatal DevelopmentCreamy VanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 4 - Week 2 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocumento7 pagineMODULE 4 - Week 2 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarsha MGNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive BehaviorDocumento10 pagineReproductive Behavioryosramr636Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Natal Development: Life Before Birth The Growth of An Unborn ChildDocumento44 paginePre Natal Development: Life Before Birth The Growth of An Unborn ChildEdward Ian BelmesNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 101.module 11Documento8 pagineEduc 101.module 11Avigale VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Early Detection 1Documento12 pagineEarly Detection 1Tiara Anggun NurartoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 ReviewerDocumento10 pagineLesson 2 ReviewerFerlynne Marie BernardinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Natal Development PDFDocumento23 paginePre Natal Development PDFMae Catampatan ArceoNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Biology: Solved Assignment-How Do Organisms Reproduce?Documento12 pagine10th Biology: Solved Assignment-How Do Organisms Reproduce?pnkj232Nessuna valutazione finora
- PIIS0002937823001564Documento2 paginePIIS0002937823001564Kalaivathanan VathananNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 Fertilization, Implantation and Fetal DevelopmentDocumento17 pagineLesson 4 Fertilization, Implantation and Fetal DevelopmentAPRIL ALAPNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocumento59 pagine2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2018Documento36 pagineAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2018Mridula PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sgi Biology Evolution Activity 10Documento17 pagineSgi Biology Evolution Activity 10CLARISSE BERNADETTE GIGATARASNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer: Chapter 1 Introduction To Scientific InvestigationDocumento13 pagineAnswer: Chapter 1 Introduction To Scientific InvestigationhidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection - ICSI.Documento9 pagineIntracytoplasmic Sperm Injection - ICSI.layyousNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocumento10 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Report of PJBL (Organa Genitalia)Documento17 pagineFinal Report of PJBL (Organa Genitalia)NASYWANessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 - Second Summative TestDocumento3 pagineQ2 - Second Summative TestMilagros ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of AmphioxusDocumento59 pagineDevelopment of AmphioxusDyah Ayu PuspitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Documento11 pagineHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fish Bio E CourseDocumento175 pagineFish Bio E CoursePratik KalbandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Centre October 10, 2017Documento66 pagineStudy Centre October 10, 2017Joshua BlackNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report BiologyDocumento8 pagineLab Report BiologyFatin NabilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Perpetuation of LifeDocumento59 paginePerpetuation of LifeJhon Jeyno Rabia CabanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan For DemoDocumento8 pagineLesson Plan For DemoAriel BadanaNessuna valutazione finora
- G11 LifeSciences DigitalSupport Web Practice Examination Paper 2-10Documento8 pagineG11 LifeSciences DigitalSupport Web Practice Examination Paper 2-10LISA LUFUSONessuna valutazione finora
- Short Vowel SoundsDocumento87 pagineShort Vowel SoundsKimberly Kate PurasNessuna valutazione finora
- HSC Biology Module 5 NotesDocumento15 pagineHSC Biology Module 5 Notesarabellatav23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Second Periodical Test in Science 7Documento3 pagineSecond Periodical Test in Science 7tolisNessuna valutazione finora
- @aakashdelhi02: Test - 1Documento12 pagine@aakashdelhi02: Test - 1Eetisha MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science (Mains MCQ Part-2)Documento24 pagineScience (Mains MCQ Part-2)Rajat KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical Issues in Nigeria's Healthcare System 2011Documento19 pagineEthical Issues in Nigeria's Healthcare System 2011Dan BingelNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Chapter - (Reproduction in Animals) Class 8 PDFDocumento11 pagineScience Chapter - (Reproduction in Animals) Class 8 PDFKhushi Kumari class 9 adm 664Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilization in Sea Urchin PDFDocumento2 pagineFertilization in Sea Urchin PDFJasime100% (1)
- 10bja Medsci - Mckenzie CheyneDocumento60 pagine10bja Medsci - Mckenzie Cheyneapi-284323075Nessuna valutazione finora
- Competency 3 DoneDocumento2 pagineCompetency 3 Doneapi-264474189Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0004.Documento6 pagineWa0004.ojas goyalNessuna valutazione finora
- SDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Documento28 pagineSDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Ma Concepcion Adriano GuansingNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 7Documento27 pagineBiology Unit 7joyNessuna valutazione finora