Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
E2 Lab 9 6 2 Instructor
Caricato da
mmcgugan75Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
E2 Lab 9 6 2 Instructor
Caricato da
mmcgugan75Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Lab 9.6.
2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab (Instructor Version)
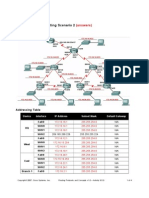
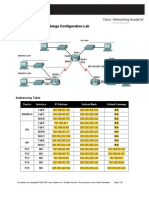
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device Interface Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 BRANCH1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 BRANCH2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 IP Address 172.16.0.1 192.168.1.17 192.168.1.21 209.165.200.225 172.16.2.1 192.168.1.18 192.168.1.25 172.16.3.1 192.168.1.26 192.168.1.22 172.16.2.254 172.16.1.254 172.16.3.126 Subnet Mask 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.128 Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 172.16.2.1 172.16.0.1 172.16.3.1
PC1 PC2 PC3
NIC NIC NIC
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Create an efficient VLSM design given requirements. Assign appropriate addresses to interfaces and document. Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state. Configure routers including EIGRP. Configure and propagate a static default route. Verify EIGRP operation. Test and verify full connectivity. Reflect upon and document the network implementation.
Scenario
In this lab activity, you will be given a network address that must be subnetted using VLSM to complete the addressing of the network shown in the Topology Diagram. A combination of EIGRP routing and static routing will be required so that hosts on networks that are not directly connected will be able to communicate with each other. EIGRP must be configured so that all IP traffic takes the shortest path to the destination address.
Task 1: Subnet the Address Space.
Step 1: Examine the network requirements. The addressing for the network has the following requirements: The 172.16.0.0/16 network must be subnetted to provide addresses for the three LANs. The HQ LAN will require 500 addresses. The BRANCH1 LAN will require 200 addresses. The Branch 2 LAN will require 100 addresses.
The loopback address representing the link between the HQ router and the ISP will use the 209.165.200.224/30 network. The 192.168.1.16/28 address space must be subnetted to obtain the addresses for the links between the three routers.
Step 2: Consider the following questions when creating your network design: How many subnets need to be created from the 172.16.0.0/16 network? _______ 3 How many total IP addresses are required from the 172.16.0.0/16 network? _______ 800 What subnet mask will be used for the HQ LAN subnet? _______________________________________ 255.255.254.0 or /23 What is the maximum number of host addresses that could be used on this subnet? _______ 510 What subnet mask will be used for the BRANCH1 LAN subnet? ___________________________________ 255.255.255.0 or /24 What is the maximum number of host addresses that could be used on this subnet? _______ 254 What subnet mask will be used for the BRANCH2 LAN subnet? ___________________________________ 255.255.255.128 or /25 What is the maximum number of host addresses that could be used on this subnet? _______126
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
What subnet mask will be used for the links between the three routers? ___________________________ 255.255.255.252 or /30 What is the maximum number of host addresses that could be used on each of these subnets? _____ 2 Step 3: Assign subnetwork addresses to the Topology Diagram. 1. Assign subnet 0 of the 172.16.0.0/16 network to the HQ LAN subnet. What is the network address of this subnet? ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/23 2. Assign subnet 1 of the 172.16.0.0/16 network to the BRANCH1 LAN subnet. What is the network address of this subnet? ________________________________________ 172.16.2.0/24 3. Assign subnet 2 of the 172.16.0.0/16 network to the BRANCH2 LAN subnet. What is the network address of this subnet? ________________________________________ 172.16.3.0/25 4. Assign subnet 0 of the 192.168.1.16/28 network to the link between the HQ and BRANCH1 routers. What is the network address of this subnet? ________________________________________ 192.168.1.16 /30 5. Assign subnet 1 of the 192.168.1.16/28 network to the link between the HQ and BRANCH2 routers. What is the network address of this subnet? ________________________________________ 192.168.1.20 /30 6. Assign subnet 2 of the 192.168.1.16/28 network to the link between the BRANCH1 and BRANCH2 routers. What is the network address of this subnet? _________________________________ 192.168.1.24 /30
Task 2: Determine Interface Addresses.
Step 1: Assign appropriate addresses to the device interfaces. 1. Assign the first valid host address of the 209.165.200.224/30 network to the Loopback interface on the HQ router. 2. Assign the first valid IP address of the HQ LAN network to the LAN interface of the HQ router. 3. Assign the last valid IP address of the HQ LAN network to PC2. 4. Assign the first valid IP address of the BRANCH1 LAN network to the LAN interface of the BRANCH1 router. 5. Assign the last valid IP address of the BRANCH1 LAN network to PC1. 6. Assign the first valid IP address of the BRANCH2 LAN network to the LAN interface of the BRANCH2 router. 7. Assign the last valid IP address of the BRANCH2 LAN network to PC3. 8. Assign the first valid IP address of the HQ to BRANCH1 link network to the Serial 0/0/0 interface of the HQ router. 9. Assign the last valid IP address of the HQ to BRANCH1 link network to the Serial0/0/0 interface of the Branch router. 10. Assign the first valid IP address of the HQ to BRANCH2 link network to the Serial 0/0/1 interface of the HQ router. 11. Assign the last valid IP address of the HQ to BRANCH2 link network to the Serial0/0/1 interface of the Branch router.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
12. Assign the first valid IP address of the BRANCH1 to BRANCH2 link network to the Serial 0/0/1 interface of the BRANCH1 router. 13. Assign the last valid IP address of the BRANCH1 to BRANCH2 link network to the Serial0/0/0 interface of the BRANCH2 router. Step 2: Document the addresses to be used in the table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Task 3: Prepare the Network.
Step 1 Cable a network that is similar to the one in the Topology Diagram. You can use any current router in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in the topology. Step 2 Clear any existing configurations on the routers.
Task 4: Perform Basic Router Configurations.
Perform basic configuration of the BRANCH1, BRANCH2, HQ, and ISP routers according to the following guidelines: 1. Configure the router hostname. 2. Disable DNS lookup. 3. Configure an EXEC mode password. 4. Configure a message-of-the-day banner. 5. Configure a password for console connections. 6. Configure a password for VTY connections. 7. Synchronize unsolicited messages and debug output with solicited output and prompts for the console and virtual terminal lines. 8. Configure an EXEC timeout of 15 minutes.
Task 5: Configure and Activate Serial and Ethernet Addresses.
Step 1: Configure the interfaces on the HQ, BRANCH1, and BRANCH2 routers. Configure the interfaces on the HQ, BRANCH1, and BRANCH2 routers with the IP addresses from the table provided under the Topology Diagram. When you have finished, be sure to save the running configuration to the NVRAM of the router. Step 2: Configure the Ethernet interfaces. Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3 with the IP addresses from the Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Task 6: Verify Connectivity to Next-Hop Device.
You should not have connectivity between end devices yet. However, you can test connectivity between two routers and between an end device and its default gateway. Step 1: Verify connectivity of routers. Verify that the HQ, BRANCH1, and BRANCH2 routers can ping each of the neighboring routers across the WAN links.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
Step 2: Verify connectivity of PCs. Verify that PC1, PC2, and PC3 can ping their respective default gateways.
Task 7: Configure EIGRP Routing on the BRANCH1 Router.
Consider the networks that need to be included in the EIGRP updates that are sent out by the BRANCH1 router. What directly connected networks are present in the BRANCH1 routing table? ________________________________________ 172.16.2.0 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.16 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.24 Will these networks need to have the subnet mask information included in the network statements? __________ yes What commands are required to enable EGIRP and include the connected networks in the routing updates? ________________________________________ router eigrp 1 ________________________________________ network 172.16.2.0 0.0.0.255 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.3 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.24 0.0.0.3 What command is required to enable EGIRP to include the VLSM information instead of summarizing routes at the classful boundary? ________________________________________ no auto summary Are there any router interfaces that do not need to have EIGRP updates sent out? __________ yes What command is used to disable EIGRP updates on these interfaces? ________________________________________ passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
Task 8: Configure EIGRP and Static Routing on the HQ Router.
Consider the type of static routing that is needed on HQ. A static default route will need to be configured to send all packets with destination addresses that are not in the routing table to the loopback address representing the link between the HQ router and the ISP. What command is needed to accomplish this? ________________________________________ ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 loopback1 What directly connected networks are present in the HQ routing table? ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.16 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.20 ________________________________________ 209.165.200.224
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
Will the networks of the HQ LAN and the links between the BRANCH1 and BRANCH2 routers need to have the subnet mask information included in the network statements? __________ yes What commands are required to enable EGIRP and include the appropriate networks in the routing updates? ________________________________________ router eigrp 1 ________________________________________ network 172.16.0.0 0.0.1.255 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.3 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.20 0.0.0.3 What command is required to enable EGIRP to include the VLSM information instead of summarizing routes at the classful boundary? ________________________________________ no auto summary Are there any router interfaces that do not need to have EIGRP updates sent out? __________ yes What command is used to disable EIGRP updates on this interface? ________________________________________ passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 The HQ router needs to send the default route information to the BRANCH1 and BRANCH2 routers in the EIGRP updates. What command is used to configure this? ________________________________________ redistribute static
Task 9: Configure EIGRP Routing on the BRANCH2 Router.
Consider the networks that need to be included in the EIGRP updates that are sent out by the BRANCH2 router. What directly connected networks are present in the BRANCH2 routing table? ________________________________________ 172.16.3.0 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.20 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.24 Will these networks need to have the subnet mask information included in the network statements? __________ yes What commands are required to enable EGIRP and include the connected networks in the routing updates? ________________________________________ router eigrp 1 ________________________________________ network 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.127 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.20 0.0.0.3 ________________________________________ network 192.168.1.24 0.0.0.3 What command is required to enable EGIRP to include the VLSM information instead of summarizing routes at the classful boundary? ________________________________________ no auto summary Are there any router interfaces that do not need to have EIGRP updates sent out? __________ yes
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
What command is used to disable EIGRP updates on these interfaces? ________________________________________ passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
Task 10: Verify the Configurations.
Answer the following questions to verify that the network is operating as expected: From PC1, is it possible to ping PC2? __________ yes From PC1, is it possible to ping the PC3? __________ yes The answer to the above questions should be yes. If any of the above pings failed, check your physical connections and configurations. Refer to your basic troubleshooting techniques used in the Chapter 1 labs. What EIGRP routes are present in the routing table of the BRANCH1 router? ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/16 Summary ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/23 ________________________________________ 172.16.3.0/25 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.0/24 Summary ________________________________________ 192.168.1.20/30 ________________________________________ 0.0.0.0/0 What is the gateway of last resort in the routing table of the BRANCH1 router? ________________________________________ 192.168.1.17 to network 0.0.0.0 What EIGRP routes are present in the routing table of the HQ router? ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/16 Summary ________________________________________ 172.16.2.0/24 ________________________________________ 172.16.3.0/25 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.0/24 Summary ________________________________________ 192.168.1.24/30 What is the gateway of last resort in the routing table of the HQ router? ________________________________________ 0.0.0.0 to network 0.0.0.0 What EIGRP routes are present in the routing table of the BRANCH2 router? ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/16 Summary ________________________________________ 172.16.0.0/23 ________________________________________ 172.16.2.0/24 ________________________________________ 192.168.1.0/24 Summary ________________________________________ 192.168.1.16/30 ________________________________________ 0.0.0.0/0 What is the gateway of last resort in the routing table of the BRANCH2 router? ________________________________________ 192.168.1.21 to network 0.0.0.0
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 8
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: EIGRP
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
Task 11: Reflection
Why is it necessary to use disable automatic summarization with this network design? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ If the routes in the routing table are summarized at the classful network boundary 17.16.0.0, the paths between the three routers will all have an equal cost and packets may not be sent using the route with the least hops.
Task 12: Document the Router Configurations.
On each router, capture the following command output to a text (.txt) file and save for future reference. Running configuration Routing table Interface summarization
Task 13: Clean Up
Erase the configurations and reload the routers. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 8 of 8
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocumento10 pagineE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorOkta WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subnetting ActivityDocumento5 pagineSubnetting ActivityaldreymartirezggNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9.1: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design: Topology DiagramDocumento6 pagineLab 9.1: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design: Topology DiagramRecky JimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- TRS2251 Routing and Switching: Name: ID No: Date: Lab 3: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design (3 %)Documento5 pagineTRS2251 Routing and Switching: Name: ID No: Date: Lab 3: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design (3 %)Kavilan RrNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 Lab 9 6 2Documento8 pagineE2 Lab 9 6 2Ninja NuggetNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 8 OspfDocumento10 pagineExperiment 8 OspfMoa AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Te Va A Servir en Cisco V2Documento4 pagineTe Va A Servir en Cisco V2Bryant GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 Lab 11 6 2 InstructorDocumento10 pagineE2 Lab 11 6 2 InstructorRuben De La CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: KULIAH 13: Lab 2.8.2Documento10 pagineFakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: KULIAH 13: Lab 2.8.2029 Dias Djati AbabilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2.8.2. Challenge Static Route ConfigurationDocumento7 pagineLab 2.8.2. Challenge Static Route ConfigurationwpadididiNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 Lab 7 5 2 InstructorDocumento8 pagineE2 Lab 7 5 2 Instructoryang210% (1)
- RipDocumento7 pagineRipchastinebayubayNessuna valutazione finora
- EIGRP E2 Lab 9 6 2Documento8 pagineEIGRP E2 Lab 9 6 2bubuxErickNessuna valutazione finora
- TP Atelier Reseau 2Documento8 pagineTP Atelier Reseau 2EMMANUEL MANGALANessuna valutazione finora
- 8215 Lab Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing SchemeDocumento13 pagine8215 Lab Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Schemeabood azizNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayDocumento9 pagineLab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayMartin O'grady0% (1)
- Jaringan Komputer: SEPTEMBER 1, 2017Documento11 pagineJaringan Komputer: SEPTEMBER 1, 2017Aulia Ahlam MardhotillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDocumento14 pagineLab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology Diagramdepeters3183Nessuna valutazione finora
- Herhesh OPSFDocumento12 pagineHerhesh OPSFSeboNessuna valutazione finora
- Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDocumento5 pagineSubnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramJermyn G EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDocumento4 pagineLab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDat LCNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 Lab 7 5 2Documento8 pagineE2 Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab AnswersDocumento3 pagineLab AnswersShi RoNessuna valutazione finora
- FixDocumento4 pagineFixReza FahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2.1.5 Lab - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing SchemeDocumento12 pagine8.2.1.5 Lab - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing SchemeVictor Andrei Villegas Ramos80% (5)
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento4 pagineLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramAnjasa Keisar EtienNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Long Test, Computer Science 4: Task 1: Subnet The Address SpaceDocumento4 pagine2 Long Test, Computer Science 4: Task 1: Subnet The Address SpaceMark Anthony FauneNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocumento4 pagineLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.5.2 Subnetting Scenario 1Documento5 pagineLab 3.5.2 Subnetting Scenario 1Edgar Alejandro Ramirez100% (3)
- E2 Lab 3 5 3Documento8 pagineE2 Lab 3 5 3Ninja Nugget100% (1)
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento4 pagineLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramMunkieBoneZNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge InstructionsJerry FullerNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyDocumento2 paginePacket Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyMaula DawilahNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 Lab 1 5 3Documento4 pagineE2 Lab 1 5 3jocko18100% (1)
- 7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1Documento9 pagine7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1белимNessuna valutazione finora
- Devoir - TP Packet Tracer Maintenance AvancéeDocumento56 pagineDevoir - TP Packet Tracer Maintenance AvancéeXenosNessuna valutazione finora
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamDa EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Computer Local Networks ReportDa EverandPersonal Computer Local Networks ReportNessuna valutazione finora
- Token Ring Technology ReportDa EverandToken Ring Technology ReportNessuna valutazione finora
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDa EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxDa EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- CompTIA Network+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Exam N10-008Da EverandCompTIA Network+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Exam N10-008Nessuna valutazione finora
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDa EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNessuna valutazione finora
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101Da EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Da EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ethernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementDa EverandEthernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GDa EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Da EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- 5G Explained: Security and Deployment of Advanced Mobile CommunicationsDa Everand5G Explained: Security and Deployment of Advanced Mobile CommunicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDa EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingDa EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNessuna valutazione finora
- StarLAN Technology ReportDa EverandStarLAN Technology ReportValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Software Networks: Virtualization, SDN, 5G and SecurityDa EverandSoftware Networks: Virtualization, SDN, 5G and SecurityNessuna valutazione finora
- Ne40e X8a/x16aDocumento8 pagineNe40e X8a/x16aRiwandetaMuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- MikroTik Routers and WirelessDocumento7 pagineMikroTik Routers and WirelessRubin LudiNessuna valutazione finora
- ACI MultiSite Forwarding CheatSheetDocumento2 pagineACI MultiSite Forwarding CheatSheetravi kantNessuna valutazione finora
- CiscoDocumento37 pagineCiscoTomCat1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Preparation Notes by Tayyab A SheikhDocumento68 pagineCCNA Preparation Notes by Tayyab A SheikhRana Tauqeer AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab3 VLSM1Documento5 pagineLab3 VLSM1Богдан РомановичNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Pools - RouterOS - MikroTik DocumentationDocumento3 pagineIP Pools - RouterOS - MikroTik DocumentationBayu RomadiNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Addressing and Subnetting ExerciseDocumento2 pagineIP Addressing and Subnetting Exercisesharaz afzal100% (1)
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstructorDocumento6 pagine3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.3.1.1 Packet Tracer - Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using CLI - InstructorDocumento8 pagine9.3.1.1 Packet Tracer - Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using CLI - InstructorEric Martial AZOMBO BALLANessuna valutazione finora
- ASA 8.3 - 8.4 Dynamic NAT - PAT Overload Migration Lab Guide - Lab 1.0Documento7 pagineASA 8.3 - 8.4 Dynamic NAT - PAT Overload Migration Lab Guide - Lab 1.0Péter BeleznayNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual: Ac750 Wifi RouterDocumento138 pagineUser Manual: Ac750 Wifi RouterKevin KimNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1 Cloud Solution Architect Sec 04 Chap 002 VPC V03 - DEMO Slides PDFDocumento7 pagine8.1 Cloud Solution Architect Sec 04 Chap 002 VPC V03 - DEMO Slides PDFPeter L. MontezNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 1 - 0xxxxxxDocumento13 pagineTest 1 - 0xxxxxxjamal jNessuna valutazione finora
- FortiGate-100A Quick Start GuideDocumento2 pagineFortiGate-100A Quick Start GuiderobotsallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fortigate CookThe FortiGate Cookbook 5.2Documento512 pagineFortigate CookThe FortiGate Cookbook 5.2Jociano BaumNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)Documento3 pagineCisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)CCNAResourcesNessuna valutazione finora
- CFGMML-BSC0-10 41 24 23-20160909030102Documento2.945 pagineCFGMML-BSC0-10 41 24 23-20160909030102Riga Wahyu AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1Documento6 pagineLab 1Shehbaz TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- B 163 Consolidated 3850 CGDocumento3.082 pagineB 163 Consolidated 3850 CGKalan KlNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Use VPCS in GNS3Documento5 pagineHow To Use VPCS in GNS3Ict labNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSM ExerciseDocumento3 pagineVLSM Exercisekashi nath DebNessuna valutazione finora
- Mtcre - I PDFDocumento5 pagineMtcre - I PDFSilvano F. Rocha100% (1)
- Url Profile Results 200128194836Documento1.601 pagineUrl Profile Results 200128194836Wafiboi O. EtanoNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersDocumento22 pagine12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersiqmalkuaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring Load Balancing On The GGSNDocumento28 pagineConfiguring Load Balancing On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.4.3 Packet Tracer - Basic Device ConfigurationDocumento2 pagine10.4.3 Packet Tracer - Basic Device ConfigurationDan jonesNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA / CCNP Routing The Total Guide For All IOS Commands: Ross From The Networks BlogDocumento52 pagineCCNA / CCNP Routing The Total Guide For All IOS Commands: Ross From The Networks BlogRajesh GatlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch7 - Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: Topology DiagramDocumento4 pagineCh7 - Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: Topology DiagramEsau AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- R 4Documento10 pagineR 4Ramon PirbuxNessuna valutazione finora