Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
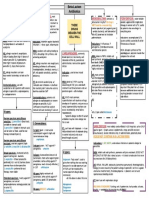
Antibiotics - Pathogen Chart
Caricato da
Yanling LiCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Antibiotics - Pathogen Chart
Caricato da
Yanling LiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AEROBES GNC CDK, TDK, AUCDK? P. vulgaris (Indole +) P. mirabilis (indole -) GNB Enterococcus faecalis Aceinetobacter spp.
Streptococcus spp. Enterobacter spp. GPC MRSA / MRSE (3%) GPB VRSA, VREF, VRE L. monocytogenes GPB
ANAEROBES GNB Atypical organisms
Salmonella spp.
Citrobacter spp.
MSSA / MSSE
N.meningitidis
P. aeruginosa
M. catarrhalis
H. influenzae
Shigella spp.
Serratia spp.
C. difficile
Klebsiella
Cloxacillin Penicillin Amoxicillin/Ampicillin Amoxicillin-Clavulanate
1 1
C C C C C C C C
2
T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T
25%
30%
B. fragilis
E. coli
PHM321Y ANTIBIOTICS
N. gonorrhoeae
Piperacillin-Tazobactam
Cephalexin/Cefadroxil/Cefazolin
2
Cefuroxime/Cefprozil/Cefaclor
2
Cefoxitin
40%
Ceftriaxone/Cefotaxime
3
C C C C C C C C C C C C C S S S S S S S C
Ceftazidime
3 4
DIM
17%
Cefixime Cefepime
Ceftobiprole
DIM
DIM
30
%
Carbapenems (DIME)
5
Gylcopeptides (VT) Daptomycin
O
3-13%
CO M M
Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim Fluoroquinolones (CON) Resp. Fluoroquinolones (LM) Aminoglycosides (TAG) Metronidazole Clindamycin Macrolides (ACE) Linezolid
3 4
T C A C C T T
C L
C
30-50%
syn syn
syn
Oral anaerobes
Cidal or Static?
AC AC
Nitrofurantoin
syn
syn
Chloramphenicol
6
Tetracyclines (TDM) Tigecycline Rifampin
syn
syn
syn
syn
PO only; IV only, both the drug has weak coverage or there is high resistance (25%) against the drug Risk of resistance given if mentioned in class these bugs have the potential to produce BSBLs (SPACE PEK bugs) and Pip/Tazo is not effective against BSBLs Enterococcus faecium is more resistant than Enterococcus faecalis against these drugs (carbapenems are not effective against E. faecium) DIME = doripenem, imipenem-cilastatin, meropenem, ertapenem CON = ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin; LM = levofloxacin, moxifloxacin; TAG = tobramycin, amikacin, gentamicin; ACE = azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin TDM = tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline syn = synergy ( 2x extent of killing compared to best agent alone) GPB = gram-positive bacilli GPC = gram-positive cocci GNB = gram-negative bacilli GNC = gram-negative cocci
1 2 3 5 4 6
Never use as a single agent: combine with aminoglycosides Only Ceftriaxone covers N. gonorrhoeae Only used in cystitis or recurrent UTI prophylaxis Glycopeptides: vancomycin, telavancin cidal against H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, N. meningitides cidal against S. pnuemoniae, S. epidermis. Does not cover Proteus spp. = drug of choice against species (bold font) Atypical Organisms Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Pneumocystitis carinii (HIV)
weak or unreliable activity against pathogen, do not use as 1st line treatment
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Legionella pneumoniae
Chlamydia trachomatis
Clamydia pneumoniae
Mycobacterium spp.
Rickettisia spp.
Brucella spp.
ORAL ANAEROBES Peptococcus Peptostreptococcus Fusobacterium Bacteroides spp. GNB THAT CAN PRODUCE BROAD SPECTRUM BETALACTAMASES (BSBLs) SPACE PEK:
Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim Fluoroquinolones (CON) Fluoroquinolones (LM) Macrolides (ACE) Tetracyclines (TDM) Chloramphenicol Rifampin CO O L CO CO
syn
syn
syn
Serratia marcescens Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acinobacter spp. Citrobacter spp. Enterobacter spp.
Proteus spp. Escherichia coli Klebsiella spp. (K. pneumoniae)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftDocumento10 pagineAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Antibiotic Chart FinalDocumento1 paginaAntibiotic Chart FinalJosh GardnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Chart FINALDocumento2 pagineAntibiotic Chart FINALjoed34543Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemotherapy NDocumento28 pagineChemotherapy NFaisal MehboobNessuna valutazione finora
- AntimicrobialsDocumento1 paginaAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocumento31 pagineTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 200 Drug ExamDocumento1 paginaTop 200 Drug ExamUyen V. NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lile Bai 1: Area/Site Common Organism Useful Abx Other NotesDocumento3 pagineLile Bai 1: Area/Site Common Organism Useful Abx Other NotesNicole BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Abx FinalDocumento3 pagineAbx Finalyanks1120Nessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal Drug InteractionsDocumento3 pagineHerbal Drug InteractionsFaradina Zulaili Ifa EvendyNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Documento16 pagineOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases IDocumento7 pagineInfectious Diseases ITiff VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics ChartDocumento10 pagineAntibiotics Chartadom09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFDocumento20 pagineBpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFVenny Tri Pahlevi IINessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocumento5 pagineNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocumento2 pagineDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Dosing For OTCsDocumento5 paginePediatric Dosing For OTCsCareyTranNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacist's Letter: Prescriber's LetterDocumento6 paginePharmacist's Letter: Prescriber's LetterJaved AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocumento16 pagineCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocumento3 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Antibiotic PrescribingDocumento1 paginaAntibiotic PrescribingJay KayNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousDocumento1 paginaDRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousJoseph De JoyaNessuna valutazione finora
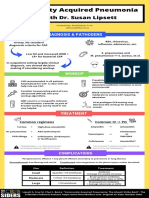
- With Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaWith Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaJayantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic GuideDocumento6 pagineAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocumento6 pagineAntibioticsOccamsRazor100% (1)
- Pedia Stickers PDFDocumento8 paginePedia Stickers PDFAshNessuna valutazione finora
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Documento48 pagineNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm I - Abx ChartDocumento4 paginePharm I - Abx ChartNicole BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Inhibit Clasification Antibiotics: (Broad Spectrum) (Narrow Spectrum)Documento1 paginaInhibit Clasification Antibiotics: (Broad Spectrum) (Narrow Spectrum)SY WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Medication MOA Side Effects: Intranasal SteroidsDocumento2 pagineClass Medication MOA Side Effects: Intranasal SteroidsChron MedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocumento4 paginePain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocumento1 paginaBeta Lactam AntibioticsCourtney TownsendNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Side EffectsDocumento2 pagineDrug Side EffectsAngelic khanNessuna valutazione finora
- PCOL Maps PDFDocumento11 paginePCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated Antibiotic Chart - 2016 PDFDocumento2 pagineUpdated Antibiotic Chart - 2016 PDFmugenzi eric100% (1)
- Top 200 Expanded 1Documento27 pagineTop 200 Expanded 1Dean HarperNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX ReviewDocumento72 pagineBrand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX Reviewbapimirab654Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChartDocumento5 pagineChartWesley CooperNessuna valutazione finora
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocumento6 paginePrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocumento28 pagineA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Empirical Prescribing Chart GlasgowDocumento1 paginaEmpirical Prescribing Chart GlasgowHariharan Narendran75% (4)
- Drug CardDocumento1 paginaDrug CardPaul AlfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- AntibioticsDocumento11 pagineAntibioticsSeshu Kelam100% (2)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocumento18 paginePharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Pharm Drug ListDocumento17 paginePharm Drug Listanon_523534678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brad Hinton CVDocumento6 pagineBrad Hinton CVapi-486072801Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Positive Cocci (GPC) Gram Neg (Rods GNR) Anaerobes Atypicals Classification AntibioticDocumento2 pagineGram Positive Cocci (GPC) Gram Neg (Rods GNR) Anaerobes Atypicals Classification AntibioticRami RaedNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocumento1 paginaDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNessuna valutazione finora
- AntibioticGuidelines PrimaryDocumento12 pagineAntibioticGuidelines PrimaryHandriyato SukmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocumento28 pagineReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Know Common Disease ManagementDocumento14 pagineKnow Common Disease Managementcdx25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics 101Documento49 pagineAntibiotics 101Tony VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Classification of Drugs: A Quick Reference GuideDa EverandStructural Classification of Drugs: A Quick Reference GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDa EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Da EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookDa EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (9)
- Clinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionDocumento12 pagineClinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionhalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic 1 PDFDocumento2 pagineAntibiotic 1 PDFmicheal1960Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Use of Antibiotics in Surgical PatientsDocumento58 pagineThe Use of Antibiotics in Surgical PatientsajcheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reclaimer Inspection ReportDocumento51 pagineReclaimer Inspection ReportThiru Malpathi100% (1)
- User's Manual Eco Friendly Park BenchDocumento35 pagineUser's Manual Eco Friendly Park BenchAmirulHanif AlyahyaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Panna CottaDocumento3 pagineHow To Make Panna CottaBintNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Composites PDFDocumento14 pagine3 Composites PDFKavya ulliNessuna valutazione finora
- MS Fresher HR DocumentDocumento4 pagineMS Fresher HR DocumentJahanvi KambojNessuna valutazione finora
- Corp Given To HemaDocumento132 pagineCorp Given To HemaPaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Make Swiss RollDocumento16 pagineMake Swiss RollFelicia LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Publication PDFDocumento152 paginePublication PDFAlicia Mary PicconeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantDocumento26 pagineNursing Care of A Family With An InfantJc GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM Report CIA 3Documento5 pagineHRM Report CIA 3SUNIDHI PUNDHIR 20221029Nessuna valutazione finora
- AdEasy Adenoviral Vector SystemDocumento43 pagineAdEasy Adenoviral Vector SystemDaniel PintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jean-Pierre Wybauw - Fine Chocolates 2 - Great Ganache Experience-Lannoo (2008)Documento209 pagineJean-Pierre Wybauw - Fine Chocolates 2 - Great Ganache Experience-Lannoo (2008)Mi na100% (1)
- Ir33+ Range: ... Continuity, Innovation and DesignDocumento4 pagineIr33+ Range: ... Continuity, Innovation and DesignbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Textiles and Clothing Industry On EnvironmentDocumento15 pagineImpact of Textiles and Clothing Industry On Environmentranjann349Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trophic Levels - 10% RuleDocumento5 pagineTrophic Levels - 10% RulerebbiegNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 WaterDocumento32 pagine2.2 WaterHelena GlanvilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Odor From A Landfill Site On Surrounding Areas: A Case Study in Ho Chi Minh City, VietnamDocumento11 pagineImpact of Odor From A Landfill Site On Surrounding Areas: A Case Study in Ho Chi Minh City, VietnamNgọc HảiNessuna valutazione finora
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin FoxDocumento32 pagineStreptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin Foxdanish sultan100% (1)
- Exercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Documento2 pagineExercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Nuraina NabihahNessuna valutazione finora
- People v. Jerry BugnaDocumento1 paginaPeople v. Jerry BugnaRey Malvin SG PallominaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2457-Article Text-14907-2-10-20120724Documento6 pagine2457-Article Text-14907-2-10-20120724desi meleniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastDocumento106 pagineMarine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastSyed Najam Khurshid100% (1)
- Eprubete. Culori. UtilizareDocumento3 pagineEprubete. Culori. UtilizareCuCUNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes About BurnsDocumento11 pagineNotes About BurnsMichelle Ann GacudNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 EN AdvancedBootkitTechniquesOnAndroid ChenZhangqiShendiDocumento66 pagine2014 EN AdvancedBootkitTechniquesOnAndroid ChenZhangqiShendihombre pocilgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Dosage Form Part 1Documento48 pagineSolid Dosage Form Part 1Claire Marie AlvaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Knopp2017 Article OnceACheaterAlwaysACheaterSeriDocumento11 pagineKnopp2017 Article OnceACheaterAlwaysACheaterSeriAnda F. CotoarăNessuna valutazione finora
- Carapace DigitalDocumento15 pagineCarapace DigitalVillain ChatNessuna valutazione finora
- Radfet DatasheetDocumento6 pagineRadfet DatasheetNicholas EspinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- q5 Nursery SchoolDocumento4 pagineq5 Nursery SchoolPK CheahNessuna valutazione finora