Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Brake System
Caricato da
Sumit KatwalTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Brake System
Caricato da
Sumit KatwalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BRAKE SYSTEM
1. Items of brakes and pneumatic auxiliaries to be attended in different schedules 1.1 Weekly: a. Air/vaccum System : i. Check the operation of automatic and independent brakes .maximum brake cylinder pressure should be 3.5+-0.1 kg/cm3. ii. Vaccum level against 35mm thick plate with engine running at idling .speed should not be less than 48cm. iii. The governer should cut out the compressor at 8kg/cm2 and cut in 7kg/cm2. iv. The shafety valve should start blowing at 8.5kg/cm2. v. Drain oil separator dirt collector. b. Brake cylinders i. Check piston travel of brake cylinder. It should not exceed 127mm with bloks and 10 mm gap b/w the brake wheels 1.2 Monthly: 1.2.1 air/vaccum system a. check the charging time of main reservoir.the pressure should rise from 0 to 8 kg/cm2 is not more than 6 minute with engine running at idiling speed. b. check and record the time for independent brake application and release. i. for brake cyclinder pressure to build up from 0 to 3.3kg/cm2 in 4-6 sec. ii. Time for brake cyclinder to fall from 3.5 to 0.4 kg/cm2 In 4.8 sec. c. check the operation of exhauster for creation of vaccum in the train pipe.it should be possible to obtain minimum of 48cm vaccum in train pipe against 6.35mm and against dummy the vaccum level should not rise beyond 50.5cm of Hg with engine running at idling speed. When the engine Speed is raised to maximum,the vaccum level against dummy should not be more than 51.5cm of Hg
d. check the operation on automatic brake valve in application and release. i. application the brake cyclinder should build up from 0 to 3.3 kg/cm2 in 912 sec. ii. release the brake cylinder pressure should fall from 3.5 to 0.4 kg/cm2 in 1015 sec 1.2.2 compressor intake filter & exhauster filter: Remove and cleans the filter element.
1.3 Quaterly: a. Air/Vaccum gauges: calliberate all the vaccum/air gauges and replace the defective units. b.Brake cyclinder lubricate the brake cyclinders.
1.4
Half yearly: a. Winds shields wipers Lubricate air chamber parts.
b. Isolating cocks and angle cocks Plugs which are shaggish should be removed, cleaned and lubricated With recommended lubricant. 1.5 Yearly:
a. Air/Vaccum system: Dismantle,clean,repair and replace the worn out parts and grease sliding parts of the following: i. Independent brake valve
ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. b.
Automatic brake valve Vaccum air proportion valve Double check valve Pressure reducing valve Strainer and check valve Loco brake releasing valve Compressor governor Automatic shut off valve Magnet valve Brake cylinder:
Remove the brake cylinder from locomotive, dismantle all compoNents,clean piston packing and check for abrassion and wear, Lightly lubricate the following parts before assembly:
i. Inside of cylinder cover, ii. Piston head with guide tip and spring, iii. The inner valve of cylinder.
c. Pneumatic auxiliaries: Dismantle ,clean repair and replace worn out parts and grease Grease sliding parts of the following: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Pneumatic control valve Sanding valve Sand ejector Automatic shut-off valve Push button valve Horn operating valve Horn
viii. ix.
Relay valve Sand ejectors
1.6 1.
Two Yearly: Air reservoirs: Clean and test hydraulically the air reservoirs. The hydraulic Pressure should be 1.5 times the maximum working pressure 8.5kg/cm2
2.
MAINTENANCE OF BRAKE GEARING:
i. Brake Hangers and Cross Beam : In maintaining the hangers and the cross beams it is of atmost Importance to ensure that they are in proper alignment . The alignment Generally gets disturbed due to excessive or unusual wear of the Hanger and cross beam bushes. Hamgers are provided with steel bush Which can be easily changed in shed . ii. Brake pull Rods: Generally all pull rods are so arranged that they are in tension and Normally they should not get bent . check & ensure that the pull rods are Straight . check for elongation of pull rods holes . change pull rods with Elongated holes when the provisions of bushing is not there.
iii.Adjustment of brake Eigging: Brake riggings are to be adjusted when brake blocks are worn.
If the clearance between the tyre and the brake bloc become 20mm the Brake rigging is to be adjusted.
WORKING PRINCIPLES 1. When diesel engine is started the power control handle remains in O or idle position and the engine runs at idiling speed . transmission oil filling pump draws the oil from the oil sump and delivers the oil through pipe ,heat exchanger and filter to the transmission control unit . the pressure relief valve is to be adjusted to limit the oil pressure to a maximum of 5 atms . when engine is idiling and when the torque convertor is empty. Oil under this pressure is also fed through a branch line into the convertor throttle valve . the oil pressure acts under piston (6). At the same time air at 6kg/cm2 pressure acts under piston (7). And lift the piston rod to its top most position. This movement causes the ports(2) to completely open for the turbine-side-oil to flow into the sump. Noew if the power control handle is slightly moved to start the locomotive after shifting the transmission switch(44) into IN position ,then ,the oil starts flowing into the convertor through the control unit. Owing to the idiling, the system pressure sharply falls from 3 to 1kg/cm2. Further as this oil is also freely through the ports (2) into the oil sump, suffient oil pressure cannot build up in the system and the torque convertor remains partially filled. The pressure in the system and hence the quantity of oil in the convertor can be increased by slowly moving the power control handle to LOW position. This increases the control air pressure from 0 to 2 atm . and corresponding increase in the filling oil pressure is about 2kg/cm2 with increased engine/pump rpm. At 2 atm pressure of control air,the relay valve (54) stops the air supply to the convertor throttle valve. This brings the piston (7) immediately to its bottom position by the action of the sprng (9).As the pre tension of springs is more than the force acting under the piston(6) due to 2kg/cm2 of oil pressure, the throttling piston(4) will reach its bottom most position fully covering the ports (2). Now, as the oil
flowing from turbine end is not by passed through the throttle valve, the oil quickly fills the convertor and builds- up pressure in the system. This gradually increases the pressure from 2kg/cm2 to a maximum of 3 kg/cm2 for which the relief valve (47) is set. At about 2.7kg/cm2 of oil pressure the throttling piston (4) is lifted by the piston (6) and ports (2) are slightly opened to by-pass the oil into the sump.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Overhauling Air Compressor On ShipsDocumento12 pagineOverhauling Air Compressor On ShipsTun Lin Naing100% (3)
- Advance Workshop Exam SolvedDocumento41 pagineAdvance Workshop Exam SolvedVinesh ThulasyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sezione 2 PDFDocumento8 pagineSezione 2 PDFMAZZI1978100% (1)
- Turbocharger Maint, Cleaning & SurgingDocumento5 pagineTurbocharger Maint, Cleaning & SurgingSayem kaif100% (1)
- Boiler Feed PumpDocumento11 pagineBoiler Feed PumpSolai100% (2)
- 5brake System Englisg-G9165Documento28 pagine5brake System Englisg-G9165George Jhonson90% (10)
- 912 Oil ChangeDocumento4 pagine912 Oil ChangeGaberNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 - Purejet EngineDocumento44 pagine9 - Purejet EngineРуслан МужиковNessuna valutazione finora
- Các Phương Pháp KH I Đ NG Nói ChungDocumento30 pagineCác Phương Pháp KH I Đ NG Nói ChungVuong PhanNessuna valutazione finora
- IMP Main Engine and Aux EngineDocumento37 pagineIMP Main Engine and Aux EngineLOKINessuna valutazione finora
- CompressorDocumento8 pagineCompressorLOKINessuna valutazione finora
- Turbonetics Installation InstructionsDocumento4 pagineTurbonetics Installation Instructionscharles whiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To The EJC 65 Hydraulic System: GeneralDocumento50 pagineGuide To The EJC 65 Hydraulic System: GeneralSanti Al ElricNessuna valutazione finora
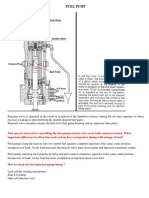
- Fuel PumpDocumento4 pagineFuel PumpRajesh Kumar100% (2)
- Slide Type Fuel ValveDocumento14 pagineSlide Type Fuel ValveNitin Sharma93% (14)
- Gravely Convertible 76 Service Manual 1174Documento30 pagineGravely Convertible 76 Service Manual 1174ducatiss900100% (1)
- 10 - Starting and ReversingDocumento4 pagine10 - Starting and ReversingAisha Zaheer100% (3)
- Engine Systems InspectionDocumento29 pagineEngine Systems InspectionGetachew Tikue100% (1)
- 清洗吸污车说明书 (1) 1 9 translateDocumento11 pagine清洗吸污车说明书 (1) 1 9 translateumerNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To CompressorDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To CompressorRam VollalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ford CarbDocumento27 pagineFord Carbsmcdonald2536100% (1)
- h2 Cooling & Seal Oil System Stage-2Documento13 pagineh2 Cooling & Seal Oil System Stage-2raghavendran raghu100% (1)
- Testing of Engines - 0Documento12 pagineTesting of Engines - 0S lenkaNessuna valutazione finora
- C210 WML 206Documento20 pagineC210 WML 206Efrén SantínNessuna valutazione finora
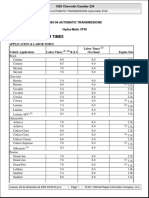
- Automatic Transmission NAG1 - Fluid and FilterDocumento4 pagineAutomatic Transmission NAG1 - Fluid and FilterKrivega88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Precautions To Avoid Barring Gear StallingDocumento2 paginePrecautions To Avoid Barring Gear StallingSrinivas BudatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Robinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601Documento32 pagineRobinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601MarcWorld100% (1)
- Turbine Shutting Down From Full LoadDocumento7 pagineTurbine Shutting Down From Full Loadrohit_0123100% (1)
- Cessna 172 POHDocumento27 pagineCessna 172 POHbrentgardnerNessuna valutazione finora
- 1959 Cessna 172 ManualDocumento25 pagine1959 Cessna 172 ManualRoberto Fernandez Sanzo100% (1)
- EOOW - Orals Questions & AnswersDocumento54 pagineEOOW - Orals Questions & Answersnkosithandile Vuke100% (1)
- Maintenance and Repair of Fuel Suppply, Lubrication and Cooling System Fuel Pump TestingDocumento12 pagineMaintenance and Repair of Fuel Suppply, Lubrication and Cooling System Fuel Pump TestingAdarsh AnilNessuna valutazione finora
- Induction and Airflow PDFDocumento4 pagineInduction and Airflow PDFmellon3duwenNessuna valutazione finora
- IAMI Revision Answers Motor and GeneralDocumento26 pagineIAMI Revision Answers Motor and GeneralStewart LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Eci Manual PDFDocumento28 pagineEci Manual PDFtrongNessuna valutazione finora
- Mep Oral AnswersDocumento28 pagineMep Oral AnswersAshjo Gamer100% (1)
- Carburetor Troubleshooting Repair Guide For HondaDocumento9 pagineCarburetor Troubleshooting Repair Guide For HondaRoyal ENessuna valutazione finora
- 04 05 Hydraulic System LG956LDocumento82 pagine04 05 Hydraulic System LG956LGeorge Jhonson100% (2)
- TT CapriDocumento12 pagineTT CapriLuis A. Rivera LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Description SpecificationDocumento20 pagineUnit Description SpecificationAnonymous 7t2BOJbNessuna valutazione finora
- ER 58.11startup ProcedureDocumento3 pagineER 58.11startup Proceduredongosuperstar100% (2)
- Four Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol Engine Test RigDocumento8 pagineFour Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol Engine Test RigJaishree ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2ZZGE Engine - Part of ManualDocumento46 pagine2ZZGE Engine - Part of ManualDavide Faelli100% (2)
- Komat'Su - HPI Fuel SystemDocumento76 pagineKomat'Su - HPI Fuel SystemKarthik Rao100% (2)
- Testing and Adjusting: D6M Track-Type Tractor Hydraulic SystemDocumento27 pagineTesting and Adjusting: D6M Track-Type Tractor Hydraulic SystemJUAN CARLOS PAZNessuna valutazione finora
- TT Oil Flooded Rotary Air CompressorDocumento2 pagineTT Oil Flooded Rotary Air Compressorajo2402Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cessna 172 POHDocumento27 pagineCessna 172 POHarnavpilotNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine CompressorsDocumento7 pagineMarine CompressorsAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Image Server HandlerDocumento12 pagineImage Server Handlerbobcat1810Nessuna valutazione finora
- PCVDocumento20 paginePCVyared abebeNessuna valutazione finora
- 01.main Engine ManualDocumento64 pagine01.main Engine ManualwilfredNessuna valutazione finora
- SM 03 BDocumento34 pagineSM 03 BMark OreschnickNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento21 pagineModule 2NithinNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Edition of Automotive QBDocumento15 pagineFinal Edition of Automotive QByoussef faroukNessuna valutazione finora
- CSHA KatalogDocumento40 pagineCSHA Kataloglist16947100% (5)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SDa EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitDa EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementDa EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNessuna valutazione finora
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingDa EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 2 CAVALIER z24 Transmision AutDocumento73 pagine2 CAVALIER z24 Transmision AutVictor GonzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Swot Analysis of SkodaDocumento23 pagineSwot Analysis of SkodaGaurav JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Euroncap 2015 Mazda CX 3 Datasheet PDFDocumento10 pagineEuroncap 2015 Mazda CX 3 Datasheet PDFcarbasemyNessuna valutazione finora
- Boomer PDFDocumento709 pagineBoomer PDFRPINILLA (EICO S.A.)Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Price ListDocumento6 pagine2011 Price ListSaurabh JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
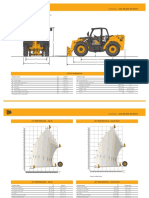
- LOADALL - 535-95/535-95 SWAY: Static DimensionsDocumento4 pagineLOADALL - 535-95/535-95 SWAY: Static Dimensionsmihai ochialbescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Autocar ProfessionalDocumento2 pagineAutocar ProfessionalRAHUL_AGRAWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Australian Motorcycle News - November 23, 2023 AUDocumento116 pagineAustralian Motorcycle News - November 23, 2023 AUOscar ValladaresNessuna valutazione finora
- 22YM Street Touring Accessories CB650R OKDocumento4 pagine22YM Street Touring Accessories CB650R OKEla BnzNessuna valutazione finora
- Alnaser - EngleskiDocumento9 pagineAlnaser - EngleskialeksandarglNessuna valutazione finora
- MLHSDocumento21 pagineMLHSElcon SultorNessuna valutazione finora
- AW55-50SN, AW55-51SN, AF23/33, RE5F22A Zip Kit: Installation DiagramDocumento10 pagineAW55-50SN, AW55-51SN, AF23/33, RE5F22A Zip Kit: Installation DiagramKalinin Pineda100% (1)
- 2022 TRA Base BEMM Publishable 25-07-2022Documento135 pagine2022 TRA Base BEMM Publishable 25-07-2022Jack Norhy100% (1)
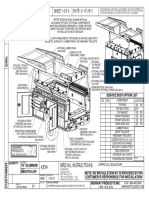
- Service Body 6212-001-AE: Sheet 1 of 6 DATE: 2/15/2011 P/NDocumento6 pagineService Body 6212-001-AE: Sheet 1 of 6 DATE: 2/15/2011 P/NmanutencaoseibNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts & Service News: Component Code Ref No. DateDocumento2 pagineParts & Service News: Component Code Ref No. DateAndree Ayma NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Archer Octubre 2019 - VendedoresDocumento4 pagineArcher Octubre 2019 - VendedoresLARRY MENDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Tata NanoDocumento25 pagineTata Nanop01p100% (1)
- Table of C Ontents: Modern A Utomotive Technology, 9th EditionDocumento1 paginaTable of C Ontents: Modern A Utomotive Technology, 9th EditionLukaz JuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- H4 9003 PDFDocumento1 paginaH4 9003 PDFdejidotun20007910Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2806a-E18tag2 Electropak Pn1871Documento2 pagine2806a-E18tag2 Electropak Pn1871Charles CallahanNessuna valutazione finora
- PDS en-MY 20220811Documento2 paginePDS en-MY 20220811MUHAMMAD AMIR BIN RASIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsmy17fm2632fm2635-0921 WebDocumento4 pagineHsmy17fm2632fm2635-0921 Webvictor hugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercedes Trans 7G Tronic PlusDocumento6 pagineMercedes Trans 7G Tronic PlusEdwin C. Walke100% (1)
- Pollution Under Control Certificate: Form 59Documento1 paginaPollution Under Control Certificate: Form 59rahul raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Folk Lift Operator SafetyDocumento24 pagineFolk Lift Operator Safetylmo.orengeNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined SpecsheetDocumento1 paginaCombined SpecsheetApurva PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 8042 Rev5Documento269 pagine8042 Rev5Хелфор УкраинаNessuna valutazione finora
- R PDFDocumento199 pagineR PDFAlex Renne ChambiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Codes : Suffix FeatureDocumento6 pagineEngine Codes : Suffix FeatureMhammet La Nina PRihatinNessuna valutazione finora