Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sub-Station & Circuit Breakers
Caricato da
Divya RengasamyDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sub-Station & Circuit Breakers
Caricato da
Divya RengasamyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sub-Station & Circuit Breakers
Dr.V.Saravanan Assistant Professor EEE Thiagarajar College of Engineering, Madurai 625 015.
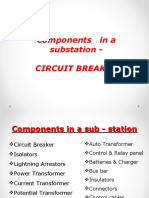
Sub-Station Equipment
Incoming & Outgoing Feeders Transformers Main & Auxiliary HV & LV CB, LB Switch & Isolators Relay, Metering, CT, PT & Control Panels Shunt Reactors, Capacitors & SVC Power & Control Cables Surge Arrestor, OH Earth wire Battery System, Communication Equip.
Types of Sub-Station
Indoor type
Small SS Up to 11KV 33KV &Above
Compact SS In City
Outdoor type
Gas Insulated type
Compensation Equipment
Shunt Reactor
EHV SS Compensate Line Charging
Reactive VAR Supply Electronic Method to control - Step less
Shunt Capacitor
Static VAR Compensator
Sub-station Equipment Role
Equipment Bus bars Functions Feeding Power Al.
Load break switches Opening loaded circuits Earthing Switch Surge Arrestor CT & PT Discharge charges Divert HV Surges to Earth Measuring & Protecting
Sequence of Operation of Isolator, C.B and Earthing Switch
While opening
Open C.B Open isolator Close earthing switch Ensure C.B is open Open earthing switch Close isolator Close C.B
while closing
Interlocks are provided to Ensure above Sequence
Difference Between Isolator & Circuit breaker
Isolator is a switch intended to make or break the circuit with out load Circuit Breaker will make or break the circuit with or without load Operation of Load Break Switch is also similar to Circuit Breaker
CB Development
Historical Development
Switch Switch with Fuse Bimetallic Relay Oil Circuit Breakers Air Circuit Breakers Vacuum Circuit Breakers SF6 Circuit Breakers
Minimum Oil Circuit Breakers
Used in large numbers for Medium voltage Distribution system
Low Capacity Applications Low Fault MVA Up to 11KV Application
Disadvantages of using oil as quenching media
Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker
Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker
Used in large numbers for High voltage Distribution system
High Capacity Applications High Fault MVA Up to 110KV Applications - Limited
Disadvantage
Flammability & High maintenance cost
Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker
Air Blast Circuit Breaker
ACBs are required to CARRY short circuit current for a specified time
Which is usually one second Is invariably more than what the downstream devices require to interrupt faults
In case the downstream devices fail to interrupt the fault current, the, breaker acts as a back-up protective device ACBs are also used for switching motors of higher rating Suitable for Medium Voltage Application
Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Vacuum as quenching media Features include high speed interrupting time Long working life due to minimized contact wear & shock Maintenance of circuit breaker is reduced
Service interval lies between 10,000 & 20,000 operations
Used for Feeders & Mains protection Rugged Housing & Small in size Superior Than SF6 Breaker
Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Vacuum Circuit Breakers
SF6 Circuit Breaker
SF6 as quenching media Service interval lies between 5000 & 20,000 operations SF6 pressure should be maintained for proper operation
SF6 Circuit Breaker
Cost of Breaker
The cost of CB depends on
Working Voltage in KV Operating Capacity in Amps Rupturing Capacity in MVA Speed of Operation in milliseconds
CB Capacity in MVA
Capacity of the CB always expressed in terms of Fault MVA Cost of CB Depends upon the fault level Fault Level Depends on
Generation end Transmission end Distribution end
Calculation of Short Circuit Level
Short Circuit Current is Equal to the Ratio between Load in Volt Amp divided by the Voltage Drop Measure the KVA of the Load Measure the Voltage No-load & Load
Difference gives the Voltage Drop
Typical Capacity Rating of CB
Voltage 0.4 3.3 6.6 In KV Rating 25 in MVA 75 150 11 22 66 110
250
500
1000 1500
Rupturing Capacity
Rupturing Capacity represents the Max. power a CB can Safely interrupt Factors Determine Rupturing Capacity
Length & Speed of Breaking Position of Arcing Contacts Dimensions of Parts Mechanical Strength of Breaker
Conditions for CB Operation
Overload Short Circuit Earth Fault Local Maintenance work Any other Abnormal operation
Auto Re-close Breaker
Auto re-close breaker
open the circuit in case of a fault Try to close the circuit with a few millisecond delay to allow the fault to clear Repeat the operation once more After the operation the circuit will break for next official command Line Ground Fault due to trees
Helpful in has of transient faults & Abnormalities
Improve Power System Stability
Time Taken for the Clearance of Fault in Power System
Fault Clearing time is the time taken
To clear the fault from sensing of relay to extinguish of Arc in CB
The time taken to trip a circuit is the sum of the time taken by the various components in the Protecting System
Relay for Sensing the Faults Relay to CB communication Time taken by the CB to open the contact & Extinguish of Arc
CB Response
In HV Circuit Breaker
Time taken to break the Circuit within 2 to 3 Cycles or within 40 to 60 MilliSecond Discrimination of fault
Grading of Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers
TROUBLE
Low insulation resistance (below 2000 M)
Between phase terminal & earthed frame with C.B closed Phase terminals of a pole
Possible Causes
Moisture Dirty Insulation Surface Internal & /OR External Poor Oil Carbon / Copper Particle Sticking to Internal Surface
POSSIBLE REMEDIAL ACTION
Circulate dry hot air or oil through the breaker pole
For four to six hours
Dismantle & Clean Reasonable insulation resistance
Above 2000 M
Resistance across terminals of pole too high( above 100)
Possible Causes
Reduced contact pressure Loose screws or bolts for flanges Contact surface damaged due to repeated operations Insufficient contact wipe Oxidation layer on terminals
Remedial Measures
Dismantle repair & assemble again If necessary, replace the contact
Unequal contact Wipe & Travel in 3 poles
Measured from top surface of interrupter flange & Contact tip by a simple rod with
breaker open breaker closed Contact erosion due to repeated load operations or short circuit operations Unequal lengths due to wrong adjustments during maintenance
Possible Causes
Remedial Action
Inspect contact tips Replace if badly eroded Adjust contact if lengths are unequal in three poles
One of the poles does not close
Possible Causes
Pull rod for contact damaged One of the links of that pole broken Contact of that pole severely damaged Dismantle the pole and repair the defect
Remedial Action
Breaker Operation too Slow During Opening
Tripping from trip command to contact separation instant too large
60ms instead of say 40ms Excessive friction in the pole unit Contact grip too high Trip coil operation sluggish Low battery voltage, hence higher trip coil pick up time
Possible Causes
Identifying the cause & take remedial action
Breaker doesnt Operate on Electrical Command
Possible Causes
Spring defective Trip coil open Trip coil /latch defective Spring not charged If breaker operates with manual operation of trip release
The mechanism is ok
Remedial Action
Check closing spring visually Identify the cause & take remedial action Check supply to spring charging motor
Drying out in Electrical Equipment
Drying out is nothing but moisture removal
From the insulation to increase insulation resistance
Drying out is carried out in huge generators
By circulation of short circuit current through windings
Re-varnish Max. drying out temp. 80C
Maintenance Required for Oil Circuit Breakers
Once in Three to Six months depending upon the usage Check the Oil Level & Colour Check the Oil BDV Value Clean the insulators Check insulation value Check Closing, Tripping & Interlock Mechanism
Maintenance Required for SF6 Circuit Breakers
Daily Basis
Check the Pressure of SF6 Gas in side the Breaker Check for SF6 Gas Leakage Refill incase of leakage
By Trained persons
Over halve once in Six months
Thank you
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 6 L 80Documento8 pagine6 L 80Transmisiones Guero75% (4)
- Testing of Circuit BreakersDocumento20 pagineTesting of Circuit BreakersVikas GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsDa EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (6)
- Testing of TransformerDocumento37 pagineTesting of TransformerVikas GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gek 45375JDocumento42 pagineGek 45375JBolivar MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Maintenance Practices/ Condition Monitoring For Reliability of EHV Substation EquipmentsDocumento76 pagineBest Maintenance Practices/ Condition Monitoring For Reliability of EHV Substation EquipmentsPhani Kumar100% (1)
- Electrical Equipment: Circuit BreakerDocumento43 pagineElectrical Equipment: Circuit BreakerKenneth LewisNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Electric Demand - US UtilityDocumento4 pagineUnderstanding Electric Demand - US UtilityVicente MatamorosNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing NotesDocumento12 pagineTesting NotesJigar TakoliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Electrical Maximum DemandDocumento4 pagineCalculation of Electrical Maximum Demandguna698650% (6)
- Transformer Repairing Auto Saved)Documento11 pagineTransformer Repairing Auto Saved)c0rr0deNessuna valutazione finora
- ADS Tutorial 1 PDFDocumento29 pagineADS Tutorial 1 PDFPuneeth yoganandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker TypesDocumento39 pagineCircuit Breaker TypesKenneth Lewis100% (1)
- How To Calculate The Circuit Breaker SizeDocumento9 pagineHow To Calculate The Circuit Breaker SizeAl Patrick Dela CalzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Switchgear PresentationDocumento2 pagineSwitchgear PresentationAhmad Yaseen100% (1)
- SwitchgearDocumento23 pagineSwitchgearAnonymous Yq9ibs100% (1)
- Equipments in SSDocumento48 pagineEquipments in SSJoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sag SwellDocumento149 pagineSag Swellfurqan mahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser Welder Manual PDFDocumento14 pagineLaser Welder Manual PDFMaurizioNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintainence of Circuit BreakerDocumento34 pagineMaintainence of Circuit Breakeramirtha_s2238Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Transformer ENUDocumento32 paginePower Transformer ENUDaniel RizzoNessuna valutazione finora
- SF6 Circuit Breaker Nameplate Details ExplanationDocumento7 pagineSF6 Circuit Breaker Nameplate Details Explanationlooyd alforqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Preventive Maintenance of Substation EquipmentDocumento37 paginePreventive Maintenance of Substation Equipmentameer036100% (3)
- DEE Module 5.3 AllDocumento55 pagineDEE Module 5.3 AllVusi MabuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Failure Modes 20130820Documento47 pagineTransformer Failure Modes 20130820Adiel Camarillo Narvaez100% (1)
- Submitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Documento15 pagineSubmitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Himanshu Soni100% (1)
- Feeder Protection FundamentalsDocumento103 pagineFeeder Protection Fundamentalssunnydargan91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Failure Modes ABB 2013-04-16Documento57 pagineTransformer Failure Modes ABB 2013-04-16supernaenergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker Concept Mocb, Abcb, VCB & Sf6 CBDocumento68 pagineCircuit Breaker Concept Mocb, Abcb, VCB & Sf6 CBRaja RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Metal-Air and Metal-Sulfur Batteries Fundamentals and Applications by Neburchilov, Vladimir Zhang, JiujunDocumento210 pagineMetal-Air and Metal-Sulfur Batteries Fundamentals and Applications by Neburchilov, Vladimir Zhang, JiujunjosephyfuNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit BreakerDocumento7 pagineCircuit BreakerajitamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety MeasuresDocumento28 pagineSafety Measuresmaryamsaleem430Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rating of Circuit BreakerDocumento10 pagineRating of Circuit BreakerhanifinsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rating of Circuit Breaker - Short Circuit Breaking Making Current - Electrical4UDocumento4 pagineRating of Circuit Breaker - Short Circuit Breaking Making Current - Electrical4Uwaqas_a_shaikh4348Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 TransformerDocumento55 pagine5 Transformer63PE007 P. SATHEESHKUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Substation LectureDocumento60 pagineBasic Substation LectureBer Salazar Jr67% (3)
- GisDocumento31 pagineGisMahmoud MoezNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Preventive MaintenanceDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To Preventive MaintenanceTEMIDAYONessuna valutazione finora
- Rana TahirDocumento35 pagineRana TahirIrfan UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- Finder CatalogueDocumento18 pagineFinder CatalogueGeorge GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Thyristor Vs ContactorDocumento3 pagineComparison Thyristor Vs ContactorZIPDASH0% (1)
- Converter Faults & ProtectionDocumento24 pagineConverter Faults & Protectionsunilkumarece88% (41)
- Method For Static and Dynamic Resistance Measurement of HV Circuit BreakerDocumento5 pagineMethod For Static and Dynamic Resistance Measurement of HV Circuit BreakerAislanGaldino100% (1)
- Presentation On Substation ProtectionDocumento25 paginePresentation On Substation Protectionatulsontakke11100% (1)
- Mee MCQ 1Documento26 pagineMee MCQ 1chetan shinkar 39Nessuna valutazione finora
- Open Circuit Faults: Why Reactor Is Necessary in Power System?Documento2 pagineOpen Circuit Faults: Why Reactor Is Necessary in Power System?Soumajit PoddarNessuna valutazione finora
- Efresher ON Ircuit Reakers: by MirDocumento15 pagineEfresher ON Ircuit Reakers: by MirmthrslNessuna valutazione finora
- 245kv GTP Sf6 BreakersDocumento4 pagine245kv GTP Sf6 BreakersTejaswi ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breakers: 15E701 - Power System Protection & Switch GearsDocumento29 pagineCircuit Breakers: 15E701 - Power System Protection & Switch GearsYugendran KumaravelNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker - Vaccuum & Water CBS, Ratings & Operating MechanismDocumento15 pagineCircuit Breaker - Vaccuum & Water CBS, Ratings & Operating MechanismMAsifNazeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Company: To Excel in Providing Engineering Goods and Services Through Continuous ImprovementDocumento20 pagineIntroduction of Company: To Excel in Providing Engineering Goods and Services Through Continuous ImprovementAbdulGhaffarNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 MV Switch TestingDocumento68 pagineModule 5 MV Switch TestingSuresh K Krishnasamy100% (1)
- Transient VoltageDocumento20 pagineTransient VoltageAshish ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No. 05 Distribution EquipmentDocumento59 pagineChapter No. 05 Distribution EquipmentNoman KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement Winding Resistance & TTRDocumento7 pagineMethod Statement Winding Resistance & TTRsite.eng1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1431928880session II CBDocumento84 pagine1431928880session II CBAnonymous i2u3XW8UJHNessuna valutazione finora
- Synchronous Generator Protection: AnswerDocumento26 pagineSynchronous Generator Protection: AnswerLuka YannamNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Circuit Breaker Types of ACBsDocumento7 pagineAir Circuit Breaker Types of ACBsNeeraj RahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Trends and Accident Prevention On Distribution and Power TransformersDocumento10 pagineModern Trends and Accident Prevention On Distribution and Power Transformersashutosh2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presention DetailsDocumento7 paginePresention DetailspvenkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque Prod Ac DrivesDocumento32 pagineTorque Prod Ac DrivesThanigaivelu SubrmanianNessuna valutazione finora
- RelayDocumento29 pagineRelayVivek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sizing of Power Cables For Circuit Breaker Controlled FeedersDocumento4 pagineSizing of Power Cables For Circuit Breaker Controlled FeedersMohanta AmritNessuna valutazione finora
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaDa EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNessuna valutazione finora
- BTS-312 (Cabinets and Boards)Documento33 pagineBTS-312 (Cabinets and Boards)sebax123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Manual: Yasnac J300LDocumento354 pagineOperating Manual: Yasnac J300Lgustavo alonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tm170tig PVCDocumento9 pagineTm170tig PVCAndrea MorsianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ulp-05 Er35c2dme7crDocumento6 pagineUlp-05 Er35c2dme7crojvp18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Smartpilot Series: Commissioning GuideDocumento80 pagineSmartpilot Series: Commissioning GuideMartin CernicNessuna valutazione finora
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDocumento25 pagineG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- LG 42pj350 Training Manual (ET)Documento132 pagineLG 42pj350 Training Manual (ET)RomelyGery Martinez89% (9)
- Owners and Service Manual: Innovative Concepts in Entertainment IncDocumento5 pagineOwners and Service Manual: Innovative Concepts in Entertainment IncmajormisfitNessuna valutazione finora
- LRB120-3 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineLRB120-3 DatasheetMatheus PadilhaNessuna valutazione finora
- EIE Unit1Documento221 pagineEIE Unit1karun karunaeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four Basic Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDocumento11 pagineChapter Four Basic Nodal and Mesh AnalysisTaufiqurrahman MczNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic CircuitDocumento5 pagineMagnetic CircuitSritaran BalakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eurl Tassili Motors: FeaturesDocumento4 pagineEurl Tassili Motors: Featuresbachir zouizaiNessuna valutazione finora
- User's ManualDocumento24 pagineUser's ManualMARKO021Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adc 24 Bits Ads1243Documento35 pagineAdc 24 Bits Ads1243juanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Key Coded LockDocumento11 pagineDigital Key Coded LockEngr. Zeeshan mohsin100% (1)
- LV 100-2000 sp5 Voltage TransducerDocumento3 pagineLV 100-2000 sp5 Voltage TransducerGilney FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pr1613adf PDFDocumento2 paginePr1613adf PDFhaerulamriNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerflex 750-Series Ac Drives: Programming ManualDocumento548 paginePowerflex 750-Series Ac Drives: Programming ManualJose GimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- AX8 Owners Manual PDFDocumento111 pagineAX8 Owners Manual PDFSoe SirawitNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Grounding Practices BenderrDocumento32 pagineDifferent Grounding Practices BenderrSaurabh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- CM8870/70C CMOS Integrated DTMF Receiver: California Micro DevicesDocumento8 pagineCM8870/70C CMOS Integrated DTMF Receiver: California Micro DevicesEdwinBeNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Ns - STR 22seDocumento28 pagineSeries Ns - STR 22seAlexandre MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Portascan Portable Bladder Scanner - Service ManualDocumento18 pagineGE Portascan Portable Bladder Scanner - Service ManualHarold MartinezNessuna valutazione finora