Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Robotics
Caricato da
aoi_blue89Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Robotics
Caricato da
aoi_blue89Copyright:
Formati disponibili
robotics - The science of designing, building and applying robots.
robot - A reprogrammable, multifunctional manipulator designed to move a material, parts, tools, or specialized devices through variable programmed motions for the performance of a variety of tasks. Roboticist person working in the field of robotics Who coined the term robotics? - Isaac Asimov - 1941 Who coined the term robot? - Karel Capek - 1921 George Devol - father of industrial robot DC motor and stepper motor used in robotics because can withstand large overload harmonic drivers in robots - High reliability first generation robot system - Robots with little if any computer power. Their only intelligent functions consist of learning a sequence of manipulative actions, choreographed by a human operator using a teach box. second generation robot system - A robot with a computer processes added to the robotic controller. This addition makes it possible to perform, in real time, the calculations required to control the motions of each degree of freedom in a cooperative manner to effect smooth motions of the end effector along predetermined paths. It also becomes possible to integrate simple sensors, such as force torque, and proximity into the robot system, providing some degree of adaptability to the robots environment. third generation robot system - A robot system characterized by the incorporation of multiple computer processors, each operating asynchronously to perform specific functions. It includes a separate low level processor for each degree of freedom and a master computer supervising and coordinating these processors, as well as providing higher-level functions. accuracy - The ability of a robot to position its end effector at a programmed location in space. analog control - Control signals that are processed by directly measuring quantities (voltages, resistances or rotation). This can be hydraulic, electronic or pneumatic. artificial intelligence - The ability of a machine system to perceived anticipated or unanticipated new conditions, decide what actions must be performed under the conditions and plan the actions accordingly. The main areas of applications are expert systems and computer vision. Expert system computer system that uses AI assembly - Also known as assembly cell or assembly station. A concentrated group of equipment such as manipulators, vision modules, parts presenters, and support tables that are dedicated to compute assembly operations at one physical location.
automated inspection - The use of any one several techniques to determine the presence or absence of features. This technique include simple mechanical probes and vision systems. automation - Automatically controlled operation of an apparatus, process or system by mechanical or electronic devices that replace human observation, effort and decision. axis - A traveled path in space, usually referred to as a linear direction of travel in any of three dimensions. Degrees of freedom Ans: Range of axis
manipulator - A mechanism usually consisting of a series of segments or links, jointed or sliding to one another, for grasping or moving objects, usually in several degrees of freedom. complex joint - An assembly between two closely related rigid members enabling on member to rotate in relation to the other around a mobile axis. orientation - Also known as positioning. The consistent movement or manipulation of an object into controlled position and altitude in space. peripheral equipment - The equipment used in conjunction with the robot for a complete robotic system. This includes grippers, conveyors, parts positioners and parts or materials feeders that are needed with the robot. programming - The act of providing the control instructions required for a robot to perform its intended task. Degrees of freedom is the number of ______ independent movements including the end effector. Ans: independent Servo controlled robots are robots within ___ mm range rather than a fraction of mm. Ans: 2 Rotational joins of the robot is called _____. Ans: Revolute joints Straight line joints movement of the robot is called. Ans: Prismatic joints end effector - Also known as end of arm tooling or simply a hand. The subsystem that links the mechanical portion of the robot (manipulator) to the part being handled or work on, and gives the robot the ability to pick yp and transfer parts and/or handle a multitude of different tools to perform work on parts. flexibility operational - Multipurpose robots that are adaptable and capable of being redirected trained or used for new purposes. simulation programming - remote computer and program is downloaded in a robot repeatabililty - ability to position the wrist at previously taught point proximity sensing - ability of a robot to tell when object is near it
base - A platform or structure to which a robot arm is attached; the end of a kinematic chain of arm links and joints opposite to which grasps or processes external objects. cycle (program) - The unit of automatic work for a robot. Within a cycle, subelements called trajectories define lesser but integral elements. Each trajectory is made up of points where the robot performs an operation or passes through depending upon the programming. degrees of freedom - The number of independent ways the end effector can move. It is defined by the number of rotational or translational axes through which motion can be obtained. Any solid object has ___ degrees of freedom Ans: 6
work envelope - Also known as the robot operating envelope. The set of points representing the maximum extent or reach of the robot tool in a directions. workspace - The envelope reached by the center of the interface between the wrist and the tool, using all available axis motions. tactile sensing - The detection by a robot though contact of touch, force, pattern slip and movement. It allows for the determination of local shape, orientation and feedback forces of a grasped workspace. slew rate - The maximum velocity at which a manipulator joint can move; a rate imposed by saturation in the servoloop controlling the joint. stereo imaging - The use of two or more cameras to pinpoint the location of an object in a three dimensional space. tilt - The orientation of a view with a video camera, in elevation.
teaching - programming for robot tracking - A continuous position control response to continuously changing input requirements. translation - A movement such that all axes remain parallel to what they were. transport - The acquisition, movement thorugh space, and release of an object by a robot. gripper - The grasping hand of a robot, which manipulates objects and tools to fulfill a given task. kinematic chain - robot akin to human skeleton degree of rotation - measure of extent to which robot joint or set of robot joints turned cycle time - robot takes from one location to next location vision system - locates a part, identifies it, directs the gripper to a suitable grasping position, picks up the part, and brings the part to the work area
computer aided design (CAD) - The use of an interactive terminal workstation usually with graphics capability to automate the design of products. It includes functions such as drafting and fit-up parts. computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) - Working from a product design likely to exist in a CAD data base, it encompases the computer based technologies that physically produce the product, including parts program preparation, process planning, tool design, process analysis and parts processing by numerically controlled machines. computerized numerical control (CNC) - A numerical control system with a dictated mini or micro computer that performs the functions of data processing and control. flexible manufacturing system (FMS) - An arrangement of machine tools that is capable of standing alone, interconnected by a workpiece transport system and controlled by a central computer. islands of automation - An approach used to introduce factory automation technology into manufacturing by selective application of automation. level of automation - The degree to which a process has been made automatic. Relevant to the level of automation are questions of automatic failure recovery, the variety of situations that will be automatically handled, and the conditions under which manual intervention or action by human beings is required. limit switch - An electrical switched positioned to be switched where a motion limit occurs, thereby deactivating the actuator that causes the motion. numerical control - A method for the control of machine tool systems. A program containing all the information, in symbolic numerical form, needed for processing a workpiece is stored on a medium such as paper or magnetic tape. off-line programming - Developing robot programs partially or completely without requiring the use of the robot itself. The program is loaded into the robots controller for subsequent automatic action of the manipulator. yaw - The angular displacement of a moving joint about an axis which is perpendicular to the line of motion and the top side of the body. roll - Also known as twist. The rotational displacement of a joint around the principal axis of its motionj, particularly at the wrist. pitch - Also known as bend. The angular rotation of a moving body about an axis that is perpendicular to its direction of motion and in the same plane as its top side. servomechanism - An automatic control mechanism consisting of a motor or actuator driven by a signal that is a function of the difference between a commanded position and/or rate and measured actual position and/or rate. More robot than worker Ans: Japan
servocontrolled robot - A robot driven by servomechanisms, that is, motors or actuators whose driving signal is a function of the difference between a commanded position and/or rate is measured actual position and/or rate. gantry robot - An overhead mounted, rectilinear robot with a minimum of three degrees of freedom and normally not exceeding six. types of robot - Cartesian, scara, anthropomorphic sequencer - A controller that operates an application though a fixed sequence of events. floor mounted robot - Also known as pedestal robot. A robot with its base permanently or semi-permanently attached to the floor or bench. Such a robot is working at one location with a maximum limited work area and in many cases servicing only one machine. fixed stop robot - Also known as nonservo robot or open robot. A robot with stoppoint control but no trajectory control. bang-bang robot - A robot in which motions are controlled by driving each axis or degree of freedom against a mechanical limit stop. anthrophomorphic robot - A robot with rotary joints that can move much like a persons arm. Nimak gantry robot has____. Pleo - Toy dinosaur robot Kismet - Robot with facial expression Antrophomorphic robot is_____. Ans: more maneuverable Kuka spot welding robot robot with 6 degrees of freedom point to point - robot with no specific path unimate - first industrial robot by Geong & Joseph Engelbert walkthrough - programming and continuou path robot serial robot - human arm kuka titan - strongest robot Ans: good precision positioning
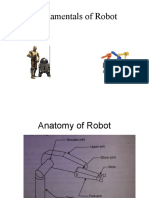
arm - An interconnected set of links and powered joints comprising a manipulator that supports or moves a wrist, hand or end effector. elbow - The joint that connects the upper arm and forearm on a robot. forearm - That portion of a jointed arm which is connected to the wrist and elbow shoulder - The manipulator arm linkage joint that is attached to the base. upper arm - The portion of a jointed arm that is connected to the shoulder. wrist - A set of joints, usually rotational, between the arm and the hand or end effector, which allow the hand or end effector to be oriented relative to the workpiece. Addition of wrist Ans: 3 degrees of freedom
Hand disguised as a regular gripper but with three or more finger and dextous finger similar to human hand gripper - 2 fingers vacuum gripper - connected to the vacuum source and handle objects mounting plate - end effector is placed Air muscle simple yet effective and act similar to human muscle SCARA - stands for Selective Compliant Assembly Robot Arm or Selective Compliant Articulated Robot Arm. - an assembly machine that installs parts or carries items SCADA - supervisory control and data acquisition - used to monitor and control a plant or equipment in industries such as telecommunications, water and waste control, energy, oil and gas refining and transportation NIVAC - good precisional position
playback robot - used to record motion NIMAC measurable autonomous robot - robot with own computer android - A robot or machine that resembles a human, technically refers to the male form gynoid - anything which resembles or pertains to the female human form humanoid - something that has an appearance resembling a human being cyborg - short for "cybernetic organism," is a human with bionic, or robotic, implants Zero moment point (ZMP) technique algorithm used in Hondas ASIMO degree of freedom of ASIMO - 34 Dynamic balancing a more advance, robust than ZMP capacity of ASEA IRb-60 - 60 Kg QRIO - "Quest for cuRIOsity", originally named Sony Dream Robot or SDR
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Irina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeDocumento4 pagineIrina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeMarinaKorzinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-11b Robotics, Automation, FMSDocumento71 pagineCh-11b Robotics, Automation, FMSprabhjotbhangalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Fundamentals of RobotDocumento43 pagineChapter 1 Fundamentals of RobotAmanMauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Provision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field DevelopmentDocumento7 pagineProvision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field Developmentriandi100% (1)
- Immigrant Italian Stone CarversDocumento56 pagineImmigrant Italian Stone Carversglis7100% (2)
- AssignmentqDocumento12 pagineAssignmentqDirajen PMNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesla Coil ProjectDocumento8 pagineTesla Coil ProjectShivam singhNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Servo Motor Position SystemDocumento28 pagineDC Servo Motor Position SystemVincent Korie100% (2)
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento76 pagineElements of Mechanical EngineeringArjun Reddy NareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- RoboticsDocumento18 pagineRoboticslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- NCP Orif Right Femur Post OpDocumento2 pagineNCP Orif Right Femur Post OpCen Janber CabrillosNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Shear and TensionDocumento16 pagineCombined Shear and TensionDAN MARK OPONDANessuna valutazione finora
- Robotic TerminologyDocumento27 pagineRobotic Terminologypreethu02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic RoboticsDocumento3 pagineBasic RoboticsHugues GeschwindenhammerNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics Chapter 1Documento11 pagineRobotics Chapter 1origafelixNessuna valutazione finora
- Motoman Robotics - Glossary of Robotics TermsDocumento15 pagineMotoman Robotics - Glossary of Robotics Termsengineer86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics and Cybernetics For Mechanical EngineersDocumento20 pagineRobotics and Cybernetics For Mechanical EngineersMichelle LucyNessuna valutazione finora
- PI RoboticGlossaryTermsDocumento24 paginePI RoboticGlossaryTermssebaszjNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Industrial RobotsDocumento35 pagineIntroduction To Industrial RobotsGurpreet Singh AnttalNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By: B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) Mr. K. Sunil Kumar, M.Tech Assistant ProfessorDocumento22 paginePresented By: B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) Mr. K. Sunil Kumar, M.Tech Assistant Professorsarath chandra satuluriNessuna valutazione finora
- CheatsheetDocumento2 pagineCheatsheetcboersma10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics EngineeringDocumento21 pagineRobotics EngineeringMihai GînțaNessuna valutazione finora
- RoboticsDocumento37 pagineRobotics9944805552Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To RoboticsDocumento35 pagineIntroduction To Roboticsرهف عبد اللهNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - IntroductionDocumento33 pagineUnit 1 - IntroductionRavi KantNessuna valutazione finora
- Working and Brief Study of Robotic ArmDocumento28 pagineWorking and Brief Study of Robotic Armanon_126479169100% (3)
- Ie 450 PP 8Documento37 pagineIe 450 PP 8vijayasarathy2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter # 1: Introduction To Robotics Mechanics & ControlDocumento51 pagineChapter # 1: Introduction To Robotics Mechanics & ControlAli AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 18BME025 - ME404 AssgnDocumento13 pagine18BME025 - ME404 AssgndevashNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Background and A Classification of RobotsDocumento90 pagineChapter 1 - Background and A Classification of RobotsRaziff HamsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Robotics Industrial Robot: Pemda40Documento8 pagineIndustrial Robotics Industrial Robot: Pemda40Sivakumar VedachalamNessuna valutazione finora
- ECEL12-LAB#4 AngeladaDocumento9 pagineECEL12-LAB#4 AngeladaAlehamarie AngeladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prash Robotics UpdatedDocumento152 paginePrash Robotics Updatedpreethu02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 5 Fundamentals of Robots 2Documento46 pagineTopic 5 Fundamentals of Robots 2Elvis OmondiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1. A Sense of HistoryDocumento8 pagine1.1. A Sense of HistoryCarlitos FerNessuna valutazione finora
- Steering Mechanism of Autonomous VehicleDocumento27 pagineSteering Mechanism of Autonomous VehicleChetan SwaroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 1Documento38 pagineLect 1Chilton FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-3 - Robotic Cell Design and Programming - Robotics and Automation - 22ETC151 - 251-1Documento12 pagineModule-3 - Robotic Cell Design and Programming - Robotics and Automation - 22ETC151 - 251-1chandanpurvey2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ime M 5Documento8 pagineIme M 5Sanjana MLNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics and Vision SystemDocumento64 pagineRobotics and Vision Systemasuras1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of RobotsDocumento20 pagineTypes of RobotsdionquernNessuna valutazione finora
- IE NOTES RoboticsDocumento16 pagineIE NOTES Roboticstest testNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8 Industrial RoboticsDocumento39 pagineCH 8 Industrial RoboticsDeepak PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Vukobratovic Stokic 1989 ADocumento26 pagineVukobratovic Stokic 1989 ABranko KaranNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 4 RoboticsDocumento78 pagineCH 4 Roboticsarvind yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- B.E Mech Batchno 107Documento57 pagineB.E Mech Batchno 107saravana murthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Les Robots HumanoidesDocumento5 pagineLes Robots HumanoidesLeduneNessuna valutazione finora
- Articulo Programacion ....Documento7 pagineArticulo Programacion ....GermanGutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Restaurant BOTSDocumento8 pagineRestaurant BOTSSaudin TantriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-8 RoboticsDocumento22 pagineChapter-8 RoboticsschrienerNessuna valutazione finora
- Robô Pêndulo 2 Rodas - 1Documento7 pagineRobô Pêndulo 2 Rodas - 1Victor PassosNessuna valutazione finora
- Fyp Script For VideoDocumento2 pagineFyp Script For VideoHassan AlviNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotic Arm12Documento13 pagineRobotic Arm12Yati SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- RoboticsDocumento32 pagineRoboticsNimmagaddadeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- Controls and Systems EngineeringDocumento22 pagineControls and Systems EngineeringSheena BejasaNessuna valutazione finora
- 112638Documento36 pagine112638NANTHINI PRIYA J 215111073Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project Title...Documento7 pagineProject Title...Abhishek ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Accelerometer-Based Control of An Industrial Robotic ArmDocumento6 pagineAccelerometer-Based Control of An Industrial Robotic ArmsanjusanjanareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cai 4th PDFDocumento3 pagineCai 4th PDFJoao CarvalhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolvable Mechanics Hardware Tools For Evolutionary RoboticsDocumento7 pagineEvolvable Mechanics Hardware Tools For Evolutionary Roboticsdinu petreNessuna valutazione finora
- Automation and Robotics AssignmentDocumento13 pagineAutomation and Robotics AssignmentMoHit LalNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics FunctionsDocumento13 pagineRobotics FunctionsNuruliawati YuwonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wlding RobotDocumento8 pagineWlding Robotameer hamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emp R Homework 6 PopDocumento1 paginaEmp R Homework 6 PopShanmugaraj VskNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas 2-TRK Lanjut Kelompok 3 Andre-Arief-IstiaDocumento18 pagineTugas 2-TRK Lanjut Kelompok 3 Andre-Arief-IstiaAndre Fahriz Perdana HarahapNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Climate ChangeDocumento3 pagineEffects of Climate Changejiofjij100% (1)
- Bulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsDocumento6 pagineBulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsHarmonica PellazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Active Faults and Other Earthquake Sources: Learning OutcomeDocumento3 pagineModule 4 Active Faults and Other Earthquake Sources: Learning OutcomeFatima Ybanez Mahilum-LimbagaNessuna valutazione finora
- DOC-20161226-WA0009 DiagramaDocumento61 pagineDOC-20161226-WA0009 DiagramaPedroNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM (Subway Project Report)Documento13 pagineSCM (Subway Project Report)Beast aNessuna valutazione finora
- G1CDocumento12 pagineG1CKhriz Ann C ÜNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaDocumento25 pagineGrade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaPenke Mejado BelenNessuna valutazione finora
- TreesDocumento69 pagineTreesADITYA GEHLAWATNessuna valutazione finora
- Dual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDocumento3 pagineDual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDino Paul Castro HidalgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Niir Integrated Organic Farming Handbook PDFDocumento13 pagineNiir Integrated Organic Farming Handbook PDFNatalieNessuna valutazione finora
- EPCC Hydrocarbon Downstream L&T 09.01.2014Documento49 pagineEPCC Hydrocarbon Downstream L&T 09.01.2014shyaminannnaNessuna valutazione finora
- EN Manual Lenovo Ideapad S130-14igm S130-11igmDocumento33 pagineEN Manual Lenovo Ideapad S130-14igm S130-11igmDolgoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Pain Medicine: Jianguo Cheng Richard W. RosenquistDocumento346 pagineFundamentals of Pain Medicine: Jianguo Cheng Richard W. RosenquistMayNessuna valutazione finora
- Percent by VolumeDocumento19 paginePercent by VolumeSabrina LavegaNessuna valutazione finora
- C.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering and Technology, Melvisharam Department of Aeronautical Engineering Academic Year 2020-2021 (ODD)Documento1 paginaC.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering and Technology, Melvisharam Department of Aeronautical Engineering Academic Year 2020-2021 (ODD)shabeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE Paper 2Documento4 pagineCambridge IGCSE Paper 2irajooo epik zizterNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 4 Phasor Diagram of P.TDocumento31 pagineFig. 4 Phasor Diagram of P.Tdon aNessuna valutazione finora
- Faa Registry: N-Number Inquiry ResultsDocumento3 pagineFaa Registry: N-Number Inquiry Resultsolga duqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Exponential NumbersDocumento5 pagineComparing Exponential NumbersMaya RahayuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsDocumento34 pagineThe Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsCandlewick PressNessuna valutazione finora
- American BreakfastDocumento4 pagineAmerican BreakfastHamilton Valenzuela ChipongianNessuna valutazione finora
- A Year On A FarmDocumento368 pagineA Year On A FarmvehapkolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scott 2001Documento20 pagineScott 2001Mariana CatiniNessuna valutazione finora