Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Medical Definitions
Caricato da
Allison JaegerCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Medical Definitions
Caricato da
Allison JaegerCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Retrieved from: http://www.acr-translations.com/medical_definitions.
htm
Medical Definitions
Sources of medical definitions
Glossary of medical definitions
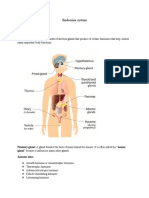
Abdomen Part of body between the chest and the hips. Abdominal hysterectomy Surgical removal of uterus through the abdomen. Ablative therapy - Removal or destruction of an organ during operation. Accessory digestive organs - Organs helping digestion, not being a part of digestive tract. Accessory movement Involuntary joint movements. Acquired deafness - Hearing loss that happens after birth. Adjuvant treatment Supplementary treatment to improve effectiveness Advanced cancer - Cancer in spreading phase. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Treatment with the help of stem cells. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor Drugs reducing blood pressure. Antihistamine drugs Drugs that reverse the effects of histamine when allergic reaction occurs. Anti-inflammatory drugs Inflammation-reducing medicine. Articular cartilage Tissues that cover the ends of bones. Artificial ventilation - Mechanical support of breathing. Assisted reproductive technology (ART) - Ways to assist infertile couples to be able to reproduce. Atrophic gastritis - Chronic stomach inflammation damaging inner surface. Auditory brainstem response (ABR) test Examination of hearing problems of young children. Augmentative devices Devices to improve speech. Balance disorder - Labyrinth damage. Basal body temperature Measuring temperature to determine ovulation activity. Blood plasma Nutritious contents of blood such as glucose, proteins, minerals, etc. Body mass index (BMI) Measurements of healthy weight by taking into account the height and weight. Breast conservation therapy Lumpectomy. Surgical removal of a part of breast to prevent cancer. Cardiac output Measurement of blood pumping. Carotid arteries - Major arteries in the neck, under the skull. Cerebral embolism - Blood clot carried to the brain artery. Clinical trials Research to discover methods and medication to prevent cancer. Complementary medicine Additional therapy to support standard medicine. Computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) - Non-invasive, cross-sectional scanning of internal organs. Cone biopsy Conization. Biopsy with the help of cone-shaped device to remove a part from the cervix. Coronary heart disease Atherosclerosis. Narrowing of coronary arteries narrow. Coronary thrombosis - Clot formation in the heart muscle. Cystic duct Tube between gallbladder to small intestine. Dental fluorosis Discoloration of teeth due to water containing excessive amount of fluor. Diastolic blood pressure - Lowest count of blood pressure between heartbeats. Digestive system - Organs breaking down the food and converting them into body nutrients. Digital rectal exam (DRE) Manual examination of rectum and prostate. Dyspraxia of speech Damaging of speech muscles impairing oral communication. Elective surgery Optional operation. Emergency surgery Instant operation due to emergency. Enteral nutrition - Tube feeding. Provision of food through a tube via the nose, the stomach, or the small intestine. Epidural anesthetic - Anesthetic injection to numb the lower extremities.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Measurement of red blood cells that settle on the bottom of a test tube to diagnose disease. Esophageal ulcer - Ulcer type caused by taking pills. Estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) - Supplying female hormone (estrogen) that cannot be produced naturally after menopause. Extra pyramidal system - Nerve cells, nerve tracts, and pathways. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - Pituitary gland hormone in the brain. Functional (motility) disorders Situation that adversely affects nerve and muscle function. Gastrointestinal (GI) tract Tube extending from mouth to the anus. General anesthetic It keeps the patient unconscious during operation. Gray matter - Dark tissues of the central nervous system, including cerebral cortex, thalamus, basal ganglia, etc. Ganglion cysts - Non-cancerous lumps around hands. Gastrocolic reflex - Activation in the gastrointestinal tract immediately after eating. Hearing disorder Loss of hearing ability. High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) - "Good" cholesterol that helps removing bad cholesterol. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) - Use of estrogen and progestin after menopause. Immunosuppressive medications Drugs used to suppress the body's immune system to prevent rejection of transplanted organs. Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) - Blood sugar levels that are high but still lower than those in diabetes. In vitro fertilization Fertilization of woman's egg outside her body. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Bowel problems related to irritation and ulcers in gastrointestinal tract. Informed consent form - Form prepared for patients explaining risks involved in the surgery. Inpatient surgery Operation conducted in the hospital. Intestinal flora - Bacteria, yeasts, and fungi in the intestines. Intrauterine insemination Injection of sperm into the uterus. Invasive cancer Spreading cancer. Joint locking Having a foreign substance between the joint surfaces. Jumper's knee - Degeneration of tendon around the knee-cap. Knee reconstruction - Mechanical knee restoration. Labyrinthine hydrops High levels of fluid in the ears resulting in hearing loss and loss of balance. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Removal of gallbladder by surgery. Local anesthesia Anesthetic fluid injected to numb a certain area for operation. Lower back - Lumbar spine connecting upper body to the lower body. Lymphatic system Organs such as bone marrow, spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes. Magnetic field therapy - Alternating magnetic fields produce electric current to affect the flow of blood. Mean blood pressure - Average blood pressure. Median nerve Nerve system related to neural function of the upper limb. Motion sickness - Dizziness, sweating, and vomiting created by motion. Musculoskeletal system - Bones, joints, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Myocardial infarction Heart attack that occurs when less amount of oxygen is allowed to pass to the heart muscle. Myofascial pain - Pain in jaw, neck and shoulder muscles. Needle biopsy Biopsy with the help of a hollow needle. Nerve sparing technique - Operation by controlling neurovascular bundles. Neural plasticity Adaptation of nervous system to impact. Neurogenic communication disorder Loss of communication skills due to damage to nervous system. Noninvasive procedures Diagnosis without entering body. Nuclear medicine Radiological technique to examine the body by using small amounts of radioactivity. Ocular hypertension - Intraocular pressure higher than 21 mm Hg. On-off effect Movement changes in patient status. Open surgery Operation by exposing organs.
Orthopaedic surgery Operation on musculoskeletal system. Otoacoustic emissions Detection of low level of sounds in ear canal with the help of a microphone. Palliative treatment Temporary therapy to reduce pain rather than complete cure. Patellar tendonitis - Patellar ligament inflammation. Peptic ulcer Ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Perilymph fistula Entry of inner ear fluid into middle ear. Peripheral stem cell transplantation Use of cancer-treated and frozen stem cells to cure. Placental abruption Serious bleeding due to premature detachment of the placenta. Plantar wart Viral foot wart. Polyunsaturated fat - Fat found in vegetable oils and margarines. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) - Nuclear scanning of heart in three-dimensional graphic. Prelingually deafened Deaf that occurs speaking. Proctalgia fugax - Rectal pain. Prostate Acid Phosphatase (PAP) High level of enzyme produced by prostate indicating the extent to which cancer was spread. Pyramidal pathway - Nerve tracts from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Radial keratotomy - Surgery to correct refractive problem. Radical mastectomy Total removal of breast by surgery. Radical retro pubic prostatectomy Surgical removal of prostate and seminal vesicles. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) Amounts of nutrients to be taken on daily basis advised by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Research Council of the National Academy of Science. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD) Over active sympathetic muscle reflex. Respiratory system - Organs that intake, carry, and use oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Rheumatic fever Disease due to heart valve damage during early ages. Self-monitoring blood glucose - Counting glucose in blood by the patient. Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Disease spread via sexual contact. Small bowel enema Radiological examination of small intestine by asking patient to drink barium. Spasmodic dysphonia Temporary loss of voice. Specific Language Impairment (SLI) Lack of communication skill with no obvious bodily disorder. Speech-language pathologist Specialist who treat problems related to speech and communication. Spinal anesthetic - Injection of anesthetic into the spinal canal fluid before surgery. Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (SIL) - Detection of precancerous change in cervix cells. Straight Leg Raise (SLR) - Measuring sciatic nerve status. Syndromic hearing impairment Hereditary hearing loss or deafness. Systolic blood pressure High blood pressure at the time of heart contraction. Telemetry unit - Transmitter to check the status of heart via radio transmission to an outside location for evaluation. Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF) Situation where food and saliva cannot go through. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) - Stroke-like event of short duration caused by blocked blood vessel. Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Partial removal of prostate without incision. Ultraviolet radiation Radiation caused by invisible sun rays. Velocardiofacial syndrome - Hereditary heart defect causing learning and other body functions. Ventricular fibrillation Inability to pump blood. Vestibular system Body mechanism relating to navigation, balance, and posture. Vibrotactile aids Devices helping deaf people to understand sound by touching. Viral hepatitis - Hepatitis caused by virus. Whole blood Complete blood with all of its components (white and red blood cells, platelets, etc.). Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) Removing eggs from ovaries, fertilizing with sperm, and inserting them into fallopian tubes.
Dictionaries and glossaries of medical definitions
Medical definitions on health topics by World Health Organization (WHO)
Meaning of abbreviations for Dosage Forms Found in Inscription, Subscription or Signa Medical definitions for pregnancy and pregnancy loss by Patty Phipps Medical definitions to describe symptoms of/or tests for Huntington's Disease (HD) or discuss other diseases or condition which have symptoms similar to HD On-Line Medical Dictionary containing medical definitions by the Department of Medical Oncology of University of Newcastle
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chabner: The Language of Medicine, 10th EditionDocumento3 pagineChabner: The Language of Medicine, 10th EditionEvaDominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho Exam 3Documento7 paginePatho Exam 3menickel3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vagus Nerve: Vagus Nerve Activities to Relieve Anxiety, Reduce Severe Illness, Relief Depression, Anxiety, Stimulate Vagal Tone, Prevent Inflammation, Trauma, and PTSDDa EverandVagus Nerve: Vagus Nerve Activities to Relieve Anxiety, Reduce Severe Illness, Relief Depression, Anxiety, Stimulate Vagal Tone, Prevent Inflammation, Trauma, and PTSDValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Medical Term PQRSTDocumento37 pagineMedical Term PQRSTTika Arizon R NNessuna valutazione finora
- GIFTED: Genetic Information For Treating Eating DisordersDa EverandGIFTED: Genetic Information For Treating Eating DisordersNessuna valutazione finora
- English Class 1Documento9 pagineEnglish Class 1Jose RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Language: These Systems AreDocumento15 pagineMedical Language: These Systems AreRani ChetriNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocumento22 pagineHirschsprung DiseaseHerry PriyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- RT 102 Medical Terminology FinalsDocumento17 pagineRT 102 Medical Terminology FinalsCalessNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical TerminologyDocumento14 pagineMedical TerminologyCharmy UbiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Sonam'sDocumento200 pagineDR Sonam'sABDULJWAD HADDADNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Assistant Key WordsDocumento5 pagineMedical Assistant Key WordsRania KhelilNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Cheat SheetJacob100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyyDocumento64 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyyDelron GarrawayNessuna valutazione finora
- Auricular MineDocumento31 pagineAuricular Mineamane72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Endocrine SystemDocumento29 pagineAssessment of The Endocrine SystemBintang Banyu Biru100% (1)
- DR Sonam's High Yield Notes For ST 2 & 5 2nd EditionDocumento251 pagineDR Sonam's High Yield Notes For ST 2 & 5 2nd EditionMuhammad Fahad100% (1)
- Prepared By: Maria Lourdes P. SagunDocumento50 paginePrepared By: Maria Lourdes P. SagunAGLDNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper Urinary SystemDocumento7 pagineResearch Paper Urinary Systemaflbojhoa100% (1)
- Speech Swallowing ImpairmentDocumento36 pagineSpeech Swallowing ImpairmentSamer FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy NotesDocumento32 pagineAnatomy NotesRufaidy IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Edwin Jonathan A. Manlapas, DDM, R.NDocumento726 paginePrepared By: Edwin Jonathan A. Manlapas, DDM, R.NQuolette ConstanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologySamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology GASTRODocumento5 pagineAnatomy and Physiology GASTROJaye DangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Structures and Functions of The Endocrine System Glands: Organs in The Endocrine SystemDocumento21 pagineEndocrine Structures and Functions of The Endocrine System Glands: Organs in The Endocrine SystemPete Cobra CobraitiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Health Terms A-CDocumento19 pagineMedical Health Terms A-CKrisha Mabel TabijeNessuna valutazione finora
- Odynophagia Is Painful SwallowingDocumento21 pagineOdynophagia Is Painful SwallowingVien CaagbayNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Vascular Accident (Stroke)Documento5 pagineCerebral Vascular Accident (Stroke)SN. CaRNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypothyroidism: Brief Definition Prevalence Risk FactorsDocumento8 pagineHypothyroidism: Brief Definition Prevalence Risk FactorsJennifer BeguinwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal DisordersDocumento48 pagineAdrenal DisordersMubeenUrRehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hereditary Diseases of Nervous SystemDocumento52 pagineHereditary Diseases of Nervous SystemAhmed Adel SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento59 pagineCerebrovascular AccidentSiwani raiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical SpecialistsDocumento1 paginaMedical Specialistsashneetbrar2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unconsciousness: Anil PatidarDocumento29 pagineUnconsciousness: Anil Patidarjinal sutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Healthy GuideDocumento5 pagineHealthy GuideJoshua VázquezNessuna valutazione finora
- MusculoskeletalDocumento119 pagineMusculoskeletalEdissa PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Documento11 pagineSpinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Sugar Capule - ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento19 pagineBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaEmmanuel MacheleleNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento18 pagineAnatomy and Physiologyeduard adrian manuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gloss Med TermsDocumento44 pagineGloss Med TermsNicoleta IacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplemental Bullets FoundationsDocumento10 pagineSupplemental Bullets FoundationsrayneamgNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological Problems of The Adult ClientDocumento185 pagineNeurological Problems of The Adult Clientangelica barretoNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurogenic BladderDocumento38 pagineNeurogenic Bladderminnalesri100% (1)
- Scie Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocumento6 pagineScie Reviewer 3rd QuarteratienzanorrayneNessuna valutazione finora
- ICP Head InjuryDocumento57 pagineICP Head InjuryWengel RedkissNessuna valutazione finora
- Nur Akbar A. Mini LectureDocumento39 pagineNur Akbar A. Mini LectureanafauziahfitriNessuna valutazione finora
- H.W Medical TerminologyDocumento6 pagineH.W Medical TerminologySaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro Reviewer 2Documento33 pagineNeuro Reviewer 2joanneNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals CA 1 - ReviewerDocumento4 pagineFinals CA 1 - ReviewerkcharmaigneNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyroidectomyDocumento52 pagineThyroidectomyWindelyn Gamaro100% (4)
- ANAPHY111Documento60 pagineANAPHY111Gerlyn MortegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical TermsDocumento8 pagineMedical TermsVimal RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Muh. Ismail Pratama A. Tenri Luwu MutmainnahDocumento34 pagineMuh. Ismail Pratama A. Tenri Luwu MutmainnahNurul Qalby AmiluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Commonly Asked Emergency DrugsDocumento17 pagineCommonly Asked Emergency DrugsrianneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Body: Abdomen. AppendixDocumento8 pagineThe Human Body: Abdomen. AppendixMubin Ebine BaridNessuna valutazione finora
- SCHEME of The PEDIATRICS' CASE HISTORYDocumento17 pagineSCHEME of The PEDIATRICS' CASE HISTORYManusheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization of The Nervous System: BT520: Principles of NeuroscienceDocumento41 pagineOrganization of The Nervous System: BT520: Principles of NeurosciencePrathyu ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistDocumento5 pagineEndocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistSakshi BishnoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eastern Football League: 5 Year Strategic Business Plan 2019-2023 SultanDocumento11 pagineEastern Football League: 5 Year Strategic Business Plan 2019-2023 SultanSajov Nhyira Sultan BarryNessuna valutazione finora
- HS-Rev.00 Hazardous Substance - Chemical Assessment SheetDocumento2 pagineHS-Rev.00 Hazardous Substance - Chemical Assessment Sheetlim kang haiNessuna valutazione finora
- Baby Led-WeaningDocumento7 pagineBaby Led-WeaningsophieNessuna valutazione finora
- Autism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptDocumento26 pagineAutism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptWanessa FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014-1 Mag LoresDocumento52 pagine2014-1 Mag LoresLi SacNessuna valutazione finora
- Diet's CardDocumento8 pagineDiet's CardJORGE ATRIANONessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Member Handbook English UHCCPforAdults NYDocumento52 pagine2011 Member Handbook English UHCCPforAdults NYpatsan89Nessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacyDocumento27 paginePharmacyJenilNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Report On Health and HygieneDocumento4 pagineSummary Report On Health and HygieneVisal ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Standards For Accreditation-Schools - 2010Documento43 pagineStandards For Accreditation-Schools - 2010Nayda Jiménez Pérez100% (1)
- Resume 3Documento2 pagineResume 3api-458753728Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Overload and Kidney Injury Score As A PredicDocumento7 pagineFluid Overload and Kidney Injury Score As A Predicmira srikandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Law Transcription Atty BatacanDocumento30 pagineEnvironmental Law Transcription Atty BatacanMa Gloria Trinidad Arafol100% (1)
- Export of SpicesDocumento57 pagineExport of SpicesJunaid MultaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Hearing Handicap Inventory For The Elderly (HHIE)Documento5 pagineHearing Handicap Inventory For The Elderly (HHIE)Is GutiérrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacific CrossDocumento27 paginePacific Crossanon_873405382Nessuna valutazione finora
- INTEGRATED CASE STUDY: Cold Supply Chains and The COVID-19 VaccineDocumento3 pagineINTEGRATED CASE STUDY: Cold Supply Chains and The COVID-19 VaccineKatia Katherine LUZON CURONessuna valutazione finora
- Intrathecal Antibiotic Administration Procedure (Paediatrics)Documento9 pagineIntrathecal Antibiotic Administration Procedure (Paediatrics)Abu Azzam Al-HadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Orofacial Dysfunction Nonnutritive Sucking Hab 2022 American Journal of OrtDocumento8 pagineOrofacial Dysfunction Nonnutritive Sucking Hab 2022 American Journal of OrtMario Ruiz RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Sleep BetterDocumento9 pagineHow To Sleep BetterMariaNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Drug Information 2000Documento66 pagineWHO Drug Information 2000Rajib ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Net Jets Pilot & Benefits PackageDocumento4 pagineNet Jets Pilot & Benefits PackagedtoftenNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Thesis 22Documento66 pagineFinal Thesis 22AdombireNessuna valutazione finora
- Futuristic Nursing: - Sister Elizabeth DavisDocumento14 pagineFuturistic Nursing: - Sister Elizabeth DavisPhebeDimple100% (2)
- Coca Cola Fairlife CaseDocumento4 pagineCoca Cola Fairlife Caseapi-315994561Nessuna valutazione finora
- Raynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1Documento2 pagineRaynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1api-340995574Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pengaruh Pijat Bayi Terhadap Frekuensi Dan Durasi Menyusu BayiDocumento11 paginePengaruh Pijat Bayi Terhadap Frekuensi Dan Durasi Menyusu BayiIzmi NasutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ericksonian Approaches To PsycDocumento15 pagineEricksonian Approaches To Psychouda houdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Promoting Smart Farming, Eco-Friendly and Innovative Technologies For Sustainable Coconut DevelopmentDocumento4 paginePromoting Smart Farming, Eco-Friendly and Innovative Technologies For Sustainable Coconut DevelopmentMuhammad Maulana Sidik0% (1)
- Pork TocinoDocumento1 paginaPork TocinoMaria Ivz ElborNessuna valutazione finora
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Da EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (31)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDa EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassDa EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (27)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingDa EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1138)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (253)