Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Med-Com's Imp Embryo
Caricato da
kamran_zarrarDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Med-Com's Imp Embryo
Caricato da
kamran_zarrarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Med-com's Important points from
Embryology
Endometrium is epithelial tissue , of uterus during menstrual cycle changes happen here when it grows it proliferating phase of menstrual cycle, when it secretes it is secreting phase of menstrual cycle both phases depends on blood supply. Intermediate layer is the thick layer, muscular layer (myometrium), proliferate during pregnancy. It is smooth muscles , hypertrophy. Outermost layer is perimetrium / epimetrium contains connective tissue, nerve + hormones Distal narrow position is cervical canal between canal & uterus canal is internal os. B/w vaginal canal & outer is external os. Cervical is opening in vaginal the surrounding space is vaginal fornix. There are four walls, two lateral + ant. + post. Pus is drained form post. Vaginal fornix Imaginary line b/w 2 uterine tube, part of uterus above it is fundus of uterus Rest b/w internal os & fundus is body of uterus. Dilation in uterine tube is Ampulla and fertilization take place normally here. The narrowest part of uterine tube is Asthmus & Sperms rest here. At 3rd month of intrauterine life of baby,the cells came from yolk sac to posterior abdominal cell called germ cells these are oogonia & start meiosis,& by age these cells are 7 million the space is insufficient , some cells will go to meiosis & other go to degeneration & at birth its number is 2 million and in childhood some cells degenerate so on puberty they are just 40,000 and only 400 used in life averagely. In meiosis 1 the reduction phases mean unusual distribution of cytoplasm , 90 :1.
Then primary oocyte goes to meiosis 2 and polar body rests in prophase(dictyotene) stage. Age of menarci (when menstrual cycle starts) is 11-13.it is actual training period towards maturity. In early infancy,primary oocyte+polar body protected by flat cells of epithelium called PRIMORDIAL FOLLICLE. Gonadotropin(FSH+LH) released at age of puberty acts on primordial follicle(flat cells+surrounding tissues) & no. increased by mitosis. Glandular epithelium forms surroundings of flat cells THECA INTERNA,& there is also a covering which is THECA EXTERNA. Steroid hormones are produced (estrogen+progesterone) FSH acts on follicular layer it goes converted into stratified. 15-20 cells of 2 million are used per month of menstrual cycle. The primary oocyte is pushed to one side of the follicle where it is surrounded by a mound of follicular cells which are cumulus oophorus. Completion of meiosis 2 is complete when sperm enters otherwise it rests in telophase stage. EPF (early pregnancy factor) presence of a immunosuppressants (healthy protein) in serum of mother after 30 hours of conceptus. EPF is different from hormone test for pregnancy. No. of 16 cells is not important but appearance of this structure like malburry tree called morula is important. Individual cell of morula is blastomere. Within zona pellucida cells will increase in no. but decrease in size and come closer. Destiny of blastomere is not decided so we can analysis (genetic) pre natal birth defects by this blastomere. Conceptus reach uterine end at day 4 (after 14th day the day of ovulation) After compaction(no. 32) not possible for cells of centre to reach peripheral area now fate of cells will be decided.
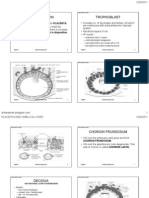
Outer mass cells will provide nutrition(trophoblast,tropho=nutrition) Inner mass cells will provide embryoblast (stem cells) LAW OF EMBRYO a cavity forms when cells gets divide rapidly. So there will be a blasto cell space in uterine tube here the age of conceptus will be 4 /5 days.. the phase of menstrual cycle here will be secretory. At the day 19(of menstrual cycle) secretions will come from endometrium,to the blastocoele in blastocyst and embryo will be pushed to one side,covered by outer cell mass (one layer only) It helps to convert it into bipolar structure, EMBRYONIC POLE+AN-EMBRYONIC POLE Breakage of zona pellucida on 6th day (of conceptus),and blastocyst will attach to the fundus of the uterus with embryonic pole USUALLY it is called implantation) WHICH IS POSTERIOR SIDE /ANTERIOR OF FUNDUS normally. Trophoblast will get signal and divide more rapidly.irregular cells with multi nuclei form. Throphoblast gives 2 type of cells .. network forming,bigger size is syncytiotrophoblast,mitotic figure is cytotrophoblast. They produce human gonadotropin,chorion,HCG because it got ve feedback to suppress progesterone by pituitary gland but we want to maintain pregnancy. HCG is seen in urine of mother after 10 days of conceptus.we can see in test after 1 week of missing periods. Cells towards blastocoele cavity are hypoblast in embryo and acquire cuboidal shape and other form columnar shape and are epiblast. Epiblast will divide rapidly and spaces will be formed (amniotic cavity),roof of this cavity is amnioblast and floor forming are still epiblast. Hypoblast also divide and forming covering for blastocoel now it is called primitive yolk sac(by langman) / primary umbilical vesicle (by K.L.M) Embryonic disc(bilaminar)=epiblast+hypoblast,surrounding by 2 cavities. Syncytiotrophoblast will also secrete proteolytic enzyme to digest mucosal cells of fundus of mother. Implantation starts on 6th day ends on 9th day and at 12th day nothing can be seen/enters in fundus.. thus conceptus is saved in fundus.
Conversion of non pregnant uterus to pregnant uterus in decidual reaction and now mucosa of pregnant woman is decidual mucosa. Immunosuppressant released by blastomere itself but not by mother and it can be detected in 24-48 hours after fertilization. Factors of implantation from langman Technique to detect ectopic implantation is abdominal pain+trans vaginal ultrasonography. From proliferative phase of menstrual cycle glycogen+lipid stores and abnormal shape of cells of uterus columnar to polygonal. ICSI ( intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection) is performed in low sperm count. Extra set of chromosome is seen at non disjunction in 24+23=47 meiosis 1 so
Exocelomic=Heusers membrane,due to migration of hypoblast,makes lining of blastocoele cavity and this is exocelomic cavity/primitive yolk sac. Chorionic villus are in spaces of syncytiotrophoblast,core is of cytotrophoblast and coat is of cytotrophoblast. Embryonic pole becomes bushy,and anembryonic pole becomes smooth. MESODERM is formed by the proliferation(outer and lateral) of hypoblasts,it is in between hausers membrane and cytotrophoblast. This forming mesoderm is extraembryonic and doesn't form anything of baby(in his body),it helps in development in uterus of mother. Chorionic cavity which is formed in extra embryonic mesoderm divides it into 2.. inner layer covering primary umbilical vesicle is splanchnic mesoderm,it will form coverings for viscera like heart,lungs etc and other is roof of chorionic cavity,covering body of embryo known as somatic mesoderm. Exocelomic cyst: remnant of primary umbilical vesicle by compression of secondary umbilical cavity and chorionic cavity.it is on head nothing to worry about it. Gastrulation is conversion of bilaminar germ disc into trilaminar germ disc, it is done in 1st half of 3rd week. Vitamin A is dangerous in pregnancy because it can cause blindness in babies (it is
for treatment of pimples)
Connecting stalk is actually upper layer of extra embryonic mesoderm,it is continuous with cytotrophoblast,it will decide the caudal end. Hypoblast is strictly adherent to epiblast by bucchopherangeal stalk,holes in this is coreacle plate. NEURAENTERIC ,neuro;nervous and enteric;GIT Canal is hollow and chord is hard. NOTOCHORD is important inducer for head region and axial skeleton(vertebral column). Tumor of notochord is chordema,1/3 of chorademas occur at the base of cranium and extend to the nasopharynx. Conversion of simple ectoderm BY SIGNAL of NOTOCHORD from mesoderm is neurulation. The new ectoderm is neuroectoderm,the cells of neuroectoderm are tall columnar and remaining ectoderm is surface ectoderm. The depressed area in neuroectoderm migrates towards mesoderm and it is neural groove. Than neural groove converts into neural canal and it is covering notochord in mesoderm. Formation of skin+nervous system and axial skeleton starts in 3rd week. Cells detach from neural ectoderm in process of conversion of neuroectoderm to canal are neural crest cells.they will participate in coverings of brain and cage for nervous system.THEY ARE NOT LOCALIZED,they reach neck region and contribute for thyroid gland+form septa of heart in thorax region.also form bones of face and ganglia+portion of adrenal gland ,suprarenal gland (medulla part). Allantois,Endoderm of yolk sac grows in extra embryonic forms bladder(urinary bladder). Derivatives of endoderm,participation of urinary blader(urachus) +GIT There is another mesoderm which is intraembryonic mesoderm which can be describe as following points: Paraxial mesoderm is medial mesoderm part surrounding notochord(which is
future vertebral column & musculoskeletal system) Intermediate mesoderm forms urogenital system Lateral plate mesoderm,its one layer surrounds yolk sac and other surrounds amniotic sac as splanchnic mesoderm and somatic mesoderm. Muscles of GIT are from yolk sac and muscles of body & dermis are from somatic mesoderm. Paraxial mesoderm gets segmented and these segments are known as somites. Somites of head region give deposition to ectodermal cells(neural crest cells) these cells are neuromas. Somites are important for age calculation of embryo. 1st pair of somites appear at 20th day,& 1st ly the somites appear in cervical region,they form at rate of 3 somites/day. Somites will divide itself in 2 ports,ventromedially & dorsolateral. Ventromedial cells will detach from somites & start surrounding growing notochord+neural canal and these cells will be known as sclerotome(forms cartilage & bone)these are fibroblastic. Dorsolateral cells have 3 groups: Central cells wull contribute in dermis (dermatomes) Dorsomedial & ventrolateral cells of dorsolateral part will join to form myotome muscles. Localized defect of spinal cord can be easily detect by study of dermatomes. Blood vessels develop from mesoderm it(b.v) may be extraembryonic like placental+umbilical & intraembryonic like cardiovascular system. Formation of blood vessels,conversion of mesoderm to vessels is VASCULOGENSIS. And sprouting of branches from any blood vessel is ANGIOGENSIS. MESENCHYMAL CELLS in splanchnic mesoderm makes isogenous group loose processes & form disc like structures known as blood island. Than arrange further in rows & centers. The central cells are angioblast which converts into R.B.Cs,W.B.Cs etc
The peripheral cells are epithelial cells and converts in continuous epithelium,endothelium. AGM is aorta gonad mesenphrone, The aorta-gonad-mesonephros is a region of embryonic mesoderm that develops during embryonic development.It has been suggested that this area, in particular the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta, is one of the primary origins of the definitive hematopoietic stem cell. The AGM region contains the dorsal aorta, genital ridges and mesonephros. The AGM region plays an important role in embryonic development, being the first autonomous intra-embryonic site for definitive hematopoiesis.
Send "MedCom" (without inverted commas) to 9900 and Receive All First Year Stuff FREE on ur Mobile via SMS Daily... Prepared By: For More Study Stuff....
Shaista Malik & Muhammad Kamran
Admins @ Med-Com
Join Us @
Facebook :
http://facebook.com/MedCom.2011
Pring:
http://pringit.com/MedCom
Twitter:
http://twitter.com/MedCom_2011
Website:
http://med-com.co.cc
All Right Reserved.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Allama Iqbal Medical College Lahore Open Merit List 2013Documento28 pagineAllama Iqbal Medical College Lahore Open Merit List 2013Shawn ParkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell InjuryDocumento8 pagineCell Injurykamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Handmade ArtDocumento31 pagineHandmade Artkamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Supple Students of Batch I and JDocumento1 paginaSupple Students of Batch I and Jkamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral Sciences MCQDocumento10 pagineBehavioral Sciences MCQMuhammad Bilal50% (4)
- Nets Certificate: Microsoft Certified System Engineer (Mcs2003)Documento2 pagineNets Certificate: Microsoft Certified System Engineer (Mcs2003)kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- GKMC DG Khan Merit List 2014-15Documento10 pagineGKMC DG Khan Merit List 2014-15kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- AIOU (Extension in Admission Date)Documento1 paginaAIOU (Extension in Admission Date)kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Medsolutions PharmacologyDocumento123 pagineMedsolutions Pharmacologykamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Lectures 2014Documento297 pagineClass Lectures 2014kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 MarksDocumento1 paginaAllama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 Markskamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mbbs Sendup TeamDocumento2 pagineMbbs Sendup Teamkamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Med-Solutions Pathology & MicrobiologyDocumento181 pagineMed-Solutions Pathology & Microbiologykamran_zarrar100% (1)
- MedCom's MCQs CH 16Documento4 pagineMedCom's MCQs CH 16kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 MarksDocumento1 paginaAllama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 Markskamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- MedCom's MCQs CH 15Documento3 pagineMedCom's MCQs CH 15kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Med-Solutions Forensic MedicineDocumento140 pagineMed-Solutions Forensic Medicinekamran_zarrar100% (3)
- Med-Com Imp LowerDocumento12 pagineMed-Com Imp Lowerkamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Med-Com's CH 14 MCQsDocumento4 pagineMed-Com's CH 14 MCQskamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- MedCom's MCQs CH 14Documento4 pagineMedCom's MCQs CH 14kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- KLM Embryo CH 5Documento3 pagineKLM Embryo CH 5kamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Med-Com's CH 14 MCQsDocumento4 pagineMed-Com's CH 14 MCQskamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Med-Com's Clinical ReviewDocumento7 pagineMed-Com's Clinical Reviewkamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- KLM Chapter 6Documento4 pagineKLM Chapter 6Ceo MedComNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : TrisomyDocumento4 pagineClinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : Trisomykamran_zarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- CH 47 Reading GuideDocumento8 pagineCH 47 Reading GuidepearlparfaitNessuna valutazione finora
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento33 paginePrenatal DevelopmentDexter Nario0% (1)
- NeurulationDocumento6 pagineNeurulationnumannazir3276Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Documento7 pagineGroup Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Kayl Dustin MalalisNessuna valutazione finora
- Embriology Hewan Michael J. F. Barresi Scott F. Gilbert Developm (B-Ok - Xyz) (2) (PDF - Io)Documento60 pagineEmbriology Hewan Michael J. F. Barresi Scott F. Gilbert Developm (B-Ok - Xyz) (2) (PDF - Io)Afriani AfidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrulation in MammalsDocumento16 pagineGastrulation in Mammalskashif manzoor75% (4)
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocumento5 pagine48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology of Heart and Fetal CirculationDocumento36 pagineEmbryology of Heart and Fetal CirculationRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Craniofacial Biology Notes Unit 1Documento37 pagineCraniofacial Biology Notes Unit 1nohacksNessuna valutazione finora
- Leifer: Maternity Nursing, 10th Edition: Chapter 3: Fetal Development Test Bank Multiple ChoiceDocumento11 pagineLeifer: Maternity Nursing, 10th Edition: Chapter 3: Fetal Development Test Bank Multiple ChoiceJennifer RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocumento5 pagine33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal DevelopmentDocumento12 pagineAnimal DevelopmentJobelle CajipoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentDocumento17 pagine7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentHussein Al SaediNessuna valutazione finora
- Islam and Embryonic Development (First 40days of Pregnancy)Documento13 pagineIslam and Embryonic Development (First 40days of Pregnancy)ahmad kaj100% (1)
- Embryology Review for Dr. ElHodibyDocumento10 pagineEmbryology Review for Dr. ElHodibyw yNessuna valutazione finora
- Process of ConceptionDocumento42 pagineProcess of ConceptionimnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Weeks 3 - 8Documento32 pagineWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-3rd Week of Embryonic DevelopmentDocumento116 pagine1st-3rd Week of Embryonic DevelopmentElizabeth OmobolanleNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology - Unraveling The Wonders of LifeDocumento4 pagineEmbryology - Unraveling The Wonders of Lifezaki4665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes TheDocumento6 pagineNeurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes Theaaliya saaheenNessuna valutazione finora
- Developmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickDocumento21 pagineDevelopmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickHoney krishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 11 Gross Morphology of The Chick Embryo Gallus Gallus PDFDocumento3 pagineExercise 11 Gross Morphology of The Chick Embryo Gallus Gallus PDFMichaela FayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 3 - Fish EmbryogenesisDocumento17 pagineGroup 3 - Fish EmbryogenesisRegina LarasatiNessuna valutazione finora
- PlacentaDocumento6 paginePlacentaKishore Singh BasnetNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Face &it's Applied AspectsDocumento95 pagineDevelopment of Face &it's Applied AspectsHansa KunduNessuna valutazione finora
- Chick Serial SectionsDocumento74 pagineChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Muscular System AtfDocumento3 pagineDevelopment of Muscular System AtfKim Sa-buNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.01 Biology EvolutionDocumento8 pagine5.01 Biology EvolutionOkoye ClappinNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Anatomy ReviewerDocumento18 pagineComparative Anatomy ReviewerCedrick GamatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 Fertilization, Implantation and Fetal DevelopmentDocumento17 pagineLesson 4 Fertilization, Implantation and Fetal DevelopmentAPRIL ALAPNessuna valutazione finora