Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Butani Data
Caricato da
Leon MukerjeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Butani Data
Caricato da
Leon MukerjeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1 CHAPTER 1INTRODUCTION The growing and the dynamic business environment of today are faced withlots of challenges and
opportunities. The dependence on the information, as adriving energy source is increasing. The business needs today stretch beyondthe transaction processing, requiring an instant real time response wherever itoccurs.The business today is a paperless operation, a wireless communication as aresult of fully transparent and automated operations at all centers in anintegrated and coordinated manner taking care of the business, actions anddecision needs. And these demands of the business are met by systems of information processing and communication.Though the tools and technologies, and the solutions for these needs areavailable but what is required is an integrated solution out of thesetechnologies and the systems offering an enterprise. Such an integratedsolution is called Enterprise Management System (EMS).In EMS, the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system plays a veryimportant role. The major decision making and it execution is done throughERP. Its the system of managing all functions of the business withinformation support coming through the ERP. It handles the operationalsystems to run business and provides the required inputs to planning andcontrol systems handled by the middle management ERP is a way to integrate the data and processes of an organization into onesingle system. Usually ERP systems will have many components including hardware and software, in order to achieve integration, most ERP systems usea unified database to store data for various functions found throughout theorganization. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a company-wide computer software system used to manage and coordinate all the resources, information,and functions of a business from shared data stores.
1.1 Objective The seminar discuss in detail about the ERP system, its features, itsadvantages and disadvantages. This seminar also explained about the differentfunctional modules, how to the implement the ERP system in an industry, howto make the ERP system user friendly etc. Thus the seminar provides the ideaon how to make the enterprise management easier and effective with the helpof an ERP system. 1.2 Report overview Chapter 1 is the introduction of the seminar. Chapter 2 discuss about the evolution of ERP system. Chapter 3 deals with the functional modules of ERPsystem. Chapter 4 explains about how to implement ERP system and how tomake a sucessesful one. Chapter 5 discusses about the next generation ERPsystem. Chapter 7 is the conclusion about this topic. The last page is thereference
CHAPTER 2 EVOLUTION OF ERP SYSTEMS
The evolution of ERP systems closely followed the spectacular developmentsin the field of computer hardware and
software systems. During the 1960smost organizations designed, developed and implemented centralizedcompu
ting systems, mostly automating their inventory control systems usinginventory control packages (IC). These were
legacy systems based on programming languages such as COBOL, ALGOL and FORTRAN. Materialrequirem ents planning
(MRP) systems were developed in the 1970s whichinvolved mainly planning the product or parts requirements
according to themaster production schedule. Following this route new software systems calledmanufacturi
ng resources planning (MRP II) were introduced in the 1980s withan emphasis on optimizing manufacturing
processes by synchronizing thematerials with production requirements. MRP II included areas such as shopfloor and
distribution management, project management, finance, humanresource and engineering. ERP systems first
appeared in the late 1980s and the beginning of the 1990s with the power of enterprise-wide interfunctionalcoordin
ation and integration. Based on the technological foundations of MRPand MRP II, ERP systems integrate business
processes includingmanufac turing, distribution, accounting, financial, human resourcemanagem ent, project
management, inventory management, service andmaintenance, and transportation, providing
accessibility, visibility andconsistency across the enterprise . During the 1990s ERP vendors
added more modules and functions asaddons to the core modules giving birth to the extended ERPs. TheseERP
extensions includ e advanced planning and scheduling (APS), ebusinesssolutions such as customer relationship
management (CRM) and supply chainmanagement (SCM). Figure
2
.1 summarizes the historical events related
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Ebook Mql5Documento22 pagineEbook Mql5cakung204Nessuna valutazione finora
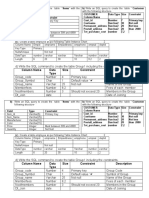
- Oracle9i Introduction To 9i SQL HandbookDocumento21 pagineOracle9i Introduction To 9i SQL Handbookemailtorakesh100% (2)
- Damon Martin: Sr. Project ManagerDocumento5 pagineDamon Martin: Sr. Project Managerashish ojhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 With Table ConstraintsDocumento1 pagina5 With Table ConstraintsshilvermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Dinesh Kumar Bhawnani, BIT DURGDocumento16 pagineUnit 1: Dinesh Kumar Bhawnani, BIT DURGDinesh BhawnaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Testing Materials PDFDocumento160 pagineSoftware Testing Materials PDFKshitij PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Kế Hoạch Học PMPDocumento4 pagineKế Hoạch Học PMPKhacNam NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- E 15175Documento216 pagineE 15175DebianReisNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Tier ArchitectureDocumento36 pagine3 - Tier ArchitectureSanjeev SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ebay Architecture: Amazon Friday Learning SeriesDocumento39 pagineThe Ebay Architecture: Amazon Friday Learning SeriesgamezzzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Prepartion For EBS R12.2Documento13 pagineDatabase Prepartion For EBS R12.2Narendra NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Mart InfoDocumento5 pagineData Mart InfosrpothulNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Migration PlanDocumento25 pagineData Migration Plankanantaram7197100% (2)
- DBMS-UNIT-1 R16 (Ref-2)Documento12 pagineDBMS-UNIT-1 R16 (Ref-2)RAJESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Business AnalyticsDocumento4 pagineBusiness AnalyticsYan Myo ZawNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practices For Training and Support FINALDocumento32 pagineBest Practices For Training and Support FINALMarissa AntoshNessuna valutazione finora
- DFo 1 1 SGDocumento12 pagineDFo 1 1 SGAl KayyisNessuna valutazione finora
- 10777a 01Documento18 pagine10777a 01JOSE LUIS GARAVITO ALEJOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Class15 - Data WarehousingDocumento76 pagineClass15 - Data Warehousingpkrsuresh2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4Documento31 pagineLecture 4chan chanchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Flow Diagram: Structuring System Process RequirementsDocumento39 pagineData Flow Diagram: Structuring System Process RequirementsIlham J.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Business Research Methods: Secondary Data Research in A Digital AgeDocumento24 pagineBusiness Research Methods: Secondary Data Research in A Digital AgesairamNessuna valutazione finora
- ADWDM (MECS-701) SyllabusDocumento1 paginaADWDM (MECS-701) Syllabusmuskanvats25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologyDocumento46 pagineFundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologychalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1. Design Goals and ObjectivesDocumento7 pagine3.1. Design Goals and ObjectivesshimelisNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Pass4sure 1z0-067 v2018-05-14 by Lily 106qDocumento63 pagineOracle Pass4sure 1z0-067 v2018-05-14 by Lily 106qGiovedi Marmolejo CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- DLF PDFDocumento20 pagineDLF PDFAditya GoswamiNessuna valutazione finora
- JUSPAY Analytics Data Set - Product Solution AnalystDocumento3 pagineJUSPAY Analytics Data Set - Product Solution AnalystPrathyusha VallabhadasNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 - ITSM - Maximo & ITIL Business Case Study by Bill AdamsonDocumento27 pagineDay 2 - ITSM - Maximo & ITIL Business Case Study by Bill Adamsonsimo20005Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2CS402 - Database Management SystemsDocumento2 pagine2CS402 - Database Management SystemsParthDesaiNessuna valutazione finora