Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma Membrane
Caricato da
Muhammad AddinDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma Membrane
Caricato da
Muhammad AddinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 3-Movement of Subtances across the Plasma membrane.
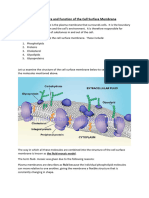
Structure of the plasma membrane -The plasma membrane consist of a phospholipid bilayer molecule
on the surface of the membrane,forming a mosaic pattern. -It consist of hydrophillic head which faces the extracellular fluid and a hydrophobic tail which faces each other in the membrane. -Proteins functions as carrier or pore for molecules to across the membrane. -Cholesterol within the phospholipid bilayer stabilises the structure. -The carbohydrates attach to glycoproteins or glycolipids on the outer surface of the membrane. -The plasma membrane acts as barrier to control the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
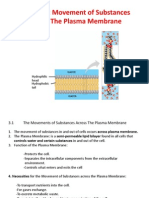
Passive transported
Simple Diffusion
-Diffusion is defined as the net movement of particles of a substances from region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration of the substances.These particles are said to be moving down the concentration gradient. -It will continue until equilibrium is reached.When equilibrium is reached,the particles still moves but there is n net movement in any particular direction. -Diffusion trough the cell membranes is affected by the permeability of the membrane and the size and type of particlesdiffusing trough it. -The phospholipid bilayer is permeable to very small uncharged molecule like oxygen and carbon dioxide.These molecules diffuse freely in and out of the cell trough the phospholipid bilayer. -Hydrophobic molecule such as steriod and fat-soluble vitamins A,D,E,K can dissolved in the phospholipid bilayer.These substances diffuse readily trough
the phospholipid bilayer down the concentration gradient by simple diffusion.
Facilitated Diffusion
-Unsoluble substaces in lipids(glucose,amino acid,nucleic acid) cannot pass trough the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. -These substances pass trough the phospholipid bilayer by facilitated diffusion. -Diffusion is facilitated by carrier protein or pore proteins. -When there is a concentration gradient of glucose molecules between the plasma membrane,the glucose molecules will bind to an active site on a specific carrier protein.The binding caused the carrier protein to change it shape and the glucose molecule is released into the cell down the concentration gradient. -Small polar molecules such as Na,HCO ions and water molecules are prevented from moving across the phospholipid bilayer.
-These hydrophilic molecules have to pass trough the plasma membrane via the hydrophilic channels formed by proteins molecules that are scattered across the phospholipid bilayer. -These pore proteins acts as tunnels trough which certain ion and polar molecules,including water, can pass through -Facilitated diffusion is passive and does not required any energy.
Osmosis
-Osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration water molecules(low solute concentration or low osmotic pressure) to a region of lower concentration of water molecule(high solute concentration or high osmotic pressure) across a semi-permeable membrane -Osmosis does not required energy as water moves across a semi-permeable membrane according to its concentration gradient. -The movement wil continue until the concentrations of water on both sides of the membranes are equal.There is no net movement of water. -A solution that contains less solute,low concentration and low osmotic pressure is known as hypotonic solution -A solution that contain more solute,high concentration,high osmotic pressure is known as hypertonic solution.
-A solution that contains equal amount of dissolved particles wil produce osmotic pressure of equal magnitudes is known as isotonic solution.There is no net movement of water molecules between both solutions.
Active Transport
-Active transports is the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membranes against their concentrations gradient;from region of lower concentration to region of higher concentrations.The process requires energy in form of ATP. -Occurs in living system that actively synthesises energy trough respiration.
Osmosis in animal cells
Isotonic solution -When the RBC are placed in an isotonic solution,there is no net movement of water molecules,thus no change in the shape or volume of the cell. Hypotonic solution -When the RBC is placed is hypotonic solution,water enters by osmosis.There is a net movement of water into the cell and cause it to expands and the thin plasma membrane bursts.The RBC is said to be haemolysed and the process is known as haemolysis. Hypertonic solution -When the cells is placed in hypertonice solutions,there is a net outflow of water by osmosis from the cells.The cell shrinks and the plasma membrane produce a crinkled appearance.The cell is said to be crenated,or so said to have undergo crenation.
Osmosis in plant cells
Hypotonic solution -When a plant cell is placed in an hypotonic solution,water enters by osmosis.The vacuole expand, and the plasma membrane stretches and exerts pressure against the cell wall. -Plant cell sap containing waters and dissolved solutes which enables soil water to enter the plant cells and maintain turgidity. -The entry of water through osmosis causes the protoplast to expand and pushes against the cell wall,exerting of hydostatic pressure,turgor pressure since it presses against the cell wall,thus maintaining the cell in a turgid condition .The plant cell is said to have turgidity. -Turgidity helps to maintain plant cell shape and form. Hypertonic solution -When a plant cell is placed is hypertonic solution,water will leaves the cell by osmosis.This results in the shrinking of the vacuole and protoplast in the cell ,causing the detachment and pulling away of the plasma membranes from the of the cell occurs and the cell becomes flaccid.A cell in this condition is said to be plasmolysed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- C3Movement Across The Plasma MembraneDocumento14 pagineC3Movement Across The Plasma Membranemagdelena100% (1)
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocumento11 pagineMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNessuna valutazione finora
- X Membrane and TransportDocumento35 pagineX Membrane and TransportHitesh MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 12 Plo b9 and b10 Transport Across Cell Membrane Vocabulary SolutionsDocumento4 pagineBio 12 Plo b9 and b10 Transport Across Cell Membrane Vocabulary SolutionsChan KarlokNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4Documento37 pagineChapter 3 Biology Form 4CuteOnion Furmon100% (1)
- Document 8Documento8 pagineDocument 8Tiana PolackNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocumento24 pagineCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell MembranesDocumento5 pagineCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Documento7 pagineBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport MembranDocumento34 pagineTransport MembranTia Herdiana WardaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Cellular Transport VidDocumento57 pagine1 Cellular Transport Vidchizy bananaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 Cell MembraneDocumento23 pagineWeek 6 Cell Membranesabeera.ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDocumento10 pagineChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocumento15 pagineCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport MechanismsDocumento1 paginaTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNessuna valutazione finora
- A Note Pre MedDocumento24 pagineA Note Pre Medwan amiera wan malekNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes: Topic-2ADocumento9 pagineBiology Notes: Topic-2Alaiba amirNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Membrane Grade 12Documento8 pagineCell Membrane Grade 12Olayinka SalmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportDocumento6 pagineCell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportKulsoom UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocumento28 pagineChapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneMohd Asraf90% (10)
- TOPIC 4 Cell Transport ReviewerDocumento7 pagineTOPIC 4 Cell Transport Reviewerashhii ramosNessuna valutazione finora
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocumento414 pagineMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals NotesDocumento21 pagineFinals NotesJoaquine ArateaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Notes FinalsDocumento4 pagineBio Notes FinalsJoaquine ArateaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Documento4 pagineGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento24 pagineChapter 2Anis PuadahNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma MembraneDocumento4 paginePlasma Membraneshalini_ganesanNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocumento10 pagineBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled PresentationDocumento24 pagineUntitled PresentationFreyacresaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2.1 Transport Mechanism 2Documento45 pagineQ2.1 Transport Mechanism 2kasandra cristy galonNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocumento10 pagineBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3Documento25 pagineTopic 3shiu ibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Documento33 pagineMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocumento30 pagineThe Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNorizan HusainNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell ConstituentsDocumento8 pagineCell ConstituentsSanaa SamkoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesDocumento11 pagineThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 2Documento14 paginePresentation 2Maya TareqNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell MembraneDocumento9 pagineThe Cell MembraneShuchi HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDocumento6 pagine2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Documento4 pagineChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Transport Across Cell MembranesDocumento10 pagineChapter 4 Transport Across Cell Membranesnoreen dorani100% (1)
- AP Bio Essay 1983Documento3 pagineAP Bio Essay 1983pezxo6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transport in Plants PDFDocumento10 pagineTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento6 pagineActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Membrane Bio QuizDocumento5 pagineCell Membrane Bio QuizMafalda SeabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocumento68 pagineFluid and ElectrolytesMara Jon Ocden CasibenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Transport Systems: Henny Rachdiati, Bpharm, MSC., PHDDocumento16 pagineCell Transport Systems: Henny Rachdiati, Bpharm, MSC., PHDMia AndiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionDocumento7 pagineChapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionIrish Jem BantolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell and Its FunctionDocumento26 pagineCell and Its FunctionMarielle MatunogNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocumento8 pagineInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- Pergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanDocumento36 paginePergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanSitiKomariahAgustinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.transport MechanismsDocumento94 pagine4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocumento8 pagineMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport MechanismDocumento19 pagineTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- Cell MembraneDocumento3 pagineCell MembraneQaran PrintingNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell MembraneDocumento2 pagineCell MembraneZei-chen LocabenNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftDocumento24 pagineTransport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftKaviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantDocumento6 pagine11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantMuskan VarlaniNessuna valutazione finora
- A Mechanico-Physiological Theory of Organic EvolutionDa EverandA Mechanico-Physiological Theory of Organic EvolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Fuel Cell and Internal Combustion Engine: AcknowledgementDocumento1 paginaComparison of Fuel Cell and Internal Combustion Engine: AcknowledgementMuhammad AddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises On Article 2Documento1 paginaExercises On Article 2Muhammad AddinNessuna valutazione finora
- PcconfigDocumento1 paginaPcconfigAnthony Calda OlanioNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Mode ACBDocumento28 pagineCheat Mode ACBMuhammad AddinNessuna valutazione finora
- PcconfigDocumento1 paginaPcconfigAnthony Calda OlanioNessuna valutazione finora
- Get Data BackDocumento1 paginaGet Data BackMuhammad AddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Identification of The Substance and CompanyDocumento6 pagineSafety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Identification of The Substance and CompanyleonardovegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hectatone Universal ProductBulletinDocumento1 paginaHectatone Universal ProductBulletinFederico ArqueroNessuna valutazione finora
- Kolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedDocumento4 pagineKolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedLeevandraaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prokaryotes and ArchaeaDocumento17 pagineProkaryotes and ArchaeaAngela CanlasNessuna valutazione finora
- TS 15280Documento1 paginaTS 15280GiveawayNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento8 pagine2api-3700944Nessuna valutazione finora
- Redubar A Register of All Gas RegulationsDocumento64 pagineRedubar A Register of All Gas RegulationsMilos BajicNessuna valutazione finora
- 263 269 JMTR Oct16Documento7 pagine263 269 JMTR Oct16Taniadi SuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenates (Alkyl Phenate Sulfides) : Product Stewardship SummaryDocumento4 paginePhenates (Alkyl Phenate Sulfides) : Product Stewardship SummaryPayal MinochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eps131-Heat of Combustion-Bsce-BsgeDocumento20 pagineEps131-Heat of Combustion-Bsce-BsgeKaye CasilNessuna valutazione finora
- UnfinishedDocumento8 pagineUnfinishedDaniel TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Q M C Delta TDocumento2 pagineNotes On Q M C Delta TDing30180Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo ChemDocumento20 pagineThermo ChemTimothy James M. MadridNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A27 (2010) PDFDocumento4 pagineAstm A27 (2010) PDFStuar TencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomass FinalDocumento12 pagineBiomass FinalAbu ikhtiarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp. - 9 Rotary FilterDocumento4 pagineExp. - 9 Rotary Filterfayaz5uin1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Fluids PDFDocumento24 pagineProperties of Fluids PDFAnthony Leire MontealtoNessuna valutazione finora
- Molycop - Tech Sheet Small Size Balls 003 MCAU - SMLTS1.3 - 290519 PDFDocumento3 pagineMolycop - Tech Sheet Small Size Balls 003 MCAU - SMLTS1.3 - 290519 PDFreza razaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Dutch Pollutant StandardsDocumento5 pagineDutch Pollutant Standardsumair2kplus492Nessuna valutazione finora
- Efficiency of Geothermal Power Plants - A Worldwide Review-AzDocumento13 pagineEfficiency of Geothermal Power Plants - A Worldwide Review-Azbitconcepts9781Nessuna valutazione finora
- KCGM XD48 Presentation ProcessDocumento152 pagineKCGM XD48 Presentation ProcessAnonymous ObQnrU100% (3)
- EN - Op.2 - EEE EXP4 - Semi Conductors - LecturesDocumento82 pagineEN - Op.2 - EEE EXP4 - Semi Conductors - LecturesImmaculee BITWAGEBWA VERONIQUENessuna valutazione finora
- PPIIDocumento1.106 paginePPIIVineeta SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moringa Oleifera Seed As Antibacterial Agent in Water TreatmentDocumento6 pagineMoringa Oleifera Seed As Antibacterial Agent in Water TreatmentStephen MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- High Strength Precipitation Hardening and Duplex Stainless Steel Bolting For Special Purpose ApplicationsDocumento6 pagineHigh Strength Precipitation Hardening and Duplex Stainless Steel Bolting For Special Purpose ApplicationsDanZel DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Miconium Btac80: Quaternary Ammonium SaltDocumento1 paginaMiconium Btac80: Quaternary Ammonium SaltJairo AlonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Thermal Effect of The Reich's DOR BusterDocumento16 pagineThe Thermal Effect of The Reich's DOR BusterAngel MalzoneNessuna valutazione finora
- DAQ Destroyer Hybrid RocketDocumento48 pagineDAQ Destroyer Hybrid Rocketprakulmittal2100% (1)
- Pneumatic Bench Vice Project-Report PDFDocumento30 paginePneumatic Bench Vice Project-Report PDFrahul bhatt100% (4)
- Chapter 3.2 Guided Reading WorksheetDocumento3 pagineChapter 3.2 Guided Reading WorksheetEvelyn QuiroaNessuna valutazione finora