Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pathophysiology of Burn
Caricato da
uaebDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology of Burn
Caricato da
uaebCopyright:
Formati disponibili
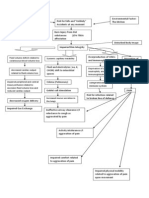
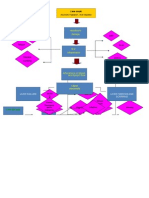
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CHEMICAL BURN
Risk Factors: Fire/Combustion Firefighter, Industrial Worker, Occupant of burning structures, Chemical Exposure, Industrial Worker Electrical Exposure Electrician, Electrical Power Distribution Worker Accidents Explosion
2nd degree burn injury in the right side of the head, face and neck, left upper extremity and chest, right ear, with noted redness over and surrounding the area, presence of blisters on the area
Risk Factors: (patient-based) Life threatening event Incidental pouring of strong acid or base Chemical spilling (strong acid) Rule of Nines: Head = 9% (front and back) Chest(front) = 9% Chest back (right side only) = 4.5% Arm (left upper extremity front and back) = 9% Total = 31.5% 2 nd degree burn
Impaired skin integrity r/t skin and tissue damage secondary to major chemical burn 2nd degree
Body in contact with the strong acid Major burn >25% body surface area in adults
Disturbed body image r/t disrupted skin and tissue membrane
Skin and tissue trauma/disruption
Hematology result as of : WBC=19.86(increa sed), Neutrophils= 0.84(increased)
Increase capillary permeability
SURGICAL TREATMENT: Emergency Debridement
Nociceptors of the dermis
Disruption of cell membrane
Open wound
Sodium, water and protein shift from IVS to ITS
Risk for deficient fluid volume r/t capillary damage (resolved)
Stimulation of the thermosensit ive pain receptors Sultamicillin 750mg TID Clindamycin 300mg BID
Inflammatory process
Site/location: Left side of the head, face and neck, left upper extremity and chest, left ear
Increase concentration of blood cells
Decrease circulating blood volume up to 50%
Hyponatremia
Migration of neutrophils
Risk for infection r/t loss of protective dermal barrier secondary to destruction of skin and tissue
Increase blood viscosity
Hypovolemia
Pain impulse
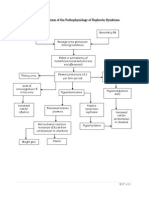
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CHEMICAL BURN Neutrophils releases lipases including phospholipase A2(produces AA from membrane phospholipids)
During admission at the ER: >Pain rated as 10/10, 10 as the highest and most painful, radiating on the head part, left upper extremity, chest and back, pain characterized as burning and pinching pain, aggravated by touch and movement >Grimacing and crying >Unable to move affected or burned area >screaming
Primary afferent neuron in the peripheral nerve
Increase myocardial depressant factor
Massive stress, SNS activation
Decreas e in BP
Second order neuron in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
Cyclooxygenase converts AA to Prostaglandin
Adrenal corticoid hormone and catecholamine release
Release of other biochemical pain mediators
Peripheral vasoconstriction
Tachycardia
Pain is modified by modulation factors Spinothalamic tract Brain stem
PAIN
thalamus
During assessment(latest) >Pain rated as 8/10, 10 as the highest and most painful, radiating on the head part, left upper extremity, chest and back, pain characterized as burning and pinching pain, aggravated by touch and movement >Grimacing >presence of numbness, tingling and burning pain on the area >with complaints of itchiness on the right arm
Peripheral resistance
Increased afterload
Decreased cardiac output (RESOLVED)
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CHEMICAL BURN Somatic sensory cortex Acute pain r/t destruction of skin and tissues secondary to major chemical burn in jury 2nd degree WDR neuron activation = spinal cord wind up = NMDA activation
PAIN PERCEPTION
Celecoxib 200mg BID Tramadol 50mg BID
Descending system
Release of endogenous opioids, serotonin, norepinephrine
Amplification of pain signals
Inhibits incoming/ ascending pain impulse
Pain persists
Inhibitory neurons are shortlived as they are reabsorbed into the nerves
NMDA receptors calcium channel opens
Pain reaches the CNS
PAIN ON THE SITE
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BurnDocumento47 pagineBurnYelle Quilatan100% (1)
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocumento5 pagineCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- Burn PathoDocumento2 pagineBurn PathoJoenaCoy Christine100% (1)
- Pathophys BURNDocumento2 paginePathophys BURNpaupaulala83% (6)
- Burn Injury PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineBurn Injury PathophysiologyGlenn Cabradilla100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Burn InjuryAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Burn PathoDocumento1 paginaBurn PathoArlan AbraganNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of BurnDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Burndm_geliNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Burn Injury (1) DVDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Burn Injury (1) DVRizzie Montes0% (1)
- Nursing - Burn InjuryDocumento39 pagineNursing - Burn Injuryamaracha2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Burn CsDocumento23 pagineBurn CsMASII100% (1)
- Burns Case StudyDocumento4 pagineBurns Case StudyJDRN14100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocumento46 paginePathophysiology of Burn InjuryIyanAsiana100% (1)
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocumento6 paginePathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue PatophyDocumento2 pagineDengue PatophyAliza Ancheta AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaNessuna valutazione finora
- BURNS - Concept MapDocumento1 paginaBURNS - Concept MapMayaPopbozhikova89% (9)
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocumento15 pagineAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisJeanne Marie ValesNessuna valutazione finora
- Left-Sided Heart FailureDocumento3 pagineLeft-Sided Heart FailureKhalid Mahmud ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- 6639burn NCPDocumento18 pagine6639burn NCPDivina Grace Renon Camba100% (1)
- Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverDocumento3 paginePathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverCyrus De AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureDocumento1 paginaRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map AsthmaDocumento4 pagineConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocumento3 pagineFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNessuna valutazione finora
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineESRD PathophysiologyMark Ronhel Gallardo PerenalNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiomegalyDocumento91 pagineCardiomegalyMariquita Buenafe100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocumento3 pagineRheumatic Heart DiseaseDee SarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Burn PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaElectrical Burn PathophysiologydanicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocumento6 pagineDiabetes PathophysiologyKatelyn CherryNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento4 pagineThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Burns Case Study TwoDocumento2 pagineBurns Case Study Twojenn1722100% (11)
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocumento5 paginePathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieNessuna valutazione finora
- CHOLANGITISDocumento1 paginaCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue PoathoDocumento6 pagineDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Tetanus PathoDocumento3 pagineTetanus PathoElisha Gine AndalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Case Study of Electric Burn Injury (Edit Nisa) Sdah Di Edit New 2Documento38 pagineNursing Case Study of Electric Burn Injury (Edit Nisa) Sdah Di Edit New 2Rizal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Documento2 paginePathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento27 pagineHemorrhagic StrokeMuhammad FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of Open FractureDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiology of Open FracturegiffersonbNessuna valutazione finora
- Left Heart FailureDocumento2 pagineLeft Heart FailureJechelle Ann Pabustan Martin-Boniquit100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology-Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 pagineAnatomy and Physiology-Liver CirrhosisHilmi Ramos100% (3)
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocumento4 paginePathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of AtherosclerosisAzrul Hakim100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Documento8 paginePathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Firenze Fil0% (1)
- Electrical BurnsDocumento28 pagineElectrical BurnsFrancis OkwerekwuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocumento6 paginePathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of PneumoniamatrixtrinityNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Types of IV FluidsDocumento10 pagineDifferent Types of IV FluidsMarinill SolimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaDocumento40 pagineUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaAy Alex0% (1)
- Case Presentation TetanusDocumento15 pagineCase Presentation TetanusukhtianitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluids Concept MappingDocumento1 paginaFluids Concept Mappingmariagarcia415100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of AppendicitisSherry Mae Rizza GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac TamponadeDocumento3 pagineCardiac TamponadeKimberly SolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatic FeverDocumento21 pagineRheumatic FeverUmar Azlan50% (2)
- Burns: Thermal/Chemical/Electrical (Acute and Convalescent Phases)Documento4 pagineBurns: Thermal/Chemical/Electrical (Acute and Convalescent Phases)makyofrancis20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Burns: Thermal/Chemical/Electrical (Acute and Convalescent Phases)Documento25 pagineBurns: Thermal/Chemical/Electrical (Acute and Convalescent Phases)markyabresNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration ConceptDocumento34 pagineIntegration ConceptJANELLA ALVAREZNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypothesis Testing - IDocumento36 pagineHypothesis Testing - Isai revanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Matters Signified by The Sublord of 11th Cusp in KP SystemDocumento2 pagineMatters Signified by The Sublord of 11th Cusp in KP SystemHarry HartNessuna valutazione finora
- Adriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineerDocumento3 pagineAdriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineeradrianorexNessuna valutazione finora
- ACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card ReaderDocumento8 pagineACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card Readersuraj18in4uNessuna valutazione finora
- SMC VM Eu PDFDocumento66 pagineSMC VM Eu PDFjoguvNessuna valutazione finora
- Filipino Construction TermsDocumento6 pagineFilipino Construction TermsAdrian Perez75% (4)
- B737-3 ATA 23 CommunicationsDocumento112 pagineB737-3 ATA 23 CommunicationsPaul RizlNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyDocumento2 pagineCarrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyVineet JogalekarNessuna valutazione finora
- GBJ0232 - en GLX 3101 T2Documento43 pagineGBJ0232 - en GLX 3101 T2mnbvqwert100% (2)
- Terminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6Documento2 pagineTerminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6jeremih alhegn100% (1)
- Rachel Joyce - A Snow Garden and Other Stories PDFDocumento118 pagineRachel Joyce - A Snow Garden and Other Stories PDFИгорь ЯковлевNessuna valutazione finora
- Javanese PeopleDocumento22 pagineJavanese PeopleDenisaNessuna valutazione finora
- FebvreDocumento449 pagineFebvreIan Pereira AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- LinkageDocumento9 pagineLinkageHarshu JunghareNessuna valutazione finora
- G-3 L-17 Internal QuestionsDocumento4 pagineG-3 L-17 Internal QuestionsActivity MLZS BarhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereDocumento4 pagine1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereNeil PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Phrasal Verbs Related To HealthDocumento2 paginePhrasal Verbs Related To HealthKnuckles El Naco Narco LechugueroNessuna valutazione finora
- Anderson, Poul - Flandry 02 - A Circus of HellsDocumento110 pagineAnderson, Poul - Flandry 02 - A Circus of Hellsgosai83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optik: Original Research ArticleDocumento6 pagineOptik: Original Research ArticlesimarpreetNessuna valutazione finora
- Conceptual Artist in Nigeria UNILAGDocumento13 pagineConceptual Artist in Nigeria UNILAGAdelekan FortuneNessuna valutazione finora
- CulvertsDocumento18 pagineCulvertsAmmar A. Ali100% (1)
- Iso 8033 2016Documento9 pagineIso 8033 2016Eric ChuNessuna valutazione finora
- ETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application NeedsDocumento106 pagineETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application Needs周小安Nessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HidupDocumento2 pagineContoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HiduprusmansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Beastlikebalsam - Muscle BuildingDocumento10 pagineBeastlikebalsam - Muscle BuildingBalsam LaaroussiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Ticket Receipt, January 27 For MS NESHA SIVA SHANMUGAMDocumento2 pagineElectronic Ticket Receipt, January 27 For MS NESHA SIVA SHANMUGAMNesha Siva Shanmugam ShavannahNessuna valutazione finora
- English Class Vii PDFDocumento101 pagineEnglish Class Vii PDFpannapurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Bardonna MenuDocumento16 pagineBardonna MenuFarley ElliottNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaffin, Biblical Theology and Westminster StandardsDocumento16 pagineGaffin, Biblical Theology and Westminster StandardstheoarticlesNessuna valutazione finora