Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Fact Cards
Caricato da
Joy QinCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Fact Cards
Caricato da
Joy QinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
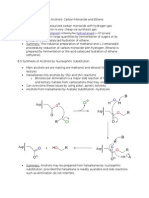
Functional Group: Halogen Nomenclature:
- Remove -ine from halogen + Add -o, and parent hydrocarbon
Halocarbon
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: fluroethane
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L Chlorine halocarbons (organochlorides) most common L Solvents, refrigerants and anesthetics. L Known as CFCs
Functional Group: Hydroxyl (OH) Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -ol
Alcohol
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanol
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L L L L
Ethanol most common Saturated carbon center (single bonds) Solvents, fuels, preservative, antiseptic Weak acid
Functional Group: Carbonyl Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -al
Aldehyde
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanal
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L L L L
Found in essential oils (produce fragrance) Highly reactive Smaller aldehydes soluble in water Always written as -CHO
Functional Group: Carbonyl
O C Nomenclature: - Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -one (middle of chain)
Ketone
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: propanone
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L General Formula: CnH2nO L Important to industry: Sugars and Acetone L Carbon-Oxygen bond highly polar as electronegativity of oxygen is stronger.
Functional Group: Carboxyl Group Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -oic acid
Carboxylic Acid
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
General Structure:
Example: ethanoic acid
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L Carboxylic acids are BrnstedLowry theory acids, they are proton (H+) donors. L Most common organic acid. L Polar. L Salts and esters of CAs are carboxylates
Functional Group: Amine Group Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -amine
Amine
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanamine
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L Derivatives of ammonia L Contain basic nitrogen atom with lone pair L H+ can bond with the electronegative Nitrogen in primary and secondary form.
Functional Group: Amide Group Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -amide
Amide
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanamide
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L L L L
Derived from carboxylic acids Contains a -CONH2 group Weak conjugate base of ammonia (amine) Small amides soluble, hydrogen can bond.
Functional Group: Ester Group Nomenclature:
Ester
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: methyl ethanoate
General Structure:
- Remove -ol from alcohol +Add -yl + Carboxylic Acid, -Remove -e + add -oate
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L Derived from Carboxylic Acid, -COOH. In an Ester, H replaced by hydrocarbon group L Ubiquitous: fats, oils, plastics (polyester) L More polar than ethers, less than alcohols
Functional Group: Acyl Group Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -oyl + halogen
Acyl Halide
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanoyl chloride
General Structure:
Other Facts:
Joy Qin 2012
L Derived from oxoacid by replacing hydroxyl group with halide group L Reactive, often synthesized & used as intermediates in synthesis of organic compounds (+alcohol=ester; +amine=amide +water & hydrolysis = carboxylic acid)
Functional Group: Nitrile Group Nomenclature:
- Remove -e from hydrocarbon + Add -nitrile
General Structure:
Nitrile
Functional Group, Nomenclature, General Structure, Example, y Other Facts. 6
Example: ethanitrile
Joy Qin 2012
Other Facts:
L Strong permanent dipole-dipole attraction/ van der Waals dispersion. L Can be hydrolyzed, reduced or ejected from a molecule as a cyanide ion
YeAH JOY!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 12 ClickersDocumento41 pagine12 ClickersIbrahim M100% (1)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionDa EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- P - Aldehydes and Ketones PDFDocumento32 pagineP - Aldehydes and Ketones PDFAyush Srivastava78% (23)
- Principles and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryDocumento56 paginePrinciples and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryappleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem1-Lec11-Other Organic CompoundsDocumento60 pagineChem1-Lec11-Other Organic CompoundsSkud GuillermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento36 pagineChapter 9 Aldehydes and KetonesRoshan GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature AllDocumento83 pagineNomenclature AllLabib HasnainNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols CarbonylDocumento8 pagineAlcohols CarbonylmuhajireenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-EthersDocumento61 pagineLectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-Ethersvintu pvNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 109-Chepter 6Documento28 pagineCHEM 109-Chepter 6naifalfarraj3Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 3 Organic Compounds PDFDocumento54 pagineCHP 3 Organic Compounds PDFzubair.gs-017Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsDocumento16 pagineExperiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsLuisGabito100% (1)
- Adiolisa Containing Two (-OH Groups) .: Chemical Compound Hydroxyl GroupsDocumento5 pagineAdiolisa Containing Two (-OH Groups) .: Chemical Compound Hydroxyl Groupsleti332Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Documento28 pagine5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Marivic TayabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter FiveDocumento24 pagineChapter FiveAbhilasha VashisthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFDocumento19 pagineModule 5 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFRica Pearl ZorillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes and Ketones 1Documento35 pagineAldehydes and Ketones 1AIRAH SALALIMANessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature - : Ol. Other Substituents Are Named and Numbered As Done in AlkanesDocumento7 pagineNomenclature - : Ol. Other Substituents Are Named and Numbered As Done in AlkanesGulshan BatraNessuna valutazione finora
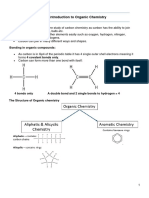
- 3.1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Bonding in Organic CompoundsDocumento20 pagine3.1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Bonding in Organic CompoundsFadhla Fadhilatul Mariyatis SolihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento34 pagineLecture 1 Introduction To Aldehydes and KetonesKoki King100% (1)
- Functional GroupDocumento45 pagineFunctional Groupmonasteriomatthew7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol, Phenols, Thiol & EtherDocumento35 pagineAlcohol, Phenols, Thiol & EtherShiki Asagami BrunestedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter16 UclassDocumento88 pagineChapter16 Uclass배석우Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Drug - 1Documento42 pagineSynthesis of Drug - 1'Nurirjawati ElRuri KawangNessuna valutazione finora
- 1: Understanding Carbon Compounds I (Textbook: Chapter 2 Page 33-92)Documento35 pagine1: Understanding Carbon Compounds I (Textbook: Chapter 2 Page 33-92)Haslimi Bin HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- AldehydeDocumento9 pagineAldehydesenkatuukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Its Compound 48Documento3 pagineCarbon Its Compound 48Krishna Prasanth rNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols, Organic ChemistryDocumento32 pagineAlcohols, Organic Chemistryclassy43390% (1)
- Chemistry Mrs Taylor: Polyesters and PolyamidesDocumento5 pagineChemistry Mrs Taylor: Polyesters and PolyamidesMatthew WestNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic For NursingDocumento6 pagineOrganic For NursingLady DanielleNessuna valutazione finora
- Organin Chemistry - Some Basic ConceptsDocumento20 pagineOrganin Chemistry - Some Basic Conceptsprashanth100% (1)
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocumento81 pagineChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade-9 Science Q2 Wk6 GLAKDocumento16 pagineGrade-9 Science Q2 Wk6 GLAKRianne MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Groups - Organic ChemistryDocumento61 pagineFunctional Groups - Organic ChemistryYoAmoNYCNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Fourteen: Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry 5th EditionDocumento37 pagineChapter Fourteen: Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry 5th EditionSCReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM Alcohol WeeklyDocumento5 pagineCHEM Alcohol WeeklypengnijiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl GroupDocumento92 pagineCarbonyl GroupWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol molecul-WPS OfficeDocumento14 pagineAlcohol molecul-WPS OfficeUSCLOUD MINERNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 12 Alkohol Dan PhenolDocumento62 pagineWeek 12 Alkohol Dan PhenolAgitha FarihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehyde and Ketones FDocumento70 pagineAldehyde and Ketones Fmichelmanirakiza591Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Class 11.Documento20 pagineOrganic Chemistry Class 11.asinriazNessuna valutazione finora
- ch20 Aldehydes and Ketones (Revised)Documento40 paginech20 Aldehydes and Ketones (Revised)Spry CylinderNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Hydrocarbons - Aliphatic Vs Aromatic Molecules - Saturated & Unsaturated CompoundsDocumento7 pagineA. Hydrocarbons - Aliphatic Vs Aromatic Molecules - Saturated & Unsaturated CompoundsChristian Josef AvelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia AlcoholesDocumento12 pagineGuia Alcoholesfalexa601Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocumento50 pagineAlcohols, Phenols and EthersAIRAH SALALIMANessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry - Q2 - Week 5-6-1Documento20 pagineGeneral Chemistry - Q2 - Week 5-6-1Paula Bianca MosinabreNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Organic-ChemistryDocumento51 pagine3 Organic-ChemistryVanna AmarilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Star Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)Documento20 pagineStar Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)hacker GodNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules BiologyDocumento37 pagineMacromolecules Biologyjulia067Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04 The Carbonyl Group (2313Spr2018) Skeletal NotesDocumento56 pagine04 The Carbonyl Group (2313Spr2018) Skeletal NotesDiana ToroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Lec Homework 020714Documento18 pagineChem Lec Homework 020714Almarie PasaoaNessuna valutazione finora
- F322 AlcoholsDocumento9 pagineF322 AlcoholsDoc_CrocNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Functional GroupsDocumento5 pagineNotes Functional GroupsFrank GaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Documento25 pagineDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydroxyl Group: EthanolDocumento8 pagineHydroxyl Group: EthanolJen AdvientoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Carbon and Its CompoundsDocumento3 pagine1-Carbon and Its CompoundsPrasan NandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes and Ketones BIOKMORDocumento18 pagineAldehydes and Ketones BIOKMORLinearNessuna valutazione finora
- AldehydesDocumento19 pagineAldehydesSeverina MamauagNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic CompoundsDocumento18 pagineOrganic CompoundsAnaya noorNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional GroupsDocumento3 pagineFunctional Groupsrache1505Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento38 pagineCarbonyl CompoundsAllyssa Gwyn Angeles PinoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 10 Paper 1Documento30 pagineTopic 10 Paper 1RawanMazen SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 23 - Alcohols and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento6 pagineChapter 23 - Alcohols and Carboxylic AcidsJERVINLIMNessuna valutazione finora
- AminoAcids in PDB 091723Documento6 pagineAminoAcids in PDB 091723Mai Abdallah El KelanyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.AcidBases FinalDocumento35 pagine3.AcidBases FinalSoham RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Group Analysis in Undergraduate Laboratory Safe, Cost-Effective and Micro-Scale AlternativesDocumento5 pagineFunctional Group Analysis in Undergraduate Laboratory Safe, Cost-Effective and Micro-Scale Alternativesbadri parthasaradhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 14Documento1 paginaExperiment No 14Saurav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes and Ketones-01 - TheoryDocumento45 pagineAldehydes and Ketones-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry AssignmentDocumento5 pagineChemistry AssignmentBettina Rose GallardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2a: Determination of The Concentration and The Acid Dissociation Constants of An Unknown Amino Acid (Part II)Documento7 pagineLecture 2a: Determination of The Concentration and The Acid Dissociation Constants of An Unknown Amino Acid (Part II)Steve LiNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1021@acs Iecr 9b02077Documento14 pagine10 1021@acs Iecr 9b02077dipen royNessuna valutazione finora
- Opening RM Erp 18Documento200 pagineOpening RM Erp 18Sujeet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry:: Functional GroupsDocumento43 pagineOrganic Chemistry:: Functional GroupsprincesschemistNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Chemistry (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Documento33 pagineSyllabus Chemistry (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- Systematic Review of The Chemical Composition of Contemporary Dental AdhesivesDocumento29 pagineSystematic Review of The Chemical Composition of Contemporary Dental AdhesivesPedro FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 OH LaNunDocumento7 pagineChapter 16 OH LaNunshehdilanun100% (1)
- 7b20d0af-82eb-46f3-ad8a-80f9b8917461Documento7 pagine7b20d0af-82eb-46f3-ad8a-80f9b8917461rmvb7cbfv9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocumento14 pagineOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationSomesh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- A Primer To Designing Organic SynthesisDocumento42 pagineA Primer To Designing Organic SynthesisMohammed100% (1)
- Chm102 Lec - FinalsDocumento21 pagineChm102 Lec - FinalsChurva EklavuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids) Topic:-Reasoning Questions. (Answers)Documento1 paginaCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids) Topic:-Reasoning Questions. (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Assignment - (JEE MainsDocumento21 pagineChemistry Assignment - (JEE Mainsnikhil sridharaNessuna valutazione finora
- 397 Pages, Chapter 1-6Documento397 pagine397 Pages, Chapter 1-6SanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidro KarbonDocumento43 pagineHidro KarbonElisabet NoviantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Alifiah 5 LampiranDocumento24 pagineAlifiah 5 LampiranalfiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acids and EsterDocumento9 pagineCarboxylic Acids and EsterNeen NaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Jo 0503299Documento6 pagineJo 0503299Kyucheol PaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Group ChemistryDocumento176 pagineFunctional Group ChemistrySurender Dilip100% (1)