Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Feeling Hot, Hot, Hot
Caricato da
The London Free PressDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Feeling Hot, Hot, Hot
Caricato da
The London Free PressCopyright:
Formati disponibili
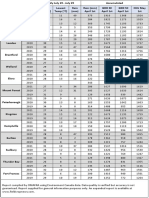
Are the summer temperatures making it feel as if you might melt on the spot?
No need to worry unless youre an ice cube, which melts at 0C, or chocolate, which melts at 35C. Read on to learn why it happens and what are the melting point of other solids
WHAT IS A MELTING POINT?
SOLID (ICE) PROCESS OF MELTING LIQUID (WATER)
Feeling hot, hot, hot
O
IN MINUTES
News and events visually
O
H
O
H
O
H
H
O
H
Hydrogen
Mercury
Helium
105
35
44
146
-259
-270
Crayons
Beeswax
Para n
Plastic wrap
Acrylic glass
160
Tin
232
54
Pewter
Polyethylene
254
64
240
65
98
Lead
327
419
In degrees celsius
659
Magnesium
670
MELTING POINT OF VARIOUS SOLIDS
Salt
8501,000
900940
801
961
Gold
1,063
1,083
Mixtures of substances, such as butter or para n, do not have specic melting points, but melt within a range of temperatures. Each substance in a mixture retains its own melting point. Since the substances with lower melting points melt before those with higher melting points, a mixture tends to become soft before changing into a liquid.
In ice crystals, hydrogen molecules adhere to nearby oxygen molecules.
When heat is absorbed by water molecules in ice, they seek a lower energy state and begin to vibrate quickly.
The vibrating molecules begin to rotate rapidly, causing them to separate from the ice.
The separated molecules transfer their excess heat to the molecules still in the ice.
1,260
When the solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium, the temperature remains constant
Asphalt doesn't have a melting point, but at temperatures over 38C, it begins to behave more like a liquid than a solid
1,363
1,420
An object that has completely melted is molten
1,452
1,500
1,530
1,555
1,723
Some solids such as solid carbon dioxide (dry ice), carbon and iodine dont melt, they sublime straight from a liquid to a gas
Cast Iron
Stainless steel
Silicon
Iron
Palladium
Platinum
1,770
Titanium
1,795
Tungsten
Chocolate
Phosphorus
Sodium
Aluminum
Common glass
Sources: garelicksteel.com; Wikipedia; engineeringtoolbox.com; van.physics.illinois.edu; h2g2.com; ehow.com
SUSAN BATSFORD, GRAPHICS EDITOR, TWITTER @SBATS1; INFOGRAPHIC BY MEGAN DINNER/QMI AGENCY
Sand (quartz)
Carbon
Ice
Sugar
Zinc
Bronze
Brass
Silver
Copper
Nickel
-39
O
H
O
H
The process continues until the ice is completely melted and all excess heat is gone.
Each chemical element has a specic melting point, which ranges from 269.7 C for helium to 3,727 C for carbon.
The temperature at which a substance passes from solid to liquid state.
O
H
H
H
H
H
O
H
O
H
O
H
H
O
O
H H
O
H
O
H
O
H
3,422
3,727
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN ICE MELTS?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The I AM 22 Chakra ChartDocumento8 pagineThe I AM 22 Chakra ChartMarina G. Giamalidi100% (22)
- Chemistry NotesDocumento10 pagineChemistry NotesRaya DhanushNessuna valutazione finora
- ALCHEMY The Philosphers Stone by Alchemist NDCDocumento3 pagineALCHEMY The Philosphers Stone by Alchemist NDCVladimir VergunNessuna valutazione finora
- Network of Global Corporate Control. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in ZurichDocumento36 pagineNetwork of Global Corporate Control. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurichvirtualminded100% (2)
- Java 8 Interview QuestionsDocumento31 pagineJava 8 Interview QuestionsAmit Sharma100% (2)
- WPS PQR CompressedDocumento5 pagineWPS PQR CompressedBalaje MantravadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermite and IceDocumento3 pagineThermite and IceAlissa GayNessuna valutazione finora
- PHASE DIAGRAMDocumento7 paginePHASE DIAGRAMMustika Dewi IkhtiariantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Name / Title Topic Learning Objective Key Science Concepts/ Main Messages Props/ MaterialsDocumento3 pagineName / Title Topic Learning Objective Key Science Concepts/ Main Messages Props/ MaterialsHaha Hoho TNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Chemistry For IGCSE Chapter 1Documento20 pagineComplete Chemistry For IGCSE Chapter 1Hubbak Khan100% (5)
- 3.2 Properities of WaterDocumento20 pagine3.2 Properities of Watermarwa.nassar19Nessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE SUMMARY PRIMARY 4 SEMESTER 1 Unit 3Documento4 pagineSCIENCE SUMMARY PRIMARY 4 SEMESTER 1 Unit 3cindy kosasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IPDocumento9 pagineChemistry IPMOHAMED IBRAHIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing Point Depression and Colligative Properties Ice creamDocumento2 pagineFreezing Point Depression and Colligative Properties Ice creamMikaela Danielle PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Decrease Freezing Point - Group 10 - Kimia B 2023 REVISIDocumento31 pagineDecrease Freezing Point - Group 10 - Kimia B 2023 REVISIS SNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing WarmerDocumento2 pagineFreezing WarmerleitninNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of MatterDocumento56 pagineProperties of MatterD. Rakesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Colligativepropertieslab OliviakwDocumento6 pagineColligativepropertieslab Oliviakwapi-355402843Nessuna valutazione finora
- MP, FP & BPDocumento3 pagineMP, FP & BPammuluhai333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet For CHP 21 To Move or Not To Move!': Aldiona Daulle 10FDocumento2 pagineWorksheet For CHP 21 To Move or Not To Move!': Aldiona Daulle 10FAldiona DaulleNessuna valutazione finora
- Melting and Freezing: States of Matter ChangesDocumento1 paginaMelting and Freezing: States of Matter ChangesHyazelle Fang-asanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Sweet Is This ActivityDocumento1 paginaHow Sweet Is This Activitypancit cantonNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Ice Teacher WorksheetDocumento2 pagineHot Ice Teacher Worksheeterica vidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Energy (11-16) PDFDocumento24 pagineHeat Energy (11-16) PDFcapricorn cassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 (5.1)Documento11 pagineChapter 5 (5.1)Aileen PoLyNessuna valutazione finora
- SupercoolingDocumento8 pagineSupercoolingGhadendra BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot IceDocumento4 pagineHot IceeunoiasantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Write UpDocumento2 pagineWrite Upapi-255950497Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallization and TGDocumento26 pagineCrystallization and TGJILLIAN DALUPONessuna valutazione finora
- Latent HeatDocumento1 paginaLatent HeatEsther SiamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Ice or SodiumDocumento3 pagineHot Ice or SodiumLai Zhi YongNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot IceDocumento5 pagineHot IcePaculba Louigi Igdon100% (1)
- Latent HeatDocumento32 pagineLatent HeatAbhijit Kar Gupta100% (11)
- Experiment 5 Sublimation and Solubility of Iodine: Required MaterialsDocumento2 pagineExperiment 5 Sublimation and Solubility of Iodine: Required MaterialsÇiğdem DÜLGERBAKİNessuna valutazione finora
- DDDDDDDocumento2 pagineDDDDDDapi-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICSDocumento8 paginePHYSICSAldrin E. Naranjo HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- SaltwaterDocumento3 pagineSaltwatersansira2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is GlassDocumento16 pagineWhat Is GlassjayanthanNessuna valutazione finora
- HotcoldpacksDocumento6 pagineHotcoldpacksJihan JuhanirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Ice ExperimentDocumento2 pagineHot Ice ExperimentMaya Buchanan-Smith100% (1)
- Clinker Manufacturing ProcessDocumento14 pagineClinker Manufacturing ProcessAnirudh100% (1)
- What Is Hot IceDocumento4 pagineWhat Is Hot Icewinnie1314Nessuna valutazione finora
- Change of State of MatterDocumento11 pagineChange of State of MatterAtashi MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Project SubmissionDocumento14 pagineScience Project SubmissionsaiqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Instant Freeze Water - Bottle Slam Science ExperimentDocumento1 paginaInstant Freeze Water - Bottle Slam Science ExperimentMarianella AbelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Material Has The Highest Melting PointDocumento3 pagineWhich Material Has The Highest Melting Pointsonic8659Nessuna valutazione finora
- Changing States of Matter - Creating The LineDocumento13 pagineChanging States of Matter - Creating The Lineapi-97385154Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 17Documento20 pagineChap 17Raghavendra PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10 Thermal Properties of MatterDocumento51 pagineCH 10 Thermal Properties of MatterHala AlawdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Fair ProjectDocumento5 pagineScience Fair Project郭奕緯Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry in CookingDocumento11 pagineChemistry in CookingPragati GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Make Ice Cream in A BaggieDocumento5 pagineMake Ice Cream in A Baggiesudhersan2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the States of Matter and Particle TheoryDocumento10 pagineUnderstanding the States of Matter and Particle TheoryAjitabh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Glass Manufacturing ProcessDocumento5 pagineGlass Manufacturing ProcesssamanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chocolate Rock CycleDocumento2 pagineThe Chocolate Rock Cycleapi-660734816Nessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Synthesizing RubyDocumento4 pagineMethods of Synthesizing RubyHandika Adhe Wardana100% (1)
- Fab Crystl AC14 PGDocumento6 pagineFab Crystl AC14 PGerica vidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem2 G2-1Documento29 pagineChem2 G2-1Mariz TanNessuna valutazione finora
- SolderingAnnealing 1544008648860Documento12 pagineSolderingAnnealing 1544008648860Cristal MuranoNessuna valutazione finora
- MeltingDocumento10 pagineMeltingediwijaya.bukitsionNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Does Ice MeltDocumento11 pagineWhy Does Ice MeltLynellAlimangohanNessuna valutazione finora
- MeltingDocumento7 pagineMeltingzeamayf.biasNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Do Chemical Tricks: Containing Over One Hundred Highly Amusing and Instructive Tricks With ChemicalsDa EverandHow to Do Chemical Tricks: Containing Over One Hundred Highly Amusing and Instructive Tricks With ChemicalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Project HobartDocumento1 paginaProject HobartThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Supports During Winter BreakDocumento2 pagineSupports During Winter BreakThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- LHSC StatementDocumento2 pagineLHSC StatementThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Climate Resilient CommunitiesDocumento57 pagineBuilding Climate Resilient CommunitiesThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Statement - Council Delegation June 21 2022Documento1 paginaStatement - Council Delegation June 21 2022The London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- PAC COVID Vaccine LetterDocumento3 paginePAC COVID Vaccine LetterThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- A COVID Journal EntryDocumento56 pagineA COVID Journal EntryThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL Single Pages Student Dress Guidelines 3Documento12 pagineFINAL Single Pages Student Dress Guidelines 3The London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Leaders Need To Be Climate LeadersDocumento3 pagineBusiness Leaders Need To Be Climate LeadersThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- WISH To BE HOME ProgramDocumento2 pagineWISH To BE HOME ProgramThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather ReportDocumento1 paginaWeather ReportThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Planning Process: Stage 1 Part A Key FindingsDocumento7 pagineMaster Planning Process: Stage 1 Part A Key FindingsThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- PAC COVID Vaccine LetterDocumento3 paginePAC COVID Vaccine LetterThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Wild Babies Do's and Don'tsDocumento2 pagineWild Babies Do's and Don'tsThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- City's Letter To Housing Affairs Minister Steve Clark November 2018Documento2 pagineCity's Letter To Housing Affairs Minister Steve Clark November 2018The London Free Press100% (1)
- McKennitt-Parlee - Xinyi Canada Glass Project - For Immediate Attention - DF11 - Nov26-2020 LM PP MMDocumento3 pagineMcKennitt-Parlee - Xinyi Canada Glass Project - For Immediate Attention - DF11 - Nov26-2020 LM PP MMThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- City's Letter To House Affairs Minister Steve Clark March 2020Documento2 pagineCity's Letter To House Affairs Minister Steve Clark March 2020The London Free Press100% (1)
- An Open Letter To The Community From Southwestern Public HealthDocumento1 paginaAn Open Letter To The Community From Southwestern Public HealthThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- City's Letter To Housing Affairs Minister Steve Clark April 2020Documento3 pagineCity's Letter To Housing Affairs Minister Steve Clark April 2020The London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Ontario Farmer - Rural Properties and MarketplaceDocumento8 pagineOntario Farmer - Rural Properties and MarketplaceThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Remembrance Program 2019Documento8 pagineRemembrance Program 2019The London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Rural Properties and MarketplaceDocumento8 pagineRural Properties and MarketplaceThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- TVDSB Employee CodeDocumento4 pagineTVDSB Employee CodeThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Walkerton TimelineDocumento1 paginaWalkerton TimelineThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Area Action PlanDocumento2 pagineCore Area Action PlanThe London Free Press100% (2)
- Blackridge Strategy StatementDocumento2 pagineBlackridge Strategy StatementThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Rail Letter From Ontario Agriculture - FinalDocumento2 pagineCN Rail Letter From Ontario Agriculture - FinalThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Bishop's LetterDocumento2 pagineBishop's LetterThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- ML Hu BlackRidge Invoice 2Documento1 paginaML Hu BlackRidge Invoice 2The London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- ML Hu BlackRidge InvoiceDocumento1 paginaML Hu BlackRidge InvoiceThe London Free PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Cork Properties Capabilities and ApplicationsDocumento22 pagineCork Properties Capabilities and ApplicationsVijay AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of LQR Controller For The Inverted Pendulum: Lili Wan, Juan Lei, Hongxia WuDocumento5 pagineDesign of LQR Controller For The Inverted Pendulum: Lili Wan, Juan Lei, Hongxia WuVictor PassosNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SDocumento23 pagine3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SHamza KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- HP ALM FeaturesDocumento51 pagineHP ALM FeaturesSuresh ManthaNessuna valutazione finora
- PermutationDocumento3 paginePermutationKhairuddin MuhamadNessuna valutazione finora
- The BCA (1) 23Documento36 pagineThe BCA (1) 23Aurobind DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity Vs ConsistencyDocumento6 pagineViscosity Vs Consistencysontakke manmathNessuna valutazione finora
- Toraiz SP-16Documento89 pagineToraiz SP-16ScappinNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity No. 5 Capacitive Circuit ObjectivesDocumento4 pagineActivity No. 5 Capacitive Circuit ObjectivesJohn Paul BaquiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductive TransducersDocumento12 pagineInductive TransducersMUKESH SUNDARARAJANNessuna valutazione finora
- CFA Level II 3 Topics - High Yield List of QuestionsDocumento4 pagineCFA Level II 3 Topics - High Yield List of QuestionsCatalinNessuna valutazione finora
- IJETR032052Documento6 pagineIJETR032052erpublicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of RivetsDocumento20 pagineDesign of RivetsRavishanker BaligaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fix Disk & Partition ErrorsDocumento2 pagineFix Disk & Partition Errorsdownload181Nessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed Air Operated Vacuum Waste Removal: Systems and ComponentsDocumento20 pagineCompressed Air Operated Vacuum Waste Removal: Systems and ComponentsDaniel RukawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing The Usage of Therapeutic Footwear in Diabetic Foot Patients Through Amit Jain's Extended SCC' Classification For Therapeutic FootwearDocumento6 pagineAuditing The Usage of Therapeutic Footwear in Diabetic Foot Patients Through Amit Jain's Extended SCC' Classification For Therapeutic FootwearJosé MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- XI-Opt. Syllabus (2023-24)Documento29 pagineXI-Opt. Syllabus (2023-24)INDERDEEPNessuna valutazione finora
- The Alveolar Gas EquationDocumento4 pagineThe Alveolar Gas Equationstewart_fNessuna valutazione finora
- Accelerate your career with online coursesDocumento22 pagineAccelerate your career with online coursesAYEDITAN AYOMIDENessuna valutazione finora
- Innovative High Throw Copper Electrolytic ProcessDocumento6 pagineInnovative High Throw Copper Electrolytic Processyonathan fausaNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Gases in LaboratoryDocumento7 paginePreparation of Gases in LaboratoryChu Wai Seng50% (2)
- Types of VerbDocumento4 pagineTypes of VerbFaisal MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrix Inversion Note in Mathematics MagazineDocumento2 pagineMatrix Inversion Note in Mathematics Magazinejuan carlos molano toroNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract (Lab 2) Ionization ConstantDocumento12 pagineAbstract (Lab 2) Ionization Constantmirdza94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modular Forms Exam - Homework RewriteDocumento2 pagineModular Forms Exam - Homework RewritejhqwhgadsNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.numerical DifferentiationDocumento20 pagine11.numerical DifferentiationAbdulselam AbdurahmanNessuna valutazione finora