Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit One Last Minute Notes
Caricato da
Rimaz RameezDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit One Last Minute Notes
Caricato da
Rimaz RameezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHEMISTRY UNIT ONE
Melting point of magnesium is higher than sodium Magnesium contributes two electrons. Magnesium ions are smaller than sodium ions. More energy required to overcome forces between cations and sea of electrons in magnesium compared to sodium.
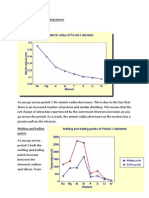
Ionisation energy increases across the period More protons, same shielding, decrease in size. Greater (force of) attraction between nucleus and outer electron First ionization energy of aluminium is less than magnesium Outermost electron in 3p sub-shell Shielded by 3s electrons Two lattice energy values for AgI are different. AgI has partial covalent character due to polarization of the anion by the cation. Ionisation energy decreases down the group More shielding, increase in size. Less (force of) attraction between nucleus and outer electron.
Enthalpy change of combustion experimental value is different than book value Heat losses and Incomplete combustion
Positive Ions are smaller than atoms Ions have one less orbital More protons than electrons Greater net force on remaining electrons Ionic compounds have higher melting point Stronger attractions between opposite charged ions So large amount of energy needed to separate the ions MgO has higher melting point than MgCl2 Oxide ion has a greater charge density than the chloride ion Attraction between ions is stronger in MgO than MgCl2 More energy is required to separate Sigma and Pi Bond Sigma bond is formed by head-on overlap Pi bond is formed by sideways overlap First ionization energy decreases from Phosphorus to Sulphur Two electrons occupy the same (p) orbital Repulsion between the paired electrons
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Periodicity: Ionisation EnergyDocumento3 paginePeriodicity: Ionisation EnergyFouziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group II ElementsDocumento20 pagineGroup II ElementsTichafara Paul ShumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization EnergyDocumento8 pagineIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transition MetalsDocumento3 pagineTransition MetalsFaith WrightNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodicity NotesDocumento5 paginePeriodicity Notescgao30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ElementsDocumento74 pagineClassification of ElementsJimit Patel BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization Energy Cape Unit 1Documento21 pagineIonization Energy Cape Unit 1Shanice JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 03Documento45 pagineChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 03Ng Swee Loong StevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Configuration of IonsDocumento8 pagineElectron Configuration of IonsGetnet BegashawNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Chemistry NotesDocumento10 pagineA-Level Chemistry NotesHannah Bryson-JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization Energy and Electron AffinityDocumento9 pagineIonization Energy and Electron AffinityKhan AaghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cfe Higher Chemistry - PeriodicityDocumento34 pagineCfe Higher Chemistry - Periodicityiapm0708Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 13 Ionisation EnergiesDocumento6 pagine2 13 Ionisation EnergiesRobertLiu100% (2)
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocumento12 pagineTrends in The Periodic Tableoanoxenosiral1211Nessuna valutazione finora
- TAQ 1-6 PaperDocumento21 pagineTAQ 1-6 PaperDavid MuneneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table.Documento16 pagineThe Periodic Table.Kizito KinuthiaNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableDocumento12 pagineHL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableMarilee HuntNessuna valutazione finora
- PeriodicityDocumento6 paginePeriodicityNetkoNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Documento11 pagineAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 122 - 2013 - 2014 PDFDocumento27 pagineCHM 122 - 2013 - 2014 PDFGlory UsoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Trends in Period 3Documento34 pagineTrends in Period 3Fildzah AdanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocumento11 paginePeriodic Table and Periodicityakeemoluwadamilare623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsDocumento2 pagineLattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsdanielmahsaNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocumento17 pagineAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 NotesMuadh Chati100% (1)
- 3 2 Physical PropertiesDocumento4 pagine3 2 Physical PropertiesNguyenHoangMinhDucNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 (Periodic Table) Test Review SheetDocumento6 pagineUnit 3 (Periodic Table) Test Review SheetTheo ZhengNessuna valutazione finora
- Qdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelDocumento1 paginaQdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelM KNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Lesson 9Documento17 pagineGeneral Chemistry Lesson 9dreih MadrigNessuna valutazione finora
- BondingDocumento12 pagineBondingPAUL KOLERENessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)Documento1 paginaChemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)--------100% (1)
- Periodic PropertiesDocumento30 paginePeriodic Propertiescleofe omas-asNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes For Period 3Documento4 pagineNotes For Period 3Ben ToNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento27 pagineUntitledFatimah AgboolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization PotentialsDocumento1 paginaIonization PotentialsJoshua SeñarosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 111 Week Three Notes BDocumento7 pagineChem 111 Week Three Notes BnyachiosirNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartDocumento31 pagineClassification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartKeshan PaudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic TrendsDocumento4 paginePeriodic TrendsBalcy GayodanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Short NotesDocumento8 pagineChemistry Short NotesZainab HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andDocumento14 paginePeriodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andbhogalsahib1408Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table 1Documento23 pagineThe Periodic Table 1Elicia BullockNessuna valutazione finora
- F321 PeriodicityDocumento3 pagineF321 PeriodicityDoc_CrocNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Group 2Documento32 pagine1.1 Group 2SN1-0622 Khairul Bariah Binti IzaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocumento105 pagineInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNessuna valutazione finora
- f321 Mod3Documento6 paginef321 Mod3api-275024237Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry s4 Notes - Unit 3Documento9 pagineChemistry s4 Notes - Unit 3UDAHEMUKA DeniseNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Structure of Atoms and The Periodic Table ExerciseDocumento7 pagineElectronic Structure of Atoms and The Periodic Table ExerciseFlorance ChiengNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization EnergyDocumento69 pagineIonization EnergyVisalakshi Venkat100% (2)
- Chem Unit 1 RevisionDocumento5 pagineChem Unit 1 RevisionAysu'z Quirky EsseNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 3 Periodic TrendsDocumento30 pagineUnit 1 3 Periodic Trendsaudrey.sengeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation Energy ClassDocumento13 pagineIonisation Energy ClassKordell McShineNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesDocumento25 paginePeriodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesJi Min LimNessuna valutazione finora
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocumento6 pagineCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureMyraNessuna valutazione finora
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocumento6 pagineCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureahumanbeinginearthNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 NotesDocumento7 pagineChapter 3 NotesNickNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerDocumento12 pagineChapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerLee AustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebenezer Matric .Hr. Sec. School: 1.what Is Ionization Energy?Documento3 pagineEbenezer Matric .Hr. Sec. School: 1.what Is Ionization Energy?r karthickNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)Documento33 pagineChemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)RANJEET SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento4 pagineChemistryAyah FNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Da EverandAn Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic TableDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic TableNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo-Mechanical Chain Branching of Commercial High Density Polyethylene During ExtrusionDocumento9 pagineThermo-Mechanical Chain Branching of Commercial High Density Polyethylene During ExtrusionRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet: PolyacrylonitrileDocumento7 pagineSafety Data Sheet: PolyacrylonitrileRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Energies: Comparative Analysis of Lithium-Ion Battery Resistance Estimation Techniques For Battery Management SystemsDocumento15 pagineEnergies: Comparative Analysis of Lithium-Ion Battery Resistance Estimation Techniques For Battery Management SystemsRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers: Ffect of Conductive Carbon Black On MechanicalDocumento11 paginePolymers: Ffect of Conductive Carbon Black On MechanicalRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- EIS LiteratureDocumento72 pagineEIS LiteratureRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Heat TransferDocumento10 pagineTransient Heat TransferRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year Laboratory Report 1Documento11 pagine1st Year Laboratory Report 1Rimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Area 3 - Preliminary Hydrolysis Reactor: Levenspiel PlotDocumento2 paginePlant Area 3 - Preliminary Hydrolysis Reactor: Levenspiel PlotRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Units HandoutDocumento14 pagineUnits HandoutRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics As - Unit 2 - Revision NotesDocumento0 paginePhysics As - Unit 2 - Revision NotesRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- As Biol Unit 2 Example QuestionsDocumento20 pagineAs Biol Unit 2 Example QuestionsRimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ry lq6: Q P (Ants) 0.t P (A) X ?(S) 0,2S R 0,5Documento2 pagineRy lq6: Q P (Ants) 0.t P (A) X ?(S) 0,2S R 0,5Rimaz RameezNessuna valutazione finora