Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physiology Clinical Diagnosis Treatment: TSI Antibodies
Caricato da
85robertDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physiology Clinical Diagnosis Treatment: TSI Antibodies
Caricato da
85robertCopyright:
Formati disponibili
HYPERTHYROIDISM
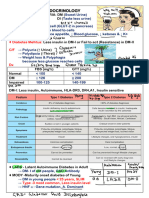
Thyroid Gland Synthesize, Secrete, Store thyroid hormone *ALL cells depend on for metabolism regulation BMR & Temperature Body & Bone Growth Anabolic & Protein Synthesis Glucose Production & Absorption (Gluconeogenesis & Glycogenolysis) Lipid Metabolism HR, CO, Contractibility Nervous System Development (CRETINISM) Composed of spherical FOLLICLES Lumen filled with colloid THYROBLOBIN MOLECULES 80% T4 Prohormone 20% T3 20-100x stronger IODIDETHYROID PEROXIDASEIODINEIODINE+TYROSINE(Amino Acid)HORMONE 75% Bound to THYROXINE BINDING GLOBULIN Carrier Protein = INACTIVE HypothalamusTRHPituitaryTSHThyroidT3/4 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Regulated by NEGATIVE Feedback PHYSIOLOGY Graves Dz *Autoimmune #1 in USA 20-40 Female TSI Antibodies T3/4 & Growth CLINICAL *THYROTOXICOSIS *Diffusely Enlarged Goiter (BRUITS) *Pretibial Myxedema (non-pitting, red/brown) Topical Corticosteroids *PROPTOSIS, Lid Lag, Photophobia, Diplopia Glucocorticoids *THYROTOXICOSIS *ENLARGED Goiter Dysphagia/Dyspnea *ASYMPTOMATIC DIAGNOSIS TSH Free T3/4 +TSI (Pathopneumonic) +/- Anti-TG/TPO RAIU diffuse uptake TSH Free T3/4 TMN/ UPTAKE TREATMENT #1 Radioactive Iodine Thioamines Methimazole PTU (PREGNANT) Iodines Beta Blockers #1 RAI *SURGERY
Toxic Multinodular AUTONOMOUSLY Goiter & functioning nodules ELDERLY >50 Toxic Adenoma #2Iodine areas SINGLE nodule Pituitary Adenomas Secrete TSH *RARE Thyroid Storm *RARE *FATAL Surgery, Trauma, Infection
*Diffuse Goiter *Bitemporal Hemianopsia *Mental Disturbance Metabolic Palpitations, Afib, Tremor, Fever, N&V, Psychosis *Coma & BP
TSH Free T3/4 MRI TSH Free T3/4
Surgery TSS
Methimazole PTU (PREGNANT) Beta Blockers Supportive 1
HYPOTHYROIDISM (#1 WORLD = IODINE)
Hashimotos #1 USA AUTOIMMUNE
PHYSIOLOGY Destruction via: Anti-thyroid peroxidase Antithyroglobulin *p URI *NOT autoimmune
CLINICAL *Enlarged NON-TENDER Goiter *risk of CA
DIAGNOSIS TSH Free T3/4 Anti-TPO Anti-TG ESR Free T3/4 TSH RAI uptake Anti-TPO RAI uptake (GRAVES VS.THYROIDITIS)
TREATMENT #1 LEVOTHYROXINE
Dequervains *5x FEMALES
*Enlarged PAINFUL Goiter *Viral Symptoms
HYPER HYPO NORMAL
Silent Thyroiditis *RARE *2x FEMALES
*AUTOIMMUNE *p AMIODARONE, LITHIUM, XRT INTERFERON *AUTOIMMUNE *1-6 months p partum *Smoking=risk
*Enlarged NON-TENDER Goiter
Supportive Self limiting NSAIDS
Post Partum Thyroiditis
*Enlarged NON-TENDER Goiter
Anti-TPO Anti-TG RAI uptake (GRAVES VS.THYROIDITIS) TSH Free T3/4 ( detectable)
Myxedema Coma *p Infection, CVA, *60% Mortality CHF, Narcotics *#1 ELDERLY Women In WINTER
*HR, BP, RR Na, Glucose Temp, COMA
*IV LEVOTHYROXIN *PASSIVE WARMING
*Subclinical HYPOthyroidism TSH N T3/4 Lipids *Subclinical HYPERthyroidism TSH N T3/4
ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY
Glucocorticoids (*CORTISOL)STRESS BP & CV function VASOCONSTRICTION ANTI-INFLAMMATORY SERUM GLUCOSE o Gluconeogenesis o Glucose Utilization o Protein Breakdown o Lipolysis Mineralocorticoids (*ALDOSTERONE) BP Na & H2O BALANCE Stimulants K (Most Sensitive) RAAS ACTH (Relatively INDEPENDENT) Physiology *Adrenal Gland DESTRUCTION ACTH CORTISOL &ALDOSTERONE AUTOIMMUNE #1(USA) Industrialized Countries INFECTION (TB, HIV, CMV) #1 World Vascular, Drugs, Mets
**SECONDARY ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY MORE COMMON THAN PRIMARY**
*STRESS OVERRIDES NEGATIVE FEEDBACK*
HypothalamusCRHAnterior PituitaryACTHAdrenal CortexCORTISOL
Addisons Dz (Primary)
Secondary
*Pituitary FAILURE to secrete ACTH CORTISOL *ALDOSTERONE intact RAAS #1 EXOGENOUS STEROIDS > 2wks Hypopituitarism (RARE)
Clinical Treatment *PRIMARY ONLY* *PRIMARY ONLY* *HYPERPIGMENTATION (#1) Synthetic Mineralocorticoid FLUDROCORTISONE *ORTHO BP, K, Na *BOTH* *BOTH* *WEAKNESS (#1) Synthetic Glucocorticoids *WT (#2) HYDROCORTISONE *ABD PAIN PREDNISONE *GLUCOSE (SECONDARY) DEXAMETHASONE #1 Emergency *Na effect Testing *ABNORMAL MENSTRATION *During ILLNESS, SURGERY, FEVER Oral Dosage to mimic N cortisol response Imaging Abdominal CT (*PRIMARY ONLY*) Autoimmune Small Atrophied Noncalcified Adrenals TB Calcification Mets/Infection Enlarged Adrenal Gland Pituitary MRI Hypopituitarism Suspected
DIAGNOSIS High Dose ACTH Stimulation Test #1 SCREENING TEST Cortisol = NORMAL Cortisol = ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY CRH Stimulation Test DIFFERENTIATES ACTH & Cortisol = PRIMARY ACTH = SECONDARY ACTH Delayed/Prolonged/Exaggerated = TERTIARY Low Dose ACTH Test Useful in NEW/RECENT ACTH (SECONDARY)
ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY
Physiology Addisonian *SUDDEN Worsening of Symptoms due to STRESSFUL EVENT Crisis Aldosterone (Primary Cause) #1 Abrupt Steroid Withdraw ( Taper) #2 Undiagnosed pt. under STRESS #3 Exacerbation of KNOWN Dz (dose under STRESS) #4 Bilateral Adrenal INFARCTION (Hemorrhage)
Clinical #1 SHOCK (Due to ALD) #2 Glucose #3 BP, Hypovolemia #4 Nonspecific
Diagnosis Treatment CBC, SMA IV Fluids NS (BP) Glucose D5NS (Glucose) Na Glucocorticoids K Dexamethasone(Undiagnosed) Hydrocortisone (Known Dz) Mineralocorticoids Fludrocortisone Tx Electrolyte Imbalance SCREENING TESTS 24hr Urine Cortisol* #1* Nocturnal Salivary Cortisol Levels Suppression c Low Dose Dex Supp Test DIFFERENTIATING TESTS High Dose Dexamethasone Suppression Test Suppression = Cushings Dz ACTH Levels N/ =Cushings Dz OR Ectopic ACTH Tumor = Adrenal Tumor
Cushings Syndrome
Cushings Dz (Pituitary Adenoma secretes = ACTH) Ectopic ACTH (SCLCA/Medullary Thyroid CA =ACTH) Adrenal Tumor (Cortisol secreting Adenoma = ACTH) *Factitious* (#1) (Chronic Exogenous Steroid = ACTH) MANAGEMENT Cushings Dz (Pituitary) TSS Ectopic/Adrenal Tumors Surgery
Redistribution of FAT Central Trunk Obesity Moon Face, Buffalo Hump Protein Catabolism Skin Atrophy Bruising, Striae BP, wt, K, Psychosis, Osteoporosis Acanthosis Nigricans
CRH Adrenal (PRIMARY) Pituitary (SECONDARY) Hypothalamus (TERTIARY)
ACTH
CORTISOL
ACTH RESPONSE TO CRH STIMULATION TEST
ALDOSTERONE N
High Dose Dexamethasone Suppression Test SUPPRESSION = CUSHINGS DZ (Pituitary Tumor)
Calcium Bone Structure Clotting Membrane Potential 99% in Bone 1% Extracellular 50% Free/Active/Ionized 40% Bound to Albumin CALCITROL (Vit D) Blood Ca PTH Blood Ca Activate OSTEOCLASTS/Renal & Intestinal Ca ABSORBTION CALCITONIN Blood Ca Inhibit OSTEOCLASTS *Primary Hyperthyroidism *MEN1 & 2A *Malignancy *Granulomatous Disorders TB, Sarcoid, Histoplasmo *Thiazides, Lithium, Vit D/A Physiology *PTH mediated* *PTH independent* PTH related protein Calcitrol by Macrophages Clinical *ASYMPTOMATIC* #1 N/V/Constipation AMS Kidney Stones Polyuria / Polydipsia
Mild Ca<12 = Tx Moderate Saline, Lasix, Bisphosphonates Severe Ca>14 OR Neuro = ADD Calcitonin
Diagnosis PTH PTH related protein Ionized Ca BUN/Cr Vit D SHORT QT Interval
HYPERCALCEMIA
Treatment IV Saline Dilute & Excrete Lasix Excrete Ca Bisphosphonates Inhibit Osteoclasts Patho Femur Fx & Erosive Esophagis Calcitonin Inhibit Osteoclasts Urine Ca excretion Steroids GRANULOMATOUS DZ Vit D = Ca
HYPOCALCEMIA
Hypoparathyroidism (Sarcoid) Autoimmune Destruction Hypoalbuminemia (Cirrhosis) Binds Ca Vit D False Ionized Ca Hepatorenal Dz Hyperphosphatemia Hypomagnesemia
Tetany SPASMS Chvostek Sign Facial Trousseaus BP Spasm
PTH PTH
Ca Ca Mild ORAL Ca & Vit D Severe IV Ca Gluconate & Mg
PROLONG QT Interval
Physiology
Clinical Stones, Bones, Abd Groans, Psych Moans
Diagnosis Serum Ca 24hr Urine Ca Intact PTH Phosphate
Treatment Parathyroidectomy Ca & Vit D Supplements
HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
Primary Hyperparathyroidism Parathyroid Adenoma #1 Hyperparathyroid Hyperplasia
Excess PTH production
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Chronic Kidney Failure #1 Ca Vit D
Response to Ca
HYPOPARATHYROIDISM
Accidental #1 Autoimmune
RARE PTH OR Insensitivity
Muscle Spasm Parasthesia
Serum Ca Intact PTH Phosphate
Ca Supplement
*RARE, INHERITED defect in tumor suppressor MENIN gene *90% Parathyroid *60% Pancreas (Gastrinoma, Insulinoma, Glucagonoma) *55% Pituitary *BENIGN *<30yrs will have some gland over activity *SCREENING ANYONE c FAMILY HX or OVERACTIVITY >2 ENDOCRINE GLANDS PTH & Calcium, Prolactin, Gastrin Hyperparathyroidism Physiology #1 Presenting Feature 90% Clinical Stones, Bones, Abd groans, Psych moans *HYPERCALCEMIA *KIDNEY STONES *ILEUS *PSYCHOSIS Pancreatic Tumors #2 **HIGHEST MALIGNANTCY** Diagnosis Ca intact PTH 24hr urine Ca phosphate Treatment *PARATHYROIDECTOMY
MEN 1
Small & Multiple Gastrinomas (ZES) #1 Insulinomas #2 Glucagonomas VIPomas Somatostatinomas 90% Solitary & Benign >6cm ?malignancy MC @ Head of Pancreas
*Multiple PEPTIC ULCERS (GI Bleed) *Epigastric Pain *wt, Reflux, N/V/D *HYPOGLYCEMIA
*REFRACTORY Ulcers Gastrin Insulin C-peptide Pro-insulin *50-80% mets @ Dx
*PPI, Monitor for CA *Surgery #1 Surgery *Octeotride *Small Freq CHO meals *Surgery *Octeotride Hydration Surgery Surgery
*70% Necrolytic Migratory Erythema *Type 2 DM *Watery Diarrhea, K *Achlorhydria *Steatorrhea, Cholelithias Pituitary Adenomas
Prolactinomas (60%) Somatotrophinomas Corticotrophinomas
#1 #2 #3
Amenorrhea, Galactorrhea, Infertility/Impotence Acromegaly Cushings Syndrome (ACTH)
Prolactin CT/MRI Pituitary
Surgery TSS
*RARE, INHERITED, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT *Defect in RET proto-oncogene MEN 2A Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma, Pheochromocytoma, HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Parathyroid Hyperplasia MEN 2B Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma, Pheochromocytoma, NEUROMAS More Aggressive MTC & Marfanoid Habitus Familial MTC Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma ALL will eventually develop *Screening PTH & Calcium, Epinephrine, Calcitonin Physiology Parafollicular C cells Secrete Calcitonin Clinical *#1 Presenting Feature *Palpable Neck Mass *Hoarseness, Dysphagia Diagnosis Thyroid Ultrasound FNA Treatment Total Thyroidectomy Parathyroids transplanted Prophylactic Thyroidectomy 2B=1st 6months of life 2A= <5-6yrs old Complete Adrenalectomy Blockades 2wks pre-op
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
MEN 2
Pheochromocytoma
Adrenal Medullary Tumor Palpitations, Headache, Sweating, that secretes catecholamines Refractory BP ITERMITTENTLY INTERMITTENTLY
*24HR Urine Methamphetamines & Catecholamines *CT/MRIAdrenal Ca intact PTH 24hr urine Ca phosphate
Hyperparathyroidism
MEN 2A ONLY
Stones, Bones, Abd groans, Psych moans *HYPERCALCEMIA *KIDNEY STONES *ILEUS *PSYCHOSIS Eyelids, Conjunctiva, Tongue, Lips, Nasal & Laryngeal Conjunctiva *Prominent Hypertrophied Lips *Marfanoid Body Habitus
PARATHYROIDECTOMY
Neuromas
MEN 2B ONLY BENIGN
Insulin blood Glucose Glucose Uptake Allowing Liver/Muscles to store as Glycogen Inhibit Gluconeogenesis *Hgb A1c > 6.5% *FPG > 126 *Oral Glucose Test > 200 *Plasma Glucose > 220
Counter regulatory Hormones Protect against HYPOGLYCEMIA Cortisol GH Glucagon Catecholamines
Dawn Phenomenon Glucose in AM due to surge of counter regulatory hormones Bedtime NPH OR Bedtime snack Somogyi Effect Nocturnal Glucose followed by Rebound Glucose Prevent Glucose by Noc NPH OR Bedtime snack Insulin Waning Progressive rise in Glucose from Bedtime till morning Move insulin dose to bedtime Rapid Lispro, Aspart Short Regular Intermediate NPH, Lente Long Ultralente, Glargine Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Biguanides -Glucosidase Inhibitors Thiazolidinediones 1 day coverage Lantus = Hypoglycemic episode MIX Secretagages Secretagages Live glucose production peripheral glucose utilization Delay absorption of glucose Insulin sensitivity Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia Lactic Acidosis Hepatitis, Flatulence, Diarrhea CHF, Bladder CA, Fx Overnight coverage 30-60min before meal Give w/meal
Physiology *Younger, Type 1 DM* 1) Hyperglycemia Insulin Counter Regulatory Hormones 2) Dehydration/Osmolarity Major factor in AMS 3) Ketonemia/Metabolic Acidosis Lipolysis Ketoacids 4) Total Body K+ Osmotic Diuresis Insulin shifts K+ extracellular HypovolemiaAldosteroneK+ Acidosis shifts K+ extracellular *May be masked by N/ Serum Levels *Serum K+ once Insulin Tx started
Clinical *Infection (UTI) 40% *Missed Insulin Dose 25% *Newly Dx/Unknown 15% CVA, Trauma, Stress, MI *Abd PAIN* *Kussmauls Breathing *Ketotic Breath
Diagnosis *PG > 250* *Anion Gap > 12*
Treatment *RESOLVED Normal Anion Gap
1) IV Fluids NS until Hypotension Resolves NS when Na Resolves NS D5 when glucose = 250 2) Insulin Bolus 0.1u/kg Drip 0.1u/kg/Hr SQ Anion Gap Resolves 3) K+ 1st Verify Renal Output <5.5 20-40 mEq/L 4) HCO3 risk of Cerebral Edema (Kids)
DKA
BMP Anion Gap/Glucose UA Ketones EKG ABG
*Older, Type 2 DM *Mortality *Fluid Intake * Hyperglycemia *NO Ketones 1) Dehydration/Osmolarity/ Hyperglycemia More SEVERE Present Later, Older (GFR) 2) K+ & Na Osmotic Diuresis
*PG > 600* *Anion Gap < 12*
*RESOLVED pOsm <315 / A&O x3
HHS
10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- HO in Spinal Cord InjuryDocumento3 pagineHO in Spinal Cord InjuryDarren Mae MosadaNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Spontaneously, Without A Known CauseDocumento6 pagineSpontaneously, Without A Known CauseAnalyn SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDa Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Uworld ReviewDocumento190 pagineComprehensive Uworld ReviewJoe JNessuna valutazione finora
- ATI Pain and InflammationDocumento3 pagineATI Pain and InflammationAnna100% (1)
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyDa EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Assessment Learning Guide Med SurgDocumento4 paginePhysical Assessment Learning Guide Med SurgTremain LinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsDa EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Deficient Fluid Volume R/T Inadequate Fluid Volume Intake Aeb Dry Mucous MembraneDocumento2 pagineDeficient Fluid Volume R/T Inadequate Fluid Volume Intake Aeb Dry Mucous MembraneimthebossNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 24 HomeworkDocumento9 pagineChapter 24 HomeworkKvn4N6Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Born Care 1Documento12 pagineNew Born Care 1gilbertgarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS Final 46 Blood or Lymphatic DisorderDocumento4 pagineMS Final 46 Blood or Lymphatic DisorderZachary T Hall0% (1)
- Nusing Skills Output (Nso)Documento3 pagineNusing Skills Output (Nso)leroux2890Nessuna valutazione finora
- GI Part 2 2016 StudentDocumento131 pagineGI Part 2 2016 StudentDaniel RayNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Maternal Health Care Edited 2015Documento43 pagineUnit 3 Maternal Health Care Edited 2015Londera BainNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurologic Conditions 1 SciDocumento5 pagineNeurologic Conditions 1 SciEdward De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- SURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenDocumento230 pagineSURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenJoan Timbol100% (1)
- Cns LectureDocumento10 pagineCns Lectureferg jeanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Sense of Humor DrivingDocumento160 pagineA Sense of Humor DrivingSidraGhafoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Card Solu-MEDROLDocumento2 pagineDrug Card Solu-MEDROLBenNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemDocumento105 pagineApproach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemprashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab FindingsDocumento4 pagineElectrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab Findingsworleyb83Nessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrineDocumento23 pagineEndocrinensvickneswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrineDocumento2 pagineEndocrineUnclePorkchopNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewDocumento24 pagineMedical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewSheena Ann L. LLarenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological Assessment: By, Ms - Keerthana.B Assistant Professor PSG College of NursingDocumento54 pagineNeurological Assessment: By, Ms - Keerthana.B Assistant Professor PSG College of NursingKeerthana BNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Laboratory Values With Nursing Consideration - UsnganDocumento8 pagineNormal Laboratory Values With Nursing Consideration - UsnganPrincess Nasima M. UsnganNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Positions Assumed by A Patient During A Physical Examination ProcedureDocumento14 pagineDifferent Positions Assumed by A Patient During A Physical Examination ProcedureAziil LiizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Male GU ExamDocumento5 pagineMale GU ExamOmar Farid ElgebalyNessuna valutazione finora
- DEMENTIA - Information For Carers, Families and Friends of People With Severe and End Stage Dementia PDFDocumento44 pagineDEMENTIA - Information For Carers, Families and Friends of People With Severe and End Stage Dementia PDFSuerte MpNessuna valutazione finora
- Surg Wound Clas TreeDocumento1 paginaSurg Wound Clas TreeCita Rahma SwastikaNessuna valutazione finora
- GI Signs and SymptomsDocumento40 pagineGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Session 2003-2004Documento246 pagineReview of Session 2003-2004The Royal Society of Edinburgh0% (1)
- Pneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocumento3 paginePneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaGayle MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 ConvulsionDocumento40 pagine4 ConvulsionMohamed Na3eemNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocumento46 pagineAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocumento3 paginePatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Spinal CordDocumento8 pagine19 Spinal Cordkarar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Documento36 pagineCardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Melodia Turqueza GandezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical MneumonicsDocumento139 pagineMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNessuna valutazione finora
- Nclex Review: The Endocrine SystemDocumento14 pagineNclex Review: The Endocrine SystemBj DuquesaNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 CP Endocrine 2Documento73 pagine21 CP Endocrine 2Aman Singh RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine NursingDocumento2 pagineEndocrine Nursingsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Endo Disorder Review NotesDocumento4 pagineEndo Disorder Review NotesKaren Joyce LasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine NursingDocumento2 pagineEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- Hypokalemia FT 2020Documento49 pagineHypokalemia FT 2020ebkai98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hormone Assays: Immuno-Serology SectionDocumento52 pagineHormone Assays: Immuno-Serology SectionjeffreyNessuna valutazione finora
- GIT Renal Endo ReviewDocumento43 pagineGIT Renal Endo Reviewshaira.maebbrnNessuna valutazione finora
- Endo Disorder Review NotesDocumento7 pagineEndo Disorder Review NotesKaren Joyce LasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Path Endocrine OutlineDocumento46 paginePath Endocrine Outlineaya derweshNessuna valutazione finora
- RACE Medicine Endocrinology ANNOTATEDDocumento10 pagineRACE Medicine Endocrinology ANNOTATEDanu radhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid StormDocumento16 pagineThyroid StormRaquid MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pituitary & AdrenalDocumento10 paginePituitary & AdrenalAfiqah So JasmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid ReportDocumento105 pagineThyroid ReportAARVNessuna valutazione finora
- DILIDocumento40 pagineDILIYunik YuliapsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDocumento166 pagineReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Quick Reference Guide Endocrine Hypertension 2 2016 VersionDocumento16 pagineQuick Reference Guide Endocrine Hypertension 2 2016 VersionParishan SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- General Signs/Symptoms Labs/Diagnosis Prevention Treatment: Hepatitis ADocumento2 pagineGeneral Signs/Symptoms Labs/Diagnosis Prevention Treatment: Hepatitis A85robertNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocumento21 pagineAutoimmune Diseases85robertNessuna valutazione finora
- Reversible Airflow ObstructionDocumento2 pagineReversible Airflow Obstruction85robertNessuna valutazione finora
- IRON Deficiency: Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Diagnosis TreatmentDocumento5 pagineIRON Deficiency: Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Diagnosis Treatment85robertNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheum at OlogyDocumento2 pagineRheum at Ology85robertNessuna valutazione finora