Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Layers
Caricato da
bijitendraDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Layers
Caricato da
bijitendraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
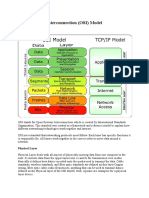
Layer
Medium Bits Frames Packets Segments Data Data Data
Layer Name Physical Layer Data link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Session Layer Presentation Layer Application Layer
Function Electrical /physical specifications for devices. Ways of transferring data between networks, detect& correct errors in the physical layer. Transferring data sequences from source host to a destination host on a different networks Controls the reliability of a given link, aacknowledge successful/failed transmissions Establish, Manage & Terminate connections between local and remote applications. Transforms data into the form that the application accepts. This layer interacts with software applications that involve communications.
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 5
Layer 6
Layer 7
Simplex Half Duplex Full Duplex
1-way eg. Keyboard to PC 1 way at a time eg. Printer Interfaces most network 2-way connections
Advantage: Cheaper
Details Relationship between devices & transmission medium, such as a copper or optical cable such as layout of pins, voltages, cable specifications, hubs, repeaters, network adapters, host bus adapters etc LAN, WAN, etc. Arrange bits, from the physical layer, into logical sequences called frames.
Includes Routers etc. Needs to maintain the QOS requested by the Transport Layer, Performs Routing functions,. Flow control & error control. Keep track of data segments & retransmit failed segments. On a loose scale, TCP is categorized as layer-4 of Osi Responsible for graceful close of sessions and also for session checkpointing and recovery Formats and encrypts data to be sent across a network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer Identifying communication partners, determining resource availability, and synchronizing communication
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Discuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsDocumento31 pagineDiscuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsNguyen Manh TaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Project ReportDocumento47 pagineNetworking Project Reportmansha9933% (3)
- MOdel OSI NoteDocumento7 pagineMOdel OSI NoteZulfadli HanaffiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4g RF Cluster Optimization Cjv007 Kpi Refarming - After ReviewDocumento32 pagine4g RF Cluster Optimization Cjv007 Kpi Refarming - After ReviewHAWLITUNessuna valutazione finora
- LG FB163 A0P - ManualDocumento23 pagineLG FB163 A0P - ManuallabonetNessuna valutazione finora
- UMA CardDocumento10 pagineUMA CardramireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- AnswerDocumento1 paginaAnswerNasir MahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes-Lec 1 - Introductory LectureDocumento75 pagineNotes-Lec 1 - Introductory LectureWaseem FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- OSItables PDFDocumento3 pagineOSItables PDF900913n008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Layer 1: Physical LayerDocumento2 pagineLayer 1: Physical LayerSasi DharNessuna valutazione finora
- 7-Layer OSI MODELDocumento11 pagine7-Layer OSI MODELBabu CamNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFDocumento20 pagineOpen Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFLink NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3Documento5 pagineWeek 3hiren_keepsmilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento18 pagineLecture 1Furqan WarisNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworksDocumento18 pagineComputer NetworksAvneetSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Protocol Is A System of Digital Rules For Message: Transport LayerDocumento3 pagineProtocol Is A System of Digital Rules For Message: Transport Layerfegungmama03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFDocumento24 pagineChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fahim Shahzad (Lecturer)Documento68 pagineFahim Shahzad (Lecturer)kaif BangashNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks: Instructor: Maqsood RaziDocumento83 pagineComputer Networks: Instructor: Maqsood RaziIqbal Uddin KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Model: 7 Layers Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link and PhysicalDocumento9 pagineOSI Model: 7 Layers Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link and PhysicalHarman Gahir0% (1)
- 02computer Network BasicsDocumento61 pagine02computer Network BasicsgladalokNessuna valutazione finora
- 02computer Network BasicsDocumento61 pagine02computer Network BasicsPeter M' MboleNessuna valutazione finora
- Computernetwork For InterviewDocumento9 pagineComputernetwork For InterviewSangeetha ShankaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Seven Layers of OSI Reference ModelDocumento4 pagineSeven Layers of OSI Reference ModelpervezkanjuNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of NetworksDocumento13 pagineTypes of NetworkssumitNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationDocumento6 pagineOSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationSanyam JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Questions For MID I CNDocumento14 pagineImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)Nessuna valutazione finora
- NetworksDocumento8 pagineNetworksGaby MbuguaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Layer: Cisco Documentation CD and Training BooksDocumento21 pagineApplication Layer: Cisco Documentation CD and Training BooksqtipwaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Backbone Network Components (Data Communications and Networking) 1Documento5 pagineBackbone Network Components (Data Communications and Networking) 1Udara YapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Net PDFDocumento49 pagineNet PDFshevaunie seniorNessuna valutazione finora
- NetworkDocumento26 pagineNetworkriddick_danishNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components ApplicationDocumento3 pagineOSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components ApplicationJohn SextonNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento4 pagineUnit 1SY ECE51 SHEJUL YUVRAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkDocumento3 pagineComputer NetworkMubashir SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingDocumento6 pagineNetwork Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingNaveen JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- SYN CH - 1 and 2Documento20 pagineSYN CH - 1 and 2IG TECHNessuna valutazione finora
- Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocumento10 pagineAddis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineeringhenok abebeNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication SystemDocumento10 pagineE-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication Systemshravan1108Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesDocumento18 pagineUNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesdoctoraseenNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERDocumento4 pagineNetworking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERRaymart BuendiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Ethernet Overview: IntelDocumento4 pagineIndustrial Ethernet Overview: IntelChusnadiNessuna valutazione finora
- RJ-45 Connectors-RJ45 Is A Standard Type of Connector For Network Cables. RJ45 ConnectorsDocumento5 pagineRJ-45 Connectors-RJ45 Is A Standard Type of Connector For Network Cables. RJ45 ConnectorsBruce AmigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Comp NWsDocumento42 pagineOverview of Comp NWsfahana abdul vahabNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks Lecture NotesDocumento50 pagineComputer Networks Lecture NotesRam Kumar0% (1)
- Computer CommunicationDocumento7 pagineComputer Communicationsaravanamuthaly1397Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report About " OSI Model "Documento9 pagineReport About " OSI Model "mahamd saiedNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of NetworkingDocumento40 pagineBasic of NetworkingPrateek Persistently PreciousNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking ConceptDocumento81 pagineNetworking ConceptMaghairNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer OSIDocumento3 pagineLayer OSIClarence Joy BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The OSI ModelDocumento5 pagineWhat Is The OSI ModelMomshad DinuryNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI ModelDocumento1 paginaOSI ModelDiana AlwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communications: Course Teacher: Md. Firoz Mridha Assistant Professor University of Asia PacificDocumento72 pagineData Communications: Course Teacher: Md. Firoz Mridha Assistant Professor University of Asia PacificRafsan Tahsin HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Standards: Required To Allow For Interoperability Between Equipment AdvantagesDocumento48 pagineStandards: Required To Allow For Interoperability Between Equipment AdvantagesChandrashekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communication & NetworksDocumento35 pagineData Communication & NetworksAnonymous oP2FCuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network PresentationDocumento165 pagineComputer Network PresentationinthuyashanNessuna valutazione finora
- NC Sem 4Documento8 pagineNC Sem 4divyasharmade98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Straight-Through Wired Cables: 2) A) What Are The Three Types of Ethernet Cables? ExplainDocumento6 pagineStraight-Through Wired Cables: 2) A) What Are The Three Types of Ethernet Cables? ExplainRohit RishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Quiz: Refer To Curriculum Topic: 2.1.1Documento12 pagineChapter 2 Quiz: Refer To Curriculum Topic: 2.1.1Angel Dario Morón FelizNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network and Network Components: M A BaigDocumento51 pagineComputer Network and Network Components: M A BaigMahamad Ali BaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksDocumento48 pagineLec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksnawafNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Reference: CCNA Study NotesDocumento29 pagineOSI Reference: CCNA Study NotesShehzad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyDa EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- TAP Testing ToolkitDocumento3 pagineTAP Testing ToolkitJuma BasilioNessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Domain Crossing (CDC) : Erik Seligman CS 510, Lecture 17, March 2009Documento39 pagineClock Domain Crossing (CDC) : Erik Seligman CS 510, Lecture 17, March 2009Rohan PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco AnyConnect VPN StatisticsDocumento6 pagineCisco AnyConnect VPN StatisticsRohan JainNessuna valutazione finora
- 210200-002 iAPX88 Book 1983Documento354 pagine210200-002 iAPX88 Book 1983kgrhoadsNessuna valutazione finora
- Code Composer StudioDocumento4 pagineCode Composer StudioPrathmesh ThergaonkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Freepbx Distro: Registering Your Freepbx System To Our License ServerDocumento5 pagineFreepbx Distro: Registering Your Freepbx System To Our License ServerAngel JiménezNessuna valutazione finora
- DockerDocumento15 pagineDockerCaleb Aaron OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- BISYNC (Binary Synchronous Comunication)Documento5 pagineBISYNC (Binary Synchronous Comunication)dhani2906Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCTV Seminar PaperDocumento32 pagineCCTV Seminar PaperTolulope 'Segun AdekoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Running Dea SolverDocumento6 pagineRunning Dea SolverFuyenNessuna valutazione finora
- EasyLobby® Secure Visitor Management (SVM) 10 PDFDocumento2 pagineEasyLobby® Secure Visitor Management (SVM) 10 PDFVictor Andres Mayorga MeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Gartner Hype Cycle For Emerging Technologies 2016Documento3 pagineGartner Hype Cycle For Emerging Technologies 2016krutarthdesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Apple ArtifactsDocumento52 pagineApple ArtifactsStevanus ColonneNessuna valutazione finora
- SOP Penerimaan Pasien Rawat JalanDocumento2 pagineSOP Penerimaan Pasien Rawat JalanRakhmat Ari Wibowo100% (3)
- (Core 2) Prepare Computer-Aided DrawingsDocumento116 pagine(Core 2) Prepare Computer-Aided DrawingsOliver Sanchez82% (11)
- Amarino-Android Meets Arduino Full Paper (Ieee Format)Documento3 pagineAmarino-Android Meets Arduino Full Paper (Ieee Format)Bala VishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Theory To Practice-KPI Optimization (A 4G Wireless Technology)Documento20 pagineLTE Theory To Practice-KPI Optimization (A 4G Wireless Technology)amanagarwal16Nessuna valutazione finora
- APD4 Install E RevQDocumento84 pagineAPD4 Install E RevQAlexandra Ionela Neaga - LicuNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Directory Domain Services in The Perimeter Network (Windows Server 2008)Documento51 pagineActive Directory Domain Services in The Perimeter Network (Windows Server 2008)Ivan Brčić100% (1)
- Oracle EBS 12.2.0 DB Migrate To Solaris 11.1 (64 Bit)Documento33 pagineOracle EBS 12.2.0 DB Migrate To Solaris 11.1 (64 Bit)craw467Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Design and Synthesis: Behavioral VerilogDocumento41 pagineDigital Design and Synthesis: Behavioral VerilogSyed AshmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communications and Computer Networks: A BusinessDocumento39 pagineData Communications and Computer Networks: A Businessmamtaarora491224Nessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Diagnosis Using DMV's & DMF's in SQL 2005 & 2008Documento37 paginePerformance Diagnosis Using DMV's & DMF's in SQL 2005 & 2008asif_listen100% (1)
- UsxrefDocumento90 pagineUsxrefsbmandalNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 SchedulingDocumento37 pagine4 Schedulingreply2amit1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMDocumento3 pagine2.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMAva BarramedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of ComputerDocumento12 pagineMeaning of ComputerManish PandeyNessuna valutazione finora