Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
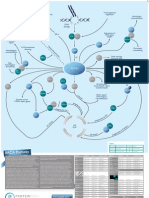
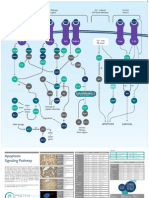
VEGF Signaling Poster
Caricato da
Proteintech GroupDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
VEGF Signaling Poster
Caricato da
Proteintech GroupCopyright:
Formati disponibili
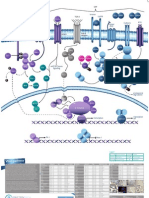
Actin Reorganisation
Focal Adhesion Turnover
Cell Survival
Permeabiliby
Migration PGI2 production Proliferation
VEGF
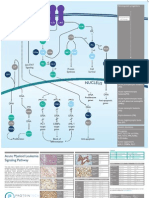
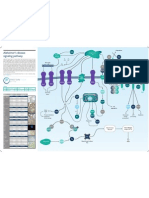
Mini-Catalog VEGF Signaling Pathway
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major regulator of new blood vessel growth and an important inducer of vascular permeability. VEGF binds the receptor VEGFR2 leading to a cascade of different signaling pathways, which result in the up-regulation of genes involved in mediating the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells and promoting their survival and vascular permeability. VEGF is expressed in virtually all cells in the body and is such a potent regulator of
vascular development that its dosage must be tightly regulated. Disruption of a single allele of the VEGF gene in mice results in embryonic lethality due to severe vascular defects. A variety of physiological and pathological processes are associated with upregulation of components of the VEGF/VEGFR-system, including embryogenesis, the female reproductive cycle, pregnancy, wound healing, tumor growth, diabetic retinopathy and ischemic diseases.
Function
Caspase 9 is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. CASP9 is processed by the caspase APAF1 and this step is thought to be one of the earliest in the caspase activation cascade.
For more information on all the antibodies featured here or to view our extensive catalog, visit www.ptglab.com
Function
This protein belongs to the Ras oncogene family, whose members are related to the transforming genes of mammalian sarcoma retroviruses. Defects in HRAS are a cause of cancer. The antibody specifically recognizes HRAS and does not bind NRAS or KRAS.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- VegfDocumento7 pagineVegfBerry BancinNessuna valutazione finora
- The Biology of Vegf and Its Receptors: Napoleone Ferrara, Hans-Peter Gerber & Jennifer LecouterDocumento8 pagineThe Biology of Vegf and Its Receptors: Napoleone Ferrara, Hans-Peter Gerber & Jennifer LecoutermonicamoniccNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 Melincovici VegfDocumento13 pagine2018 Melincovici Vegfdusseldorf27Nessuna valutazione finora
- VEGF and AngiogénesisDocumento7 pagineVEGF and AngiogénesisMiranda YareliNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumor Angiogenesis Cyynnn...Documento11 pagineTumor Angiogenesis Cyynnn...RadityaPriambodoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adj 12752Documento9 pagineAdj 12752Irfan HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis: Molecular NeuroscienceDocumento8 paginePI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis: Molecular NeuroscienceAbu KhairNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth Factors Involved in Angiogenesis: Deepak Kumar Gupta Roll No:16 REGISTRATION NO:201801032Documento13 pagineGrowth Factors Involved in Angiogenesis: Deepak Kumar Gupta Roll No:16 REGISTRATION NO:201801032Rajkamal SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Activity of Bevacizumab, A Humanized anti-VEGF Antibody in VitroDocumento11 pagineBiological Activity of Bevacizumab, A Humanized anti-VEGF Antibody in VitroNguyễn Thị Yến NhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancers 03 008411 PDFDocumento32 pagineCancers 03 008411 PDFNikolaevich KiorNessuna valutazione finora
- Kep Anak 2Documento195 pagineKep Anak 2Yuliana BklNessuna valutazione finora
- Koutras 2015Documento16 pagineKoutras 2015Ngurah BagusNessuna valutazione finora
- ZD6474 Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Growth Following Oral AdministrationDocumento11 pagineZD6474 Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Growth Following Oral AdministrationGregory PeckNessuna valutazione finora
- A1 PDFDocumento17 pagineA1 PDF2begeniusNessuna valutazione finora
- PS Mahar 1Documento5 paginePS Mahar 1ErickeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Angiogenesis During Exercise and TrainingDocumento9 pagineAngiogenesis During Exercise and TrainingDAVID AYANLOWONessuna valutazione finora
- Expressions of VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 in Placentae From GDM PregnanciesDocumento9 pagineExpressions of VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 in Placentae From GDM PregnanciesMayra PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Source: The Role of Anti-Angiogenic Agents (VEGF)Documento4 pagineSource: The Role of Anti-Angiogenic Agents (VEGF)Tabitha UyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Biology of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors: Tuomas Tammela, Berndt Enholm, Kari Alitalo, Karri PaavonenDocumento14 pagineThe Biology of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors: Tuomas Tammela, Berndt Enholm, Kari Alitalo, Karri PaavonenmonicamoniccNessuna valutazione finora
- Therapeutic Targeting of Angiogenesis Molecular Pathways in Angiogenesis-Dependent DiseasesDocumento11 pagineTherapeutic Targeting of Angiogenesis Molecular Pathways in Angiogenesis-Dependent Diseasesfelipe duarteNessuna valutazione finora
- J. Virol.-2000-Savory-10699-706Documento9 pagineJ. Virol.-2000-Savory-10699-706Mestesanu ElisabetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endometriosis and Angiogenic Factors: P. G. Artini, M. Ruggiero, F. Papini, G. Simi, V. Cela and A. R. GenazzaniDocumento29 pagineEndometriosis and Angiogenic Factors: P. G. Artini, M. Ruggiero, F. Papini, G. Simi, V. Cela and A. R. GenazzaniDauz ArashNessuna valutazione finora
- Ovário 2Documento9 pagineOvário 2Sandro PinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- HematologyDocumento8 pagineHematologyBoris Ramirez LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- THE BIOLOGY OF AngiogenesisDocumento4 pagineTHE BIOLOGY OF AngiogenesisSimran PhutelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijo 29 2 305 PDFDocumento10 pagineIjo 29 2 305 PDFdr faathirNessuna valutazione finora
- Procyanidin Vegf CokDocumento12 pagineProcyanidin Vegf CokAmelia SellyNessuna valutazione finora
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocumento20 pagineNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptJason MarshallNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Review: Structure and Function of VEGF ReceptorsDocumento8 pagineCritical Review: Structure and Function of VEGF ReceptorsmonicamoniccNessuna valutazione finora
- Jak2 PDFDocumento4 pagineJak2 PDFHanachanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Aspects of Tumour Angiogenesis: 1.1 Vasculogenesis, Angiogenesis, and Arterio-GenesisDocumento22 pagineBiological Aspects of Tumour Angiogenesis: 1.1 Vasculogenesis, Angiogenesis, and Arterio-Genesisoverlord5555Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel Human-Specific Soluble Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1Documento21 pagineA Novel Human-Specific Soluble Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1edelinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tylophora-8 AntitumorDocumento16 pagineTylophora-8 AntitumorAtrimed F & DNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti VEGFsDocumento4 pagineAnti VEGFsVishNessuna valutazione finora
- GATA-1 and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Maintenance in HIV: Mechanisms and ImplicationsDocumento18 pagineGATA-1 and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Maintenance in HIV: Mechanisms and ImplicationsKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Corto CTCF VegfDocumento6 pagineCorto CTCF Vegfunknowncountdown167Nessuna valutazione finora
- Patofisiologi Polisitemia VeraDocumento2 paginePatofisiologi Polisitemia VeraErni PanjaitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Pre EclampsiaDocumento50 pagineSeminar Pre EclampsiaManan BoobNessuna valutazione finora
- Angiogenesis PDFDocumento19 pagineAngiogenesis PDFapi-240712915Nessuna valutazione finora
- Split For The Cure: VEGF, PDGF-BB and Intussusception in Therapeutic AngiogenesisDocumento6 pagineSplit For The Cure: VEGF, PDGF-BB and Intussusception in Therapeutic AngiogenesispakemainmainNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Dr. Noor Pramono, M.med, SC, SP - Og (K)Documento29 pagineProf. Dr. Noor Pramono, M.med, SC, SP - Og (K)ponekNessuna valutazione finora
- Placenta: SciencedirectDocumento8 paginePlacenta: SciencedirectMayra PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal 1Documento13 pagineJurnal 1Aulia Rahma NoviastutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Artigo 31Documento25 pagineArtigo 31Ana Catarina De Oliveira Da Silv LaborinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors 8Documento9 pagineVascular Endothelial Growth Factors 8nazlibesirikNessuna valutazione finora
- 387 06 13 ArticleDocumento5 pagine387 06 13 ArticleREHAB AMBULATORIO HOSPITAL VITARTENessuna valutazione finora
- Angiogenic Factors in The Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia A Mini ReviewDocumento7 pagineAngiogenic Factors in The Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia A Mini ReviewedelinNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription Factors Having Impact On VEGF Gene Expressions in Angiogenesis - 2004Documento11 pagineTranscription Factors Having Impact On VEGF Gene Expressions in Angiogenesis - 2004nazlibesirikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaiworapongsa 2004Documento7 pagineChaiworapongsa 2004Lintang SuroyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 39350-57729-1-SM-VEGF-A y PDGF-BB - Factores Angiogénicos y La Etapa de Avance Síndrome Del Pie DiabéticoDocumento7 pagine39350-57729-1-SM-VEGF-A y PDGF-BB - Factores Angiogénicos y La Etapa de Avance Síndrome Del Pie DiabéticolobocazadorMHNessuna valutazione finora
- Ewing AngiogenesisDocumento14 pagineEwing Angiogenesisjulianantillon@hotmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Ghid Globo BpocDocumento3 pagineGhid Globo Bpocodiseu81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis & Cancer Write UpDocumento9 pagineGlycolysis & Cancer Write UpMarvin JeaNessuna valutazione finora
- GRANULOPEISISDocumento39 pagineGRANULOPEISISkemalmiaNessuna valutazione finora
- JAK2 Gene: Genetics Home ReferenceDocumento5 pagineJAK2 Gene: Genetics Home ReferenceveronicaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of GATA-1 in Megakaryocyte Function and Platelet Production During HIV Infection: A ReviewDocumento18 pagineThe Role of GATA-1 in Megakaryocyte Function and Platelet Production During HIV Infection: A ReviewKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Aragon ChingDocumento7 pagineAragon Chingprasana_biophysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloning, Expression and Purification of Mouse Vegf (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) in E. Coli 01 FebDocumento4 pagineCloning, Expression and Purification of Mouse Vegf (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) in E. Coli 01 FebGJESRNessuna valutazione finora
- 6Documento8 pagine6soledadDC329Nessuna valutazione finora
- WNT Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaWNT Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- p53 Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginap53 Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- mTOR Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginamTOR Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- BRCA Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaBRCA Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Apoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaApoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaAcute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Alzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterDocumento1 paginaAlzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora