Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
mTOR Signaling Pathway Poster
Caricato da
Proteintech Group0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
34 visualizzazioni1 paginaMTOR appears to play a central role in signaling caused by nutrients and mitogens. Rapamycin acts on mammalian cells through the mTOR protein kinase. MTOR was also found to act as an ATP sensor to regulate cell growth.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoMTOR appears to play a central role in signaling caused by nutrients and mitogens. Rapamycin acts on mammalian cells through the mTOR protein kinase. MTOR was also found to act as an ATP sensor to regulate cell growth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
34 visualizzazioni1 paginamTOR Signaling Pathway Poster
Caricato da
Proteintech GroupMTOR appears to play a central role in signaling caused by nutrients and mitogens. Rapamycin acts on mammalian cells through the mTOR protein kinase. MTOR was also found to act as an ATP sensor to regulate cell growth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
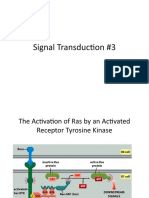
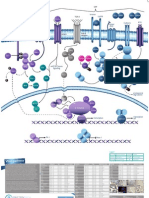
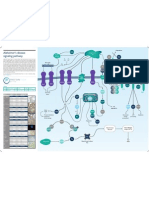
Growth Factors / Hormones
Insulin Signaling Pathway MAPK Signaling Pathway Amino Acids Cell growth
PIP3
Rapamycin
Regulation of autophagy
Hypoxia Energy stress
mTOR Signaling Pathway
mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) appears to play a central role in signaling caused by nutrients and mitogens such as growth factors to regulate translation. The drug rapamycin acts on mammalian cells through the mTOR protein kinase, also known as FRAP. When bound to the immunophilin binding protein FKBP12, rapamycin inhibits mTOR kinase activity and has immunosuppressant activity. Recently, mTOR was also found to act as an ATP sensor to regulate cell growth. Upstream activation of PI3 kinase activity that leads to oncogenic transformation can be blocked by inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin. Growth factor receptors first stimulate PI3 kinase, and through inositol phosphates activate PDK-1 and AKT (protein kinase B). The phosphorylation of S6K1 and 4EBP1 by mTOR and the phosphorylation downstream of RPS6 and eIF4B stimulate translational initiation and contribute to cell growth. For more information on all the antibodies featured here or to view our extensive catalog, visit www.ptglab.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FullDocumento10 pagineFullWalida FadillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviews: Regulation of Innate Immune Cell Function by mTORDocumento16 pagineReviews: Regulation of Innate Immune Cell Function by mTORAlicia Cerpa LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- mTOR Signaling Interactive PathwayDocumento6 paginemTOR Signaling Interactive PathwayKiki GirindraNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Transduction Lecture 3Documento32 pagineSignal Transduction Lecture 3chrystalNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitogene Activated Protien Kinase (Mapk) Pathway: A Presentation ONDocumento21 pagineMitogene Activated Protien Kinase (Mapk) Pathway: A Presentation ONKotupalli SindhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- P13K/AKT/mTOR Pathway-Based Novel Biomarkers For Breast CancerDocumento9 pagineP13K/AKT/mTOR Pathway-Based Novel Biomarkers For Breast CancerVarruchi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid Sensing and Activation of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1: Implications For Skeletal MuscleDocumento7 pagineAmino Acid Sensing and Activation of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1: Implications For Skeletal MuscleSajid Mohy Ul DinNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Thomson 2009 Immunoregulatory Functions of MTOR InhibitionDocumento14 pagine8 - Thomson 2009 Immunoregulatory Functions of MTOR InhibitionEduardo VianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fonc 04 00064Documento11 pagineFonc 04 00064Jeremias CancinoNessuna valutazione finora
- mTOR Signaling: Mathieu Laplante and David M. SabatiniDocumento3 paginemTOR Signaling: Mathieu Laplante and David M. SabatiniRJNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapamycin and mTOR Kinase Inhibitors 12154 - 2008 - Article - 3Documento10 pagineRapamycin and mTOR Kinase Inhibitors 12154 - 2008 - Article - 3Nicholas FeatherstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Modulators of Protein Misfolding and Neurodegenerative DiseaseDa EverandChemical Modulators of Protein Misfolding and Neurodegenerative DiseaseNessuna valutazione finora
- BJ 4040191Documento6 pagineBJ 4040191seda selyamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Effects of Dietary Flavonoids On AdipogenesisDocumento21 pagineDifferential Effects of Dietary Flavonoids On AdipogenesisEsNessuna valutazione finora
- Accelerated PublicationDocumento5 pagineAccelerated PublicationFrancisco Antonó Castro WeithNessuna valutazione finora
- The mTOR Pathway in The Control of Protein SynthesisDocumento8 pagineThe mTOR Pathway in The Control of Protein SynthesisKennedy LadeiaNessuna valutazione finora
- AngelaDocumento27 pagineAngelaMehedi HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pfnf-Yb Transcription Factor Is A Downstream Target of Melatonin and Camp Signalling in The Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium FalciparumDocumento13 pagineThe Pfnf-Yb Transcription Factor Is A Downstream Target of Melatonin and Camp Signalling in The Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium FalciparumWania LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of mTOR Signaling in Cardioprotection: Anindita Das and Rakesh C. KukrejaDocumento18 pagineRole of mTOR Signaling in Cardioprotection: Anindita Das and Rakesh C. Kukrejaanjali SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal TransductionDocumento42 pagineSignal TransductionchinnnababuNessuna valutazione finora
- Autophagy & TomorigenisisDocumento22 pagineAutophagy & TomorigenisisKirk CobainNessuna valutazione finora
- 26S Proteasomes Are Rapidly Activated by Diverse Hormones and Physiological States That Raise cAMP and Cause Rpn6 PhosphorylationDocumento10 pagine26S Proteasomes Are Rapidly Activated by Diverse Hormones and Physiological States That Raise cAMP and Cause Rpn6 PhosphorylationAndonis AngelovNessuna valutazione finora
- CAMP PathwayDocumento14 pagineCAMP PathwaySree Lakshmi NNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthrax Toxin Mechanism of ActionDocumento8 pagineAnthrax Toxin Mechanism of ActionWendy FXNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Invest 2014131 ADocumento12 pagineLab Invest 2014131 AGeorge Sebastian AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- AMP-activated Protein Kinase Is Activated As A Consequence J. Biol. Chem.-2008-Gauthier-16514-24Documento12 pagineAMP-activated Protein Kinase Is Activated As A Consequence J. Biol. Chem.-2008-Gauthier-16514-24evanconstantine77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Function: Protein: Gene: Organism: StatusDocumento1 paginaFunction: Protein: Gene: Organism: StatusZia Ashraf ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nao PerderDocumento5 pagineNao PerderSara SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unacademy 4 PDFDocumento16 pagineUnacademy 4 PDFANUPAM ANAND KUMAR PANDEY MBA-INessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs HomeworkDocumento2 pagineDrugs HomeworkEmily JanimakNessuna valutazione finora
- Rac1/Pi3K/Pkb-Dependent Caspase-1 Activation Release Through Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibition Induces Il-1Documento12 pagineRac1/Pi3K/Pkb-Dependent Caspase-1 Activation Release Through Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibition Induces Il-1Josse BouwhuisNessuna valutazione finora
- The PI3K Akt Pathway Is One of The Most Important Survival Signaling Cascades Altered in Human Solid Tumors Including Pros Tate CancerDocumento2 pagineThe PI3K Akt Pathway Is One of The Most Important Survival Signaling Cascades Altered in Human Solid Tumors Including Pros Tate Cancerpumahell25Nessuna valutazione finora
- NST110, Toxicology Department of Nutritional Sciences and Toxicology University of California, BerkeleyDocumento29 pagineNST110, Toxicology Department of Nutritional Sciences and Toxicology University of California, BerkeleyAitheng LumNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Article 181Documento12 pagine2019 Article 181Khoirotul HidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ref 17Documento10 pagineRef 17Lateecka R KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Second MessengersDocumento42 pagineSecond MessengersYunonNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Transduction PathwaysDocumento6 pagineSignal Transduction PathwaysSHREYA SENTHIL KUMAR IMS21286Nessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Mechanisms of Action of FSH: Livio Casarini and Pascale CrépieuxDocumento10 pagineMolecular Mechanisms of Action of FSH: Livio Casarini and Pascale CrépieuxKamila AlejandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer BiologyDocumento9 pagineCancer BiologyemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (Mapks) : Erks, JNKS, and P38SDocumento8 pagineMitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (Mapks) : Erks, JNKS, and P38SazzaassNessuna valutazione finora
- Froy Et Al 2011Documento10 pagineFroy Et Al 2011Roee GutmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Jegathiswary A/P Ganasan Matrics: S56094 Code: BIO4102 Date: 11/07/2021Documento2 pagineName: Jegathiswary A/P Ganasan Matrics: S56094 Code: BIO4102 Date: 11/07/2021Jegathiswary GanasanNessuna valutazione finora
- s56094 Bio4102 Section BDocumento2 pagines56094 Bio4102 Section BJegathiswary GanasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Translation in Developmental ProcessDocumento5 pagineRegulation of Translation in Developmental ProcessattiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitogen Activated Protein KinasesDocumento13 pagineMitogen Activated Protein KinasesVeer BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mtorc1 Complex1 PDFDocumento13 pagineMtorc1 Complex1 PDFFfabio DeangelisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseDa EverandCellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseAlfredo Ulloa-AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein2Documento2 pagineGrowth Factor Receptor Bound Protein2rajeshmangalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Language of CellsDocumento25 pagineThe Language of Cellsdry_ice123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of Aging and Treatment Option: The Sirtuin Pathway Intersects With The insulin/IGF1 PathwayDocumento4 pagineMechanism of Aging and Treatment Option: The Sirtuin Pathway Intersects With The insulin/IGF1 PathwayWilliam MurphyNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Journal::Methanolic Extract of Red Ginseng Marc Induces Apoptosis On Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma HSC-3Documento12 pagineEngineering Journal::Methanolic Extract of Red Ginseng Marc Induces Apoptosis On Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma HSC-3Engineering JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Proliferation, Survival and Metabolism: The Role of PI3K/AKT/ mTOR Signalling in Pluripotency and Cell Fate DeterminationDocumento11 pagineProliferation, Survival and Metabolism: The Role of PI3K/AKT/ mTOR Signalling in Pluripotency and Cell Fate DeterminationAlicia Cerpa LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- CDD Is 2013151 ADocumento10 pagineCDD Is 2013151 ADalton JLNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 SREBF1 AR:MTOR Nuclear Axis in Prostate CancerDocumento11 pagine0 SREBF1 AR:MTOR Nuclear Axis in Prostate CancerShuang LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Apoa Gene Expression With Acidosis: Requirement For A Transcriptional RepressorDocumento15 pagineRegulation of Apoa Gene Expression With Acidosis: Requirement For A Transcriptional RepressorAbdur Rachman Ba'abdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cddis 2014463 ADocumento13 pagineCddis 2014463 ATA TranNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene RegulationsDocumento11 pagineGene Regulationsmahadi.infsduNessuna valutazione finora
- Fol I Culo GenesisDocumento22 pagineFol I Culo GenesisDIANA LIZETTE ROJAS GARCIANessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To The Webinar!Documento44 pagineWelcome To The Webinar!maorpeNessuna valutazione finora
- Peran Sistem Flbrinol1S1S Pada Berbagai Proses Fisiologis Dan PatologisDocumento12 paginePeran Sistem Flbrinol1S1S Pada Berbagai Proses Fisiologis Dan PatologisBima JonnaediNessuna valutazione finora
- WNT Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaWNT Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- VEGF Signaling PosterDocumento1 paginaVEGF Signaling PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- p53 Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginap53 Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- BRCA Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaBRCA Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Apoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaApoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterDocumento1 paginaAcute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Alzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterDocumento1 paginaAlzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterProteintech GroupNessuna valutazione finora