Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet
Caricato da
Nathan Korean KimDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet
Caricato da
Nathan Korean KimCopyright:
Formati disponibili
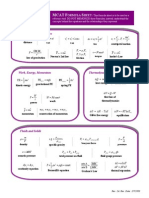
MCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet
Nuclear and Atomic Chemistry Avogadro's number: N A = 6.02 10 N A amu (u) = 1 gram
23
Electron Configurations e quantum numbers: n , l, m l , m s n = 1, 2, K l = 0, 1, K , n 1 [l = 0 s , l = 1 p , l =2 d, l = 3 f ] m l = l, ( l 1), K , ( l 1), l 5f
1 u = 1.66 10 24 g = 1.66 10 27 kg mp = 1.0073 u, mn = 1.0087 u
7p 6d 5d 4d 3d 6p 5p 4p 3p 2p
7s 6s 5s 4s 3s 2s 1s
Z = # protons, N = # neutrons mass defect: m = ( Zmp + Nmn ) mnucleus
nuclear binding energy: E B = ( m ) 1 eV = 1.6 10 19 J, 1 MeV = 10 6 eV E photon = hf = hc electron energy levels: E n = for any 1-electron atom Radioactive Decay
Z2 n2
931 MeV 1u
ms = +
1 2
or
1 2
4f
in subshell l, max # of electrons = 4 l + 2 in energy level n , max # of electrons = 2n 2
( 13.6 eV)
Z = # protons = atomic number, N = # neutrons, A = Z + N = mass number Decay Description Z N A eject = 4 He 2 2 4 2 +1 1 0 n p + e 1 +1 0 + p n + e+ 1 +1 0 EC p+e n X* X + 0 0 0
Periodic Trends & Bonding
Atomic Radius
se rea s
Stoichiometry / Lewis Structures mass in grams moles of solute # moles = ; molarity: M = MW L of solution mass of X % composition by mass of X = 100% mass of molecule 1 formal charge: FC = V ( 2 B + L) V = (# of valence e ' s), B = ( # of bonding e ' s), L = (# of lone-pair e ' s)
Molecular Geometry (VSEPR theory)
# lone pairs on central atom 0
Electron Affinity
re mo e ativ neg
Geometric Family
Linear Trigonal planar Tetrahedral Trigonal bipyramid Octahedral
inc
Ionization Energy
inc rea ses
Electronegativity
inc rea ses
shape = geometry
Acidity
inc rea ses
Basicity
inc rea ses
1
2001 by The Princeton Review, Inc. Unauthorized reproduction prohibited.
shape =
Bent
Trigonal pyramid
See-saw
Square pyramid
electronegativity of some common atoms: F > O > Cl > N > Br > (I S C) > H intermolecular forces (D = dipole, I = induced, i = instantaneous): ionD > DD (incl. H-bonds) > DID > iDID (London)
shape =
Bent
T-shaped
Square planar
Gases Avogadros law: V n Vat STP = n(22.4 L) STP: T = 0 C = 273 K, P = 1 atm Boyles law: V 1/P (at constant T ) Charles law: V T (at constant P ) Combined: P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 Ideal-Gas law: PV = nRT Daltons law of partial pressures: P = pi Grahams law of effusion: rate of effusion of gas 2 m v 2,rms = v 1,rms m 1 = 2 rate of effusion of gas 1
Colligative Properties moles of solute molality: m = kg of solvent equivalents (eq) normality: N = L of solution BP elevation: Tb = kbim FP depression: Tf = kfim moles of S mole fraction: XS = total moles o Raoults law: PA = X APA o vapor pressure depression: PA = (1 X A )PA osmotic pressure: = iMRT Thermochemistry
m1 m2
T (in K) = TC + 273, 1 cal 4.2 J q = mc T = C T (no phase change) q = n Hphase change enthalpy change: H = heat of rxn at const P H < 0 exothermic, H > 0 endothermic Arrhenius equation: k = Ae E a RT standard state: one most stable at 25C, 1 atm o o o H rxn = nH f,products nH f,reactants for generic balanced reaction a A + b B c C + d D, Laws of Thermodynamics: excluding [C]c eq [D]d eq at at pure solids 1) Energy is conserved: E = q + W equilibrium constant: K eq = a b [A]at eq [B]at eq and liquids 2) spontaneous rxn S [entropy] 0 3) S = 0 for pure crystal at T = 0 K (gas rxns use partial pressures in K eq expression) Gibbs Free Energy: G = H TS [const. T ] K eq is a constant at a given temperature. G < 0 spontaneous K eq < 1 equilibrium favors reactants G = 0 at equilibrium K eq > 1 equilibrium favors products G > 0 reverse rxn is spontaneous c d kJ [C] [D] G o RT ln K 2.3RT log K (5.7 mol ) log K reaction quotient: Q = [A]a [B]b Redox and Electrochemistry Law of Mass Action (Le Chtelier's principle): Rules for determining oxidation state (OS ): Q < K eq rxn proceeds forward 1) sum of OS s = 0 in neutral molecule; Q = K eq rxn at equilibrium sum of OS s = charge on ion Q > K eq rxn proceeds in reverse 2) Group 1 metals: OS = +1; Group 2 metals: OS = +2 Acids and Bases + + pH = log [H ] = log [H3O ] 3) OS of F = 1 pOH = log [OH] 4) OS of H = +1 Kw = [H+][OH] = 1 1014 at 25 C 5) OS of O = 2 pH + pOH = 14 at 25 C 6) OS of halogens = 1; OS of O family = 2 If one rule contradicts another, rule higher in [H + ][A ] , pK a = log K a Ka = list takes precedence. [HA] F = faraday 96,500 C/mol e [ OH][HB + ] G = nFEcell , pK b = log K b Kb = Ecell > 0 spontaneous [B] Ecell < 0 reverse rxn is spontaneous K aK b = K w = ion-product constant for water 0.06 logQ HendersonHasselbalch equations: Nernst equation: E = E o n [weak acid] Faradays Law of Electrolysis: pH = pK a log [conjugate base] The amount of chemical change is [weak base] pOH = pK b log [conjugate acid] proportional to the amount of electricity that flows through the cell. acidbase neutralization: N V = N V
a a b b
Kinetics and Equilibrium [reactant] [product] concentration rate = or + time time 1 [reactant] 1 [product] reaction rate = or + coeff time coeff time rate law for elementary reaction: rate = k [reactant1 ]coeff1 L
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDa EverandMCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Sterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsDa EverandSterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet: Nuclear and Atomic Chemistry Electron ConfigurationsDocumento2 pagineMCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet: Nuclear and Atomic Chemistry Electron ConfigurationsGreenINVNessuna valutazione finora
- Mnemonics For The MCATDocumento11 pagineMnemonics For The MCATsujsam100% (2)
- MCAT Biology Complete OutlinesDocumento34 pagineMCAT Biology Complete OutlinesJacob Mikhail90% (10)
- Atoms Molecules Quantum MechanicsDocumento20 pagineAtoms Molecules Quantum Mechanicsrvar839100% (3)
- MCAT Crash CourseDocumento15 pagineMCAT Crash CourseDe ShepNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Organic Summary SheetDocumento6 pagineMCAT Organic Summary SheetSpencer Thomas100% (2)
- MCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetDocumento3 pagineMCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber0971% (7)
- MCAT Formula Sheet Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineMCAT Formula Sheet Cheat Sheetdjanisz2100% (3)
- MCAT - BiologyDocumento15 pagineMCAT - BiologyEmily Teo100% (1)
- General Chemistry MCAT - 1Documento63 pagineGeneral Chemistry MCAT - 1pparik10100% (2)
- MCAT MetabolismDocumento4 pagineMCAT MetabolismNawledge9308100% (1)
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDocumento16 pagineMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT MnemonicsDocumento14 pagineMCAT Mnemonicskmulqs100% (1)
- Jack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryDocumento52 pagineJack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryLora100% (2)
- McatDocumento6 pagineMcatapi-383289428Nessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular structure and reaction mechanismsDocumento20 pagineMolecular structure and reaction mechanismsrvar839100% (2)
- MCAT CoverageDocumento10 pagineMCAT Coveragecapt_zoe100% (1)
- 500 Review Questions For The MCAT Biology, 2 EditionDocumento192 pagine500 Review Questions For The MCAT Biology, 2 EditionAaron GohNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT ShortcutsDocumento12 pagineMCAT ShortcutsShafqat Shakeel100% (2)
- MCAT ReviewDocumento114 pagineMCAT Reviewjustinwendel100% (4)
- TBR OChem2 OptDocumento305 pagineTBR OChem2 OptRamski90% (10)
- MCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetDocumento6 pagineMCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetChris_Barber09Nessuna valutazione finora
- TBR Bio1 OptDocumento333 pagineTBR Bio1 OptChris Daniels90% (10)
- MCAT Lab TechniquesDocumento17 pagineMCAT Lab TechniquesJim Smith100% (1)
- MCAT Math PortionMCATDocumento22 pagineMCAT Math PortionMCATwbowen92888100% (1)
- Selective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesDocumento28 pagineSelective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesMahdeeHaqueSyed100% (2)
- MCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesDocumento4 pagineMCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesNicole Ann LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Mnemonics for MCAT Biology/BiochemistryDocumento57 pagineMnemonics for MCAT Biology/BiochemistryBlinka199100% (2)
- Examkrackers General Chemistry NotesDocumento16 pagineExamkrackers General Chemistry NotesddNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Documento30 pagineMCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Chris_Barber09100% (2)
- Complete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFDocumento172 pagineComplete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFWollo NeftegnawNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Physics ReviewDocumento57 pagineMCAT Physics ReviewrinieroxNessuna valutazione finora
- 500 Review Questions For The MCAT Behavioral SciencesDocumento177 pagine500 Review Questions For The MCAT Behavioral Sciencesimperiouxx100% (5)
- General Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsDocumento14 pagineGeneral Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsCodie SimoneauxNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Hormones SummaryDocumento1 paginaMCAT Hormones Summaryrvar839Nessuna valutazione finora
- TBRBiology 1Documento372 pagineTBRBiology 1Fabliha Huq100% (10)
- MCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Documento74 pagineMCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Chris_Barber09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas For The MCAT: General ChemistryDocumento1 paginaFormulas For The MCAT: General Chemistrymissee728Nessuna valutazione finora
- Berkeley Review MCAT 1Documento10 pagineBerkeley Review MCAT 1Ishita SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Sample Questions Template 1Documento42 pagineMCAT Sample Questions Template 1gendut_novri0% (1)
- Testing Solutions Section Bank Notes V1.8Documento85 pagineTesting Solutions Section Bank Notes V1.8megNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lecture 1 Key ConceptsDocumento3 paginePhysics Lecture 1 Key ConceptsRobert Velázquez LucianoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Physics Review: Key Concepts and Paradigms for Solving ProblemsDocumento46 pagineMCAT Physics Review: Key Concepts and Paradigms for Solving Problemsdana milstein100% (1)
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocumento4 pagineMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéNessuna valutazione finora
- TBR Bio2 OptDocumento495 pagineTBR Bio2 Optmeyangli88% (25)
- Molecular Biology - DNA and Protein SynthesisDocumento23 pagineMolecular Biology - DNA and Protein SynthesisChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Sterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDa EverandSterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsDa EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDa EverandMCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDa EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsDa EverandMCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewDa EverandMCAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDa EverandMCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (3)
- Don's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesDa EverandDon's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- MCAT General Chemistry Review 2024-2025: Online + BookDa EverandMCAT General Chemistry Review 2024-2025: Online + BookNessuna valutazione finora
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- MCAT Biology Review 2024-2025: Online + BookDa EverandMCAT Biology Review 2024-2025: Online + BookValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Residence Features: Studio 1 Bathroom 428 INT SF / 39 SMDocumento1 paginaResidence Features: Studio 1 Bathroom 428 INT SF / 39 SMNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- 08.14 NL - (Lecture 3) 119 Vital Signs 2017 POST-lecture PDFDocumento61 pagine08.14 NL - (Lecture 3) 119 Vital Signs 2017 POST-lecture PDFNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- General Surgery OME PDFDocumento25 pagineGeneral Surgery OME PDFNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Thorax and Lungs: Jason Scalia, PH.DDocumento25 pagineThorax and Lungs: Jason Scalia, PH.DNathan Korean Kim100% (1)
- 08.14 NL - (Lecture 3) 119 Vital Signs 2017 POST-lecture PDFDocumento61 pagine08.14 NL - (Lecture 3) 119 Vital Signs 2017 POST-lecture PDFNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Filter Sizing Methods Application NoteDocumento6 pagineFilter Sizing Methods Application NoteNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- General Surgery OME PDFDocumento25 pagineGeneral Surgery OME PDFNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect Size and Confidence Intervals: Unit 5: Asynchronous K Benker MD MPHDocumento7 pagineEffect Size and Confidence Intervals: Unit 5: Asynchronous K Benker MD MPHkngs12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet For LIUDocumento1 paginaCheat Sheet For LIUNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Nov17 Web2 PDFDocumento10 pagineNov17 Web2 PDFNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes: - Registra9on-In Addi9on To The Astronomy Courses I Men9oned Earlier, There's Also Mechanical andDocumento10 pagineNotes: - Registra9on-In Addi9on To The Astronomy Courses I Men9oned Earlier, There's Also Mechanical andNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam+1 AnswersDocumento2 pagineExam+1 AnswersNathan Korean KimNessuna valutazione finora
- MSTE 1 April 2024 RefDocumento1 paginaMSTE 1 April 2024 Refrando12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Astrophysics Project Reaction PaperDocumento2 pagineAstrophysics Project Reaction PaperEdson DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Flash and False SetDocumento2 pagineFlash and False Setpxt90100% (3)
- SDA Professional Standards 2020 v8Documento80 pagineSDA Professional Standards 2020 v8Johan ZarragaNessuna valutazione finora
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMDocumento3 pagineREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Spring EquinoxDocumento17 pagineSpring EquinoxkkpereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFDocumento27 pagineBsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFLaurence CervoNessuna valutazione finora
- Arabic SyntaxDocumento26 pagineArabic SyntaxagahNessuna valutazione finora
- Idea Proposal Format E-Yantra Innovation Challenge 2020-21: Project NameDocumento5 pagineIdea Proposal Format E-Yantra Innovation Challenge 2020-21: Project NameNishant MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Đề Thi Học Sinh Giỏi Thành Phố Lớp 12 TP Hải Phòng Môn Tiếng Anh Bảng Không Chuyên 2019-2020Documento4 pagineĐề Thi Học Sinh Giỏi Thành Phố Lớp 12 TP Hải Phòng Môn Tiếng Anh Bảng Không Chuyên 2019-2020Ý Nguyễn Thị NhưNessuna valutazione finora
- Co Op Housing Cover LetterDocumento6 pagineCo Op Housing Cover Lettere7dhewgp100% (1)
- Project Execution Strategy for Barwa City Phase 2Documento17 pagineProject Execution Strategy for Barwa City Phase 2marydell12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Andrew M. Evens Kristie A. Blum EditorsDocumento343 pagineNon-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Andrew M. Evens Kristie A. Blum EditorsBianca100% (1)
- Electronic Tongue Plant Rasa AIIMS NMRDocumento4 pagineElectronic Tongue Plant Rasa AIIMS NMRMSKCNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 ResourcesDocumento144 pagineTopic 2 ResourcesTia WardNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 SetDocumento34 pagine5 SetQuynh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsDocumento115 pagineNobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsd7an7pijpkerNessuna valutazione finora
- ITM Unit 2 - Tutorial Sheet - StudentsDocumento4 pagineITM Unit 2 - Tutorial Sheet - StudentsalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Why NAM remains relevant todayDocumento2 pagineWhy NAM remains relevant todaySourabh PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Trading Using Harmonic PatternsDocumento1 paginaTrading Using Harmonic PatternsBiantoroKunartoNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning and Reference Guide: 5265602-1EN Rev.3 (2008/08/28)Documento340 pagineLearning and Reference Guide: 5265602-1EN Rev.3 (2008/08/28)joseNessuna valutazione finora
- Science: Quarter 3, Week 6 - 7 Module 5Documento27 pagineScience: Quarter 3, Week 6 - 7 Module 5NRIZA MAE CACHONessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 9 January 15 2019 EIMDocumento4 pagineDaily Lesson Log Grade 9 January 15 2019 EIMBrufal Michael AngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition James S TrieschmannDocumento24 pagineTest Bank For Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition James S TrieschmannGeorgeWangeprm100% (41)
- Lec-19 Ethical Framework For Helath ResearchDocumento17 pagineLec-19 Ethical Framework For Helath ResearchNishant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Exemplar Art 6Documento3 pagineLesson Exemplar Art 6Arranguez Albert ApawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mothly Supervisory PlanDocumento6 pagineMothly Supervisory Planclaire alcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover Letter For Drilling Engineering PDFDocumento1 paginaCover Letter For Drilling Engineering PDFHein Htet ZawNessuna valutazione finora
- BWG CalculatorDocumento10 pagineBWG CalculatorELIECER SANCHEZNessuna valutazione finora
- IP UK Pine Needle Power Generation PDFDocumento23 pagineIP UK Pine Needle Power Generation PDFSunny DuggalNessuna valutazione finora