Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Atypical Nevus - Simplified Criteria
Caricato da
Deba P SarmaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Atypical Nevus - Simplified Criteria
Caricato da
Deba P SarmaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Atypical nevus simplified.
Deba P Sarma, MD, Omaha
Architectural changes: ( Recognized under scanning or low power examination)
1. Asymmetry
2. Subepidermal fibroplasia, concentric eosinophilic/ lamellar
3. Lentiginous melanocytic hyperplasia
4. Spindle or epitheloid melanocytes aggregating in nests and
fusing with adjacent rete ridges to form bridges
5. “Shouldering” phenomenon- single or nests of intraepidermal
melanocytes extending beyond the main dermal component.
6. Variable dermal lymphocytic infiltration
Melanocytic nuclear changes:
1. Increased nuclear size, nuclear membrane irregularity,
prominent nucleoli. nuclear and cytoplasmic pleomorphism,
variable hyperchromatism. Single or nest of atypical cells
are seen in lacuna due to fixation artifact.
2. Cytologic atypia is random ( normal and atypical cells are
admixed in a nevus) in contrast to confluent atypia in in-situ
melanoma.
3. Grading of atypia:
Low: Mild- nuclear size that of keratinocyte
nuclear pleomorphism-mild
nucleoli- absent or small
Moderate- nuclear size, 1-2X keratinocyte nucleus
nuclear pleomorphism-moderate
nucleoli-absent or small
High: Severe- nuclear size-2x or more keratinocyte nucleus
nuclear pleomorphism- severe
nucleoli- prominent and enlarged
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Pilar Cyst With Crystals. Deba P Sarma, MDDocumento2 paginePilar Cyst With Crystals. Deba P Sarma, MDDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Acanthoma (Epidermolytic Acanthoma), M 65, NeckDocumento5 pagineAcantholytic Acanthoma (Epidermolytic Acanthoma), M 65, NeckDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDocumento8 pagineAcantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Acanthoma (Epidermolytic Acanthoma), M 65, NeckDocumento5 pagineAcantholytic Acanthoma (Epidermolytic Acanthoma), M 65, NeckDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Publications of Deba P Sarma With The Pathology Residents and Medical Students, CUMC 2006-12Documento14 paginePublications of Deba P Sarma With The Pathology Residents and Medical Students, CUMC 2006-12Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Bullous DiseaseDocumento4 pagineAcantholytic Bullous DiseaseDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accessory TragusDocumento3 pagineAccessory TragusDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilar Cyst With CrystalsDocumento2 paginePilar Cyst With CrystalsDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deba P Sarma, MD Publications 1974 To 2010 DSDocumento12 pagineDeba P Sarma, MD Publications 1974 To 2010 DSDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Documento3 pagineAcantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
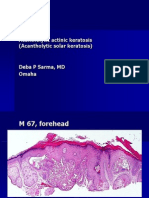
- Acantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDocumento6 pagineAcantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deba P Sarma's Publication With Bryan Teruya, Creighton University Medical School, 2006-2012Documento1 paginaDeba P Sarma's Publication With Bryan Teruya, Creighton University Medical School, 2006-2012Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accessory Tragus, M, 1 MonthDocumento3 pagineAccessory Tragus, M, 1 MonthDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDocumento11 pagineAcantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Actinic KeratosisDocumento4 pagineAcantholytic Actinic KeratosisDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Actinic Keratosis, M 67, ForeheadDocumento6 pagineAcantholytic Actinic Keratosis, M 67, ForeheadDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Documento6 pagineBalanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDocumento8 pagineAcantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
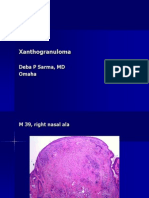
- Xanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDocumento9 pagineXanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDocumento7 pagineXanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deba P Sarma's Dermatology Publications1975-2012Documento8 pagineDeba P Sarma's Dermatology Publications1975-2012Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Sarma's Melanoma Template 2013Documento1 paginaDR Sarma's Melanoma Template 2013Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Results of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Documento28 pagineResults of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Deba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDocumento6 pagineXanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDocumento7 pagineXanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDocumento4 pagineXanthogranuloma: Deba P Sarma, MD OmahaDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDocumento4 pagineXanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma PPT DSDocumento9 pagineXanthogranuloma PPT DSDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- XanthogranulomaDocumento9 pagineXanthogranulomaDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthogranuloma CasesDocumento38 pagineXanthogranuloma CasesDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)