Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sree Sastha Institute of Engineering and Technology Department of Automobile Engineering
Caricato da
jaycee680 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
63 visualizzazioni2 pagineThis document contains a practice test for the subject Engineering Mechanics. It has two parts:
Part A contains 7 multiple choice questions testing concepts like equations of equilibrium, cross products of vectors, Lami's theorem, and different types of forces.
Part B contains 3 numerical problems testing equilibrium concepts. The first problem involves finding the resultant of two coplanar forces. The second determines tensions in ropes pulling a barge. The third finds components of a force keeping an electric post in equilibrium.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
113201-1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document contains a practice test for the subject Engineering Mechanics. It has two parts:
Part A contains 7 multiple choice questions testing concepts like equations of equilibrium, cross products of vectors, Lami's theorem, and different types of forces.
Part B contains 3 numerical problems testing equilibrium concepts. The first problem involves finding the resultant of two coplanar forces. The second determines tensions in ropes pulling a barge. The third finds components of a force keeping an electric post in equilibrium.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
63 visualizzazioni2 pagineSree Sastha Institute of Engineering and Technology Department of Automobile Engineering
Caricato da
jaycee68This document contains a practice test for the subject Engineering Mechanics. It has two parts:
Part A contains 7 multiple choice questions testing concepts like equations of equilibrium, cross products of vectors, Lami's theorem, and different types of forces.
Part B contains 3 numerical problems testing equilibrium concepts. The first problem involves finding the resultant of two coplanar forces. The second determines tensions in ropes pulling a barge. The third finds components of a force keeping an electric post in equilibrium.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
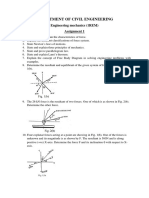
SREE SASTHA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
Subject Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Subject Code: 113201
Year: I Semester: II
Date: 18-3-2011 Duration: 1Hr 30 mts
CYCLE TEST-I
PART- A (7X2=14 Marks)
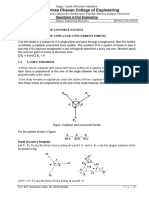
1. State the equations of equilibrium of a coplanar system of forces.
2. Two vectors A and B are given. Determine their cross product and the unit vector along
it. A=2i+3j+k and B=3i-3j+4k.
3. State and explain Lami’s theorem of triangle law of equilibrium.
4. Explain the difference between kinematics and kinetics.
5. A force of 500 N forms angles 60o, 45o and 120o respectively with x,y and z axes. Write
the force in vector form.
6. A force of magnitude 750 N is directed along AB where A is (0.8, 0, 1.2) m and B is
(1.4, 1.2, 0) m. Write the vector form of the force.
7. Distinguish the following types of forces with suitable sketch: (a) Collinear (b) Co-planar
PART- B (3X12=36 Marks)
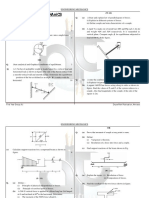
1. (a). Two forces A and B act on a stud as shown in Fig.1. Find their resultant. Use triangle
law of forces.
Or
(b) Find the magnitude and the direction of the force A shown in Fig.2, so that the
resultant of the forces acting at P is zero.
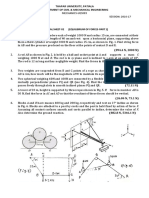
2. (a). A barge is pulled by two tugboats as shown in Fig.3. If the resultant of the forces
exerted by the tugboats is a 5000N directed along the axis of the barge, determine (a) the
tension in each of the ropes, knowing that α=45o (b) the value of α for which the tension
in rope 2 is minimum.
Or
(b). Determine the magnitude and the direction of the force F shown in Fig.4, so that the
particle A is in equilibrium.
3. (a). A metal guy rope tied to a peg at P shown in Fig.4 keeps an electric post in
equilibrium. The force in the guy rope is 1.25 KN. Find the components of the force at P
and the angles of inclination with the three rectangular axes.
Or
(b) A container weighing 10 KN is suspended at P by using two cables PA and PB
anchored as shown in Fig.6. A horizontal force F keeps the container in equilibrium
position. Find the magnitude of the force F and tension in cables PA and PB.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Tu 1-5Documento8 pagineTu 1-5Made easy classes0% (2)
- Engineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionsDocumento38 pagineEngineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionskganesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kings: Engineering MechanicsDocumento16 pagineKings: Engineering Mechanicsgovind4ever5Nessuna valutazione finora
- EM QBDocumento16 pagineEM QBJeganNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento37 pagineEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento18 pagineEngineering MechanicsSiva ChidambaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Tut 1-5Documento7 pagineTut 1-5Dipanshu SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 2151 - Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocumento3 pagineMe 2151 - Engineering Mechanics Question BankAnonymous RJfsy8PtNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1-Engg MechDocumento3 pagineAssignment 1-Engg Mechsanjay50% (2)
- Emech Assesment IDocumento6 pagineEmech Assesment IVivekanandhan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics QUESTION PAPERSDocumento31 pagineEngineering Mechanics QUESTION PAPERSgotu123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module1 - Set 1aDocumento2 pagineModule1 - Set 1aindhubalab200413chNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento4 pagineUnit 4Alok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EM Coaching QBDocumento10 pagineEM Coaching QBsaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Documento8 pagineE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101Nessuna valutazione finora
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Documento19 pagineQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento5 pagine1reddiNessuna valutazione finora
- Seatwork No. 2Documento3 pagineSeatwork No. 2Glenford Rene Pabularcon0% (1)
- Tutorial 2Documento2 pagineTutorial 2ShashiKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tut Applied-I PDFDocumento34 pagineTut Applied-I PDFMadan PanditNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsDocumento4 pagineEngineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsShrey SanwariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Assignment 1-SolDocumento4 pagineHomework Assignment 1-SolDragon ball LegendNessuna valutazione finora
- GE6253-Engineering Mechanics Qustion BankDocumento20 pagineGE6253-Engineering Mechanics Qustion Banknanthakumar91100% (1)
- Equilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Documento34 pagineEquilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Hemant JadhaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mechanics I 2015 FDocumento4 pagineApplied Mechanics I 2015 FRajeshGuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assgn 1Documento7 pagineAssgn 1rajkumardotcom100% (1)
- Assignment 1Documento3 pagineAssignment 1Dayanand HR 1SI19ME032MechanicalNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1Documento3 pagineTutorial 1A SкNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mechanics I 2015 FDocumento4 pagineApplied Mechanics I 2015 FRajeshGuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics1Documento8 pagineEngineering Mechanics1Srikrishna JanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359Documento19 pagineEg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359NINEBO MWEWANessuna valutazione finora
- BITMESRAIMPORTANTTutorial Sheets-Applied MechanDocumento34 pagineBITMESRAIMPORTANTTutorial Sheets-Applied MechanmonumunduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. TechDocumento7 pagineSecond Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. Techlatendra kumar srivastavNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 MarksDocumento23 pagine12 Markslakshmigsr6610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of TechnologyDocumento15 pagineChennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of TechnologyEdifice Placement SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1,2,3Documento8 pagineTutorial 1,2,3RameshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics QuestionsDocumento6 pagineMechanics QuestionsPranjalShankhdharNessuna valutazione finora
- Module1 - Set 2aDocumento2 pagineModule1 - Set 2aindhubalab200413chNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics ProblemsDocumento36 pagineStatics ProblemsGiang TruongNessuna valutazione finora
- Btes103 203 em QBDocumento10 pagineBtes103 203 em QBSurajNessuna valutazione finora
- S1S1516 AssignmentDocumento5 pagineS1S1516 AssignmentHafizHumbleNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 01 - Statics of ParticlesDocumento3 pagineTutorial 01 - Statics of ParticlesPulathisi KahawitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Resultant ForceDocumento12 pagine02 Resultant ForceCiarrabell AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No3Documento3 pagineAssignment No3Bharat SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics AssignmentDocumento4 pagineEngineering Mechanics AssignmentManda Ramesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 MOSDocumento47 pagineAssignment 1 MOSGaurav RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied MechanicsDocumento3 pagineApplied MechanicssushilNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento9 pagineQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Assignment 3: Moment and Equivalent System of Forces Due Date: July 29, 2019 (Shrawan 13)Documento5 pagineAssignment 3: Moment and Equivalent System of Forces Due Date: July 29, 2019 (Shrawan 13)Ganga DahalNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Jss Academy of Technical EducationDocumento3 pagineDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Jss Academy of Technical EducationHarshit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDa EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNessuna valutazione finora
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Da EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclatur 1Documento3 pagineNomenclatur 1jaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Belt Drives and Chain DrivesDocumento39 pagineBelt Drives and Chain Drivesjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vtu Question Paper Peic A38Documento30 pagineVtu Question Paper Peic A38jaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- TE-334: Elements of Machine Dynamics and Design Lecture: Belt Drive and DesignDocumento30 pagineTE-334: Elements of Machine Dynamics and Design Lecture: Belt Drive and Designjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Simulation of Spark-Ignition Engine ProcessesDocumento10 pagineComputer Simulation of Spark-Ignition Engine Processesjaycee68100% (2)
- University College of Engineering KanchipuramDocumento1 paginaUniversity College of Engineering Kanchipuramjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- When You Are in The Highest Tax BracketDocumento3 pagineWhen You Are in The Highest Tax Bracketjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Alcohol As An Alternative Fuel in DieselDocumento13 pagineUse of Alcohol As An Alternative Fuel in Dieseljaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pascal's Calculator. Babbage's Analytical EngineDocumento2 paginePascal's Calculator. Babbage's Analytical Enginejaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- I.C. Engines QP-1Documento1 paginaI.C. Engines QP-1jaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDocumento2 pagineDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Full Advertisement DepartmentDocumento3 pagineFull Advertisement Departmentjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Importatnt Points To Fill Candidate Registration Form Personal InformationDocumento2 pagineImportatnt Points To Fill Candidate Registration Form Personal Informationjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lec Cturer (Vo Cational P Pedagogy) : Prepares A and Invigilates e ExaminationsDocumento1 paginaLec Cturer (Vo Cational P Pedagogy) : Prepares A and Invigilates e Examinationsjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento116 pagineUnit IV Internal Combustion Enginesjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 & 4 QBDocumento5 pagineUnit 3 & 4 QBjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan AcDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan Acjaycee68Nessuna valutazione finora
- School Based INSET Interim EvaluationDocumento8 pagineSchool Based INSET Interim Evaluationprinces arcangelNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableDocumento51 pagineBSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableAryan SinglaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsDocumento7 pagineUpes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsSuvedhya ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Mock Exam 2015Documento4 pagineMathematics Mock Exam 2015Ian BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- EVOM ManualDocumento2 pagineEVOM ManualHouston WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Эквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Documento7 pagineЭквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Алексей ЯмаNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 08 - Change in Accounting Policy: Problem 8-1 (AICPA Adapted)Documento5 pagineChapter 08 - Change in Accounting Policy: Problem 8-1 (AICPA Adapted)Kimberly Claire AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ritesh Agarwal: Presented By: Bhavik Patel (Iu1981810008) ABHISHEK SHARMA (IU1981810001) VISHAL RATHI (IU1981810064)Documento19 pagineRitesh Agarwal: Presented By: Bhavik Patel (Iu1981810008) ABHISHEK SHARMA (IU1981810001) VISHAL RATHI (IU1981810064)Abhi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento3 pagine1Stook01701Nessuna valutazione finora
- LspciDocumento4 pagineLspciregistroosNessuna valutazione finora
- Maritime Academy of Asia and The Pacific-Kamaya Point Department of AcademicsDocumento7 pagineMaritime Academy of Asia and The Pacific-Kamaya Point Department of Academicsaki sintaNessuna valutazione finora
- Editan - Living English (CD Book)Documento92 pagineEditan - Living English (CD Book)M Luthfi Al QodryNessuna valutazione finora
- HSCC SRH 0705 PDFDocumento1 paginaHSCC SRH 0705 PDFBhawna KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Intelligent DesignDocumento21 pagineIntelligent DesignDan W ReynoldsNessuna valutazione finora
- Architectural ConcreteDocumento24 pagineArchitectural ConcreteSaud PathiranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elpodereso Case AnalysisDocumento3 pagineElpodereso Case AnalysisUsama17100% (2)
- Ilocos Norte Youth Development Office Accomplishment Report 2Documento17 pagineIlocos Norte Youth Development Office Accomplishment Report 2Solsona Natl HS MaanantengNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerDocumento9 pagineManual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerboirxNessuna valutazione finora
- Product NDC # Compare To Strength Size Form Case Pack Abcoe# Cardinal Cin # Mckesson Oe # M&Doe#Documento14 pagineProduct NDC # Compare To Strength Size Form Case Pack Abcoe# Cardinal Cin # Mckesson Oe # M&Doe#Paras ShardaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cam 18 Test 3 ListeningDocumento6 pagineCam 18 Test 3 ListeningKhắc Trung NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- BackgroundsDocumento13 pagineBackgroundsRaMinah100% (8)
- BARUDocumento53 pagineBARUhueuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Native VLAN and Default VLANDocumento6 pagineNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lesson 2Documento31 pagineModule 1 Lesson 2Angela Rose BanastasNessuna valutazione finora
- Angle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Documento128 pagineAngle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Kartik ParmeshwaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Computers in Industry: Hugh Boyes, Bil Hallaq, Joe Cunningham, Tim Watson TDocumento12 pagineComputers in Industry: Hugh Boyes, Bil Hallaq, Joe Cunningham, Tim Watson TNawabMasidNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1Documento11 pagineSteel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Poetry UnitDocumento212 paginePoetry Unittrovatore48100% (2)
- Agency Canvas Ing PresentationDocumento27 pagineAgency Canvas Ing Presentationkhushi jaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid Pattern PortraitDocumento8 pagineGrid Pattern PortraitEmma FravigarNessuna valutazione finora