Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Panel 2.07b
Caricato da
chinurathoreDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Panel 2.07b
Caricato da
chinurathoreCopyright:
Formati disponibili
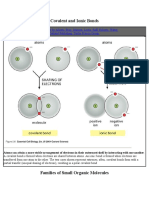
Types of Weak Non-covalent Bonds - Part 2
©1998 by Alberts, Bray, Johnson, Lewis, Raff, Roberts, Walter
. http://www.essentialcellbiology.com
Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group.
HYDROPHOBIC FORCES
Water forces hydrophobic groups together
in order to minimize their disruptive
effects on the hydrogen-bonded water
H network. Hydrophobic groups held
H
together in this way are sometimes said
C to be held together by “hydrophobic
C
H bonds,” even though the attraction is
H
actually caused by a repulsion from the
H water.
H
H H IONIC BONDS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
H
Charged groups are shielded by their
C H C interactions with water molecules.
Ionic bonds are therefore quite weak
H in water.
H
H
O
H O H
O H
O P O H O H
H
O H H
O
H O O H
H
O H O + H
+ Mg
H
H O
IONIC BONDS H H
Ionic interactions occur either between
fully charged groups (ionic bond) or
Similarly, other ions in solution can cluster around
between partially charged groups.
charged groups and further weaken ionic bonds.
d + d – Cl
Na Na
+ +
Cl H
O
+ Na H N
C +
The force of attraction between the two H
O + Na Cl
charges, d + and d –, falls off rapidly as the
distance between the charges increases. + Cl
Na Cl
In the absence of water, ionic forces
are very strong. They are responsible
Despite being weakened by water and
for the strength of such minerals as
salt, ionic bonds are very important
marble and agate.
in biological systems; an enzyme that
binds a positively charged substrate
will often have a negatively charged
amino acid side chain at the
Cl– appropriate place.
Na+
substrate
hand drawn
fig 2.105/2.07
a crystal of +
salt, NaCl
–
enzyme
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Who Is IndiaDocumento15 pagineWho Is IndiachinurathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel 2.05bDocumento1 paginaPanel 2.05bchinurathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Covalent and Ionic BondsDocumento6 pagineCovalent and Ionic BondschinurathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Unity in DiversityDocumento6 pagineUnity in DiversitychinurathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic HRMDocumento2 pagineStrategic HRMjamalahmed1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Year 8 - Higher - Autumn 2019Documento16 pagineYear 8 - Higher - Autumn 2019nooraNessuna valutazione finora
- SOCI 223 Traditional Ghanaian Social Institutions: Session 1 - Overview of The CourseDocumento11 pagineSOCI 223 Traditional Ghanaian Social Institutions: Session 1 - Overview of The CourseMonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial LawDocumento61 pagineCommercial LawthebfilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyrons College Philippines Inc. Sto. Niño, Tukuran, Zamboanga Del Sur SEC. No.: CN200931518 Tel. No.: 945 - 0158Documento5 pagineHyrons College Philippines Inc. Sto. Niño, Tukuran, Zamboanga Del Sur SEC. No.: CN200931518 Tel. No.: 945 - 0158Mashelet Villezas ValleNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenna Wave Propagation Lab Manual CSTDocumento13 pagineAntenna Wave Propagation Lab Manual CSTPrince Syed100% (3)
- Caucasus University Caucasus Doctoral School SyllabusDocumento8 pagineCaucasus University Caucasus Doctoral School SyllabusSimonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-British Parliamentary Debate FormatDocumento8 pagineChapter-British Parliamentary Debate FormatNoelle HarrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Proven GPAT Preparation Tips To Top PDFDocumento7 pagine10 Proven GPAT Preparation Tips To Top PDFALINessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base AnswersDocumento4 pagineAcid Base Answersapi-232466940Nessuna valutazione finora
- Admission English Test 10thDocumento4 pagineAdmission English Test 10thEduardo100% (1)
- 580 People vs. Verzola, G.R. No. L-35022Documento2 pagine580 People vs. Verzola, G.R. No. L-35022Jellianne PestanasNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Statistics For Business AnalyticsDocumento15 pagineBasic Statistics For Business AnalyticsNeil Churchill AniñonNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Report-2020Documento77 pagineInternship Report-2020Hossen ImamNessuna valutazione finora
- Florentino Vs EncarnacionDocumento2 pagineFlorentino Vs EncarnacionJay Mark Esconde50% (2)
- DonatelloDocumento12 pagineDonatelloGiorgia Ronfo SP GironeNessuna valutazione finora
- People Vs GonaDocumento2 paginePeople Vs GonaM Azeneth JJ100% (1)
- K Unit 1 SeptemberDocumento2 pagineK Unit 1 Septemberapi-169447826Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Social Movement, Based On Evidence, To Reduce Inequalities in Health Michael Marmot, Jessica Allen, Peter GoldblattDocumento5 pagineA Social Movement, Based On Evidence, To Reduce Inequalities in Health Michael Marmot, Jessica Allen, Peter GoldblattAmory JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Call Option Agreement Free SampleDocumento2 pagineCall Option Agreement Free Sampleapi-235666177Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consti II Case ListDocumento44 pagineConsti II Case ListGeron Gabriell SisonNessuna valutazione finora
- SANCHEZ V DEMETRIOUDocumento3 pagineSANCHEZ V DEMETRIOUShenna SunicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sepulveda v. de Las CasasDocumento2 pagineSepulveda v. de Las CasasNova GaveNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 ActivityDocumento3 pagine8 ActivityNICOOR YOWWNessuna valutazione finora
- Swimming Pool - PWTAG CodeofPractice1.13v5 - 000Documento58 pagineSwimming Pool - PWTAG CodeofPractice1.13v5 - 000Vin BdsNessuna valutazione finora
- FrankensteinDocumento51 pagineFrankensteinapi-272665425100% (1)
- Lara CroftDocumento58 pagineLara CroftMarinko Tikvicki67% (3)
- MNT-Notes Pt. 2Documento58 pagineMNT-Notes Pt. 2leemon.mary.alipao8695Nessuna valutazione finora
- Script For Demo TeachingDocumento9 pagineScript For Demo TeachingDindz SurioNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem-Solution Essay Final DraftDocumento4 pagineProblem-Solution Essay Final Draftapi-490864786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Recurrent: or Reinfection Susceptible People: Adult With Low Im Munity (Especially HIV Patient) Pathologic ChangesDocumento36 pagineRecurrent: or Reinfection Susceptible People: Adult With Low Im Munity (Especially HIV Patient) Pathologic ChangesOsama SaidatNessuna valutazione finora