Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Table 1
Caricato da
OceanChan Qd0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni2 pagineInsufficiency or failure with any of the hemodynamically following that cannot otherwise be unstable patient controlled. Fluid overload Hyperkalemia Hypercalcemia Metabolic acidosis Pericarditis Uremic symptoms GFR 10 mL / min / 1. M2 BSA (chronic renal failure, no diabetes)
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoInsufficiency or failure with any of the hemodynamically following that cannot otherwise be unstable patient controlled. Fluid overload Hyperkalemia Hypercalcemia Metabolic acidosis Pericarditis Uremic symptoms GFR 10 mL / min / 1. M2 BSA (chronic renal failure, no diabetes)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni2 pagineTable 1
Caricato da
OceanChan QdInsufficiency or failure with any of the hemodynamically following that cannot otherwise be unstable patient controlled. Fluid overload Hyperkalemia Hypercalcemia Metabolic acidosis Pericarditis Uremic symptoms GFR 10 mL / min / 1. M2 BSA (chronic renal failure, no diabetes)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
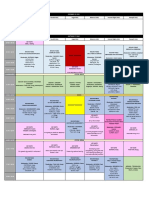
Table 1
Indications and Contraindications to Common Renal Replacement
Therapies
Renal Indications Contraindications
Replacement
Therapy
Hemodialysis Renal insufficiency or failure Uncooperative or
(acute or chronic) with any of the hemodynamically
following that cannot otherwise be unstable patient
controlled:
Fluid overload
Hyperkalemia
Hypercalcemia
Metabolic acidosis
Pericarditis
Uremic symptoms
GFR < 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 BSA
(chronic renal failure, no diabetes)
GFR < 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 BSA
(chronic renal failure, diabetes)
Some poisonings (see Poisoning)
Peritoneal Same indications as for Absolute: Loss of
dialysis hemodialysis (except for peritoneal function or
poisonings) in patients who: adhesions that limit
Have inadequate vascular access dialysate flow, recent
or abdominal wounds,
Prefer self-therapy abdominal fistulas,
abdominal wall defects
that prevent effective
dialysis or increase
infection risk (eg,
irreparable inguinal or
diaphragmatic hernia,
bladder extrophy),
patient's condition not
amenable to dialysis
Relative: Abdominal
wall infection, frequent
episodes of diverticulitis,
inability to tolerate large
volumes of peritoneal
dialysate, inflammatory
bowel disease, ischemic
colitis, morbid obesity,
peritoneal leaks, severe
undernutrition
Hemoperfusion Poisoning or toxicity (eg, due to Uncooperative or
barbiturates, many antidepressants, hemodynamically
ethchlorvynol,meprobamate unstable patient
, paraquat, glutethimide, metals
such aslithium
and barium, toxic doses of
aminoglycosides or cardiovascular
drugs)
BSA = body surface area.
For calculation of GFR see Approach to the Genitourinary Patient: GFR
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- MESOTHERAPYDocumento39 pagineMESOTHERAPYAtid Amanda100% (2)
- Nutritional assessment pregnancy lactationDocumento11 pagineNutritional assessment pregnancy lactationKathleen Martinez100% (1)
- Referral for dietitian assessment of swallowing riskDocumento72 pagineReferral for dietitian assessment of swallowing riskjykaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Handbook PDFDocumento184 pagineLaboratory Handbook PDFReymi Then50% (2)
- NCP (Rheumatic Heart Disease)Documento2 pagineNCP (Rheumatic Heart Disease)Jenny Ajoc75% (4)
- Abdominoperineal Resection MilesDocumento17 pagineAbdominoperineal Resection MilesHugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibrous Proteins - 3 Lecture (7-9) - PPT - Chapter 4Documento78 pagineFibrous Proteins - 3 Lecture (7-9) - PPT - Chapter 4OceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Renr Practice Test 9 FinalDocumento12 pagineRenr Practice Test 9 FinalTk100% (2)
- MBBS-BSC in The School of MedicineDocumento8 pagineMBBS-BSC in The School of MedicineOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximize nutrient absorption in the GI tractDocumento15 pagineMaximize nutrient absorption in the GI tractOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Recurrent Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento12 pagineRecurrent Nephrotic SyndromeOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Axr Easy 1Documento2 pagineAxr Easy 1aboelfotohbadrNessuna valutazione finora
- List Common NonDocumento1 paginaList Common NonOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Git BleedDocumento1 paginaGit BleedOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Health N DiseaseDocumento9 pagineMeasurement of Health N DiseaseOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- DENGUEDocumento4 pagineDENGUEOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- RelationshipDocumento1 paginaRelationshipOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Spinal Cord NotesDocumento7 pagine1 - Spinal Cord NotesOceanChan QdNessuna valutazione finora
- Khushboo PPT Covid 19Documento17 pagineKhushboo PPT Covid 19Birlal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Tara's Intro To Critical CareDocumento6 pagineTara's Intro To Critical CareTara McNeillNessuna valutazione finora
- Yes, it hurts here.Roxana: I'm going to give you an injection to numb the area. Now I'm going to check the tooth with the probe again. Does it still hurtDocumento5 pagineYes, it hurts here.Roxana: I'm going to give you an injection to numb the area. Now I'm going to check the tooth with the probe again. Does it still hurtCristian IugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smriti Mishra BCG NCCDocumento1 paginaSmriti Mishra BCG NCCashish bondiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 International Symposium on Pediatric Audiology ScheduleDocumento3 pagine2019 International Symposium on Pediatric Audiology ScheduleEulalia JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyper-Reflexia in Guillain - Barré Syndrome: Systematic ReviewDocumento7 pagineHyper-Reflexia in Guillain - Barré Syndrome: Systematic ReviewVladimir BasurtoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.Documento2 pagineCHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.MAHESH GAUTAMNessuna valutazione finora
- HHS Public Access: Cannabis and Cannabinoid Biology in Stroke: Controversies, Risks, and PromisesDocumento13 pagineHHS Public Access: Cannabis and Cannabinoid Biology in Stroke: Controversies, Risks, and PromisesGustavo EspíndolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaDocumento43 pagineClinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaAna Cristina BrazNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotationof 180 Degreesof Bilateral Mandibular First Molarsin Pediatric Patient ACase ReportDocumento5 pagineRotationof 180 Degreesof Bilateral Mandibular First Molarsin Pediatric Patient ACase Reportsaja IssaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 2Documento66 paginePractical Research 2Cris Antonette AbataNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Pain After AppendectomyDocumento2 pagineManaging Pain After AppendectomyChatoh SanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocumento6 pagineCardiovascular DisorderClara De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerDocumento12 pagineLec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerProfessor GhoulNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Project - BPDocumento22 pagineTeaching Project - BPapi-283482759Nessuna valutazione finora
- Periodontal Disease May Increase Risk of Oral CancerDocumento8 paginePeriodontal Disease May Increase Risk of Oral Cancerمحمد العراقيNessuna valutazione finora
- Leucorrhea KnowledgeDocumento3 pagineLeucorrhea KnowledgeAnamika ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety and Depression in TeensDocumento2 pagineAnxiety and Depression in TeensHenry Alexander Gerena SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Amacon2022 - Total Paper Poster List: SR No Presentor Name Contact Number Institute Type of Present Ation Title SubjectDocumento35 pagineAmacon2022 - Total Paper Poster List: SR No Presentor Name Contact Number Institute Type of Present Ation Title SubjectViraj ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento6 pagineCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseSimran JosanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity No. 7.1 BloodDocumento2 pagineActivity No. 7.1 BloodDree SermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Efects of Inspiratory Muscle Training in Older AdultsDocumento10 pagineEfects of Inspiratory Muscle Training in Older AdultsMaría Camila Zuluaga AriasNessuna valutazione finora
- Aminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineDocumento4 pagineAminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineRosalie SepayaNessuna valutazione finora