Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Exam I Redo 2010
Caricato da
Benjamin FerreiraDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Exam I Redo 2010
Caricato da
Benjamin FerreiraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
xam I Redo
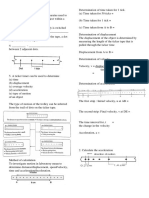
1. The speed, , of an object is given by the equation , where t
v v = At 3 − Bt + C
refers to time. What are the dimensions (or SI units) of A, B, and C?
2. Sketch a plot of velocity vs. time for a cart on an incline being tracked by a
motion sensor after it is initially pushed away from the sensor, climbs the hill
and then rolls back to its starting point.
v0
3. A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which situation are both the
instantaneous velocity and the acceleration zero?
(a) On the way up
(b) At the top of the flight path
(c) On the way down
(d) Halfway up and halfway down
(e) None of these
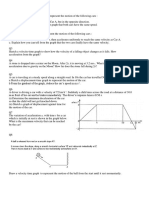
1. A caveman trained in physics wishes to determine the speed a slingshot
imparts to a rock. How can this be done using only a meter stick, a rock, and
the slingshot?
2. Use arrows to sketch the x- and y-components of the velocity vectors at each
second in the flight of the ball kicked horizontally from the roof of a tall
building. The first arrow is provided.
Problems: (10 points each)
1. The best leaper in the animal kingdom is the puma, which can jump to a
height of 4 meters when leaving the ground at an angle of 45o. With what
speed, in SI units, must the animal leave the ground to reach that height?
2. A river flows due east at 1.5 m/s. A boat crosses the river from the south
shore to the north shore by maintaining a constant velocity of 10 m/s due
north relative to the water. (a) What is the velocity of the boat relative to the
shore? (b) If the river is 300 m wide, how far downstream has the boat
moved by the time it reaches the north shore?
3. A parachutist with a camera descends at a constant downward velocity of 10
m/s. The parachutist releases the camera at an altitude of 50 m. What is
the camera’s velocity when it strikes the ground?
4. A car starts from rest and travels for 5 s with a uniform acceleration of +1.5
m/s2. The driver then applies the brakes, causing a uniform acceleration of -2
m/s2. If the brakes are applied for 3 s, (a) how fast is the car going at the end
of the braking period, and (b) how far has the car gone?
5. A person travels by car from one city to another with different constant
speeds between pairs of cities. She drives for 30 min at 80 km/h, 12 min at
100 km/h, and 45 min at 40 km/h and spends 15 min eating lunch and buying
gas. Determine the average speed for the trip.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MISDocumento3 pagineMISAshmith MonteiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsDocumento6 pagineTutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsSamson ManyanyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsDocumento5 pagineChapter 1 - KinematicsĐức Nguyễn HữuNessuna valutazione finora
- GR XI Motion in A Straight Line Chapter TestDocumento3 pagineGR XI Motion in A Straight Line Chapter TestKevin AgeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit TestDocumento4 pagineUnit TestNicholas ChevalierNessuna valutazione finora
- Copperbelt University tutorial on kinematics problemsDocumento4 pagineCopperbelt University tutorial on kinematics problemsDanny MutamboNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento4 pagineUntitledDenisse Torizo OlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreDocumento5 pagineExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- AS-Unit-1 Student Book (Question&Answer)Documento18 pagineAS-Unit-1 Student Book (Question&Answer)Mirza Galib0% (2)
- Physics 106 Set 2 Corrected Motion Along A Straight Line Algebra CalculusDocumento1 paginaPhysics 106 Set 2 Corrected Motion Along A Straight Line Algebra CalculusJPH EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematicsschool 2009Documento7 pagineKinematicsschool 2009EzhilarasiPazhanivelNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinema TicsDocumento7 pagineKinema Ticsapcc1Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #01Documento2 paginePHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #01Sabine MohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Test W SolutionsDocumento5 pagineKinematics Test W SolutionsNicholas ChevalierNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 1Documento9 pagineSheet 1Tony AtefNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Test Velocity SET BDocumento6 pagineUnit Test Velocity SET BNandhu RamkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics - QuestionsDocumento48 pagineKinematics - QuestionsMohamud JamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Documento11 pagineKinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Mohit GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics AssignmentDocumento3 pagineKinematics Assignmentkarandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- ODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level PhysicsDocumento40 pagineODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level Physicsduncon100% (1)
- Unit 1 ExercisesDocumento4 pagineUnit 1 Exercises张书Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Mechanics 1D Motion KinematicsDocumento2 paginePhysics Mechanics 1D Motion KinematicsSuman SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Test STUDY QuestionDocumento11 paginePhysics Test STUDY QuestionFiedDinieNessuna valutazione finora
- PP 150 ProblemsDocumento17 paginePP 150 ProblemsRanda CarterNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Work (Physics) Class:XI Chapter:03: Motion in Straight LineDocumento4 pagineAssignment Work (Physics) Class:XI Chapter:03: Motion in Straight Linekarandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics Quiz SolutionsDocumento3 pagineDynamics Quiz SolutionsTom AlterNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in One DimensionDocumento32 pagineMotion in One DimensionChrister John UyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 D Motion ProblemsDocumento3 pagine1 D Motion ProblemsAbhay GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Kamal Chapter Cont. 2Documento57 pagineKamal Chapter Cont. 2Nida Bagoyboy NatichoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 General Physics 1 q1Documento12 pagineModule 3 General Physics 1 q1Jazelle DignoNessuna valutazione finora
- G11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsDocumento4 pagineG11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsterabaapNessuna valutazione finora
- ABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Documento2 pagineABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Ashish GargNessuna valutazione finora
- University Physics Chapter2Documento9 pagineUniversity Physics Chapter2Karlo OrnietaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test PhysicsDocumento56 pagineRevision Test PhysicsAkshay Khanzode100% (4)
- Analysis of MotionDocumento5 pagineAnalysis of MotionDong Chooi YingNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 DassignmentDocumento8 pagine1 DassignmentDgjnNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 1: Kinematics QuestionsDocumento2 pagineSession 1: Kinematics Questionsapi-3804363100% (1)
- 2.1 Practice QDocumento3 pagine2.1 Practice QLanTsyNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chapter on Kinematics Formulas and ConceptsDocumento22 paginePhysics Chapter on Kinematics Formulas and ConceptsSubho Bhattacharya0% (1)
- Motion Physics Grade 11 AssignmentDocumento4 pagineMotion Physics Grade 11 Assignmentmn m,n m, bm43% (7)
- Chapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeDocumento25 pagineChapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeShashank ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- MechanicsDocumento2 pagineMechanicsfroilance100% (2)
- 11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Documento15 pagine11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Sathiya RNessuna valutazione finora
- As Physics Paper1 AnswersDocumento26 pagineAs Physics Paper1 AnswersahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocumento4 pagineUnit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsmanojNessuna valutazione finora
- JHL RNRX QPX AMVzpwd 4 U4Documento50 pagineJHL RNRX QPX AMVzpwd 4 U4Soujany Agnihotri 9th ENessuna valutazione finora
- Physic Itb Bab 1Documento9 paginePhysic Itb Bab 1Emmyr FaiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions CH-1 To 7Documento10 pagineQuestions CH-1 To 7ajaysahu1441Nessuna valutazione finora
- NNNNNNNNNNNNDocumento20 pagineNNNNNNNNNNNNcarlolagang1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Grade Physics Mid Test Prep - Semester 2Documento7 pagine7th Grade Physics Mid Test Prep - Semester 2William RyandinataNessuna valutazione finora
- Example 2.1: Calculating The Average Velocity and SpeedDocumento20 pagineExample 2.1: Calculating The Average Velocity and Speed3 stacksNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Fiitjee AssignmentDocumento14 pagineKinematics Fiitjee AssignmentGod is every whereNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3Documento3 pagineAssignment 320 Subhojit Maji 10HNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Physics Unit 1 Test ReviewDocumento4 pagineAp Physics Unit 1 Test ReviewnfnfehiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nsci 111Documento70 pagineNsci 111Ed Pasion100% (2)
- College PhysicsDocumento23 pagineCollege PhysicsDiana Lync SapurasNessuna valutazione finora
- File 30-01-24 872Documento8 pagineFile 30-01-24 872himalacharya86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 2 Term 1 STPMDocumento10 pagineExercise 2 Term 1 STPMLiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- A Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionDa EverandA Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4.2 Polya's StrategyDocumento2 pagineActivity 4.2 Polya's StrategyQueenNessuna valutazione finora
- Forecasting Mortality Trends in The 1980 Cohort - A Comparative Analysis of Cairns Blake Dowd (CBD) and Lee-Carter ModelsDocumento34 pagineForecasting Mortality Trends in The 1980 Cohort - A Comparative Analysis of Cairns Blake Dowd (CBD) and Lee-Carter Modelsngahuemily76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Using Hot-Vapor Bypass For Pressure Control in Distillation ColumnsDocumento8 pagineUsing Hot-Vapor Bypass For Pressure Control in Distillation ColumnsDWNLD USRMLNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5: 3-D Rotation Matrices.: 3.7 Transformation Matrix and Stiffness Matrix in Three-Dimensional SpaceDocumento17 pagineLecture 5: 3-D Rotation Matrices.: 3.7 Transformation Matrix and Stiffness Matrix in Three-Dimensional SpaceGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 LinqDocumento19 pagineL4 LinqSaitejNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 PDFDocumento5 pagineAssignment 3 PDFanon_929121264Nessuna valutazione finora
- G Codes & M CodesDocumento3 pagineG Codes & M Codessumeet tanavade tanavadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Performance Measures: A Brief Survey and Hypothesis TestingDocumento2 paginePortfolio Performance Measures: A Brief Survey and Hypothesis Testingaurorashiva1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ms Word Practical Assignment PDFDocumento52 pagineMs Word Practical Assignment PDFgithuikoechNessuna valutazione finora
- ASC Sublord/MOON Starlord Connection - A Revised StudyDocumento3 pagineASC Sublord/MOON Starlord Connection - A Revised StudyMadhavaKrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fourier Transform GuideDocumento41 pagineFourier Transform GuideSakshi ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- CATIA Full Book 2 Print - 2Documento147 pagineCATIA Full Book 2 Print - 2Sum Sumne SumanthNessuna valutazione finora
- 209 - 2017 Regulation SyllabusDocumento107 pagine209 - 2017 Regulation SyllabussivakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem 1 SolutionDocumento24 pagineProblem 1 Solutionnitte5768Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Module 2 SummaryDocumento13 paginePhysics Module 2 SummaryJessica JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan About Normal DistributionDocumento11 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan About Normal DistributionMai LaNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ OOP Course with Classes, Inheritance, TemplatesDocumento3 pagineC++ OOP Course with Classes, Inheritance, TemplatesCharmi GogriNessuna valutazione finora
- Validation Report On The 2-Phase Line SizingDocumento18 pagineValidation Report On The 2-Phase Line SizingEbby Onyekwe100% (1)
- Finite Element Based Analysis of Rotating Robot PedestalDocumento5 pagineFinite Element Based Analysis of Rotating Robot PedestalAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNessuna valutazione finora
- Grace Mission College Catiningan Socorro Oriental Mindoro Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Quarter 1 Subject Verb Agreement I. ObjectivesDocumento12 pagineGrace Mission College Catiningan Socorro Oriental Mindoro Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Quarter 1 Subject Verb Agreement I. ObjectivesJefferson SociasNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory in GrammarDocumento47 pagineTheory in GrammarJulia CareyNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering PDFDocumento339 pagineEarthquake Geotechnical Engineering PDFLj JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial, Treasury and Forex ManagementDocumento542 pagineFinancial, Treasury and Forex ManagementPraveen100% (1)
- Classification of Control SystemsDocumento15 pagineClassification of Control SystemsMohankumar V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento13 pagineChapter 4Solo NunooNessuna valutazione finora
- FIR FilterDocumento32 pagineFIR FilterWan TingNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Six SigmaDocumento286 pagineManaging Six SigmaSharandeep100% (1)
- Unit 6 VBADocumento32 pagineUnit 6 VBAapi-3842522100% (1)
- Basic Math PresentationDocumento6 pagineBasic Math PresentationGrayPrinceleyChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE - PHYSICS - Mensuration DPPDocumento6 pagineCBSE - PHYSICS - Mensuration DPPAncha RambabuNessuna valutazione finora