Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
03rec3 Exercise
Caricato da
junaid1626Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
03rec3 Exercise
Caricato da
junaid1626Copyright:
Formati disponibili
MIT Sloan School of Management
J. Wang 15.407
E52-456 Fall 2003
Recitation Notes 10/2/2002
1. Company XYZ’s year-end dividend will be $1. It will grow at 10% for 10 years and
then slows down to 5% per year forever. The cost of capital for XYZ is 15%. What is
the price of company XYZ?
Answer:
We consider the second stage-growth first.
So in 10 years, the value of XYZ will be
1∗(1+10%)1 0
15%−5%
= $25.937
So the value today is:
1
15%
∗ [1 − ( 1+10%
1+15%
25.937
)1 0] + (1+15%) 1 0 = $13.589
2. MetaTrend Corps. earns a book rate of return (ROE) of 12%. It reinvests one-half its
earnings and pays out the other half as cash dividends. The nominal cost of capital is
12%.
(a) Given this ROE and dividend payout ratio, what is the growth rate of MetaTrend’s
earnings and dividends?
(b) Assume this growth rate is expected to continue in perpetuity. What is the present
value of MetaTrend shares? Assume that book value per share is $10.
(c) Suppose MetaTrend decideds to pay out all its earnings as cash dividends. There-
fore it does not grow. What is the change, if any, in MetaTrend’s stock price?
Why?
Answer:
(a) We can use the growth formula
growth = ROE × (1 − payout ratio)
= 0.12 × (1 − 0.5)
= 0.06
(b) We can apply the formula of DDM with constant growth
book value × ROE × payout ratio
PMetaTrend =
cost of capital - growth
10 × 0.12 × 0.5
=
0.12 − 0.06
= 10
(c) We can apply the formula of DDM with no growth
book value × ROE × payout ratio
PMetaTrend =
cost of capital
10 × 0.12
=
0.12
= 10
The price is same as that of part a. The reason is that the dividends gave up
exactly offset the present value of the increase of future cash flows, ie ROE =
cost of capital.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sampa Video Case Analysis-Submission by Abhishek Ojha (ePGP-04B-003), Saurabh Singh (ePGP-04B-102) and Toban Varghese (ePGP-04B-116)Documento11 pagineSampa Video Case Analysis-Submission by Abhishek Ojha (ePGP-04B-003), Saurabh Singh (ePGP-04B-102) and Toban Varghese (ePGP-04B-116)sks6184280Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Assignment 1 KeyDocumento6 pagineHomework Assignment 1 KeymetetezcanNessuna valutazione finora
- Deluxe Corporation Case StudyDocumento3 pagineDeluxe Corporation Case StudyHEM BANSALNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource WasDocumento9 pagineThis Study Resource WasVishalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampa VideoDocumento24 pagineSampa VideoHenny ZahranyNessuna valutazione finora
- Michael McClintock Case1Documento2 pagineMichael McClintock Case1Mike MCNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Finance Case Write UpDocumento3 pagineManagerial Finance Case Write Upvalsworld100% (1)
- Stryker LTP Final PaperDocumento33 pagineStryker LTP Final Paperapi-239845860Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tire City IncDocumento3 pagineTire City IncAlberto RcNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 4 Winfield Refuse Management, Inc.: Raising Debt vs. EquityDocumento5 pagineCase Study 4 Winfield Refuse Management, Inc.: Raising Debt vs. EquityAditya DashNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of Capital - MidlandDocumento5 pagineCost of Capital - MidlandOmar ChaudhryNessuna valutazione finora
- Case PPLS Questions 20170412Documento2 pagineCase PPLS Questions 20170412Ernest ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Radent Case QuestionsDocumento2 pagineRadent Case QuestionsmahieNessuna valutazione finora
- Facebook IPO caseHBRDocumento29 pagineFacebook IPO caseHBRCrazy Imaginations100% (1)
- Corning Convertible Preferred Stock PDFDocumento6 pagineCorning Convertible Preferred Stock PDFperwezNessuna valutazione finora
- Dell CaseDocumento22 pagineDell CaseShaikh Saifullah KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14. Tool Kit For Distributions To Shareholders: Dividends and RepurchasesDocumento9 pagineChapter 14. Tool Kit For Distributions To Shareholders: Dividends and RepurchasesHenry RizqyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bond Problem - Fixed Income ValuationDocumento1 paginaBond Problem - Fixed Income ValuationAbhishek Garg0% (2)
- Landmark Facility Solutions - QuestionsDocumento1 paginaLandmark Facility Solutions - QuestionsFaig0% (1)
- Case Analysis - Compania de Telefonos de ChileDocumento4 pagineCase Analysis - Compania de Telefonos de ChileSubrata BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Cash Flow To Equity (Fcfe)Documento3 pagineFree Cash Flow To Equity (Fcfe)Rahul lodhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marriott Corporation Case SolutionDocumento6 pagineMarriott Corporation Case Solutionanon_671448363Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wrigley Gum 21Documento18 pagineWrigley Gum 21Fidelity RoadNessuna valutazione finora
- Peachtree A Complete AnswersDocumento5 paginePeachtree A Complete AnswersPhilip JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- CASEDocumento1 paginaCASESanskar VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampa SolnDocumento13 pagineSampa SolnAnirudh KowthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Corp Fin Case 1 NextelDocumento5 pagineCorp Fin Case 1 NextelPedro José ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- Case: Flash Memory, Inc. (4232)Documento1 paginaCase: Flash Memory, Inc. (4232)陳子奕Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dell Working CapitalDocumento7 pagineDell Working CapitalARJUN M KNessuna valutazione finora
- Bed Bath Beyond (BBBY) Stock ReportDocumento14 pagineBed Bath Beyond (BBBY) Stock Reportcollegeanalysts100% (2)
- Mckenzie CorporationDocumento2 pagineMckenzie CorporationVipin KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wrigley Case AnswerDocumento4 pagineWrigley Case AnswerYehan MatuilanaNessuna valutazione finora
- ch14 Exercises (Written Q) Q+A - WACCDocumento4 paginech14 Exercises (Written Q) Q+A - WACCNurayGulNessuna valutazione finora
- Valuation ProblemsDocumento5 pagineValuation ProblemsAparna KalaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dell CaseDocumento3 pagineDell CaseJuan Diego Vasquez BeraunNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study CCI11Documento11 pagineCase Study CCI11Jennifer Bello AraquelNessuna valutazione finora
- The WM Wringley JR CompanyDocumento3 pagineThe WM Wringley JR Companyavnish kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CM FinanceforUndergradsDocumento5 pagineCM FinanceforUndergradsChaucer19Nessuna valutazione finora
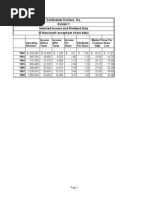
- Continental CarriersDocumento10 pagineContinental Carriersnipun9143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes Topic 6 Final PDFDocumento109 pagineLecture Notes Topic 6 Final PDFAnDy YiMNessuna valutazione finora
- Final AssignmentDocumento15 pagineFinal AssignmentUttam DwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study-Finance AssignmentDocumento12 pagineCase Study-Finance AssignmentMakshud ManikNessuna valutazione finora
- Winfield Refuse Management Inc. Raising Debt vs. EquityDocumento13 pagineWinfield Refuse Management Inc. Raising Debt vs. EquitynmenalopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lyonscasesolution 141026100118 Conversion Gate02Documento9 pagineLyonscasesolution 141026100118 Conversion Gate02Ankur ChughNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: 1 Hill Country Snack Foods CoDocumento9 pagineThis Study Resource Was: 1 Hill Country Snack Foods CoPavithra TamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampa VideoDocumento24 pagineSampa VideodoiNessuna valutazione finora
- General Mills PillsburyDocumento8 pagineGeneral Mills PillsburyteenabansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Willison TowerDocumento2 pagineWillison TowerOdiseGrembiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacific Grove Spice CompanyDocumento1 paginaPacific Grove Spice CompanyLauren KlaassenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Review in ClassDocumento32 pagineChapter 6 Review in Classjimmy_chou1314Nessuna valutazione finora
- Orion Systems Case StudyDocumento12 pagineOrion Systems Case StudyKandarpGuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nike Case AnalysisDocumento9 pagineNike Case AnalysisFami FamzNessuna valutazione finora
- What Dividend Policy Would Be Appropriate For TelusDocumento4 pagineWhat Dividend Policy Would Be Appropriate For Telusmalaika12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ocean Carriers Executive SummaryDocumento2 pagineOcean Carriers Executive SummaryAniket KaushikNessuna valutazione finora
- Coursehero 40252829Documento2 pagineCoursehero 40252829Janice JingNessuna valutazione finora
- Continental CarriersDocumento3 pagineContinental CarriersCharleneNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrefour S.A.: Ruskin Lisa Crystal WeiDocumento16 pagineCarrefour S.A.: Ruskin Lisa Crystal WeiThái Hoàng NguyênNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cost of Capital: HKD 100,000,000 HKD 250,000,000 HKD 150,000,000 HKD 250,000,000Documento24 pagineThe Cost of Capital: HKD 100,000,000 HKD 250,000,000 HKD 150,000,000 HKD 250,000,000chandel08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6 - SolutionsDocumento8 pagineTutorial 6 - SolutionsNguyễn Phương ThảoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas 8 - C11 - Cost of CapitalDocumento5 pagineTugas 8 - C11 - Cost of CapitalIqbal BaihaqiNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 16Documento28 pagineCH 16junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Finance: Part DDocumento4 pagineCorporate Finance: Part Djunaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- CapmDocumento31 pagineCapmtandavkrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13Documento17 pagineCH 13roha_rizvi5972Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch12 ArbitrageDocumento18 pagineCh12 Arbitragejence85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Valuation Using Startigic OptionDocumento15 pagineValuation Using Startigic Optionahmedh_98Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChamberEy Summer 2009 (Web)Documento36 pagineChamberEy Summer 2009 (Web)junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio TheoryDocumento48 paginePortfolio Theoryzhongyi87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch07 12Documento4 pagineCh07 12junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- OptionsDocumento39 pagineOptionsMarlyn RichardsNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 09Documento37 pagineCH 09junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 07Documento7 pagineCH 07junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 08Documento13 pagineCH 08junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Future and ForwardsDocumento24 pagineFuture and ForwardsamitgtsNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 02Documento18 pagineCH 02junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- OptionsDocumento39 pagineOptionsMarlyn RichardsNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 04Documento24 pagineCH 04ahsan1379Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 04Documento24 pagineCH 04ahsan1379Nessuna valutazione finora
- 407 Me 02Documento12 pagine407 Me 02junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Future and ForwardsDocumento24 pagineFuture and ForwardsamitgtsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch03 06Documento8 pagineCh03 06junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing To FinanceDocumento38 pagineIntroducing To FinancejuliancaoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento49 pagineCH 03junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asset BetaDocumento15 pagineAsset Betaahsan1379Nessuna valutazione finora
- 66448Documento3 pagine66448junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Rec 7Documento11 pagine03 Rec 7junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- MIT Sloan School of Management: Saving 2Documento4 pagineMIT Sloan School of Management: Saving 2junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- MIT Sloan School of Management: Saving 2Documento4 pagineMIT Sloan School of Management: Saving 2junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Rec 8Documento10 pagine03 Rec 8junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Rec 6Documento11 pagine03 Rec 6junaid1626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Conference Call Results January - September 2014: WelcomeDocumento21 pagineConference Call Results January - September 2014: WelcomeToni HercegNessuna valutazione finora
- Gay v. Axline, JR., 1st Cir. (1994)Documento31 pagineGay v. Axline, JR., 1st Cir. (1994)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamalpur 100 MW PQDocumento32 pagineJamalpur 100 MW PQZahirul QuayumNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Dilution WorkingsDocumento4 pagineAnti Dilution Workingsanshuman_28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abejo V Dela Cruz. GR L-63558. May 19, 1987. 149 SCRA 654Documento11 pagineAbejo V Dela Cruz. GR L-63558. May 19, 1987. 149 SCRA 654Charles DumasiNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 SolutionDocumento55 pagine13 Solutiontisha10rahman100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Financial ManagementDocumento15 pagineChapter 1-Introduction To Financial ManagementfatinfyNessuna valutazione finora
- Apple CaseDocumento10 pagineApple CaseIgnas VėgelėNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Text and Cases: Case 8-1 - Norman Corp ADocumento2 pagineAccounting Text and Cases: Case 8-1 - Norman Corp AAB D'oria100% (4)
- Pravilnik Za Sostav I Vodenje Na Maticnii Knigi Od 1954Documento648 paginePravilnik Za Sostav I Vodenje Na Maticnii Knigi Od 1954Милена СпасовскаNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Report 09 10 Oil India LTDDocumento123 pagineAnnual Report 09 10 Oil India LTDmadhura1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainability Reporting & Financial Performance by Priyanka Aggarwal (Assistant Professor, SRCC)Documento22 pagineSustainability Reporting & Financial Performance by Priyanka Aggarwal (Assistant Professor, SRCC)Priyanka AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsu Fu Chi Ar2010-SgxDocumento79 pagineHsu Fu Chi Ar2010-SgxPaul PriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Company Law Saudi ArabiaDocumento5 pagineCompany Law Saudi ArabiaAamir ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Adani Wilmar Limited DRHPDocumento363 pagineAdani Wilmar Limited DRHPDheeraj BatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting For Treasury SharesDocumento2 pagineAccounting For Treasury SharesCharles Reginald K. Hwang100% (1)
- Corporate GovernanceDocumento17 pagineCorporate GovernanceAshhish GangulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate RestructuringDocumento54 pagineCorporate RestructuringBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (2)
- The Impact of Corporate Governance On The Profitability: An Empirical Study of Indian Textile IndustryDocumento5 pagineThe Impact of Corporate Governance On The Profitability: An Empirical Study of Indian Textile IndustryKirubakar RadhakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- ALR 20180427172542 2017-Annual-Report PDFDocumento130 pagineALR 20180427172542 2017-Annual-Report PDFAnonimu256Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP - Mockboard ExaminationDocumento10 pagineAP - Mockboard Examinationjc limNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management IIBMDocumento5 pagineFinancial Management IIBMcarnowalt100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Caselette Audit of SheDocumento26 pagineChapter 9 Caselette Audit of SheBusiness MatterNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Note On LBO Valuation and Modeling - 150309 - 4!10!2015 - SAMPLEDocumento30 pagineTechnical Note On LBO Valuation and Modeling - 150309 - 4!10!2015 - SAMPLEJayant Sharma100% (1)
- Adjuidcation Order Against 16 Entities in The Matter of Gee Gee Granites LTDDocumento9 pagineAdjuidcation Order Against 16 Entities in The Matter of Gee Gee Granites LTDShyam SunderNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 KYBP Profile and Services (Latest Promo)Documento14 pagine2023 KYBP Profile and Services (Latest Promo)Kenny Diego ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Uti ScamDocumento7 pagineUti ScamAbhishek ChadhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity With Youtube Video Shareholders Equity Part 1Documento2 pagineActivity With Youtube Video Shareholders Equity Part 1Krestyl Ann GabaldaNessuna valutazione finora
- BhushanDocumento143 pagineBhushanAnonymous SwJu9Hi5mNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 6 Dividend Decision RevisedDocumento49 pagineChap 6 Dividend Decision RevisedGizachew AlazarNessuna valutazione finora