Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1
Caricato da
dhuulhudaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1
Caricato da
dhuulhudaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS
PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE
Question Explanation Marks
1(a)(i) Diffusion 1
Molecules
(ii) 1
- Made of tiny / discrete particles/ molecules
(iii) - Move faster / rapidly 1+1+1
- Between air / another particles
(b)(i) 83 oC 1
(ii) Remain, because heat absorbed is used to overcome the forces between 1+1
particles.
(iii) Move faster 1
Particles gain kinetic energy. 1
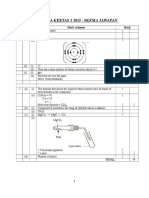
2(a)(i) White fume 1
(ii) Ammonium chloride 1
(iii) Diffusion 1
(b) Ammonia, because ammonia is lighter than hydrogen chloride. 1+1
(c) NH3 + HCl NH4Cl 1
3(a)(i) Number of proton in the nucleus of an atom. 1
(ii) 12 1
(b) X and Y. Because they have same proton number but different neutron or 1+1
nucleon number.
(c) 2.8.7 1
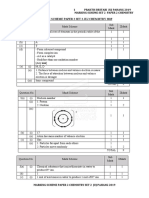
(d)(i)
1+1
Y
(ii) 7
1
-
(iii) Y
1
35
(e) 17 X 1
4(a)(i) - Both axis are labeled with unit and consistent scales 3
- All points transfer correctly
- Size of graph at least ½ of the page of the graph paper
- Curve of the graph is correct and smooth
(ii) 80oC 1
(iii) Heat is absorbed is used to overcome the forces of attraction between particles. 2
(iv) 1
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 1
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
(b) To ensure uniform heating 1
(c) Solid X is highly flammable 1
5(a) Iodine and ethanol 2
(b) copper 1
(c) copper 1
(d) ion 1
PAPER : ESSAY
No. 6 Rubric Marks
(a)
Particle Relative charge Relative mass
Proton +1 1 1+1
Neutron 0 (neutron) 1 1+1
Electron -1 1/1840 1+1
Any 2 pairs 4
(b)(i) 1. Nucleus contains 7 protons and 7 neutrons. 1
2. Electrons moves around the nucleus. 1
3. Two shells filled with electrons. 1
4. 5 valance electrons / electrons arrangement 2.5 1
4
(ii)
14
X
7 1
Nucleon number 1
Proton number 2
(c)
Stage/Time State of matter Particle arrangement Change in 1
energy
to – t 1 Solid Closely packed Kinetic energy 1+1+1
increases 3
t1 – t 2 Solid –liquid Close together but not in Higher kinetic 1+1+1
orderly arrangement energy 3
t2 – t 3 Liquid Further apart Highest kinetic 1+1+1
energy 3
10
Total 20
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 2
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
No. 7 Rubric Marks
7 (a) Melting point is the temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid at a 1
particular pressure. 1
Because the energy absorbed by the naphthalene is used to overcome the forces 1
of attraction between the molecules of naphthalene. 1 4
7(b) Before condensation
The kinetic energy is high 1
The particles are very far apart from each other 1
The attraction forces between particles are very weak. 1
During condensation
The kinetic energy decreases 1
The particles begin to move closer toward one another 1
/ the distance between the particles decrease
The attraction forces between particles become stronger. 1
After condensation
The kinetic energy is low 1
1
The particles are packed closely together NOT in an orderly manner
1+1
The attraction forces between particles are strong.
1
10
7(c)(i) Proton number = 13 1
Nucleon number = 14 + 13 = 27 1 2
7(c)(ii) 10.8 1
Number of moles of Y = = 0.4
27
1
Number of moles of Y2O3 = 0.4 ÷ 2 = 0.2
1
Relative formulas mass of Y2O3 = 2(27) + 3(16) = 102
1 4
Mass of Y2O3 = 0.2 102 = 20.4 g
Total 20
PAPER 3: STRUCTURE
8 Rubric Marks
(a) To study the rate of diffusion in the three states of matter. 3
(b) The rate of diffusion in matter decreases in the order of gas > liquid > solid 3
(c)(i) Manipulated : medium of diffusion gas, liquid and solid 3
(ii) Responding : rate of diffusion
(iii) Fixed : temperature of each medium
(d) Solid , liquid, gas 3
(e) Solid – the particles are very closely pack 3
Liquid – the particles closely but there are more space between them
Gas – the particles far apart from each other
(f) Smell perfume / smell gas from leaked pipe or gas cylinder 3
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 3
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND EQUATION
1.
Ion Chloride Nitrate Hydroxide Sulphate Carbonate oxide
Sodium NaCl NaNO3 NaOH Na2SO4 Na2CO3 Na2O
Magnesium MgCl2 Mg(NO3)2 Ma(OH)2 MgSO4 MgCO3 MgO
Lead(II) PbCl2 Pb(NO3)2 Pb(OH)2 PbSO4 PbCO3 PbO
Copper (II) CuCl2 Cu(NO3)2 Cu(OH)2 CuSO4 CuCO3 CuO
Iron (II) FeCl2 Fe(NO3)2 Fe(OH)2 FeSO4 FeCO3 FeO
Iron (III) FeCl3 Fe(NO3)3 Fe(OH)3 Fe2 (SO4)3 Fe2( CO3)3 Fe2O3
Aluminium AlCl3 Al(NO3)3 Al(OH)3 Al2 (SO4)3 Al2( CO3)3 Al2O3
2. (a) CuCO3 CuO + CO2
(b) HNO3 + NaOH NaNO3 + H2O
(c) 2HCl + Zn ZnCl2 + H2
(d) Cu(NO3)2 + Mg Mg(NO3)2 + Cu
(e) Cl2 + 2LiOH LiCl + LiOCl + H2O
3. (a) 0.1 x 6.02 x 1023 = 6.02 x 1022 atoms
(b) 1.5 x 6.02 x 1023 = 9.05 x 1023 atoms
(c) 2.0 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.2 x 1024 molecules
(d) 1.5 x 6.02 x 1023 = 9.05 x 1023 atoms
(e) 2.0 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.2 x 1024 molecules
4. (a) 6.02 x 1023 ÷ 6.02 x 1023 = 1.0 mol
(b) 1.8 x 1021 ÷ 6.02 x 1023 = 30.0 mol
(c) 1.2 x 1023 ÷ 6.02 x 1023 = 0.2 mol
(d) 2.4 x 1020 ÷ 6.02 x 1023 = 4.0 x 10-4 mol
(e) 3.0 x 1023 ÷ 6.02 x 1023 = 0.5 mol
5. (a) 1.5 x 71 = 106.5 g
(b) 2.5 x 32 = 80 g
(c) 2 x 98 = 196 g
(d) 0.5 x 17 = 8.5 g
(e) 2.5 x 267 = 667.5 g
(f) 0.5 x 188 = 94 g
6. (a) 0.5 mol x 22.4 dm3 mol-1 = 11.2 dm3
(b) 0.2 mo x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 4.8 dm3
(c) 1.5 mol x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 36 dm3
(d) 0.5 mol x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 12.0 dm3
(e) 2.5 mol x 22.4 dm3 mol-1 = 56 dm3
7. (a) 250 cm3 ÷ 24000 cm3 mol-1 = 0.01 mol
(b) 500 cm3 ÷ 22400 cm3 mol-1 = 0.02 mol
(c) 200 cm3 ÷ 24000 cm3 mol-1 = 8.3 x 10-3 mol
(d) 750 cm3 ÷ 24000 cm3 mol-1 = 0.03 mol
(e) 300 cm3 ÷ 22400 cm3 mol-1 = 0.013 mol
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 4
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
8. (a) Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
(b) (i) 1. Mol of Mg = 2.4 /24 = 0.1 mol
2. ration : 1 mol of Mg produced 1 mol MgCl2
0.1 mol Mg produced 0.1 mol MgCl2
3. mass of MgCl2 = 0.1 x 95 = 9.5 g
(ii) 1. Ratio : 1 mol of Mg produced 1 mol of H2
0.1 mol of Mg produced 0.1 mol of H2
2. volume of H2 = 0.1 mol x ÷ 24 dm3 mol-1 = 2.4 dm3
9. (a) C + 2PbO CO2 + 2Pb
(b) 2 mol of PbO produced 2 mol of Pb
0.5 mol of PbO produced 0.5 mol of Pb
(c) 2 mol of PbO reacts with 1 mol of C
0.5 mol of PbO reacts with 0.25 mol of C
(d) (i) mol of PbO = 44.6 / 223 = 0.2 mol
(ii) mass of Pb produced = 0.2 x 207 = 41.4 g
10. (a) CuCl2 + Na2CO3 2NaCl + CuCO3
(b) (i) mol of CuCl2 = 0.5 x 50 / 1000 = 0.025 mol
(ii) 1 mol of CuCl2 produced 1 mol of CuCO3
0.025 mol of CuCl2 produced 0.025 mol of CuCO3
(iii) mass of salt = 0.025 x 124 = 3.1 g
11. (a) CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
(b) (i) mol CaCO3 = 5 /100 = 0.05 mol
(ii) 1 mol of CaCO3 produced 1 mol of CO2
0.05 mol of CaCO3 produced 0.05 mol of CO2
(iii) Volume of CO2 = 0.05 mol x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 1.2 dm3
12. (a) 2NaHCO3 Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
(b) (i) mol of NaHCO3 = 8.4 /84 = 0.1 mol
2 mol of NaHCO3 produced 1 mol of CO3
0.1 mol of NaHCO3 produced 0.05 mol of CO3
Volume of CO2 = 0.05 x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 1.2 dm3
(ii) Mass of Na2CO3 = 0.05 x 106 = 5.3 g
13. (i) Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2
(ii) mol of HCl = 2 x 100 / 1000 = 0.2 mol
(iii) volume of H2 = 0.1 x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 2.4 dm3
14. (i) CaCO3 + 2HNO3 Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
(ii) mol of CaCO3 = 5/100 = 0.05 mol
(iii) 1 mol of CaCO3 reacts with 2 mol of HNO3
0.05 mol of CaCO3 reacts with 0.1 mol of HNO3
(iv) 1 mol of CaCO3 produced 1 mol of CO2
0.05 mol of CaCO3 produced 0.05 mol of CO2
Volume of CO2 = 0.05 mol x 24 dm3 mol-1 = 1.2 dm3
15. (i) Na2CO3 + 2 HCl 2 NaCl + CO2 + H2O
(ii) mol of HCl = 1 x 100 /1000 = 0.1 mol
(iii) 2 mol of HCl reacts with 1 mol Na2CO3
0.1 mol of HCl reacts with 0.05 mol Na2CO3
mass of Na2CO3 = 0.05 x 106 = 5.3 g
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 5
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
16. (i) CuO + 2 HCl CuCl2 + H2O
(ii) mol of CuO = 10 / 80 = 0.125 mol
1 mol CuO reacts with 2 mol HCl
0.125 mol CuO reacts with 0.25 mol HCl
Molarity of HCl = 0.25 x1000 / 100 = 2.5 mol dm-3
17. (a) mol of NaOH = 8/40 = 0.2 mol
Molarity of NaOH = 0.2 mol dm-3
(b) M1V1 = M2V2
0.2 x 50 = M2 x 150
M2 = 0.67 mol dm-3
18. (a) 2NaOH + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(b) mol NaOH = 2 x 25 /1000 = 0.05 mol
(c) 2 mol of NaOH reacts with 1 mol of H2SO4
0.05 Mol NaOH racts with 0.025 mol of H2SO4
(d) molarity of H2 SO4 = 0.025 x 1000 / 18.5 = 1.35 mol dm-3
19. (a) 2HCl + Na2CO3 2NaCl + CO2 + H2O
(b) mol of Na2CO3 = 1 x 25 /1000 = 0.025 mol
(c) (i) mol of HCl = 0.025 x 2 = 0.05 mol
(ii) volume of HCl = 0.05 x 1000 / 1.25 = 40 cm3
PAPER 2 :STRUCTURE
Question Explanation Mark
1(a) Chemical formula that shows the simplest whole ratio of atom of each
elements in the compound.
(b)(i) Mass of Cu = 20.35 – 18.75 = 1.6 g
Mass of O = 20.75 – 20.35 = 0.4 g
(ii) Mol of Cu = 1.6 / 64 = 0.025 mol
Mol of O = 0.4 / 16 = 0.025 mol
Mol ratio : Cu : O = 0.025 : 0.025 = 1 : 1
(iii) Empirical formula CuO
(iv) CuO + H2 Cu + H2 O
(c) 1.flow dry hydrogen
2.collect the gas
3. place lighted splinter at the mouth of the test tube.
Question Explanation Mark
2 (a) (i) 46 1
(ii) 189 1
(b) (i) 2.408 × 1024 molecules 1
(ii) 4.816 × 1024 atoms 1
(c) 0.0015 mol 1
(d) 434 g 1
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 6
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
Question Explanation Mark
(e) 8.28 1
= 0.03 mol Ag2CO3
276
1
2 mol of Ag2CO3 produce 2 mol of CO2
0.03 mol of Ag2 CO3 produce 0.03 mol of CO2
0.03 × 24 dm3 = 0.72 dm3 1
Total 9
Question Explanation Mark
3(a) 1. green turns black 2
2. lime water turns cloudy
(b) CuCO3 CuO + CO2 1
(c) Mol of CuCO3 = 3.1 / 124 = 0.025 mol 1
(d) 1 mol of CuCO3 produced 1 mol of CO2 1
0.025 mol of CuCO3 produced 0.025 mol of CO2 1
Volume of CO2 = 0.025 mol x 22.4 dm3 mol-1 = 0.56 dm3 1
(e)(i) Black turns brown 1
(ii) CuO + H2 Cu + H2 O 1
Mass of Cu = 0.025 x 64 = 1.6 g 1
10
ESSAY
4.
(a) (i) C H
mol 85.70 14.30
12 1 1
7.14 14.30
7.14 7.14 1
ratio 1 2
The empirical formula CH2 1………..3
(ii) ( CH2 )n = 56
[ 12 + 2(1) ]n = 56 1
56 // 4
14 1
The molecular formula C4H8 1………..3
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 7
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
(iii) Empirical formula Molecular formula
The formula shows that carbon The formula shows that carbon and
and hydrogen are present hydrogen are present
2
The formula shows that the The formula shows that one
ratio of carbon to hydrogen is molecule of X consists of 4 carbon
1:2 atoms and 8 hydrogen atoms
(b) 1 An empty crucible and its lid are weighed and the mass are recorded 1
2 Magnesium ribbon is cleaned with sandpaper, placed in crucible and 1
weighed again. The mass are recorded
3 The crucible and its contents are heated over a strong flame 1
4 The crucible lid opened once in a while during the experiment 1
5 When the magnesium does not burn anymore, the crucible and its contents
are cooled in room temperature,
1
6 and then weighed. The mass is recorded 1
7 The heating, cooling and weighing is repeated until the final mass becomes
constant
1
8 Result
Mass of crucible + lid = ag
Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium ribbon = b g 1
Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium oxide = c g
9 Mass of magnesium = (b – a) g 1
Mass of oxygen = (b – c) g
10 Mol of magnesium atom = b-a 1
24
Mol of oxygen atom = b-c
16
11 Simplest ratio mol of magnesium atom to mol of oxygen atom = x:y/ 1:1 1
12 Empirical formula : MgxOy / MgO 1
PAPER 3 : STRUCTURE
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 8
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 2010
5(a)
Rubric Score
[Able to state three inferences according to the observations correctly] 3
Example:
Observations Inferences
i) white fumes is released. magnesium oxide is produced //
magnesium has been oxidised.
ii) Bright burning. magnesium is a reactive metal.
iii) The mass increases. magnesium has combined with oxygen.
5(b)
Rubric Score
[Able to record the data correctly] 3
Example:
Description Mass / g
The crucible and lid. 123.36
The crucible, lid and magnesium powder. 128.16
The crucible, lid and magnesium oxide. 131.36
5(c)
Rubric Score
[Able to calculate the mass of magnesium, mass of oxygen and show the steps to
determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide accurately]
Example:
i) Mass of magnesium = 128.16 – 123.36 = 4.80 g
ii) Mass of oxygen = 131.36 – 128.16 = 3.2 g
iii)The empirical formula of magnesium oxide:
Element Mg O
No. of moles 4.8 3.2 3
24 16
= 0.2 = 0.2
Simplest ratio 1 1
Empirical formula : MgO
5(d)
Rubric Score
Cannot. Lead is less reactive metal 3
Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2010 Marking Scheme Set 1 9
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemeDocumento47 pagineChemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemedhuulhudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Pemarkahan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2022Documento8 pagineSkema Pemarkahan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2022Keeshnavi KumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 20B ANSWER KEY WITH EXPLANATIONS FOR CHEMISTRY CONCEPTSDocumento3 pagine20B ANSWER KEY WITH EXPLANATIONS FOR CHEMISTRY CONCEPTSMelor DihatiNessuna valutazione finora
- SOALAN 1: Multiple Choice Chemistry QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSOALAN 1: Multiple Choice Chemistry QuestionsLeena SaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Jawapan Paper 2 Kimia PDFDocumento9 pagineSkema Jawapan Paper 2 Kimia PDFAMIRA EZZATIE BINTI MOHD HATTA -Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Radioactivity and ParticlesDocumento6 pagine07 Radioactivity and ParticlesVenant HakizimanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2223 S3 Chemistry 1st Exam Suggested AnswersDocumento3 pagine2223 S3 Chemistry 1st Exam Suggested Answerselenana710Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Upk1 Kimia 2019Documento8 pagineSkema Upk1 Kimia 2019donutNessuna valutazione finora
- UPK1 2019 CHEMISTRY MARKING SCHEMEDocumento8 pagineUPK1 2019 CHEMISTRY MARKING SCHEMEFadyana GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- C1 Revision Booklet Exam Questions Mark Scheme M1. (A)Documento13 pagineC1 Revision Booklet Exam Questions Mark Scheme M1. (A)عبدالعزيز المنيعNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding ADocumento55 pagineCHM1 Structure & Bonding AHakim AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioactivity AnswersDocumento13 pagineRadioactivity AnswersPavit SuphawirojlertNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5Documento7 pagineAnswer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5sahira othmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Answer SchemeDocumento16 pagineForm 4 Answer SchemeHee Ting WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Skima Kimia Tingkatan 4 Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2019Documento8 pagineSkima Kimia Tingkatan 4 Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2019ahbingNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1Documento14 pagineSkema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1lilysuhanyNessuna valutazione finora
- p2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMADocumento8 paginep2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMAIzzati NorNessuna valutazione finora
- Kim SKEMA K2 2020 PerlisDocumento11 pagineKim SKEMA K2 2020 PerlisPEAJINYOUNGNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Penilaian 1 Kimia T5Documento10 pagineSkema Penilaian 1 Kimia T5NIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- SBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009Documento15 pagineSBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Pat Form 4 2015 Kimia Paper2 Jawapan SebenarDocumento6 paginePat Form 4 2015 Kimia Paper2 Jawapan Sebenardasima83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table 5 MSDocumento5 paginePeriodic Table 5 MSYabhijit DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- KIMIA K2 SkimaDocumento7 pagineKIMIA K2 SkimaTay Poh Leng0% (1)
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSDocumento7 pagineThe Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSKHANNessuna valutazione finora
- The phases of nitrogen and factors affecting molecular motionDocumento7 pagineThe phases of nitrogen and factors affecting molecular motionAdeeba iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Concentration calculations and empirical formula determinationDocumento68 pagineConcentration calculations and empirical formula determinationG M Ali KawsarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 A Simple Atomic Model MSDocumento15 pagine1.1 A Simple Atomic Model MSagyekumeunice76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Structured QuestionsDocumento10 pagineChapter 7 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms & Isotopes 1 MSDocumento9 pagineAtoms & Isotopes 1 MSMagd OsamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NDocumento3 pagine1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NalexisNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme Test 1 Atomic StructureDocumento4 pagineMark Scheme Test 1 Atomic Structuremaku1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Structured QuestionsDocumento8 pagineChapter 5 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Scheme P2 Chemistry 2016Documento10 pagineMarking Scheme P2 Chemistry 2016Farid SallehNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 SchemeDocumento41 pagineChemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 Schemespm_victim2010100% (5)
- Electron Configuration MSDocumento5 pagineElectron Configuration MShmtarar.2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Chemistry Revision Notes on Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocumento8 pagineSPM Chemistry Revision Notes on Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryMiesya87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Documento8 paginePeperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Lee Li JieNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure and Mass Spectroscopy AnswersDocumento5 pagineAtomic Structure and Mass Spectroscopy AnswersSuzy SazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Paper Marking Scheme for 2012 Paper 2 ChemistryDocumento7 pagineExam Paper Marking Scheme for 2012 Paper 2 Chemistry钟㛃彤Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding Structure and Periodicity Assessed HW MsDocumento10 pagineBonding Structure and Periodicity Assessed HW MsKizzy Anne Boatswain CarbonNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM1 Qualitative Chemistry ADocumento67 pagineCHM1 Qualitative Chemistry AGM Ali KawsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaDocumento5 pagineKedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaHelmi TarmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- TH He Total 7 Chemactive ComDocumento10 pagineTH He Total 7 Chemactive ComNavNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Chemistry Skema Set 9 Paper 2Documento8 pagineSPM Chemistry Skema Set 9 Paper 2Miesya87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State Physics: SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Solid State Physics ExamDocumento4 pagineSolid State Physics: SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Solid State Physics ExamJagdish ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Documento21 pagineChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Coimbatore District Common Exam Committee 10 STD First Revision Test - FEB 2022 SCIENCE Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineCoimbatore District Common Exam Committee 10 STD First Revision Test - FEB 2022 SCIENCE Answer KeyShanthi VinodNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study of Metal Structures and Their Mechanical Properties: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesDa EverandThe Study of Metal Structures and Their Mechanical Properties: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectures on Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyDa EverandLectures on Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural PhilosophyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Properties of Group-IV, III-V and II-VI SemiconductorsDa EverandProperties of Group-IV, III-V and II-VI SemiconductorsNessuna valutazione finora
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State Helium-4Da EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State Helium-4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Da EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Valutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Chronic Radiation Hazards: An Experimental Study with Fast NeutronsDa EverandChronic Radiation Hazards: An Experimental Study with Fast NeutronsNessuna valutazione finora
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)Da EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modulation, Resolution and Signal Processing in Radar, Sonar and Related Systems: International Series of Monographs in Electronics and InstrumentationDa EverandModulation, Resolution and Signal Processing in Radar, Sonar and Related Systems: International Series of Monographs in Electronics and InstrumentationNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateDa EverandChlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of AtomDocumento3 pagineThe History of Atomariel frejasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cottrell A.-An Introduction To Metallurgy PDFDocumento567 pagineCottrell A.-An Introduction To Metallurgy PDFQuraisy Amri100% (2)
- Ch02 AtomicNucleusDocumento8 pagineCh02 AtomicNucleusPrichindel MorocanosNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Grade 9Documento2 pagineAtomic Structure Grade 9Ratna PuspitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- ForceDocumento64 pagineForceAashka GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Power MCQs - Top 88 QuestionsDocumento18 pagineNuclear Power MCQs - Top 88 QuestionsNagaraj MuniyandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Properties Testing & SelectionDocumento40 pagineMaterials Properties Testing & Selectionpokeboy1950% (2)
- Science 4 Quarter 3 Compendium OriginalDocumento88 pagineScience 4 Quarter 3 Compendium Originaljamel mayorNessuna valutazione finora
- A Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionDocumento16 pagineA Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionjimNessuna valutazione finora
- To Understand The Structure of Atom-Game:: Worksheets/Atomic Structure Worksheet-PKT - PDF Atom - en - HTMLDocumento18 pagineTo Understand The Structure of Atom-Game:: Worksheets/Atomic Structure Worksheet-PKT - PDF Atom - en - HTMLSaumya ThakkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Jam PH2021Documento20 pagineJam PH2021Rahul Satapathy100% (1)
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State College: I. Learning ObjectivesDocumento7 pagineCarlos Hilado Memorial State College: I. Learning ObjectivesLarry RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Physics Previous (2009-2016) Questions Chapter WiseDocumento44 pagine1 Physics Previous (2009-2016) Questions Chapter WiseJulienJosephThomas89% (19)
- Hsslive-XII-Physics-ch-8. ATOMS AND NUCLEIDocumento12 pagineHsslive-XII-Physics-ch-8. ATOMS AND NUCLEIKeshav JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Planner - Physics - PDF Only - (12th Board Booster 2024)Documento3 pagineLecture Planner - Physics - PDF Only - (12th Board Booster 2024)Shivam SandilyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questionnaire: Phiếu Đề Thi Trắc NghiệmDocumento2 pagineMultiple Choice Questionnaire: Phiếu Đề Thi Trắc NghiệmTrung SơnNessuna valutazione finora
- g485 5 3 4 Fission and FusionDocumento14 pagineg485 5 3 4 Fission and Fusionapi-236179294Nessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE Sample Papers For Class 8 Physics Paper 1 (2019-2020)Documento12 pagineICSE Sample Papers For Class 8 Physics Paper 1 (2019-2020)Ayush YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK BANDAR UTAMA DAMANSARA CHEMISTRY TEST 1 2018Documento5 pagineSMK BANDAR UTAMA DAMANSARA CHEMISTRY TEST 1 2018Amirah Noor AffandiNessuna valutazione finora
- English For Chemists Unit 2Documento6 pagineEnglish For Chemists Unit 2Lucas MonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Classification of Elements-1Documento14 paginePeriodic Classification of Elements-1LàXsun ShrèsthàNessuna valutazione finora
- March 2023 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CAIE Physics IGCSEDocumento16 pagineMarch 2023 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CAIE Physics IGCSEjanggodanxdNessuna valutazione finora
- Depedgeneralchemistrymodulesquarters1 2bytapayan 210125043948Documento250 pagineDepedgeneralchemistrymodulesquarters1 2bytapayan 210125043948Christine Kaye SacoteNessuna valutazione finora
- Geiger and Marsden's gold foil experimentDocumento4 pagineGeiger and Marsden's gold foil experimentNurlailie Md JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Sources Lesson - Plasma BallDocumento12 paginePower Sources Lesson - Plasma BallAriunboldNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocumento1 paginaAtomic Theory TimelineIsabella LeónNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions To CAPE Physics 2003 To 2015 Unit 2Documento286 pagineSolutions To CAPE Physics 2003 To 2015 Unit 2Swishanie100% (4)
- Pioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Inorganic Chemistry The Periodic Table: Chemical PeriodicityDocumento22 paginePioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Inorganic Chemistry The Periodic Table: Chemical PeriodicityTimothy HandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure: The History of Atomic TheoryDocumento57 pagineAtomic Structure: The History of Atomic TheoryPatrick AlimuinNessuna valutazione finora
- MarkschemeDocumento14 pagineMarkschemeMehek AhujaNessuna valutazione finora