Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretation
Caricato da
josh082572Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretation
Caricato da
josh082572Copyright:
Formati disponibili
5 Steps to Rhythm Strip Interpretation
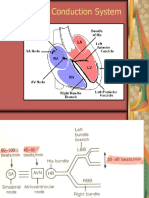
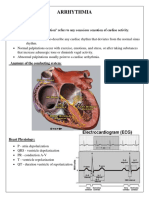
Brief A&P:
SA node; AV Junction; Bundle of His; Perkinje Fibers; Automaticity; Depolarization; Repolarization;
Cardiac Output;
It is important to think of arrhythmias in terms of – can a patient tolerate that rhythm and how it is
affecting cardiac output or perfusion?
The 5 Steps
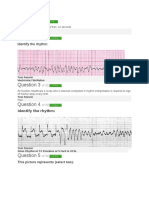
1. What is the Rate?
2. What is the Rhythm? Is it regular? If not, regularly or irregularly?
3. Is there a P for every QRS? Upright? Look the same?
4. P-R interval?
5. Do all the QRS complexes look the same? QRS length?
Defines the graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart only; NOT the action of the
heart…….You can have electrical activity without contractility. CHECK THE PATIENT!!!!
Where its coming from:
– Sinus; SA node – normally 60 - 100bpm
– Atrial; SA node fails, impulse comes from the atria (the AV node) 40 - 60bpm
– Ventricular; SA node or AV junction fails, ventricles will shoulder responsibility of pacing the heart. Up to
40bpm
Sinus Rhythms
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) – rate of 60 – 100bpm
Sinus Bradycardia (SB) - rate < 60bpm
Sinus Tachycardia (ST) – rate > 100bpm
Atrial Rhythms – SA node fails to generate the rhythm or is overridden. Generally not considered life
threatening unless too slow or too fast. Think about it! What’s happening when it’s too fast?
Atrial Flutter (A Flutter)
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Ventricular Rhythms – SA node or AV node Fail or is overridden by ventrical. !!!!SERIOUS!!!!, Can be
lethal. Check Patient.
Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) – not so much..
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Ventricular Fibrillation/Torsades (VF)
Asystole
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA): The absence of a palpable pulse and myocardial muscle activity
with the presence of organized electrical activity (excluding VT and VF) on cardiac monitor. It is
not an actual rhythm, it represents a clinical condition wherein the patient is clinically dead,
despite the fact that some type of organized rhythm appears on the monitor.
Types of Heart Blocks
First Degree AV Block
Second-Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type I) or Wenckebach
Second-Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type II)
Third Degree AV Block (Complete)
Rate Ruler : I use this. You don’t have to, but if you want to let me know! An easier and quicker way to
estimate the heart rate. As seen in the diagram below, when QRS complexes are 1 box apart the rate is
300 bpm. 2 boxes apart...150 bpm, etc. So if you memorize these simple numbers you can estimate the
heart rate at a glance!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ECG Interpretation UnismaDocumento178 pagineECG Interpretation UnismadefinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocumento69 pagineEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachDa EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNessuna valutazione finora
- Acls TachiDocumento1 paginaAcls TachiratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsDa EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 PrimerDocumento51 pagineTemporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 Primerwaqas_xsNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic Root FinalDocumento82 pagineAortic Root FinalMustafa KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart BlocksDocumento6 pagineHeart BlocksMark Hammerschmidt100% (1)
- Braunwald Lecture Series #2Documento33 pagineBraunwald Lecture Series #2usfcards100% (2)
- HUTTDocumento25 pagineHUTTdrdj14100% (1)
- Pacemaker NotesDocumento7 paginePacemaker Notesrohit860Nessuna valutazione finora
- Life Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementDocumento40 pagineLife Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementRuki HartawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacing Week PresentationsDocumento54 paginePacing Week PresentationsjoejenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic EP IntervalsDocumento13 pagineBasic EP IntervalsdrharoonmohdNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento52 pagineElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhNessuna valutazione finora
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, DiagnosisDocumento10 pagineFocal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, Diagnosisapi-26166949Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Pacemakers NewDocumento108 pagineCardiac Pacemakers NewAlif Fanharnita BrilianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDocumento155 pagineElectrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDeepika PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast and Lung CancerDocumento141 pagineBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- MVR CabgDocumento57 pagineMVR CabgRoshani sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Chest Pain PDFDocumento2 pagineEvaluation of Chest Pain PDFJaredNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Documento46 pagineValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanNessuna valutazione finora
- MapseDocumento6 pagineMapseRaul GascueñaNessuna valutazione finora
- CPRDocumento4 pagineCPRjeetNessuna valutazione finora
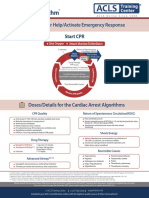
- Start CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorDocumento2 pagineStart CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorFelicia ErikaNessuna valutazione finora
- EKG Clep TestDocumento13 pagineEKG Clep TestElissa LafondNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentDocumento54 pagineDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentadela_97line100% (2)
- Swan Ganz CathetersDocumento27 pagineSwan Ganz CatheterschadchimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Pacing CombinedDocumento54 pagineBasics of Pacing CombinedMichael Susanto100% (1)
- ECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersDocumento7 pagineECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersAANessuna valutazione finora
- AHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardsDocumento8 pagineAHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardssallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac NotesDocumento24 pagineCardiac NotesYary MayorNessuna valutazione finora
- EkgDocumento67 pagineEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sNessuna valutazione finora
- Ekg FastlaneDocumento10 pagineEkg FastlaneAida UzunovicNessuna valutazione finora
- CARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDocumento54 pagineCARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDavi DzikirianNessuna valutazione finora
- Difficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaDocumento41 pagineDifficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaYuri SadewoNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG InterpretationDocumento82 pagineECG InterpretationIin Widya Sari Siregar100% (1)
- Sample Acls For DummiesDocumento3 pagineSample Acls For DummiesTodd Cole100% (1)
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyDocumento66 pagineDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationDocumento36 pagineArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac SarcoidosisDocumento13 pagineCardiac SarcoidosisEmeric Jorge Macedo VendezuNessuna valutazione finora
- HW InotropesDocumento3 pagineHW InotropesNatalie YeohNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationDocumento15 pagineAnaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationNaresh Dhawan100% (1)
- Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With DysrhythmiasDocumento19 pagineSelected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With Dysrhythmiaslanie_jecielNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Ventricular ArrhythmiasDocumento18 pagineApproach To Ventricular ArrhythmiasDavid CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysrhytmia NotesDocumento11 pagineDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrocardiogram (E.C.G)Documento51 pagineElectrocardiogram (E.C.G)Jamuna PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- BLS and Advance Cardiac Life SupportDocumento135 pagineBLS and Advance Cardiac Life SupportSteffiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acuterespiratorydistress Syndrome: Ventilator Management and Rescue TherapiesDocumento16 pagineAcuterespiratorydistress Syndrome: Ventilator Management and Rescue TherapiessamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocumento24 pagineCardiopulmonary Bypass: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice StripsDocumento9 paginePractice StripsErica Yamamoto50% (4)
- Invasive Devices On CXRDocumento1 paginaInvasive Devices On CXRLaurensia Erlina NataliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationDocumento16 pagineCare of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationirzehronNessuna valutazione finora
- Diastolic DysfunctionDocumento6 pagineDiastolic DysfunctionMarina SecureanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaDocumento5 pagineDysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- Basic EKG InterpretationDocumento48 pagineBasic EKG InterpretationAimee Ann Pauco MacaraegNessuna valutazione finora
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocumento50 pagineAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocumento62 pagineCardiopulmonary BypassNidya Putri100% (1)
- اسئلة علم الدواءDocumento2 pagineاسئلة علم الدواءMohamedErrmaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocumento1 paginaPoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFPierf-17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ECG Interpretation - LeonardDocumento33 pagineBasic ECG Interpretation - LeonardAyen FornollesNessuna valutazione finora
- DefibrillatorDocumento47 pagineDefibrillatorTIPSY ANTONYNessuna valutazione finora
- Elektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDocumento71 pagineElektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityNadyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart AnatomyDocumento178 pagineHeart AnatomysubbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13Documento6 pagineChapter 13Teehee Jones100% (1)
- Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice 2nd EditionDocumento157 pagineRapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice 2nd EditionVanessa MartuscelliNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Short Note Chula EP PDFDocumento62 pagineECG Short Note Chula EP PDFKhuniok SixcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDocumento36 pagineApical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDeliberate self harmNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg MCQSDocumento2 pagineEcg MCQSZafar Iqbal Manj100% (2)
- Ecg Interpretation: Intervals and ComplexesDocumento7 pagineEcg Interpretation: Intervals and ComplexesBobet ReñaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Official GuideDocumento11 pagineACLS Official GuideICU RSPGNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximal Pre-Excitation Based Algorithm For Localization of Manifest Accessory Pathways in AdultsDocumento10 pagineMaximal Pre-Excitation Based Algorithm For Localization of Manifest Accessory Pathways in AdultsFredy TandriNessuna valutazione finora
- HBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnDocumento35 pagineHBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnRichiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineECG Cheat SheetDaanishNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Exercise 3Documento3 pagineLab Exercise 3amarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah EKG AritmiaDocumento38 pagineKuliah EKG AritmiaJeanetteMarchi100% (1)
- ECG Reading & InterpretationDocumento52 pagineECG Reading & InterpretationRoy Francis B. CaspeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg For InternsDocumento25 pagineEcg For InternszeshooNessuna valutazione finora
- TV 2021Documento17 pagineTV 2021c4fcz9dj4fNessuna valutazione finora
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: Anatomy, Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocumento46 pagineWolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: Anatomy, Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis - UpToDateKarla ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrocardiography: Quicktime™ and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This PictureDocumento31 pagineElectrocardiography: Quicktime™ and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This PicturemkhandakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluDocumento214 pagineCara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluGiriNessuna valutazione finora
- INTERPRETASI EKG MahasiswaDocumento43 pagineINTERPRETASI EKG MahasiswaMartin Susanto, MDNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Ecg Interpretation For NursesDocumento4 pagineBasic Ecg Interpretation For Nurseskimberly dobleNessuna valutazione finora
- Patofisiologi AritmiaDocumento27 paginePatofisiologi AritmiaVedora Angelia GultomNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology-5 DysrhythmiaDocumento16 pagineCardiology-5 DysrhythmiaMahmoud RamadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Membrane PotentialsDocumento24 pagineMembrane PotentialsJeff ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeats) Symptoms, Types, and TreatmentDocumento5 pagineArrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeats) Symptoms, Types, and TreatmentCyberMeow100% (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Da EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (34)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (46)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeDa EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDa EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1412)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingDa EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (2)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Da EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDa EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsDa EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (39)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (254)