Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Test 4 Essay Questoin Meiosis and Gametogenesis
Caricato da
InactiveAccountDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Test 4 Essay Questoin Meiosis and Gametogenesis
Caricato da
InactiveAccountCopyright:
Formati disponibili
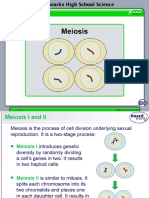
Meiosis and Gametogenesis
A. What features of meiosis are important in sexual reproduction?
• The two most important features of meiosis are genetic variation and the production of haploid
cells also called gametes. Genetic variation is very important because it allows the offspring to
be different from its parents by obtaining half of the chromosomes from the mother and the other
half from the father. This genetic variation makes it possible for multi-cellular organisms to
adapt to a changing environment by passing on traits which are necessary for survival. Some
examples of these traits may be a specific skin color, the ability to camouflage, etc. The plays a
great role in the survival of the fittest, which is a Darwinian theory. The second feature of
meiosis which is very important is the ability to produce a haploid cell from a diploid cell.
Humans for example contain 46 chromosomes. Without meiosis cutting the chromosome
number in half in gametes each new generation would have double the chromosome number than
their parents. Ultimately, this would lead to an entirely new species of humans. By cutting the
number of chromosomes in half in gametes, meiosis preserves the number of chromosomes, 46
in humans.
B. Why is meiosis important to heredity?
• Meiosis is important to heredity because it allows traits to be passed on from one generation to
the next. The first way this is done is through independent assortment. Independent assortment
occurs in metaphase one. This is important to heredity because depending on the arrangement of
the chromosomes the there is a fifty-fifty chance that a particular daughter cell of meiosis I will
get the maternal chromosome of a certain homologous pair and a fifty-fifty chance that it will
receive the paternal chromosome. The second way is by crossing over. Crossing over produces
recombinant chromosomes, which combine genes inherited from two parents. Crossing over
begins in prophase I, in which homologous portions of two nonsister chromatids trade places.
Crossing over increases the number of genetic types of gametes that result from meiosis. This
allows a great variety of traits that can be passed on to the offspring.
C. How is meiosis related to gametogenesis?
• Meiosis is just the beginning of creating a gamete. Gametogenesis, which involves both Meiosis
I and Meiosis II, converts the haploid cells into functional sperm or ova. In human males for
example, gametogenesis produces four sperm cells from the four haploid cells produced from
meiosis and in females it creates 1 ovum, the other three are just polar bodies that degenerate and
do not survive.
D. What are the similarities and differences between gametogenesis in plants and gemetogenesis in
animals?
• In animals, gametogenesis occurs in the gonads and produces gametes. Gametogenesis in males
occurs in the testes and in females it occurs in the ovaries. In plants, gametogenesis occurs in
flowers and it produces spores. In males it occurs in the anther of the stamen and in females it
occurs in the ovule of the ovary. The two phases involved in both are meiosis I and meiosis II.
The end results are 4 haploid gametes. In males, four sperm cells are produced and in females
one ovum is produces. The other three in females are just polar bodies which degenerate and do
not survive.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Understand Cancer & Reduce Cancer Risk - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Empowering You To Safeguard Against ItDa EverandUnderstand Cancer & Reduce Cancer Risk - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Empowering You To Safeguard Against ItNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiology 2 PDFDocumento11 pagineEpidemiology 2 PDFJawad TatlahNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicinal Chemistry—III: Main Lectures Presented at the Third International Symposium on Medicinal ChemistryDa EverandMedicinal Chemistry—III: Main Lectures Presented at the Third International Symposium on Medicinal ChemistryP. PratesiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 2 Issue 1013Documento22 pagineVol 2 Issue 1013Wardatul MukhlishohNessuna valutazione finora
- Genome & Personality-2ndDocumento28 pagineGenome & Personality-2ndVrendra Kumar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 15 PT 1Documento28 pagineCH 15 PT 1Kathleen Anne JoreNessuna valutazione finora
- H.A Assessing Thorax and LungsDocumento68 pagineH.A Assessing Thorax and LungsMc Ramil B. Pradero100% (1)
- Biomedical Final PaperDocumento6 pagineBiomedical Final PaperMiss DNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Basis of CancerDocumento6 pagineMolecular Basis of CancerguptaamitalwNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Answers PostDocumento12 pagineMock Answers PostRu LiliNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Cellular Respiration-KEYDocumento7 pagine13 Cellular Respiration-KEYZOE STONENessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Lung and ChestDocumento50 pagineAssessment of Lung and ChestAbdurehman Ayele100% (1)
- Chapter 15 SummaryDocumento27 pagineChapter 15 SummaryCharlotteNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor Patient RelationshipDocumento7 pagineDoctor Patient RelationshipMuhamad AgungNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Introduction: Organic InorganicDocumento1 paginaUnit 1: Introduction: Organic InorganicEllah GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Waves As PhysicsDocumento8 pagineWaves As PhysicsRija MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye ExamDocumento43 pagineEye ExamTapon Sarkar100% (1)
- JEE 2009 Paper 1Documento17 pagineJEE 2009 Paper 1Animesh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional and Ethics in Medical FeildDocumento6 pagineProfessional and Ethics in Medical FeildMeighalah ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Introduction To Epidemiology and Descriptive Epidemiology AIADocumento5 pagine08 Introduction To Epidemiology and Descriptive Epidemiology AIAAia DollisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18 SummaryDocumento7 pagineChapter 18 SummaryCharlotteNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory AssessmentDocumento43 pagineRespiratory AssessmentLui Andrei AnilaNessuna valutazione finora
- PancreatitisDocumento6 paginePancreatitisMary AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibroids: 1. Red DegenerationDocumento2 pagineFibroids: 1. Red Degenerationcgao30Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1 and 8.2 Group AssignmentDocumento7 pagine8.1 and 8.2 Group AssignmentDaniel CondreayNessuna valutazione finora
- BASC02 Full PDFDocumento70 pagineBASC02 Full PDFndarubagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Starson v. Swayze: The Supreme Court Speaks Out (Not All That Clearly) On The Question of "Capacity"Documento7 pagineStarson v. Swayze: The Supreme Court Speaks Out (Not All That Clearly) On The Question of "Capacity"John Jannsen100% (1)
- What Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFDocumento7 pagineWhat Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFAlexis CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- HypothesisDocumento42 pagineHypothesisGautam PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento16 pagineWhat Is Rheumatoid ArthritisDurge Raj GhalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Section One - About Disability: Sensory: Neurological: PhysicalDocumento4 pagineSection One - About Disability: Sensory: Neurological: Physicalvenkata ramakrishnaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 SummaryDocumento8 pagineChapter 4 SummaryCharlotteNessuna valutazione finora
- How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy - Cellular RespirationDocumento25 pagineHow Cells Harvest Chemical Energy - Cellular RespirationMohamad Saadatian SipanNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of Cell Growth & NeoplasiaDocumento62 pagineDisorders of Cell Growth & NeoplasiaPrakash PanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento5 pagineCellular RespirationCaptain MarvelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Quiz General Biology 2Documento7 pagineChapter Quiz General Biology 2Nikki San GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiology EpidemiologyDocumento13 pagineEpidemiology EpidemiologyBiratNagarNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 PANDEMIC - Specific COVID-19 Benefits - AG ReportDocumento92 pagineCOVID-19 PANDEMIC - Specific COVID-19 Benefits - AG ReportToronto StarNessuna valutazione finora
- Krebs Cycle: TCA/ Citric Acid CycleDocumento24 pagineKrebs Cycle: TCA/ Citric Acid Cyclejahanzeb aliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Doctor-Patient Relationship and Interviewing TechniquesDocumento50 pagineThe Doctor-Patient Relationship and Interviewing TechniquesPranay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Review For The 2° Semester Exam Alessandro Mo6a, UVVG, 3 YearDocumento9 pagineReview For The 2° Semester Exam Alessandro Mo6a, UVVG, 3 Yeardjxela89Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Evidence For Rest, Ice, Compression, AndElevation TherapyDocumento9 pagineWhat Is The Evidence For Rest, Ice, Compression, AndElevation Therapymiftah hurrohmanNessuna valutazione finora
- (EPI) 1.01 - Overview of Epidemiology & Descriptive Epidemiology - Dr. ButacanDocumento5 pagine(EPI) 1.01 - Overview of Epidemiology & Descriptive Epidemiology - Dr. Butacanpasambalyrradjohndar0% (1)
- Basic Molecular Biology & Biotechnology Training ManualDocumento23 pagineBasic Molecular Biology & Biotechnology Training Manualsameer420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis V MeiosisDocumento5 pagineMitosis V MeiosisddaarrsshhiittNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Chemical Education-Old MacDonald Named A Compound-Animales de Granja en Química OrgánicaDocumento2 pagineJournal of Chemical Education-Old MacDonald Named A Compound-Animales de Granja en Química OrgánicaMikhangBNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of CancerDocumento7 pagineTypes of CancerRegina SABSNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain Management Cases in Palliative CareDocumento45 paginePain Management Cases in Palliative Carecaturprianwari100% (1)
- Iit 2011 Paper 1 Official SolutionDocumento30 pagineIit 2011 Paper 1 Official Solutionsaurav guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Examination of Anterior and Posterior Chest WallDocumento64 paginePhysical Examination of Anterior and Posterior Chest WallCASSANDRAJUL VARIN100% (1)
- HypersensitivityDocumento50 pagineHypersensitivityayeasha siddikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Genetics: Sreekutty S 2 MSC ZoologyDocumento34 pagineCancer Genetics: Sreekutty S 2 MSC ZoologyShamsudheen maharajasNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid: Prepared By: Anthonette Ann Alemania-STEM 12Documento28 pagineAmino Acid: Prepared By: Anthonette Ann Alemania-STEM 12Anthonette Alemania100% (1)
- Homeopathy & AcupunctureDocumento8 pagineHomeopathy & AcupuncturemalofulNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid: Navigation SearchDocumento11 pagineAmino Acid: Navigation SearchSamiuddin YezdaniNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5NotesDocumento43 pagineBIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5Notesnasonfreeman63Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction and GeneticsDocumento53 pagineSexual Reproduction and GeneticsNellen BastismoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Documento14 pagineMeiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Selenia BonoNessuna valutazione finora
- BLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineBLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetIndraragini AnpalakanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento15 pagineUnit 2Jhon Rey RodeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab1 4Documento14 pagineVocab1 4InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre TestDocumento4 paginePre TestInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurDocumento15 pagineTerminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- TN1Documento13 pagineTN1InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735Documento10 pagineTerminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- MYCAA Spouse Education and Training PlanDocumento3 pagineMYCAA Spouse Education and Training PlanInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 9-12Documento7 pagineStudy Guide 9-12InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5Documento15 pagineLab 5InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 7Documento6 pagineLab 7InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Soci1306 Exam 2Documento15 pagineSoci1306 Exam 2InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6Documento9 pagineLab 6InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1Documento9 pagineLab 1InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Out of 3 PointsDocumento10 pagine3 Out of 3 PointsInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Shakers: at Their Height in The 1830s, Attracted Some 6000 Followers. The Shakers Traced TheirDocumento5 pagineShakers: at Their Height in The 1830s, Attracted Some 6000 Followers. The Shakers Traced TheirInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Four: MidlifeDocumento3 pagineAssignment Four: MidlifeInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Forum 1Documento3 pagineForum 1InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1Documento11 pagineExam 1InactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 Reproduction in Animlas TetsDocumento6 pagineClass 8 Reproduction in Animlas TetsSanjay RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic 3 ModuleDocumento46 pagineForensic 3 ModuleJezronzamri Peral Saso100% (1)
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants NotesDocumento17 pagineReproduction in Lower and Higher Plants NotesNisha vankhadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes For FungiDocumento10 pagineNotes For FungiФMuhammdф Atif .Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant ReproductionDocumento28 paginePlant ReproductionLorine ChoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module General Biology 1 Week 5 SHS.Documento26 pagineModule General Biology 1 Week 5 SHS.yeon gyuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle - Meiosis NotesDocumento63 pagineCell Cycle - Meiosis NotesKathleen Claire MontefalcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introductory Notes On Pro Life ApologeticsDocumento30 pagineIntroductory Notes On Pro Life ApologeticskedronjNessuna valutazione finora
- Perpetuation of LifeDocumento56 paginePerpetuation of Lifejoyceline sarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationDocumento62 pagine3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationNick YamNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Vol 2 Master The Ncert WWW - Examsakha.inDocumento426 pagineBiology Vol 2 Master The Ncert WWW - Examsakha.inSiddhartha Singh100% (1)
- SCI 11 Module 4Documento10 pagineSCI 11 Module 4Sebastian SmytheNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersDocumento3 pagineBiology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0004.Documento6 pagineWa0004.ojas goyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis WorksheetDocumento1 paginaMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- J5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis StudentDocumento3 pagineJ5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis Studentkristhel ann caringal reyes0% (1)
- Perpetuation of LifeDocumento12 paginePerpetuation of LifeSomeone SomethingNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2011 (v1) MS - Paper 2 CIE Biology IGCSEDocumento11 pagineJune 2011 (v1) MS - Paper 2 CIE Biology IGCSESriyashas KalluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesDocumento138 pagineGrade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesLulo NnenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocumento11 pagineSexual and Asexual ReproductionJungwon and FriendsNessuna valutazione finora
- Brs Embryology Q&ADocumento41 pagineBrs Embryology Q&ASURG BLOCK100% (1)
- Bio Yr 12 AnswersDocumento121 pagineBio Yr 12 AnswersAnneleise ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento66 pagine2 - Prenatal DevelopmentParameswary PerumalNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Science Biology Term 1Documento17 pagineCombined Science Biology Term 1AFuentesCaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual ReproductionDocumento25 pagineSexual Reproductioncxmic19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gender and Society Module 2Documento15 pagineGender and Society Module 2Allan Igbuhay100% (1)
- Reproduction Asexual Sporulation BuddingDocumento5 pagineReproduction Asexual Sporulation BuddingGermaeGonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocumento2 pagineQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Questionameema100% (2)
- BILD 3 Practice Midterm WI07Documento15 pagineBILD 3 Practice Midterm WI07George Chen100% (1)
- Biology I Teacher S Edition TE PDFDocumento600 pagineBiology I Teacher S Edition TE PDFphyaravi67% (3)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (597)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (411)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (110)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthDa EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDa EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindDa EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (115)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsDa EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2083)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)