Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Acute Gastroenteritis NCP
Caricato da
Xhla NgDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acute Gastroenteritis NCP
Caricato da
Xhla NgCopyright:
Formati disponibili
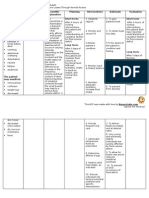
Situation:
Rosalka Kuba, a 30 years old mother of 2 was admitted last August 9, 2010 with a chief complaint of Epigastric pain. She was
diagnosed to have Acute Gastroenteritis ( AGE ). Today, August 12, 2010, you have assessed the patient with the following data:
Sunken eyeballs, poor skin turgor, BP: 170/100, PR: 82 bpm, RR: 40 bpm, and T: 36.7°C. The patient verbalizes pain the scale of
8/10.
CUES NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING NUSING RATIONALE EXPECTED
DIAGNOSIS EXPLANATION INTERVENTIONS OUTCOMES°
S: “ Kanina pa Deficient Fluid Volume After 8° of • Monitor and • Tachycardia, After 8° of
ako dumudumi Volume related depletion, or Nursing record vital dypnea, or Nursing
ng malambot na to active fluid extracellular Interventions, signs q 2° or hypotension Interventions,
malambot.” volume loss. fluid (ECF) the patient fluid as often as may indicate the patient’s
volume and blood necessary fluid volume fluid and blood
contraction, volume will until stable. deficit or volume return to
O: occurs as a return to Then monitor electrolyte normal as
( + ) sunken result of loss of normal. and record imbalance. evidenced by
eyeballs. total body vital signs q stable vital
( + ) poor skin sodium. Causes 4°. signs.
turgor. include vomiting,
Pain scale of excessive • Measure • Low urine
8/10 sweating, intake and output and
V/S as follows: diarrhea, burns, output q 4°. high specific
BP: diuretic use, and Record and gravity
170/100mmHg kidney failure. report indicates
PR: 82 bpm Clinical features significant hyovolemia.
RR: 40 bpm, include changes.
and diminished skin Include urine,
T: 36.7°C turgor, dry and stools.
mucous
membranes, • Administer • To replace
tachycardia, and fluids, blood, fluids and
orthostatic or blood whole blood
hypotension. products, or loss and
plasma facilitate fluid
expanders. movement
into
intravascular
space.
• Assess skin • To check for
turgor and dehydration.
oral mucous
membranes q
4°.
• Give • To avoid
oral/mouth dehydrating
care q 4° mucous
membranes
• Don’t allow • To avoid
patient to sit orthostatic
or stand up hypotension
quickly as and possible
long as syncope.
circulation is
compromise.
• Administer • To prevent
and monitor further fluid
medications. loss.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Med Surg Study GuideDocumento24 pagineMed Surg Study Guidekylie100% (4)
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 paginaNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Pediatric (Diarrhea and Impaired Mucous Membrane)Documento8 pagineNCP Pediatric (Diarrhea and Impaired Mucous Membrane)Flauros Ryu Jabien60% (5)
- Theodore Hong, Prajnan Das (Eds.) - Radiation Therapy For Gastrointestinal Cancers (2017, Springer InternatiDocumento244 pagineTheodore Hong, Prajnan Das (Eds.) - Radiation Therapy For Gastrointestinal Cancers (2017, Springer InternatiTolga ŞanlıNessuna valutazione finora
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocumento2 pagineDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
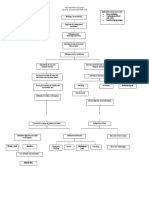
- Pathophy (Age)Documento1 paginaPathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNessuna valutazione finora
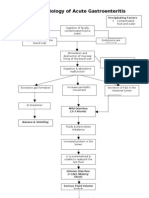
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiology of Acute Gastroenteritisromeo rivera100% (16)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDocumento2 pagineRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPAlbean DelojeroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - AgeDocumento5 pagineNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- NCP DehydrationDocumento4 pagineNCP DehydrationYnah Sayoc100% (2)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento12 pagineFluid Volume DeficitKersee GailNessuna valutazione finora
- Provide Ensuresbedside comfort,commode as privacy andneeded. convenience for patientDocumento4 pagineProvide Ensuresbedside comfort,commode as privacy andneeded. convenience for patientImang Dela Cruz100% (9)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisKita kita100% (1)
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP Fluid Volume DeficitRez Apego0% (1)
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 15Documento42 pagineACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 15Đạt NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisJohn Glenn Bianzon79% (29)
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Diarrheaderic95% (43)
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento7 pagineNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisAlliah Grejie AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP DengueDocumento3 pagineNCP DengueYeana Alon50% (4)
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocumento2 pagineCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento1 paginaDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- NCP For FeverDocumento2 pagineNCP For FeverDominises Jade Corpuz82% (17)
- Diarrhea NCPDocumento3 pagineDiarrhea NCPCharles Michael Azagra0% (1)
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Documento1 paginaNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCP DiarrheaDocumento2 pagineNCP DiarrheaElisha Faith Sevilla Espineli0% (1)
- NCP For Delivery RoomDocumento4 pagineNCP For Delivery RoomGiselle EstoquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricDocumento11 pagineNCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricJhoevina Dulce Capicio0% (1)
- Gastroenteritis NCPDocumento1 paginaGastroenteritis NCPVenus Bactol67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocumento10 pagineNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Neumovent PDFDocumento94 pagineNeumovent PDFMustafa SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADocumento2 pagineNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- NCP HemothoraxDocumento3 pagineNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)Documento6 pagineNCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)abcel76% (21)
- NCP-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP-Fluid Volume Deficitanon_207994234100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento12 pagineNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.Documento8 pagineRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.eleinsamNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For DehydrationDocumento3 pagineNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- NURSING Review Session (Nur 220) Part 1Documento8 pagineNURSING Review Session (Nur 220) Part 1Mariel EstoniloNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Gastroenteritis Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineAcute Gastroenteritis Nursing Care PlanVhiance Czaramae LahuranNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 pagineNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Documento4 pagineDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento1 paginaFluid Volume DeficitventimiglionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento1 paginaNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNessuna valutazione finora
- ATI Fluids, AcidBase, DietsDocumento9 pagineATI Fluids, AcidBase, DietsBernardo AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP TorresDocumento7 pagineNCP TorresbabiNessuna valutazione finora
- FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES UpdatedDocumento8 pagineFLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES UpdatedSJane FeriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbances in Fluids & ElectrolytesDocumento65 pagineDisturbances in Fluids & ElectrolytesShenaNessuna valutazione finora
- SepsisDocumento3 pagineSepsisapi-673621869Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento10 pagineNursing Care PlanZerica Andaca83% (6)
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocumento9 pagineNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Dengue Spectrum FinalDocumento43 pagineDengue Spectrum Finalshyam kumar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocumento3 pagineNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocumento12 pagineMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaIneffective Tissue Perfusion Nursing Care PlankimmybapkiddingNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Fluid and Electrolytes 2022Documento42 pagineIntro To Fluid and Electrolytes 2022David Dwane Art SilorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolyte Disorders - 1Documento29 pagineElectrolyte Disorders - 1sanketh bhat.sNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Volume DisturbancesDocumento25 pagineFluid Volume Disturbancesmoonlight ariNessuna valutazione finora
- Abc Case 5Documento19 pagineAbc Case 5Christian Dave EndinoNessuna valutazione finora
- S1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency CasesDocumento70 pagineS1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency Casesgriya medicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento20 pagineCase StudyYiella AlagarNessuna valutazione finora
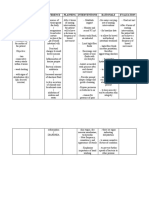
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE GUIDEDocumento45 pagineFLUID AND ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE GUIDEPranshu Prajyot 67Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis 1Documento5 pagineNursing Diagnosis 1Kim TangoNessuna valutazione finora
- FluidelectrolytebalanceDocumento87 pagineFluidelectrolytebalancePavi MuruganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - IV Resuscitation and Blood TransfusionDocumento17 pagine5 - IV Resuscitation and Blood Transfusionضبيان فرحانNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthropometric Profile Evaluation of The Midface in Patients With Cleft Lip and PalateDocumento10 pagineAnthropometric Profile Evaluation of The Midface in Patients With Cleft Lip and PalateAndy HongNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiographic Pathology For Technologists 6th Edition Kowalczyk Test BankDocumento6 pagineRadiographic Pathology For Technologists 6th Edition Kowalczyk Test Bankbeatrixkhuyen9rm100% (26)
- Social Sciences in DentistryDocumento39 pagineSocial Sciences in DentistryPrabhu AypaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12-Year-Old Female with RLQ Pain and Possible AppendicitisDocumento4 pagine12-Year-Old Female with RLQ Pain and Possible AppendicitiskymhanNessuna valutazione finora
- الرب قريب لمن يدعوهDocumento27 pagineالرب قريب لمن يدعوهAhmed MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Occlusion Vs MalocclusionDocumento5 pagineNormal Occlusion Vs MalocclusionAnjiZareerNessuna valutazione finora
- First FormativeDocumento7 pagineFirst Formativeola nagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety and Related DisordersDocumento23 pagineAnxiety and Related DisordersSimón Ortiz LondoñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Traditional Fermented MilkDocumento5 pagineTraditional Fermented MilkPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Upper Limb Disorders in The Workplace: A Brief GuideDocumento9 pagineManaging Upper Limb Disorders in The Workplace: A Brief GuideCarlos LopézNessuna valutazione finora
- Institut Latihan Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia: Nama PelatihDocumento12 pagineInstitut Latihan Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia: Nama PelatihIkmal HakimiNessuna valutazione finora
- USAID Impact of Health Systems Strengthening On HealthDocumento66 pagineUSAID Impact of Health Systems Strengthening On HealthMamadou Selly LyNessuna valutazione finora
- Davao Medical School Foundation College of Medicine Case Report - Weight Loss, Polyuria, PolydipsiaDocumento6 pagineDavao Medical School Foundation College of Medicine Case Report - Weight Loss, Polyuria, PolydipsiaVie TNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Statement Against EuthanasiaDocumento6 pagineThesis Statement Against Euthanasiadwg1pv0n100% (2)
- Chapter24 PDFDocumento43 pagineChapter24 PDFCindy MaslagNessuna valutazione finora
- PROGNOSIS EbmDocumento25 paginePROGNOSIS EbmcarinasheliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic First Aid For Medical EmergenciesDocumento27 pagineBasic First Aid For Medical EmergenciesCOngNessuna valutazione finora
- LONDON đã chuyển đổiDocumento4 pagineLONDON đã chuyển đổiThiện MinhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Care ProcessDocumento9 pagineNutrition Care ProcesssharlethNessuna valutazione finora
- Infecciones NosocomialesDocumento16 pagineInfecciones NosocomialesCarolina Duque RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding HIV/AIDS: Causes, Symptoms, PreventionDocumento17 pagineUnderstanding HIV/AIDS: Causes, Symptoms, PreventionphilNessuna valutazione finora
- Otitis MediaDocumento55 pagineOtitis MediaJollyann SedaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Eacsguidelines 8 0-English Rev-20160124Documento94 pagine2015 Eacsguidelines 8 0-English Rev-20160124Gloria WinnNessuna valutazione finora
- Zani - Et - Al 2023 Nature (01 04)Documento4 pagineZani - Et - Al 2023 Nature (01 04)nataliaNessuna valutazione finora