Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKE
Caricato da
Ma. Elaine Carla Tating0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
3K visualizzazioni2 pagineCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
3K visualizzazioni2 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKE
Caricato da
Ma. Elaine Carla TatingCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
West Visayas State University
COLLEGE OF NURSING
La Paz, Iloilo City
NURSING CARE PLAN
CLUSTERED NURSING OUTCOME NURSING
RATIONALE RATIONALE EVALUATION
CUES DIAGNOSIS CRITERIA INTERVENTIONS
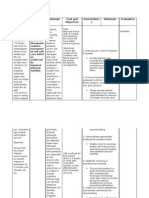
Impaired gas Excess or deficit in The patient will be able Assess for signs and Collapse of alveoli
exchange related oxygenation and/or to demonstrate symptoms of atelectasis: increases shunting
to alveolar- carbon dioxide improved ventilation diminished chest (perfusion without
capillary elimination at the and adequate excursion, limited ventilation) resulting in
membrane alveolar-capillary oxygenation of tissues diaphragm excursion, hypoxemia.
changes membrane. by ABGs within client’s bronchial or tubular
normal limits as breath sounds, crackles,
By the process of evidenced by increase tracheal shift to affected
diffusion, the in GCS, RR and BP site.
exchange of within normal range,
oxygen and carbon and absence of pale Monitor vital signs. With initial hypoxia and
dioxide occurs in skin by hypercapnia, BP, heart
the alveolar- rate, and respiratory rate
capillary membrane all increase. As the
area. The hypoxia and/or
relationship hypercapnia becomes
between ventilation severe, BP and heart rate
(air flow) and decrease, and arrhythmias
perfusion (blood may occur. Respiratory
flow) affects the failure may ensue when
efficiency of the the patient is unable to
gas exchange. maintain the rapid
Normally there is a respiratory rate.
balance between
ventilation and Assess skin color for For cyanosis to be
perfusion; however, development of present, 5 grams of
certain conditions cyanosis. hemoglobin must be
can offset this desaturated. Cool, pale
balance, resulting skin may be secondary to
in impaired gas a compensatory
exchange. vasoconstrictive response
to hypoxemia.
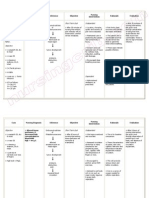
Older patients have
a decrease in Maintain oxygen This provides for adequate
pulmonary blood administration device as tissue oxygenation.
flow and diffusion ordered, attempting to
as well as reduced maintain oxygen
ventilation in the saturation at 90% or
dependent regions greater.
of the lung where
perfusion is Position the patient with This may improve exercise
greatest. proper body alignment tolerance by maintaining
for optimal respiratory adequate oxygen levels
excursion (if tolerated, during activity.
head of bed at 45
Source: degrees when supine).
Gulanick/Myers.
(2007). Nursing Routinely check the This would cause the
Care Plans, 6th patient’s position so that abdomen to compress the
edition. he does not slide down diaphragm, which would
in bed. cause respiratory
embarrassment.
Change the patient’s This facilitates secretion
position every two movement and drainage
hours. and decreases atelectasis.
Suction as needed. Suction removes
secretions if the patient is
unable to effectively clear
the airway.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Documento3 pagineNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP of MGH PatientDocumento2 pagineNCP of MGH PatientMaverick LimNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternNecheal BaayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocumento5 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 pagineNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- CVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineCVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoanne Kaye Taylor100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento2 pagineIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PneumoniaDocumento2 pagineNCP PneumoniaChristian Apelo Serquillos100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Documento1 paginaIneffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Danna Tan50% (2)
- NCPDocumento1 paginaNCPnictan 140% (1)
- Risk For Infection Related To Inadequate Primary Defenses: Broken SkinDocumento2 pagineRisk For Infection Related To Inadequate Primary Defenses: Broken SkinReylan Garcia100% (8)
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 pagineNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP AnxietyDocumento1 paginaNCP AnxietyGrace MellaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocumento3 paginePcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocumento1 paginaDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocumento3 pagineNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocumento7 pagine6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Weakness NCPDocumento1 paginaBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LocDocumento2 pagineNCP LocMel RodolfoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen RegalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pleural EffusionDocumento5 paginePleural EffusionTerizla MobileNessuna valutazione finora
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Documento2 pagineIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Let'S Dive Deeply!: Discussion Points: Read The Case Scenario and Relate It To The TheoryDocumento1 paginaLet'S Dive Deeply!: Discussion Points: Read The Case Scenario and Relate It To The TheoryAnn Mariz DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP DobDocumento3 pagineNCP DobLester BuhayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - BedriddenDocumento4 pagineNCP - Bedriddenadelaigner_racho589475% (4)
- NCP For LeptospirosisDocumento1 paginaNCP For LeptospirosiskyawNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - GlaucomaDocumento1 paginaNCP - GlaucomaKath CuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Ineffective Breathing Pattern - RMC CasepressDocumento2 pagineNCP For Ineffective Breathing Pattern - RMC Casepressmissyuri08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cad NCPDocumento1 paginaCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 1Documento1 paginaNCP 1hsiriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Thought ProcessAira AlaroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP HemoDocumento2 pagineNCP HemoJigs HechNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed SleepDocumento1 paginaDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineActivity Intolerancelouie roderos0% (1)
- NCP Risk For FallDocumento2 pagineNCP Risk For FallHero Tauro0% (2)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineActivity IntoleranceGen RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CTTDocumento2 pagineNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain (Fronto-Temporal Mass)Documento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Acute Pain (Fronto-Temporal Mass)deric100% (1)
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 paginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocumento2 pagineRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocumento3 pagineNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocumento1 paginaImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento4 pagineNCPEsther RefuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocumento6 pagineESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: StoDocumento7 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: StoKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocumento2 pagineAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocumento4 pagineNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 1 N 2Documento5 pagineNCP 1 N 2Cuttie Anne GalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Requirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CDocumento4 pagineRequirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CFremelen Rose CadalinNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocumento3 pagineImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Ma. Elaine Carla A. TatingDocumento60 paginePrepared By: Ma. Elaine Carla A. TatingMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocumento7 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocumento5 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMADocumento5 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMAMa. Elaine Carla Tating50% (2)
- NCP Anxiety Related To Unconscious Conflict About Essential Goals and Values of Life Into Financial Instability Causing DistressDocumento2 pagineNCP Anxiety Related To Unconscious Conflict About Essential Goals and Values of Life Into Financial Instability Causing DistressMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNDocumento2 pagineNCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEADocumento2 pagineNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEAMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYODocumento10 pagineDrug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYOMARIA JULIANA RENGIFO LARANessuna valutazione finora
- Quick PharmaDocumento4 pagineQuick Pharmahva.terrenceavillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento3 pagineDaftar Pustakaipan_romanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of HumoursDocumento19 pagineTheory of HumoursSyed Ahad0% (1)
- Icu Guideline: Management of Diarrhea: StartDocumento1 paginaIcu Guideline: Management of Diarrhea: StartGracia VionaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Note Sample 17Documento6 pagineNursing Note Sample 17Lanzen Dragneel100% (1)
- 3 On Your Side Investigates: Jailed and AbusedDocumento102 pagine3 On Your Side Investigates: Jailed and AbusedShaCamree GowdyNessuna valutazione finora
- White Paper On Medical Device (Issue 1)Documento4 pagineWhite Paper On Medical Device (Issue 1)Rishabh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- L Carnitine PDFDocumento6 pagineL Carnitine PDFtilaran1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocumento152 pagineGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- PancreasDocumento35 paginePancreasPaskalisNessuna valutazione finora
- Seizure Updated ILAE ClassificationDocumento12 pagineSeizure Updated ILAE ClassificationNasheei RadjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencyDocumento15 pagineDaftar Obat Alkes Trolley EmergencydevitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading 9thDocumento3 pagineReading 9thicemangdNessuna valutazione finora
- Scripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Documento68 pagineScripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Zdravko GrubacNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal HematuriaDocumento6 pagineJurnal HematuriaErlin IrawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Microdosing Mushrooms: Fruiting Bodies Introduction ToDocumento12 pagineMicrodosing Mushrooms: Fruiting Bodies Introduction ToPaulo Das Nuvens100% (2)
- CostIt-example (Primary Health Care Facility)Documento69 pagineCostIt-example (Primary Health Care Facility)Parimalakrishnan100% (1)
- Contoh Soal Pas BingDocumento8 pagineContoh Soal Pas BingAnnisa AuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionDocumento26 pagineArixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionTri Purma SariNessuna valutazione finora
- AMCA Study Guide PhlebotomyDocumento34 pagineAMCA Study Guide Phlebotomyayoonia100% (1)
- Free Dive Training Schedules - Land and Pool Based Training SessionsDocumento10 pagineFree Dive Training Schedules - Land and Pool Based Training Sessionssjf540100% (1)
- LO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Documento38 pagineLO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Alan Dwi SetiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Braddom Lower Extremity DrillsDocumento4 pagineBraddom Lower Extremity DrillsKennie RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- DkaDocumento32 pagineDkanatheNessuna valutazione finora
- Twin Block Appliance ThesisDocumento6 pagineTwin Block Appliance Thesisjessicahillnewyork100% (2)
- Developing A Clinically Important Class of Glycan-Targeted Biologics With Unprecedented Tumor Specificity Funding First Human DataDocumento17 pagineDeveloping A Clinically Important Class of Glycan-Targeted Biologics With Unprecedented Tumor Specificity Funding First Human DataNuno Prego RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Genetics: Co-Dominance & Multiple AllelesDocumento2 pagineTheoretical Genetics: Co-Dominance & Multiple AllelesMARIANA BERNAL MEJIANessuna valutazione finora
- KalanchoeDocumento1 paginaKalanchoeAnonymous iOYpj92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mwalya Wambua Final ProjectDocumento49 pagineMwalya Wambua Final ProjectWILSON MACHARIANessuna valutazione finora