Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHN
Caricato da
Ma. Elaine Carla Tating38%(8)Il 38% ha trovato utile questo documento (8 voti)
7K visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related to Fluid Loss DHN
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
38%(8)Il 38% ha trovato utile questo documento (8 voti)
7K visualizzazioni2 pagineNCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHN
Caricato da
Ma. Elaine Carla TatingCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
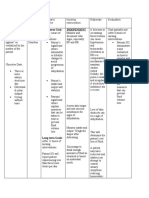
West Visayas State University
College of Nursing
La Paz, Iloilo City
NURSING CARE PLAN
Clustered Cues Nursing Rationale Outcome Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Criteria Interventions
Deficient fluid Decreased intravascular,
volume related to interstitial, and/or
fluid loss intracellular fluid. This The client will Assess for dry skin, To determine the degree
refers to dehydration maintain fluid poor skin turgor, of dehydration. It helps
without changes in sodium. volume at a peripheral edema, determine the amount
functional level muscle weakness, and route of rehydration
Infectious agents usually through etc. needed.
cause acute gastroenteritis. adequate oral
These agents cause and IV fluid
diarrhea by adherence, rehydration as Monitor vital signs; To obtain baseline data
mucosal invasion, evidenced by compare with for comparison during
enterotoxin production, moist mucous patient's previous evaluation. Postural
and/or cytotoxin membranes, BP = readings. Tale blood hypotension reflects a
production. These 110-90/70- pressure in lying, decrease in circulating
mechanisms result in 60mmHg and the sitting, standing volume.
increased fluid secretion resolution of positions when
and/or decreased edema by possible.
absorption. This produces
an increased luminal fluid Maintain an accurate To determine fluid
content that cannot be record of intake and balance.
adequately reabsorbed, output and correlate
leading to dehydration and with weight changes.
the loss of electrolytes and
nutrients. Measure and record Help differentiate
liquid stool as well as individual disease and
During diarrhea there is an the frequency of assesses the severity of
increased loss of water and bowel movement, each episode.
electrolytes in the liquid noting its
stool. Water and consistency and
electrolytes are also lost appearance.
through vomit, sweat, urine
and breathing. Provide frequent oral To prevent injury from
as well as eye care. dryness.
If the body loses a
substantial amount of fluids Start/administern To correct dehydration.
and is not quickly replaced, oral and IV fluid Oral therapy can
the body starts to "dry up" rehydration therapy rehydrate most patients.
or get dehydrated. as indicated. Oral rehydration therapy
is a strategy used to
Dehydration occurs when reduce the severe
these losses are not complications of
replaced adequately and a diarrheal disease
deficit of water and regardless of causative
electrolytes develops. agent. Intravenous
therapy is necessary for
rapid fluid replacement.
References:
Books To limit gastric losses.
Diseases and Disorders: A
Nursing Therapeutic
Manual 2007 3rd Edition by
Sommers et al
Nurse’s Pocket Guide 2008
11th Edition by Doenges et
al
Medical-Surgical Nursing
2004 7th Edition by Black &
Hawks
Brunner and Suddarth’s
Textbook of Medical-
Surgical Nursing 2004 10th
Edition by Smeltzer & Bare
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Intravenous Therapy For BSN StudentsDocumento30 pagineIntravenous Therapy For BSN StudentsKevin Cervantes FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lactated RingersDocumento3 pagineLactated RingersE100% (5)
- Prepared By: Ma. Elaine Carla A. TatingDocumento60 paginePrepared By: Ma. Elaine Carla A. TatingMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- PN NCLEX Integrated A 1Documento75 paginePN NCLEX Integrated A 1jedisay1100% (1)
- Hemodialysis NCPDocumento2 pagineHemodialysis NCPAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 paginaNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerDocumento3 pagineRisk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerdanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 pagineRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNessuna valutazione finora
- VILLALOBOS, A. E. Quality-Of-Life Assessment Techniques For Veterinarians. Veterinary Clinics of North America - Small Animal Practice. 2011 PDFDocumento11 pagineVILLALOBOS, A. E. Quality-Of-Life Assessment Techniques For Veterinarians. Veterinary Clinics of North America - Small Animal Practice. 2011 PDFFran WermannNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento7 pagineImpaired Skin Integrityprickybiik100% (8)
- Urinary Tract Infection - NCPDocumento2 pagineUrinary Tract Infection - NCPIssa Farne0% (1)
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (352-542)Documento191 pagineFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (352-542)MAYRA ESTEFANIA PEREZ CANCHALANessuna valutazione finora
- IV Fluid Replacement TherapyDocumento12 pagineIV Fluid Replacement TherapyKamran Sheraz100% (1)
- NCP - Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento2 pagineNCP - Fluid Volume ExcessIngrid Sasha Fong100% (4)
- NCP DehydrationDocumento4 pagineNCP DehydrationYnah Sayoc100% (2)
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEADocumento2 pagineNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEAMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Surgery SummaryDocumento30 paginePlastic Surgery SummaryLailaAliNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP UtiDocumento2 pagineNCP UtiAlyanna Arañez50% (2)
- Burn Lecture NotesDocumento7 pagineBurn Lecture NotesMarcus, RN100% (3)
- NCP Anxiety Related To Unconscious Conflict About Essential Goals and Values of Life Into Financial Instability Causing DistressDocumento2 pagineNCP Anxiety Related To Unconscious Conflict About Essential Goals and Values of Life Into Financial Instability Causing DistressMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Documento1 paginaNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocumento5 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDocumento3 pagineFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocumento1 paginaNCP Deficient KnowledgeLouie Siazon Vasquez100% (1)
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocumento2 pagineDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- NCP EdemaDocumento1 paginaNCP EdemaKurtt Evan Valino100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyMa. Elaine Carla TatingNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Documento9 pagineNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel100% (2)
- NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitJeanineReyes44% (9)
- NCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineNCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityRI NA100% (1)
- AGE Pedia CaseDocumento83 pagineAGE Pedia CaseLadybelle GototosNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODocumento3 pagineNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- (NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaDocumento3 pagine(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio100% (4)
- NCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento2 pagineNCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocumento7 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- NCP-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP-Fluid Volume Deficitanon_207994234100% (1)
- NCP - AgeDocumento5 pagineNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- NCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocumento4 pagineNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento2 pagineNCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeRedwing_Dc_854758% (12)
- NCPDocumento4 pagineNCPRachel PerandoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocumento3 pagineNCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceVitha100% (1)
- NCP-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP-Fluid Volume Deficitjava_biscocho122979% (33)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPDocumento2 pagineRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPAyla Mar100% (1)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento4 pagineFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Documento2 pagineFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)Documento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)rei_alina75% (4)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDocumento2 pagineRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPAlbean DelojeroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocumento3 pagineNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMADocumento5 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMAMa. Elaine Carla Tating50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentThomas FarrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocumento7 pagineNursing Care Plan PediaYvonne Niña Aranton100% (1)
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP Fluid Volume DeficitRez Apego0% (1)
- NCP For DehydrationDocumento3 pagineNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- NCP-Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento3 pagineNCP-Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitJai Go100% (1)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocumento7 pagineCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNessuna valutazione finora
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento1 paginaNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For ConstipationDocumento1 paginaNCP Risk For Constipationjorgeacct50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan AGNDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan AGNAlexis Coronado50% (2)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento3 pagineNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 pagineNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For DM1Documento2 pagineNCP For DM1Pau Hipol MadriagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Volume Deficit BatuDocumento2 pagineFluid Volume Deficit Batumecz26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Deficit)Documento2 pagineDeficit)Lee DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan PediaLenie DegraciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Documento3 pagineAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Short-Term Goal: IndependentDocumento2 pagineShort-Term Goal: IndependentShanelle Mary Genanda LordaNessuna valutazione finora
- But He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleDocumento4 pagineBut He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleJiv Rouziell DoroteoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Documento5 pagineSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNessuna valutazione finora
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADocumento2 pagineAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 1Documento3 pagineModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP DrugstudyDocumento2 pagineNCP DrugstudyAbegail MierNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Lab ResultDocumento5 pagineNCP Lab ResultJoy Mariel Isadora BurgosNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Burns: Priyanka JayakumarDocumento132 pagineBurns: Priyanka JayakumarPriyankaNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Therapy AdultsDocumento9 pagineIV Therapy AdultsRuo ZhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Management of BurnDocumento40 pagineNursing Management of BurnSalinKaur0% (1)
- AJEERNA (Indigestion)Documento37 pagineAJEERNA (Indigestion)m gouriNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectal FluidtherapyDocumento7 pagineRectal FluidtherapyIan SabogalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Combination of Parkland Formula Using Normal Saline With Muir and Barclay FormulaDocumento8 pagineThe Combination of Parkland Formula Using Normal Saline With Muir and Barclay FormulaMichelle AthinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Difficult IV Access C PGDocumento42 pagineDifficult IV Access C PGFitrii WulanDari FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency and Acute Phase in Burns - Afriyanti SandhiDocumento45 pagineEmergency and Acute Phase in Burns - Afriyanti SandhiPtunk Ndu PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Management in Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento8 pagineFluid Management in Acute Kidney InjuryHGZ 83 MoreliaNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraDocumento41 pagineIV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraIslam AwniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Therapy: Adesola Odunayo, DVM, MS, DACVECCDocumento6 pagineFluid Therapy: Adesola Odunayo, DVM, MS, DACVECCSamantha Orozco PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient Timing and Training: The Warfighter Nutrition GuideDocumento15 pagineNutrient Timing and Training: The Warfighter Nutrition GuideBenNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Nursing Reviewer Part 3Documento13 paginePerioperative Nursing Reviewer Part 3JUDE MARIANO JR. ALBANCES CARLOSNessuna valutazione finora
- ACSM Position Stand - Exercise and Fluid Replacement - Medicine & Science in Sports & ExerciseDocumento7 pagineACSM Position Stand - Exercise and Fluid Replacement - Medicine & Science in Sports & ExerciseDiógenes OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratih Sumirat - Kegawatdaruratan Klinik ATLS UpdateDocumento16 pagineRatih Sumirat - Kegawatdaruratan Klinik ATLS UpdateRatih Nurdiany SumiratNessuna valutazione finora
- Monitoreo Hemodinamico FuncionalDocumento27 pagineMonitoreo Hemodinamico FuncionalGabriel Lopez MNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulated Exam RationalesDocumento20 pagineSimulated Exam Rationalesrhymes2u100% (3)
- Albumin and Hetastarch For Fluid ResuscitationDocumento13 pagineAlbumin and Hetastarch For Fluid Resuscitationrulli_pranandaNessuna valutazione finora
- XcaretDocumento9 pagineXcaretmubarek abdurohemanNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerDocumento2 pagineWHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerKathleen DyNessuna valutazione finora
- Monterozo, Ronel Von O. Prime 4Documento7 pagineMonterozo, Ronel Von O. Prime 4Ronel MonterozoNessuna valutazione finora